C# Dictionary(字典)源码解析&效率分析
通过查阅网上相关资料和查看微软源码,我对Dictionary有了更深的理解。
Dictionary,翻译为中文是字典,通过查看源码发现,它真的内部结构真的和平时用的字典思想一样。
我们平时用的字典主要包括两个两个部分,目录和正文,目录用来进行第一次的粗略查找,正文进行第二次精确查找。通过将数据进行分组,形成目录,正文则是分组后的结果。
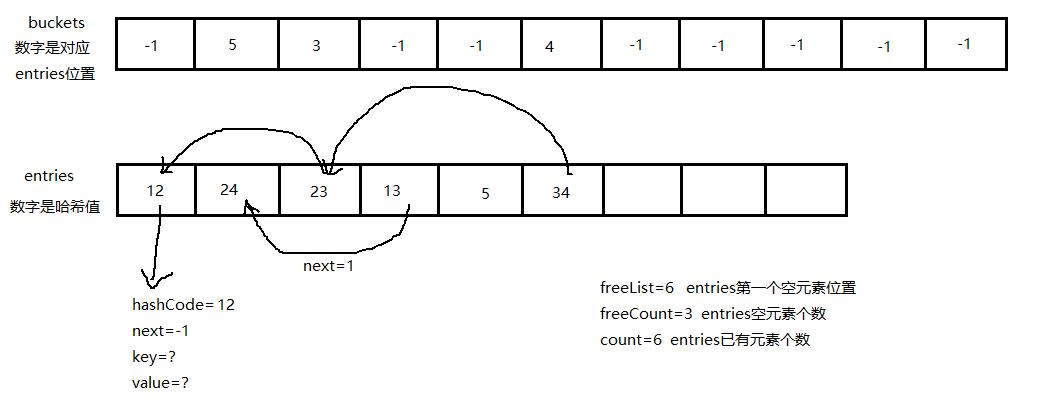
而Dictionary对应的是 int[] buckets 和 Entry[] entries,buckets用来记录要查询元素分组的起始位置(这么些是为了方便理解,其实是最后一个插入元素的位置没有元素为-1,查找同组元素通过 entries 元素中的 Next 遍历,后面会提到),entries记录所有元素。分组依据是计算元素 Key 的哈希值与 buckets 的长度取余,余数就是分组,指向buckets 位置。通过先查找 buckets 确定元素分组的起始位置,再遍历分组内元素查找到准确位置。与对应的目录和正文相同,buckets的 长度大于等于 entries(我理解是为扩展做准备的),buckets 的长度使用 HashHelpers.GetPrime(capacity) 计算,是一个计算得到的最优值。capacity是字典的容量,大于等于字典中实际存储元素个数。
Dictionary与真实的字典不同之处在于,真实字典的分组结果的物理位置是连续的,而 Dictionary 不是,他的物理位置顺序就是插入的顺序,而分组信息记录在 entries 元素中的 Next 中,Next 是个 int 字段,用来记录同组元素的下一个位置(若当前为该组第一个插入元素则记录-1,第一个插入元素在分组遍历的最后一个)
解析一下Dictionary的几个关键方法
1.Add(Insert 新增&更新方法)
Add和使用[]更新实际就是调用的Insert,代码如下。
首先计算key的哈希值,与buckets取余后确定目录位置,找到entries的位置,然后通过.next方式遍历分组内元素,确定是否存在同key元素,再进行新增或更新操作
public void Add(TKey key, TValue value)
{
Insert(key, value, true);
}
Add
public TValue this[TKey key]
{
get
{
int i = FindEntry(key);
if (i >= 0) return entries[i].value;
ThrowHelper.ThrowKeyNotFoundException();
return default(TValue);
}
set
{
Insert(key, value, false);
}
}
索引器
private void Insert(TKey key, TValue value, bool add)
{ if (key == null)
{
ThrowHelper.ThrowArgumentNullException(ExceptionArgument.key);
} if (buckets == null) Initialize(0);
int hashCode = comparer.GetHashCode(key) & 0x7FFFFFFF;
int targetBucket = hashCode % buckets.Length; #if FEATURE_RANDOMIZED_STRING_HASHING
int collisionCount = 0;
#endif for (int i = buckets[targetBucket]; i >= 0; i = entries[i].next)
{
if (entries[i].hashCode == hashCode && comparer.Equals(entries[i].key, key))
{
if (add)
{
ThrowHelper.ThrowArgumentException(ExceptionResource.Argument_AddingDuplicate);
}
entries[i].value = value;
version++;
return;
} #if FEATURE_RANDOMIZED_STRING_HASHING
collisionCount++;
#endif
}
int index;
if (freeCount > 0)
{
index = freeList;
freeList = entries[index].next;
freeCount--;
}
else
{
if (count == entries.Length)
{
Resize();
targetBucket = hashCode % buckets.Length;
}
index = count;
count++;
} entries[index].hashCode = hashCode;
entries[index].next = buckets[targetBucket];
entries[index].key = key;
entries[index].value = value;
buckets[targetBucket] = index;
version++; #if FEATURE_RANDOMIZED_STRING_HASHING #if FEATURE_CORECLR
// In case we hit the collision threshold we'll need to switch to the comparer which is using randomized string hashing
// in this case will be EqualityComparer<string>.Default.
// Note, randomized string hashing is turned on by default on coreclr so EqualityComparer<string>.Default will
// be using randomized string hashing if (collisionCount > HashHelpers.HashCollisionThreshold && comparer == NonRandomizedStringEqualityComparer.Default)
{
comparer = (IEqualityComparer<TKey>) EqualityComparer<string>.Default;
Resize(entries.Length, true);
}
#else
if(collisionCount > HashHelpers.HashCollisionThreshold && HashHelpers.IsWellKnownEqualityComparer(comparer))
{
comparer = (IEqualityComparer<TKey>) HashHelpers.GetRandomizedEqualityComparer(comparer);
Resize(entries.Length, true);
}
#endif // FEATURE_CORECLR #endif }
Insert
private int FindEntry(TKey key) {
if( key == null) {
ThrowHelper.ThrowArgumentNullException(ExceptionArgument.key);
}
if (buckets != null) {
int hashCode = comparer.GetHashCode(key) & 0x7FFFFFFF;
for (int i = buckets[hashCode % buckets.Length]; i >= 0; i = entries[i].next) {
if (entries[i].hashCode == hashCode && comparer.Equals(entries[i].key, key)) return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
FindEntry
2.Resize(重新调整大小)
虽然这是个私有方法,但我认为关键。它会在元素个数即将超过容量时调用,代码如下,简单说明一下。
该方法会声明一个 newBuckets 和 newEntrues 用来替换之前的 buckets 和 entrues,声明后会重构这两个数组,将 entrues 的值复制到 entrues,重新计算 newBuckets 的值,如果频繁触发该方法消耗是较大的,所以创建 Dictionary 时建议指定合理的 capacity(容量)
private void Resize(int newSize, bool forceNewHashCodes)
{
Contract.Assert(newSize >= entries.Length);
int[] newBuckets = new int[newSize];
for (int i = 0; i < newBuckets.Length; i++) newBuckets[i] = -1;
Entry[] newEntries = new Entry[newSize];
Array.Copy(entries, 0, newEntries, 0, count);
if (forceNewHashCodes)
{
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
if (newEntries[i].hashCode != -1)
{
newEntries[i].hashCode = (comparer.GetHashCode(newEntries[i].key) & 0x7FFFFFFF);
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
if (newEntries[i].hashCode >= 0)
{
int bucket = newEntries[i].hashCode % newSize;
newEntries[i].next = newBuckets[bucket];
newBuckets[bucket] = i;
}
}
buckets = newBuckets;
entries = newEntries;
}
Resize
3.Remove(移除)
依据key查到元素,将元素赋值为初始值,freeList记录该位置,下次新增会填充该位置
public bool Remove(TKey key)
{
if (key == null)
{
ThrowHelper.ThrowArgumentNullException(ExceptionArgument.key);
} if (buckets != null)
{
int hashCode = comparer.GetHashCode(key) & 0x7FFFFFFF;
int bucket = hashCode % buckets.Length;
int last = -1;
for (int i = buckets[bucket]; i >= 0; last = i, i = entries[i].next)
{
if (entries[i].hashCode == hashCode && comparer.Equals(entries[i].key, key))
{
if (last < 0)
{
buckets[bucket] = entries[i].next;
}
else
{
entries[last].next = entries[i].next;
}
entries[i].hashCode = -1;
entries[i].next = freeList;
entries[i].key = default(TKey);
entries[i].value = default(TValue);
freeList = i;
freeCount++;
version++;
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
Remove
展示一个 Dictionary 实际存储效果图
效率对比
新增效率:
| 时间ms | |
| Dictionary | 0.5643 |
| Array | 0.0238 |
| List | 0.0853 |
这是新增10000个元素操作耗费时间,Dictionary要比Array和List差不多高一个数量级。Array耗时最小是因为最开始就把所有空间申请好了。
查询效率:
| 10 | 100 | 1000 | 10000 | |
| Dictionary | 0.0056 | 0.0062 | 0.0056 | 0.0079 |
| Array遍历 | 0.0022 | 0.0142 | 0.1228 | 1.2396 |
| Array迭代器 | 0.0574 | 0.4278 | 6.1383 | 82.0934 |
| List遍历 | 0.0028 | 0.0238 | 0.2588 | 2.3558 |
| List.Find | 0.0654 | 0.091 | 0.3384 | 2.8768 |
| List迭代器 | 0.0079 | 0.029 | 0.2958 | 3.6625 |
可以看出元素在10个时除了Array迭代器和List.Find外,其他的没有较大差异。Array迭代器耗时的原因是涉及拆箱操作,List.Find可能是Lambda表达式的原因。当元素个数达到100时,Dictionary查询速度就相对快很多。随着元素数量增加,Dictionary查询速度并无太大差异,而其他查询呈倍数增长。
内存对比(元素个数10000)
| 字节差异 | |
| Dictionary | 350456 |
| Array | 40000左右 |
| List | 65572 |
通过VS查看内存情况(太菜了不知道Array对应的内存怎么看,估计40000左右)
附测试代码
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using Microsoft.VisualStudio.TestTools.UnitTesting;
using System.Diagnostics; namespace ToolBoxTest
{
/// <summary>
/// CommonTest 的摘要说明
/// </summary>
[TestClass]
public class CommonTest
{
[TestMethod]
public void Test1()
{
Stopwatch sw = new Stopwatch();
sw.Start();
List<int> list = new List<int>();
Dictionary<int, int> dic = new Dictionary<int, int>();
int count = 10000;
int key = count / 2;
int[] arr = new int[count];
sw.Stop(); sw.Restart();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
arr[i] = i;
}
sw.Stop();
TimeSpan tt1 = sw.Elapsed; sw.Restart();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
list.Add(i);
}
sw.Stop();
TimeSpan tt2 = sw.Elapsed; sw.Restart();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
dic.Add(i, i);
}
sw.Stop();
TimeSpan tt3 = sw.Elapsed; //字典
sw.Restart();
for(int j=0;j<100;j++)
{
int index2 = dic[key];
}
sw.Stop();
TimeSpan ts0 = sw.Elapsed; //数组 遍历
sw.Restart();
for (int j = 0; j < 100; j++)
{
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
if (arr[i] == key) break;
}
sw.Stop();
TimeSpan ts11 = sw.Elapsed; //数组 迭代器
sw.Restart();
for (int j = 0; j < 100; j++)
{
var p = arr.GetEnumerator();
while (p.MoveNext())
{
if ((int)p.Current == key)
break;
}
}
sw.Stop();
TimeSpan ts12 = sw.Elapsed; //列表 遍历
sw.Restart();
for (int j = 0; j < 100; j++)
{
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
if (list[i] == key) break;
}
sw.Stop();
TimeSpan ts21 = sw.Elapsed; //列表 Find
sw.Restart();
for (int j = 0; j < 100; j++)
{
list.Find(x => x == key);
}
sw.Stop();
TimeSpan ts22 = sw.Elapsed; //列表 迭代器
sw.Restart();
for (int j = 0; j < 100; j++)
{
var q = list.GetEnumerator();
while (q.MoveNext())
{
if (q.Current == key)
break;
}
}
sw.Stop();
TimeSpan ts23 = sw.Elapsed;
}
}
}
测试代码
总结一下
Dictionary 和我们日常用到的字典原理是一样的,通过目录→正文两次查找的方式查找元素,是一种空间换时间的方式,查询效率很高,大多数情况经过2次查询即可查到(需计算hashCode),但是相应的,开辟了多几倍的内存空间。另外,新增效率Dictionary明显较差,所以使用时要分情况而定,查询>新增(编辑)时优先考虑字典,它的查询效率真的很高。
使用注意点:
1.使用前尽量指定合适的容量,字典内元素个数应尽量避免超过容量
2.查询时应避免使用 Contains + [] 的方式取值,建议使用 TryGetValue,因为前者实际上是进行了两次查询,而后者是一次
参考:
https://www.cnblogs.com/zhili/p/DictionaryInDepth.html
https://referencesource.microsoft.com/#mscorlib/system/collections/generic/dictionary.cs
C# Dictionary(字典)源码解析&效率分析的更多相关文章
- Thinkphp6源码分析之解析,Thinkphp6路由,Thinkphp6路由源码解析,Thinkphp6请求流程解析,Thinkphp6源码
Thinkphp6源码解析之分析 路由篇-请求流程 0x00 前言: 第一次写这么长的博客,所以可能排版啊,分析啊,什么的可能会比较乱.但是我大致的流程已经觉得是说的够清楚了.几乎是每行源码上都有注释 ...
- Common.Logging源码解析二
Common.Logging源码解析一分析了LogManager主入口的整个逻辑,其中第二步生成日志实例工厂类接口分析的很模糊,本随笔将会详细讲解整个日志实例工厂类接口的生成过程! (1).关于如何生 ...
- 04、NetCore2.0下Web应用之Startup源码解析
04.NetCore2.0Web应用之Startup源码解析 通过分析Asp.Net Core 2.0的Startup部分源码,来理解插件框架的运行机制,以及掌握Startup注册的最优姿势. - ...
- 【转载】Scroller源码解析
原文地址:https://github.com/Skykai521/AndroidSdkSourceAnalysis/blob/master/article/Scroller%E6%BA%90%E7% ...
- Spring系列(五):Spring AOP源码解析
一.@EnableAspectJAutoProxy注解 在主配置类中添加@EnableAspectJAutoProxy注解,开启aop支持,那么@EnableAspectJAutoProxy到底做了什 ...
- java基础解析系列(十)---ArrayList和LinkedList源码及使用分析
java基础解析系列(十)---ArrayList和LinkedList源码及使用分析 目录 java基础解析系列(一)---String.StringBuffer.StringBuilder jav ...
- Mybaits 源码解析 (九)----- 全网最详细,没有之一:一级缓存和二级缓存源码分析
像Mybatis.Hibernate这样的ORM框架,封装了JDBC的大部分操作,极大的简化了我们对数据库的操作. 在实际项目中,我们发现在一个事务中查询同样的语句两次的时候,第二次没有进行数据库查询 ...
- MapReduce中一次reduce方法的调用中key的值不断变化分析及源码解析
摘要:mapreduce中执行reduce(KEYIN key, Iterable<VALUEIN> values, Context context),调用一次reduce方法,迭代val ...
- 【Spring源码分析】.properties文件读取及占位符${...}替换源码解析
前言 我们在开发中常遇到一种场景,Bean里面有一些参数是比较固定的,这种时候通常会采用配置的方式,将这些参数配置在.properties文件中,然后在Bean实例化的时候通过Spring将这些.pr ...
随机推荐
- nginx日志详细说明
Nginx日志主要分为两种:访问日志和错误日志.日志开关在Nginx配置文件(/etc/nginx/nginx.conf)中设置,两种日志都可以选择性关闭,默认都是打开的. 访问日志 访问日志主要记录 ...
- awk中的if ,else
local pct="$(awk -v one="$1" -v two="$2" 'BEGIN{ if (two > 0) { printf & ...
- xtrabackup 备份与恢复
书上摘抄 ---深入浅出mysql 448页 grant reload on *.* to 'backup'@'localhost' identified by '123456'; grant re ...
- 【TNS】listener.ora模板;tnsnames.ora模板
好多人使用监听的时候误操作,将监听弄的不好使了,这次这个模板,不光是针对大家出现的这种问题,也是给我自己留一个记录,方便他人,方便自己. listener.ora模板样例 -------------- ...
- 【Oracle】11G 11.2.0.4 RAC环境打补丁
一.准备工作 1,数据库环境 操作系统版本 : RedHat 7.2 x64 数据库版本 : Oracle 11.2.0.4 x64 RAC Grid : 11.2 ...
- 5V充8.4V,5V升压8.4V给电池充电的芯片电路
5V充8.4V的锂电池,需要把USB口的5V输入,升压转换成8.4V来给两串电池充电. 5V升压8.4V给锂电池充电的专门充电IC 集成了5V升压8.4V电路和充电管理电路的PL7501C 如果不需要 ...
- 转 1 认识开源性能测试工具jmeter
1 认识开源性能测试工具jmeter 典型的性能测试工具主要有2个,Load Runner和jmeter.Load Runner是商业化的,Jmeter是开源的.下面我们认识一下开源性能测试工具j ...
- SDNU_ACM_ICPC_2021_Winter_Practice_4th [个人赛]
传送门 D - Odd Divisor 题意: 给你一个n,问你n是否至少有一个奇数因子(这里题意没说清,没说是不是只有一个还是可以有多个!AC以后才发现是不止一个 思路: 如果这个数没有奇数因子,那 ...
- UT /SIT/ UAT
UT /SIT/ UAT - 云+社区 - 腾讯云 https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1541268 我们公司只有测试环境--准生产环境--生产环 ...
- LOJ10145郁闷的出纳员
传送门:https://loj.ac/problem/10145 简单的平衡树 ------------------------------------ 1 #include<bits/stdc ...
