Linux高性能server编程——定时器
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章。未经博主允许不得转载。 https://blog.csdn.net/walkerkalr/article/details/36869913
定时器
服务器程序通常管理着众多定时事件。因此有效组织这些定时事件,使之能在预期的时间点被触发且不影响服务器的主要逻辑,对于服务器的性能有着至关重要的影响。位置我们要将每一个定时事件封装成定时器。并使用某种容器类型的数据结构,比方链表、排序链表和时间轮将全部定时器串联起来,以实现对定时事件的统一管理。
Linux提供三种定时方法:
1.socket选项SO_RECVTIMEO和SO_SNDTIMEO。
2.SIGALRM信号
3.I/O复用系统调用的超时參数
socket选项SO_RCVTIMEO和SO_SNDTIMEO
SO_RCVTIMEO和SO_SNDTIMEO选项分别用来设置socket接收数据超时时间和发送数据超时时间。因此这两个选项仅对数据接收和发送相关的socket专用系统调用有效。这些系统调用包含send、sendmsg、recv、recvmsg、accept和connect。
程序清单1展示了使用SO_SNDTIMEP选项来定时:
SIGALRM信号
由alarm和setitimer函数设置的实时闹钟一旦超时。将触发SIGALRM信号。
因此,我们能够利用该信号的信号处理函数来处理定时任务。
可是。假设要处理多个定时任务,我们就须要不断触发SIGALRM信号,并在其信号处理函数中运行到期的任务。一般而言,SIGALRM信号依照固定频率生成,即由alarm或setitimer函数设计的定时周期T保持不变。假设某个定时任务的超时时间不是T的整数倍,那么它实际被运行的时间和预期的时间将略有偏差。
因此定时周期T反映了定时的精度。
程序清单2定义了一个定时器链表,程序清单3展示怎样使用SIGALRM信号处理非活动连接。
I/O复用系统调用
Linux下的3组I/O复用系统调用都带有超时參数,因此他们不仅能允许处理信号和I/O事件。也能统一处理定时事件。
可是因为I/O复用系统可能在超时时间到期之前就返回。所以假设我们能要利用它们来定时,就须要不断更新定时參数以反映剩余的时间:
程序清单4展示了利用I/O复用系统调用定时:
高性能定时器
时间轮
基于排序链表的定时器存在一个问题:加入定时器的效率偏低。
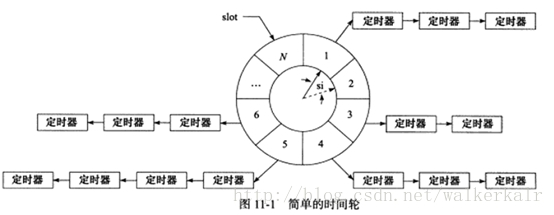
以下我们要讨论的时间轮攻克了这个问题,一种简单的时间轮如图所看到的:
上图所看到的的时间轮,实现指针指向轮子的一个槽。
它以恒定的速度顺时转动。每转动一步就指向下一个槽。每次转动称为一个滴答。
一个滴答的时间称为时间轮的槽间隔si。它时间上就是心搏时间。该时间轮共同拥有N个槽。因此转一圈时间是N*si。每一个槽指向一跳定时器链表,每条链表上的定时器具有同样的特征:他们的定时时间差JN*si的整数倍。非常显然,对时间轮而言,要提高定时精度。就要使si值足够小;要提高运行效率。则要求N值足够大。
时间堆
前面讨论的定时方案都是以固定是频率调用心搏函数tick,并在当中一次检測到期的定时器,然后运行到期定时器上的回调函数。设计定时器的还有一种思路是:将全部定时器中超时时间最小的一个定时器的超时值作为心搏间隔。
这样,一旦心搏函数tick被调用,超时时间最小的定时器必定到期,我们就能够在tick函数中处理该定时器。
然后,再次从剩余的定时器中找出超时时间最小的一个,并将这段最小时间设置为下一次心搏间隔。时间堆就是利用最小堆来是实现上述方案。
程序清单1:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
int timeout_connect( const char* ip, int port, int time )
{
int ret = 0;
struct sockaddr_in address;
bzero( &address, sizeof( address ) );
address.sin_family = AF_INET;
inet_pton( AF_INET, ip, &address.sin_addr );
address.sin_port = htons( port );
int sockfd = socket( PF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0 );
assert( sockfd >= 0 );
struct timeval timeout;
timeout.tv_sec = time;
timeout.tv_usec = 0;
socklen_t len = sizeof( timeout );
ret = setsockopt( sockfd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_SNDTIMEO, &timeout, len );
assert( ret != -1 );
ret = connect( sockfd, ( struct sockaddr* )&address, sizeof( address ) );
if ( ret == -1 )
{
if( errno == EINPROGRESS )
{
printf( "connecting timeout\n" );
return -1;
}
printf( "error occur when connecting to server\n" );
return -1;
}
return sockfd;
}
int main( int argc, char* argv[] )
{
if( argc <= 2 )
{
printf( "usage: %s ip_address port_number\n", basename( argv[0] ) );
return 1;
}
const char* ip = argv[1];
int port = atoi( argv[2] );
int sockfd = timeout_connect( ip, port, 10 );
if ( sockfd < 0 )
{
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
程序清单2:
#ifndef LST_TIMER
#define LST_TIMER
#include <time.h>
#define BUFFER_SIZE 64
class util_timer;
struct client_data
{
sockaddr_in address;
int sockfd;
char buf[ BUFFER_SIZE ];
util_timer* timer;
};
class util_timer
{
public:
util_timer() : prev( NULL ), next( NULL ){}
public:
time_t expire;
void (*cb_func)( client_data* );
client_data* user_data;
util_timer* prev;
util_timer* next;
};
class sort_timer_lst
{
public:
sort_timer_lst() : head( NULL ), tail( NULL ) {}
~sort_timer_lst()
{
util_timer* tmp = head;
while( tmp )
{
head = tmp->next;
delete tmp;
tmp = head;
}
}
void add_timer( util_timer* timer )
{
if( !timer )
{
return;
}
if( !head )
{
head = tail = timer;
return;
}
if( timer->expire < head->expire )
{
timer->next = head;
head->prev = timer;
head = timer;
return;
}
add_timer( timer, head );
}
void adjust_timer( util_timer* timer )
{
if( !timer )
{
return;
}
util_timer* tmp = timer->next;
if( !tmp || ( timer->expire < tmp->expire ) )
{
return;
}
if( timer == head )
{
head = head->next;
head->prev = NULL;
timer->next = NULL;
add_timer( timer, head );
}
else
{
timer->prev->next = timer->next;
timer->next->prev = timer->prev;
add_timer( timer, timer->next );
}
}
void del_timer( util_timer* timer )
{
if( !timer )
{
return;
}
if( ( timer == head ) && ( timer == tail ) )
{
delete timer;
head = NULL;
tail = NULL;
return;
}
if( timer == head )
{
head = head->next;
head->prev = NULL;
delete timer;
return;
}
if( timer == tail )
{
tail = tail->prev;
tail->next = NULL;
delete timer;
return;
}
timer->prev->next = timer->next;
timer->next->prev = timer->prev;
delete timer;
}
void tick()
{
if( !head )
{
return;
}
printf( "timer tick\n" );
time_t cur = time( NULL );
util_timer* tmp = head;
while( tmp )
{
if( cur < tmp->expire )
{
break;
}
tmp->cb_func( tmp->user_data );
head = tmp->next;
if( head )
{
head->prev = NULL;
}
delete tmp;
tmp = head;
}
}
private:
void add_timer( util_timer* timer, util_timer* lst_head )
{
util_timer* prev = lst_head;
util_timer* tmp = prev->next;
while( tmp )
{
if( timer->expire < tmp->expire )
{
prev->next = timer;
timer->next = tmp;
tmp->prev = timer;
timer->prev = prev;
break;
}
prev = tmp;
tmp = tmp->next;
}
if( !tmp )
{
prev->next = timer;
timer->prev = prev;
timer->next = NULL;
tail = timer;
}
}
private:
util_timer* head;
util_timer* tail;
};
#endif
程序清单3
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/epoll.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include "lst_timer.h"
#define FD_LIMIT 65535
#define MAX_EVENT_NUMBER 1024
#define TIMESLOT 5
static int pipefd[2];
static sort_timer_lst timer_lst;
static int epollfd = 0;
int setnonblocking( int fd )
{
int old_option = fcntl( fd, F_GETFL );
int new_option = old_option | O_NONBLOCK;
fcntl( fd, F_SETFL, new_option );
return old_option;
}
void addfd( int epollfd, int fd )
{
epoll_event event;
event.data.fd = fd;
event.events = EPOLLIN | EPOLLET;
epoll_ctl( epollfd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, fd, &event );
setnonblocking( fd );
}
void sig_handler( int sig )
{
int save_errno = errno;
int msg = sig;
send( pipefd[1], ( char* )&msg, 1, 0 );
errno = save_errno;
}
void addsig( int sig )
{
struct sigaction sa;
memset( &sa, '\0', sizeof( sa ) );
sa.sa_handler = sig_handler;
sa.sa_flags |= SA_RESTART;
sigfillset( &sa.sa_mask );
assert( sigaction( sig, &sa, NULL ) != -1 );
}
void timer_handler()
{
timer_lst.tick();
alarm( TIMESLOT );
}
void cb_func( client_data* user_data )
{
epoll_ctl( epollfd, EPOLL_CTL_DEL, user_data->sockfd, 0 );
assert( user_data );
close( user_data->sockfd );
printf( "close fd %d\n", user_data->sockfd );
}
int main( int argc, char* argv[] )
{
if( argc <= 2 )
{
printf( "usage: %s ip_address port_number\n", basename( argv[0] ) );
return 1;
}
const char* ip = argv[1];
int port = atoi( argv[2] );
int ret = 0;
struct sockaddr_in address;
bzero( &address, sizeof( address ) );
address.sin_family = AF_INET;
inet_pton( AF_INET, ip, &address.sin_addr );
address.sin_port = htons( port );
int listenfd = socket( PF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0 );
assert( listenfd >= 0 );
ret = bind( listenfd, ( struct sockaddr* )&address, sizeof( address ) );
assert( ret != -1 );
ret = listen( listenfd, 5 );
assert( ret != -1 );
epoll_event events[ MAX_EVENT_NUMBER ];
int epollfd = epoll_create( 5 );
assert( epollfd != -1 );
addfd( epollfd, listenfd );
ret = socketpair( PF_UNIX, SOCK_STREAM, 0, pipefd );
assert( ret != -1 );
setnonblocking( pipefd[1] );
addfd( epollfd, pipefd[0] );
// add all the interesting signals here
addsig( SIGALRM );
addsig( SIGTERM );
bool stop_server = false;
client_data* users = new client_data[FD_LIMIT];
bool timeout = false;
alarm( TIMESLOT );
while( !stop_server )
{
int number = epoll_wait( epollfd, events, MAX_EVENT_NUMBER, -1 );
if ( ( number < 0 ) && ( errno != EINTR ) )
{
printf( "epoll failure\n" );
break;
}
for ( int i = 0; i < number; i++ )
{
int sockfd = events[i].data.fd;
if( sockfd == listenfd )
{
struct sockaddr_in client_address;
socklen_t client_addrlength = sizeof( client_address );
int connfd = accept( listenfd, ( struct sockaddr* )&client_address, &client_addrlength );
addfd( epollfd, connfd );
users[connfd].address = client_address;
users[connfd].sockfd = connfd;
util_timer* timer = new util_timer;
timer->user_data = &users[connfd];
timer->cb_func = cb_func;
time_t cur = time( NULL );
timer->expire = cur + 3 * TIMESLOT;
users[connfd].timer = timer;
timer_lst.add_timer( timer );
}
else if( ( sockfd == pipefd[0] ) && ( events[i].events & EPOLLIN ) )
{
int sig;
char signals[1024];
ret = recv( pipefd[0], signals, sizeof( signals ), 0 );
if( ret == -1 )
{
// handle the error
continue;
}
else if( ret == 0 )
{
continue;
}
else
{
for( int i = 0; i < ret; ++i )
{
switch( signals[i] )
{
case SIGALRM:
{
timeout = true;
break;
}
case SIGTERM:
{
stop_server = true;
}
}
}
}
}
else if( events[i].events & EPOLLIN )
{
memset( users[sockfd].buf, '\0', BUFFER_SIZE );
ret = recv( sockfd, users[sockfd].buf, BUFFER_SIZE-1, 0 );
printf( "get %d bytes of client data %s from %d\n", ret, users[sockfd].buf, sockfd );
util_timer* timer = users[sockfd].timer;
if( ret < 0 )
{
if( errno != EAGAIN )
{
cb_func( &users[sockfd] );
if( timer )
{
timer_lst.del_timer( timer );
}
}
}
else if( ret == 0 )
{
cb_func( &users[sockfd] );
if( timer )
{
timer_lst.del_timer( timer );
}
}
else
{
//send( sockfd, users[sockfd].buf, BUFFER_SIZE-1, 0 );
if( timer )
{
time_t cur = time( NULL );
timer->expire = cur + 3 * TIMESLOT;
printf( "adjust timer once\n" );
timer_lst.adjust_timer( timer );
}
}
}
else
{
// others
}
}
if( timeout )
{
timer_handler();
timeout = false;
}
}
close( listenfd );
close( pipefd[1] );
close( pipefd[0] );
delete [] users;
return 0;
}
程序清单4
#define TIMEOUT 5000
int timeout = TIMEOUT;
time_t start = time( NULL );
time_t end = time( NULL );
while( 1 )
{
printf( "the timeout is now %d mill-seconds\n", timeout );
start = time( NULL );
int number = epoll_wait( epollfd, events, MAX_EVENT_NUMBER, timeout );
if( ( number < 0 ) && ( errno != EINTR ) )
{
printf( "epoll failure\n" );
break;
}
if( number == 0 )
{
// timeout
timeout = TIMEOUT;
continue;
}
end = time( NULL );
timeout -= ( end - start ) * 1000;
if( timeout <= 0 )
{
// timeout
timeout = TIMEOUT;
}
// handle connections
}
Linux高性能server编程——定时器的更多相关文章
- Linux高性能server编程——Linux网络基础API及应用
Linux网络编程基础API 具体介绍了socket地址意义极其API,在介绍数据读写API部分引入一个有关带外数据发送和接收的程序,最后还介绍了其它一些辅助API. socket地址API 主 ...
- Linux高性能server编程——信号及应用
信号 信号是由用户.系统或者进程发送给目标进程的信息.以通知目标进程某个状态的改变或系统异常. Linux信号可由例如以下条件产生: 对于前台进程.用户能够通过输入特殊的终端字符来给它发送信号. ...
- Linux高性能server编程——多线程编程(下)
多线程编程 条件变量 假设说相互排斥锁是用于同步线程对共享数据的訪问的话.那么条件变量则是用于线程之间同步共享数据的值. 条件变量提供了一种线程间的通信机制:当某个共享数据达到某个值得时候,唤醒等待这 ...
- Linux高性能server编程——I/O复用
IO复用 I/O复用使得程序能同一时候监听多个文件描写叙述符.通常网络程序在下列情况下须要使用I/O复用技术: client程序要同一时候处理多个socket client程序要同一时候处理用户 ...
- Linux 高性能server编程——高级I/O函数
重定向dup和dup2函数 #include <unistd.h> int dup(int file_descriptor); int dup2(int file_descriptor_o ...
- Linux高性能server编程——系统检測工具
系统检測工具 tcpdump tcpdump是一款经典的抓包工具,tcpdump给使用者提供了大量的选项,泳衣过滤数据报或者定制输出格式. lsof lsof是一个列出当前系统打开的文件描写叙述符的工 ...
- Linux高性能server编程——高级I/O函数
高级I/O函数 pipe函数 pipe函数用于创建一个管道,实现进程间的通信. #include <unistd.h> int pipe(int pipefd[2]); 通过pipe ...
- Linux 高性能服务器编程——TCP协议详解
问题聚焦: 本节从如下四个方面讨论TCP协议: TCP头部信息:指定通信的源端端口号.目的端端口号.管理TCP连接,控制两个方向的数据流 TCP状态转移过程:TCP连接的任意一 ...
- linux高性能服务器编程
<Linux高性能服务器编程>:当当网.亚马逊 目录: 第一章:tcp/ip协议族 第二章:ip协议族 第三章:tcp协议详解 第四章:tcp/ip通信案例:访问Internet 第五章: ...
随机推荐
- Ubuntu 安装 phpredis扩展
官网 https://github.com/phpredis/phpredis 下载->然后解压->上传服务器 /etc/phpredis 进行 cd /etc/phpredisphpiz ...
- 1.2 rust cargo
cargo是rust的编译与打包工具,可将rust打包成为一个可执行性文件.生成的可执行性文件不能跨系统的大版本,比如在linux7上打包,那么程序无法在linux6上执行. # cargo new ...
- mgo03_linux7上安装mongo4.0
下载地址https://www.mongodb.com/download-center#community tar -xvf mongodb-linux-x86_64-rhel70-4.0.0.tgz ...
- yii2下的路由重写
1.在config/main.php中添加配置信息 文件位置如图所示(图中展示的是backend下的config,也可以在fronted和common的config中添加) 配置的代码标准格式如下 ' ...
- java——newInstance()方法和new关键字
https://www.cnblogs.com/liuyanmin/p/5146557.html 这两个都可以创建一个对象,那么这样个东西有什么不一样呢?什么时候用new,什么时候用newInstan ...
- Window 远程连接 Ubuntu 系统
安装XRDP 服务, 用windows远程连接ubuntu 1. Step 1 – Install xRDP sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install xrdp ...
- http 协议的简单学习 虽然有点老但是 还不错
HTTP简介 HTTP协议是Hyper Text Transfer Protocol(超文本传输协议)的缩写,是用于从万维网(WWW:World Wide Web )服务器传输超文本到本地浏览器的传送 ...
- c++ primer 中讲的顶层const 和 底层 const 理解
c++ primer 中讲的 顶层const 和 底层 const 以前没搞懂的顶层const和底层const,这次看了后感觉明白了. 首先,const是一个限定符,被它修饰的变量的值不能改 ...
- python 层次索引交换级别以及排序问题
- Java基础01-JVM内存分析
JVM java虚拟机 java编译后的class文件就是在java虚拟机上运行的 1.栈区(stacksegment)存放函数的参数值,局部变量的值等,在超过这个变量的作用域时就会被系统自动释放掉存 ...