Android学习(四) Layout五大布局
我们知道Android系统应用程序一般是由多个Activity组成,而这些Activity以视图的形式展现在我们面前, 视图都是由一个一个的组件构成的。组件就是我们常见的Button、TextEdit等等。那么我们平时看到的Android手机中那些漂亮的界面是怎么显示 出来的呢?这就要用到Android的布局管理器了,网上有人比喻的很好:布局好比是建筑里的框架,组件按照布局的要求依次排列,就组成了用于看见的漂亮界面了。
在分析布局之前,我们首先看看控件:Android中任何可视化的控件都是从android.veiw.View继承而来的,系统提供了两种方法来设置视图:第一种也是我们最常用的的使用XML文件来配置View的相关属性,然后在程序启动时系统根据配置文件来创建相应的View视图。第二种是我们在代码中直接使用相应的类来创建视图。
如何使用XML文件定义视图:
每个Android项目的源码目录下都有个res/layout目录,这个目录就是用来存放布局文件的。布局文件一般以对应activity的名字命名,以 .xml 为后缀。在xml中为创建组件时,需要为组件指定id,如:android:id="@+id/名字"系统会自动在gen目录下创建相应的R资源类变量。
如何在代码中使用视图:
在代码中创建每个Activity时,一般是在onCreate()方法中,调用setContentView()来加载指定的xml布局文件,然后就可以通过findViewById()来获得在布局文件中创建的相应id的控件了,如Button等。
如:
private Button btnSndMag;
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main); // 加载main.xml布局文件
btnSndMag = (Button)this.findViewById(R.id.btnSndMag); // 通过id找到对于的Button组件
....
}
下面我们来介绍Android系统中为我们提供的五大布局:LinearLayout(线性布局)、FrameLayout(单帧布局)、AbsoluteLayout(绝对布局)、TablelLayout(表格布局)、RelativeLayout(相对布局)。其中最常用的的是LinearLayout、TablelLayout和RelativeLayout。这些布局都可以嵌套使用。
(1)LinearLayout 线性布局
线性布局是按照水平或垂直的顺序将子元素(可以是控件或布局)依次按照顺序排列,每一个元素都位于前面一个元素之后。线性布局分为两种:水平方向和垂直方向的布局。分别通过属性android:orientation="vertical" 和 android:orientation="horizontal"来设置。
android:layout_weight 表示子元素占据的空间大小的比例,有人说这个值大小和占据空间成正比,有人说反比。我在实际应用中设置和网上资料显示的刚好相反,这个问题后面会专门写一篇文章来分析。现在我们只需要按照正比例来设置就可以。
android:gravity:可以设置元素的所在的位置,表示布局标签中所有元素的位置。
android:layout_gravity:也可以给单独每个子元素添加layout_gravity,可以单独设置元素所在的位置。
例如下面我们实现一个如图所示的简易计算器界面:
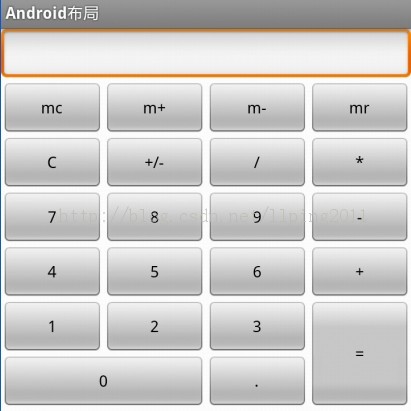
代码:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#FFFFFF"
tools:context=".MainActivity" > // 这里第一行显示标签为一个水平布局
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal" >
<EditText
android:id="@+id/msg"
android:inputType="number"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="">
</EditText>
</LinearLayout> // 第二行为 mc m+ m- mr 四个Button构成一个水平布局
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal" >
<Button
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="mc" android:layout_weight="1">
</Button>
<Button
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="m+" android:layout_weight="1">
</Button>
<Button
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="m-" android:layout_weight="1">
</Button>
<Button
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="mr" android:layout_weight="1">
</Button>
</LinearLayout> // 同上 C +/- / * 四个Button构成一个水平布局
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal" >
<Button
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="C" >
</Button>
<Button
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="+/-" >
</Button>
<Button
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="/" >
</Button>
<Button
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="*" >
</Button>
</LinearLayout> <LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal" >
<Button
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="7" android:layout_weight="1">
</Button>
<Button
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="8" android:layout_weight="1">
</Button>
<Button
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="9" android:layout_weight="1">
</Button>
<Button
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="-" android:layout_weight="1">
</Button>
</LinearLayout> <LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal" >
<Button
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="4" >
</Button>
<Button
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="5" >
</Button>
<Button
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="6" >
</Button>
<Button
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="+" >
</Button>
</LinearLayout> // 最外层是一个水平布局,由左边上面一行1 2 3三个Button,下面一行的0 . 两个Button 和 右边的=构成
<LinearLayout android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
// 这里 1 2 3 和 下面的 0 . 构成一个垂直布局
<LinearLayout android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_weight="3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
// 这里的 1 2 3 构成一个水平布局
<LinearLayout android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="1"></Button>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="2"></Button>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="3"></Button>
</LinearLayout>
// 这里的 0 和 . 构成一个水平布局,注意这里的android_weight参数设置
<LinearLayout android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<Button
android:layout_width="0px"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="2"
android:text="0"></Button>
<Button
android:layout_width="0px"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="."></Button>
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
// 这里一个单独Button构成的垂直布局
<LinearLayout android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<Button
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:text="="></Button>
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout> </LinearLayout>
(2)TableLayout 表格布局
表格布局,适用于多行多列的布局格式,每个TableLayout是由多个TableRow组成,一个TableRow就表示TableLayout中的每一行,这一行可以由多个子元素组成。实际上TableLayout和TableRow都是LineLayout线性布局的子类。但是TableRow的参数android:orientation属性值固定为horizontal,且android:layout_width=MATCH_PARENT,android:layout_height=WRAP_CONTENT。所以TableRow实际是一个横向的线性布局,且所以子元素宽度和高度一致。
注意:在TableLayout中,单元格可以为空,但是不能跨列,意思是只能不能有相邻的单元格为空。
在TableLayout布局中,一列的宽度由该列中最宽的那个单元格指定,而该表格的宽度由父容器指定。可以为每一列设置以下属性:
Shrinkable 表示该列的宽度可以进行收缩,以使表格能够适应父容器的大小
Stretchable 表示该列的宽度可以进行拉伸,以使能够填满表格中的空闲空间
Collapsed 表示该列会被隐藏
TableLayout中的全局属性:
android:collapseColumns="1,3",表示第2列和第4列被隐藏,多列必须以,隔开
android:shrinkColumns="1,3",表示第2列和第4列被收缩,多列以,隔开,*表示所有列。
android:stretchColumns = "0,1,2,3",表示该列被拉伸
TableLayout的局部属性:
android:layout_column="1",该控件显示在第二列
android:layout_span="2",该控件占据2列
Demo:我们想设计一个如下所以的一个三行三列的表格,但是第二行我们只想显示2个表格:
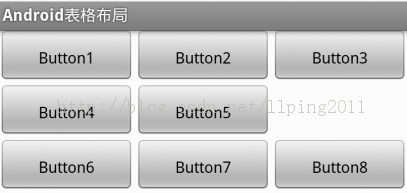
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<TableLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:shrinkColumns="0,1,2" // 设置三列都可以收缩
android:stretchColumns="0,1,2" // 设置三列都可以拉伸 如果不设置这个,那个显示的表格将不能填慢整个屏幕
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent" >
<TableRow android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<Button android:gravity="center"
android:padding="10dp"
android:text="Button1">
</Button> <Button android:gravity="center"
android:padding="10dp"
android:text="Button2">
</Button>
<Button android:gravity="center"
android:padding="10dp"
android:text="Button3">
</Button>
</TableRow>
<TableRow android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<Button android:gravity="center"
android:padding="10dp"
android:text="Button4">
</Button> <Button android:gravity="center"
android:padding="10dp"
android:text="Button5">
</Button>
</TableRow>
<TableRow android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<Button android:gravity="center"
android:padding="10dp"
android:text="Button6">
</Button>
<Button android:gravity="center"
android:padding="10dp"
android:text="Button7">
</Button>
<Button android:gravity="center"
android:padding="10dp"
android:text="Button8">
</Button>
</TableRow>
</TableLayout>
(3)RelativeLayout 相对布局
RelativeLayout继承于android.widget.ViewGroup,其按照子元素之间的位置关系完成布局的,作为Android系统五大布局中最灵活也是最常用的一种布局方式,非常适合于一些比较复杂的界面设计。
注意:在引用其他子元素之前,引用的ID必须已经存在,否则将出现异常。
常用的位置属性:
android:layout_toLeftOf 该组件位于引用组件的左方
android:layout_toRightOf 该组件位于引用组件的右方
android:layout_above 该组件位于引用组件的上方
android:layout_below 该组件位于引用组件的下方
android:layout_alignParentLeft 该组件是否对齐父组件的左端
android:layout_alignParentRight 该组件是否齐其父组件的右端
android:layout_alignParentTop 该组件是否对齐父组件的顶部
android:layout_alignParentBottom 该组件是否对齐父组件的底部
android:layout_centerInParent 该组件是否相对于父组件居中
android:layout_centerHorizontal 该组件是否横向居中
android:layout_centerVertical 该组件是否垂直居中
Demo:利用相对布局设计一个如下图所示的界面:
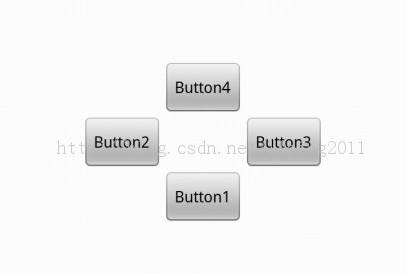
源码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent" >
<Button android:id="@+id/btn1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:text="Button1"
></Button>
<Button android:id="@+id/btn2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_toLeftOf="@id/btn1"
android:layout_above="@id/btn1"
android:text="Button2"
></Button>
<Button android:id="@+id/btn3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_toRightOf="@id/btn1"
android:layout_above="@id/btn1"
android:text="Button3"
></Button>
<Button android:id="@+id/btn4"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_toRightOf="@id/btn2"
android:layout_toLeftOf="@id/btn3"
android:layout_above="@id/btn2"
android:text="Button4"
></Button>
</RelativeLayout>
(4)FrameLayout 框架布局
将所有的子元素放在整个界面的左上角,后面的子元素直接覆盖前面的子元素,所以用的比较少。
(5) AbsoluteLayou 绝对布局
绝对布局中将所有的子元素通过设置android:layout_x 和 android:layout_y属性,将子元素的坐标位置固定下来,即坐标(android:layout_x, android:layout_y) ,layout_x用来表示横坐标,layout_y用来表示纵坐标。 屏幕左上角为坐标(0,0),横向往右为正方,纵向往下为正方。实际应用中,这种布局用的比较少,因为Android终端一般机型比较多,各自的屏幕大小。分辨率等可能都不一样,如果用绝对布局,可能导致在有的终端上显示不全等。
除上面讲过之外常用的几个布局的属性:
(1)layout_margin
用于设置控件边缘相对于父控件的边距
android:layout_marginLeft
android:layout_marginRight
android:layout_marginTop
android:layout_marginBottom
(2) layout_padding
用于设置控件内容相对于控件边缘的边距
android:layout_paddingLeft
android:layout_paddingRight
android:layout_paddingTop
android:layout_paddingBottom
(3) layout_width/height
用于设置控件的高度和宽度
wrap_content 内容包裹,表示这个控件的里面文字大小填充
fill_parent 跟随父窗口
match_parent
(4) gravity
用于设置View组件里面内容的对齐方式
top bottom left right center等
(5) android:layout_gravity
用于设置Container组件的对齐方式
android:layout_alignTop 本元素的上边缘和某元素的的上边缘对齐
android:layout_alignLeft 本元素的左边缘和某元素的的左边缘对齐
android:layout_alignBottom 本元素的下边缘和某元素的的下边缘对齐
android:layout_alignRight 本元素的右边缘和某元素的的右边缘对齐
Android学习(四) Layout五大布局的更多相关文章
- Android UI基础之五大布局
Android UI基础之五大布局 Android的界面是有布局和组件协同完成的,布局好比是建筑里的框架,而组件则相当于建筑里的砖瓦.组件按照布局的要求依次排列,就组成了用户所看见的界面.Andro ...
- Android培训准备资料之五大布局简单介绍
本篇博客主要简单的给大家介绍一下Android五大布局 (1)LinearLayout(线性布局) (2)RelativeLayout(相对布局) (3)FrameLayout(帧布局) (4)Abs ...
- Android学习笔记④——页面的布局方式
FrameLayout(帧布局) 这个布局的特点是简单的默认把每一个视图组件都放在边框内且放在左上角,即使添加多个视图组件,他们也都是重叠在左上角,新的视图会遮挡住旧的视图.可以根据gravity来改 ...
- Android学习笔记(11):线性布局LinearLayout
线性布局LinearLayout是指在横向或是竖向一个接一个地排列.当排列的组件超出屏幕后,超出的组件将不会再显示出来. LinearLayout支持的XML属性和相应方法如表所看到的: Attrib ...
- android学习笔记三--Activity 布局
1.线性布局 标签 :<LinearLayout></LinearLayout> 方向:android:orientation, 垂直:vertical 水平:Horizont ...
- android学习四(Activity的生命周期)
要学好活动(Activity).就必需要了解android中Activity的声明周期.灵活的使用生命周期.能够开发出更好的程序,在android中是使用任务来管理活动的,一个任务就是一组存放在栈里的 ...
- Xamarin 学习笔记 - Layout(布局)
本文翻译自CodeProject文章:https://www.codeproject.com/Articles/1227733/Xamarin-Notes-Xamarin-Forms-Layouts ...
- Android学习系列(5)--App布局初探之简单模型
人类科技的进步源自探索,探索来自于发现本原,当然App布局没这么先进,本文也只是一个归类总结.这篇文章是Android开发人员的必备知识,是我特别为大家整理和总结的,不求完美,但是有用. Androi ...
- android学习四---Activity和Intent
1.android项目资源深入了解 在深入学习android之前,先好好玩玩手机上的应用,大部分程序都有一个图标,点开图标,程序启动,一定时间后,程序会跳转到第一个界面,比如手机QQ,点开图标,会跳出 ...
随机推荐
- 用Sublime搭建Python开发环境(windows)
1.安装Python 3 去官网下载Python 3,网址:https://www.python.org/downloads/release/python-363/ 双击安装,勾选添加到环境变量. 有 ...
- Objective-C类族和工厂模式
http://www.cocoachina.com/ios/20141124/10296.html 相信大家都了解GoF的<Design Patterns>中提到的23种设计模式,其中将常 ...
- usb驱动---linux ACM驱动详解ACA【转】
转自:http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-9185047-id-3404684.html DTE提供或接收数据,连接到网络中的用户端机器,主要是计算机和终端设备.与此相对地,在 ...
- SQLSERVER2008以上版本的数据恢复
这哥们真不错... http://blog.csdn.net/dba_huangzj/article/details/8491327
- 最近有点把b/s架构什么的,和web发展搞晕了,现在来总结总结
Web是一种典型的分布式应用架构 分布式计算技术的架构:目前成熟的技术包括J2EE, CORBA和.NET(DCOM) 在流行c/s的1992年, OMG组织提出CORBA,很大程度的提高了分布式应用 ...
- python爬虫搜片利器fmovice【转载】
本篇转自博客:上海-悠悠 原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/yoyoketang/tag/python/ 前言 讲真!小编不管看什么电影(大的.小的),不管什么电视剧,小编都没买 ...
- JavaScript基础之原型对象和原型链
原型对象 原型对象简单来说就是函数的原型所指向的对象.前面说原型的时候,说了Object.prototype所指对象就是Object(函数)的原型对象.在每个函数的原型对象中,默认会有construc ...
- UVA 11149.Power of Matrix-矩阵快速幂倍增
Power of Matrix UVA - 11149 代码: #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include < ...
- (1) C语言 基础1
VS scanf 安全错误 在预处理器定义那里添加一行_CRT_SECURE_NO_DEPRECATE vs编译头错误 一.打印helloworld #include<stdio.h> ...
- CF987A Infinity Gauntlet【STL】
[链接]:CF987A [分析]:运用map [代码]: #include <iostream> #include<queue> #include<string.h> ...
