Java基础 韩顺平老师的 集合 的部分笔记
498,集合介绍


499,集合体系图(两个图背下)

package com.hspedu.collection; import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap; public class Collection01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//老韩解读
//1,集合主要是两组(单列集合,双列集合)
//2,Collection 接口有两个重要的子接口 List Set,他们的实现子类都是单列集合
//3,Map 接口的实现子类 是双列集合,存放的 K-V
//4,把老师梳理的两张图记住
//Collection
//Map //存放的数据是单个的,就是单列集合
ArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList();
arrayList.add("jack"); //存放的数据是两个的,就是双列集合
HashMap hashMap = new HashMap();
hashMap.put("NO1","北京");
}
}
500,Collection方法


package com.hspedu.collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Collection01 {
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList();
//add:添加单个元素
list.add("jack");
list.add(10);//list.add(new Integer(10)),传进的是一个对象
list.add(true);
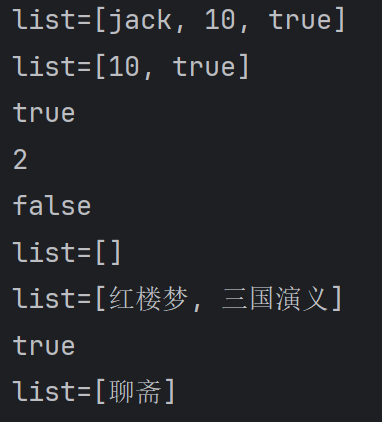
System.out.println("list=" + list);
//remove:删除指定的元素
//list.remove(0);//删除第一个元素
list.remove("jack");//指定删除某个元素
System.out.println("list=" + list);
//contains:查找元素是否存在
System.out.println(list.contains(10));//T
//size:获取元素个数
System.out.println(list.size());//2
//isEmpty:判断是否为空
System.out.println(list.isEmpty());//F
//clear:清空
list.clear();
System.out.println("list=" + list);
//addAll:添加多个元素
ArrayList list2 = new ArrayList();
list2.add("红楼梦");
list2.add("三国演义");
list.addAll(list2);
System.out.println("list=" + list);
//containsAll:查找多个元素是否都存在
System.out.println(list.containsAll(list2));//T
//removeAll:删除多个元素
list.add("聊斋");
list.removeAll(list2);
System.out.println("list=" + list);//[聊斋]
}
}
501,java迭代器遍历



package com.hspedu.collection; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator; public class Collection01 {
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection col = new ArrayList();//向上转型,Collection是接口 col.add(new Book("三国演义", "罗贯中", 10.1));
col.add(new Book("小李飞刀", "古龙", 5.1));
col.add(new Book("红楼梦", "曹雪芹", 34.6)); //System.out.println("col=" + col);
//遍历集合
//1,先得到 col 对应的 迭代器
Iterator iterator = col.iterator();
//2,使用while循环遍历,快捷键 itit
while (iterator.hasNext()) { //判断是否还有数据
//返回下一个元素,类型是Object
Object obj = iterator.next();
System.out.println("obj=" + obj);
}
//3,当退出while循环后,这时iterator迭代器,指向最后的元素
//iterator.next();//NoSuchElementException
//4,如果希望再次遍历,需要重置我们的迭代器
iterator = col.iterator();
System.out.println("===第二次遍历===");
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Object obj = iterator.next();
System.out.println("obj=" + obj);
}
}
}
class Book {
private String name;
private String author;
private double price; public Book(String name, String author, double price) {
this.name = name;
this.author = author;
this.price = price;
} public String getName() {
return name;
} public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
} public String getAuthor() {
return author;
} public void setAuthor(String author) {
this.author = author;
} public double getPrice() {
return price;
} public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
} @Override
public String toString() {
return "Book{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", author='" + author + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
'}';
}
}

502,集合增强for

package com.hspedu.collection; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator; public class Collection01 {
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection col = new ArrayList();//向上转型,Collection是接口 col.add(new Book("三国演义", "罗贯中", 10.1));
col.add(new Book("小李飞刀", "古龙", 5.1));
col.add(new Book("红楼梦", "曹雪芹", 34.6)); //老韩解读
//1,使用增强for循环,在Collection集合
//2,增强for,底层仍然是迭代器
//3,增强for可以理解成就是简化版本的 迭代器遍历
//4,快捷键方式 I
for(Object book : col) {
System.out.println("book=" + book);
}
}
}
class Book {
private String name;
private String author;
private double price; public Book(String name, String author, double price) {
this.name = name;
this.author = author;
this.price = price;
} public String getName() {
return name;
} public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
} public String getAuthor() {
return author;
} public void setAuthor(String author) {
this.author = author;
} public double getPrice() {
return price;
} public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
} @Override
public String toString() {
return "Book{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", author='" + author + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
'}';
}
}

503,测试题

package com.hspedu.collection; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List; public class Collection01 {
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add(new Dog("小白",1));
list.add(new Dog("小黑",2));
list.add(new Dog("大黄",3)); //使用迭代器遍历
System.out.println("===使用迭代器遍历===");
Iterator iterator = list.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
Object d = iterator.next();
System.out.println(d);
} System.out.println("===使用for循环遍历===");
for(Object d : list) {
System.out.println(d);
}
}
}
class Dog {
private String name;
private int age; public Dog(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
} @Override
public String toString() {
return "name:" + name + " " + "age=" + age;
}
}

504,List接口方法
package com.hspedu.collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Collection01 {
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public static void main(String[] args) {
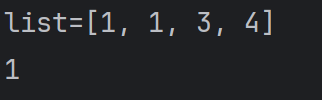
//1,List集合类中元素有序(即添加顺序和取出顺序一致),且可重复
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add(1);
list.add(1);
list.add(3);
list.add(4);
System.out.println("list=" + list);
//2,List集合中的每个元素都有其对应的顺序索引,即支持索引
// 索引是从0开始
System.out.println(list.get(0));
}
}

package com.hspedu.collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Collection01 {
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add("张三丰");
list.add("贾宝玉");
//1,void add(int index, Object ele):在index位置插入ele元素
list.add(1,"刘备");
System.out.println("list=" + list);
//2,boolean addAll(int index, Collection eles):从index位置开始将eles中的所有元素添加进来
List list1 = new ArrayList();
list1.add(1);
list1.add(2);
list.addAll(1,list1);
System.out.println("list=" + list);
//3,int indexOf(Object obj):返回obj在集合中首次出现的位置
System.out.println(list.indexOf("张三丰"));
//4,int lastIndexOf(Object obj):返回obj在当前集合中末次出现的位置
list.add(1);
System.out.println("list=" + list);
System.out.println(list.lastIndexOf(1));
//5,Object remove(int index):移除指定index位置的元素,并返回此元素
list.remove(0);
System.out.println("list=" + list);
//6,Object set(int index, Object ele):设置指定index位置的元素为ele,
// 相当于是替换,index不能是最后一个位置和不存在的位置
list.set(1,"玛丽");
System.out.println("list=" + list);
//7,List subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex):返回从fromIndex到toIndex位置的子集合
// 返回的子集合 fromIndex <= subList < toIndex
List returnlist = list.subList(0,2);
System.out.println("returnlist=" + returnlist);
}
}

505,List接口练习

package com.hspedu.collection; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List; public class Collection01 {
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList();
for (int i = 0; i < 12; i++) {
list.add("hello"+ i);
}
System.out.println("list=" + list); //在2号位插入一个元素"韩顺平教育"
list.add(1,"韩顺平教育");
System.out.println("list=" + list); //获得第5个元素
System.out.println("第5个元素=" + list.get(4)); //删除第6个元素
list.remove(5);
System.out.println("list=" + list); //修改第7个元素
list.set(6, "三国演义");
System.out.println("list=" + list); //使用迭代器遍历
Iterator iterator = list.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
Object obj = iterator.next();
System.out.println(obj);
}
}
}

506,List三种遍历方式

package com.hspedu.collection; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List; public class Collection01 {
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add("jack");
list.add("tom");
list.add("鱼香肉丝");
list.add("北京烤鸭"); //遍历
//1,迭代器
Iterator iterator = list.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Object obj = iterator.next();
System.out.println(obj);
} System.out.println("=====增强for=====");
//2,增强for
for (Object o : list) {
System.out.println("o=" + o);
} System.out.println("=====使用普通for=====");
//3,使用普通for
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
System.out.println("对象=" + list.get(i));
}
}
}

507,List排序练习

package com.hspedu.collection; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public class Collection01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add(new Book("红楼梦","曹雪芹",100));
list.add(new Book("西游记","吴承恩",10));
list.add(new Book("水浒传","施耐庵",9));
list.add(new Book("三国","罗贯中",80));
list.add(new Book("西游记","吴承恩",10)); for (Object o : list) {
System.out.println(o);
}
//冒泡排序
sort(list); System.out.println("===排序后===");
for (Object o : list) {
System.out.println(o);
}
}
//静态方法
//价格要求是从小到大
public static void sort(List list) {
int listSize = list.size();
for (int i = 0; i < listSize - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < listSize - 1 - i; j++) {
//取出对象Book
Book book1 = (Book)list.get(j); //list.get(j)返回的是Object对象,所以这里强转
Book book2 = (Book)list.get(j+1);
if(book1.getPrice() > book2.getPrice()) { //交换
list.set(j, book2);
list.set(j+1, book1);
}
}
}
}
}
class Book {
private String name;
private String author;
private double price; public Book(String name, String author, double price) {
this.name = name;
this.author = author;
this.price = price;
} public String getName() {
return name;
} public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
} public String getAuthor() {
return author;
} public void setAuthor(String author) {
this.author = author;
} public double getPrice() {
return price;
} public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
} @Override
public String toString() {
return "名称: " + name + "\t\t" + "价格: " + price + "\t\t" + "作者: " + author;
}
}

508,ArrayList注意事项

package com.hspedu.collection; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public class Collection01 {
public static void main(String[] args) { //ArrayList 是线程不安全的,可以看源码 没有 synchronized(互斥的)
// public boolean add(E e) {
// modCount++;
// add(e, elementData, size);
// return true;
// } ArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList();
arrayList.add(null);
arrayList.add("jack");
arrayList.add(null);
System.out.println(arrayList);
}
}

509,ArrayLish扩容机制

自己补充序列化的知识点:
序列化是将Java对象转变为字节序列,便于持久化到本地磁盘,避免程序运行结束后对象从内存中消失,字节序列也方便在网络中传输。
序列化的主要目的是通过网络传输对象或者说是将对象存储到文件系统、数据库、内存中。

由于时间有限,从这以后的笔记只记自己理解的和敲的代码
514,双向链表模拟
package com.hspedu.list_;
public class LinkedList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//模拟一个简单的双向链表
Node jack = new Node("jack");
Node tom = new Node("tom");
Node hsp = new Node("老韩");
//连接三个节点,形成双向链表
//jack -> tom -> hsp
jack.next = tom;
tom.next = hsp;
//hsp -> tom -> jack
hsp.pre = tom;
tom.pre = jack;
Node first = jack;//让first引用指向jack,就是双向链表的头节点
Node last = hsp;//让last引用指向hsp,就是双向链表的尾节点
//演示,从头到尾进行遍历
System.out.println("===从头到尾进行遍历===");
while (true) {
if(first == null) {
break;
}
//输出first信息
System.out.println(first);
first = first.next;
}
//演示,从尾到头的遍历
System.out.println("===从尾到头进行遍历===");
while (true) {
if(last == null) {
break;
}
//输出last信息
System.out.println(last);
last = last.pre;
}
//演示链表的添加对象/数据,是多么的方便
//要求,是在 tom-----老韩之间插入一个对象 smith
//1,先创建一个 Node 节点,name 就是 smith
Node smith = new Node("smith");
//先改插入节点smith的指向
smith.next = hsp;
smith.pre = tom;
//再改hsp,tom的指向
hsp.pre = smith;
tom.next = smith;
//让first 再次指向jack
first = jack; //让first引用指向jack,就是双向链表的头节点
System.out.println("===从头到尾进行遍历===");
while (true) {
if(first == null) {
break;
}
//输出first信息
System.out.println(first);
first = first.next;
}
}
}
//定义一个 Node 类, Node 对象 表示双向链表的一个结点
class Node {
public Object item;//真正存放数据
public Node next;//指向后一个节点
public Node pre;//指向前一个节点
public Node(Object name) {
this.item = name;
}
public String toString() {
return "Node name=" + item;
}
}

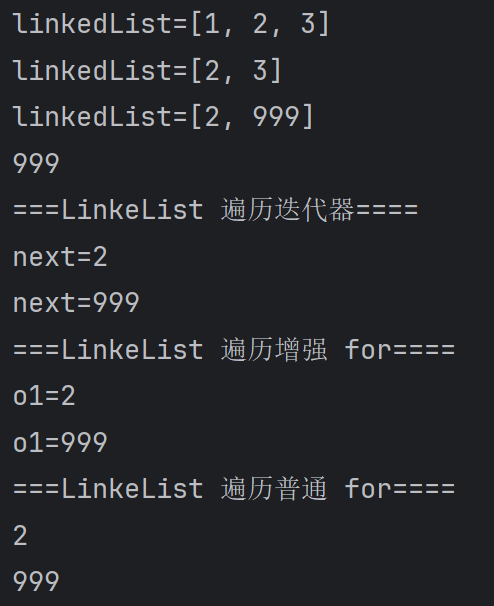
515,LinkedList增删改查案例
package com.hspedu.list_;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedList; @SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public class LinkedListCRUD {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList();
linkedList.add(1);
linkedList.add(2);
linkedList.add(3);
System.out.println("linkedList=" + linkedList);
//演示一个删除结点的
linkedList.remove(); // 这里默认删除的是第一个结点
//linkedList.remove(2);
System.out.println("linkedList=" + linkedList);
//修改某个结点对象
linkedList.set(1, 999);
System.out.println("linkedList=" + linkedList);
//得到某个结点对象
//get(1) 是得到双向链表的第二个对象
Object o = linkedList.get(1);
System.out.println(o);//999
//因为 LinkedList 是 实现了 List 接口, 遍历方式
System.out.println("===LinkeList 遍历迭代器====");
Iterator iterator = linkedList.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Object next = iterator.next();
System.out.println("next=" + next);
}
System.out.println("===LinkeList 遍历增强 for====");
for (Object o1 : linkedList) {
System.out.println("o1=" + o1);
}
System.out.println("===LinkeList 遍历普通 for====");
for (int i = 0; i < linkedList.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(linkedList.get(i));
}
}
}
517,Set接口方法
package com.hspedu.list_;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.HashSet; @SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public class SetMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1,以Set接口的实现类 HashSet来讲解Set接口的方法
//2. set 接口的实现类的对象(Set 接口对象), 不能存放重复的元素, 可以添加一个 null
//3. set 接口对象存放数据是无序(即添加的顺序和取出的顺序不一致)
Set set = new HashSet();
set.add("john");
set.add("lucy");
set.add("john");//重复
set.add("jack");
set.add(null);//再次添加null
//4. 注意: 取出的顺序的顺序虽然不是添加的顺序, 但是他的固定.
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
System.out.println("set=" + set);
}
//遍历
//方式1:使用迭代器
System.out.println("====使用迭代器====");
Iterator iterator = set.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
Object obj = iterator.next();
System.out.println("obj=" + obj);
}
//方式2:增强for
System.out.println("====增强for====");
for(Object o : set) {
System.out.println("o=" + o);
}
//set 接口对象, 不能通过索引来获取,就是set.get[i] }
}

518,HashSet案例说明
package com.hspedu.list_;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedList; @SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public class HashSet1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet set = new HashSet();
//1. 在执行 add 方法后, 会返回一个 boolean 值
//2. 如果添加成功, 返回 true, 否则返回 false
System.out.println(set.add("john"));//T
System.out.println(set.add("lucy"));//T
System.out.println(set.add("john"));//F
System.out.println(set.add("jack"));//T
System.out.println(set.add("Rose"));//T
System.out.println("set=" + set);//5个
//3. 可以通过 remove 指定删除哪个对象
set.remove("john");
System.out.println("set=" + set);//3个 set = new HashSet();
System.out.println("set=" + set);//0
//4 Hashset 不能添加相同的元素/数据?
set.add("lucy");//添加成功
set.add("lucy");//添加不了
//两个tom地址不一样
set.add(new Dog("tom"));
set.add(new Dog("tom"));
System.out.println("set=" + set); //在加深一下. 非常经典的面试题,看下节的HashMap底层 数组链表模拟
set.add(new String("hsp"));//ok
set.add(new String("hsp"));//加入不了.
System.out.println("set=" + set);
}
}
//定义Dog类
class Dog {
private String name; public Dog(String name) {
this.name = name;
} @Override
public String toString() {
return "Dog{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}

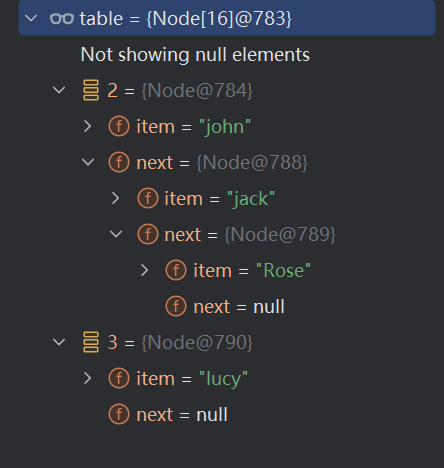
519,数组链表模拟(HashSet底层机制是数组+链表+红黑树)
package com.hspedu.list_;
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public class HashSetStructure {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//模拟一个HashSet的底层(HashSet的底层结构)
//1,创建一个数组,数组的类型是 Node[]
//2,有些人,直接把 Node[] 数组称为 表
Node[] table = new Node[16];
System.out.println("table=" + table);
//3,创建节点
Node john = new Node("john", null);
//把lucy放到table表的索引为2的位置
table[2] = john;
Node jack = new Node("jack", null);
//将jack节点挂载到john
john.next = jack;
Node rose = new Node("Rose", null);
//将rose节点挂载到jack
jack.next = rose;
Node lucy = new Node("lucy", null);
//把lucy放到table表的索引为3的位置
table[3] = lucy;
System.out.println("table=" + table);
}
}
//节点,存储数据,可以指向下一个节点,从而形成链表
class Node {
Object item; //存放数据
Node next; //指向下一个节点
public Node(Object item, Node next) {
this.item = item;
this.next = next;
}
}
表的结构
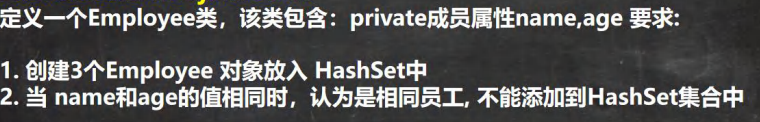
525,HashSet最佳实践
package com.hspedu.list_;
import java.util.*;
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public class Map_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet hashSet = new HashSet();
hashSet.add(new Employee("milan", 18));
hashSet.add(new Employee("smith", 28));
hashSet.add(new Employee("milan", 18));
System.out.println("hashSet=" + hashSet);
}
}
class Employee {
private String name;
private int age;
public Employee(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Employee{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
//重写 equals 方法 和 hashCode, 快捷键 fn+Alt+Insert 选 equals()' and 'hashCode()'
//当 name 和 price 相同时, 就返回相同的 hashCode 值, equals 返回 true
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Employee employee = (Employee) o;
return age == employee.age && Objects.equals(name, employee.name);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(name, age);
}
}
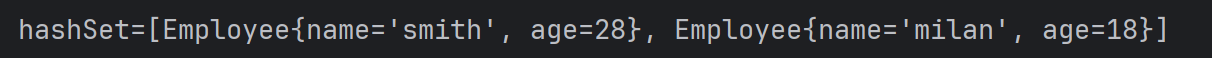
529,LHashSet课堂练习

package com.hspedu.list_;
import java.util.*;
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public class Map_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedHashSet linkedHashSet = new LinkedHashSet();
linkedHashSet.add(new Car("奥拓", 1000));//OK
linkedHashSet.add(new Car("奥迪", 300000));//OK
linkedHashSet.add(new Car("法拉利", 10000000));//OK
linkedHashSet.add(new Car("奥迪", 300000));//加入不了
linkedHashSet.add(new Car("保时捷", 70000000));//OK
linkedHashSet.add(new Car("奥迪", 300000));//加入不了
System.out.println("linkedHashSet=" + linkedHashSet);
}
}
class Car {
private String name;
private int price;
public Car(String name, int price) {
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(int price) {
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "\nCar{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
'}';
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Car car = (Car) o;
return price == car.price && Objects.equals(name, car.name);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(name, price);
}
}

530,Map接口特点1
package com.hspedu.list_; import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map; @SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public class Map_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Map 接口实现类的特点,使用实现类HashMap
//1,Map与Collection并列存在,用于保存具有映射关系的数据:Key-Value(双列元素)
//2,Map中的key和value可以是任何引用类型的数据,会封装到HashMap$Node对象中 Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("no1", "韩顺平");//k-v
map.put("no2", "张无忌");
//3,Map中的key不允许重复,原因和HashSet 一样,前面分析过源码。底层会用 equals函数
map.put("no1", "张三丰");//当有相同的k,就等价于替换
//4,Map中的value可以重复
map.put("no3", "张三丰");
//5,Map的key可以为null,value也可以为null,注意key为null,只能有一个,value为null,可以多个
map.put(null, null);
map.put(null, "abc");//等价替换
map.put("no4", null);
map.put("no5", null);
map.put(1, "赵敏");
map.put(new Object(), "金毛狮王");
//6,常用的String类作为Map的key
//7,key和value之间存在单向一对一关系,即通过指定的key总能找到对应的value
//通过get方法,传入key,会返回对应的value
System.out.println(map.get("no2"));//张无忌 System.out.println("map=" + map); }
}

532,Map接口方法
package com.hspedu.list_;
import java.util.*;
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public class Map_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//演示 map 接口常用方法
//put:添加
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("邓超", new Book("", 100));//OK
map.put("邓超", "孙俪");//替换-> 一会分析源码
map.put("王宝强", "马蓉");//OK
map.put("宋喆", "马蓉");//OK
map.put("刘令博", null);//OK
map.put(null, "刘亦菲");//OK
map.put("鹿晗", "关晓彤");//OK
map.put("hsp", "hsp 的老婆");
System.out.println("map=" + map);
//remove:根据键删除映射关系
map.remove(null);
System.out.println("map=" + map);
//get:根据键获取值
Object val = map.get("鹿晗");
System.out.println("val=" + val);
//size:获取元素个数
System.out.println("k-v键值对的数量=" + map.size());
//isEmpty:判断个数是否为0
System.out.println(map.isEmpty());
//clear:清空k-v
//map.clear();
System.out.println("map=" + map);
//containsKey:查找键是否存在
System.out.println(map.containsKey("hsp"));
}
}
class Book {
private String name;
private int num;
public Book(String name, int num) {
this.name = name;
this.num = num;
}
}
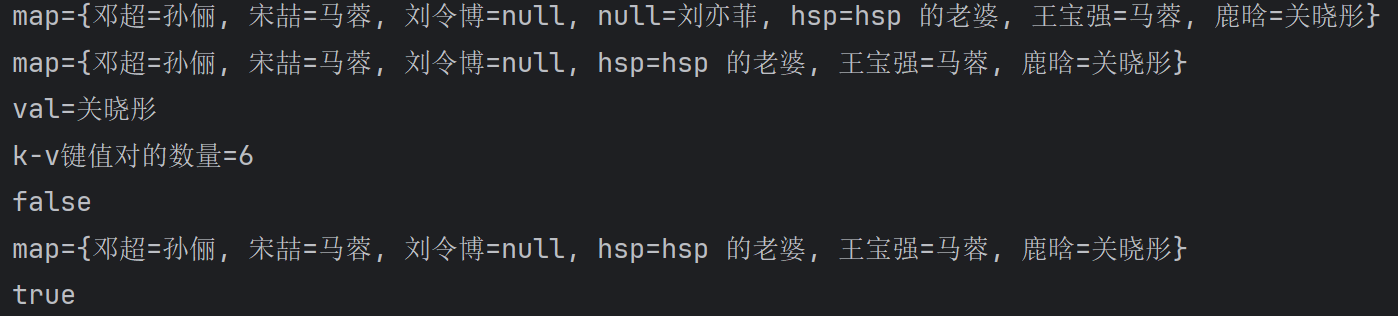
533,Map六大遍历方式
package com.hspedu.list_;
import java.util.*;
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public class Map_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("邓超", "孙俪");
map.put("王宝强", "马蓉");
map.put("宋喆", "马蓉");
map.put("刘令博", null);
map.put(null, "刘亦菲");
map.put("鹿晗", "关晓彤");
System.out.println("map=" + map);
//第一组: 先取出 所有的 Key , 通过 Key 取出对应的 Value
Set keyset = map.keySet();
//(1) 增强 for
System.out.println("------第一种方式------");
for(Object key : keyset) {
System.out.println(key + "-" + map.get(key));
}
//(2) 迭代器
System.out.println("----第二种方式--------");
Iterator iterator = keyset.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Object key = iterator.next();
System.out.println(key + "-" + map.get(key));
}
//第二组: 把所有的 values 取出
Collection values = map.values();
//这里可以使用所有的 Collections 使用的遍历方法
//(1) 增强 for
System.out.println("---取出所有的 value 增强 for----");
for (Object value : values) {
System.out.println(value);
}
//(2) 迭代器
System.out.println("---取出所有的 value 迭代器----");
Iterator iterator1 = values.iterator();
while(iterator1.hasNext()) {
Object value = iterator1.next();
System.out.println(value);
}
//第三组: 通过 EntrySet 来获取 k-v
Set entrySet = map.entrySet();// EntrySet<Map.Entry<K,V>>
//(1) 增强 for
System.out.println("----使用 EntrySet 的 for 增强(第 3 种)----");
for (Object entry : entrySet) {
//将 entry 转成 Map.Entry
Map.Entry m = (Map.Entry) entry;//向下转型,因为要从EntrySet中取到Map.Entry
System.out.println(m.getKey() + "-" + m.getValue());
}
//(2) 迭代器
System.out.println("----使用 EntrySet 的 迭代器(第 4 种)----");
Iterator iterator2 = entrySet.iterator();
while (iterator2.hasNext()) {
Object entry = iterator2.next();
//System.out.println(entry.getClass());//HashMap$Node -实现-> Map.Entry (getKey,getValue)
//向下转型 Map.Entry
Map.Entry m = (Map.Entry) entry;
System.out.println(m.getKey() + "-" + m.getValue());
}
}
}
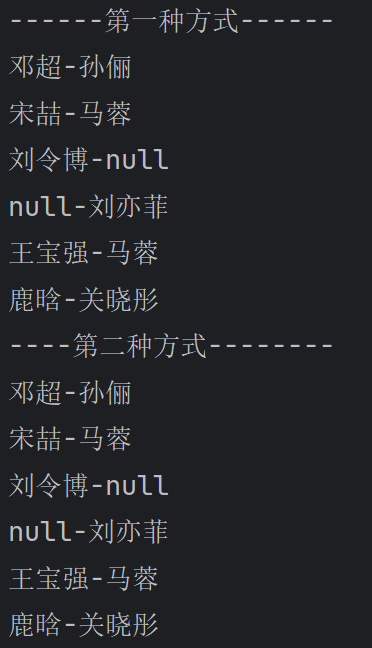


534,Map课堂练习

package com.hspedu.list_;
import java.util.*;
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public class Map_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map hashMap = new HashMap();
//添加对象
hashMap.put(1, new Emp("jack", 300000, 1));
hashMap.put(2, new Emp("tom", 21000, 2));
hashMap.put(3, new Emp("milan", 12000, 3));
//遍历 2 种方式
//并遍历显示工资>18000 的员工(遍历方式最少两种)
//1. 使用 keySet -> 增强 for
Set keySet = hashMap.keySet();
System.out.println("====第一种遍历方式====");
for (Object key : keySet) {
//先获取 value,因为要遍历显示工资>18000 的员工,value是Emp对象,所以下面要转成Emp
Emp emp = (Emp) hashMap.get(key);
if (emp.getSal() > 18000) {
System.out.println(emp);
}
}
//2. 使用 EntrySet -> 迭代器
// 体现比较难的知识点
// 慢慢品, 越品越有味道.
Set entrySet = hashMap.entrySet();
System.out.println("======迭代器======");
Iterator iterator = entrySet.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry)iterator.next();
//通过 entry 取得 key 和 value
Emp emp = (Emp) entry.getValue();
if (emp.getSal() > 18000) {
System.out.println(emp);
}
}
}
}
class Emp {
private String name;
private double sal;
private int id;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Emp{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", sal=" + sal +
", id=" + id +
'}';
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getSal() {
return sal;
}
public void setSal(double sal) {
this.sal = sal;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public Emp(String name, double sal, int id) {
this.name = name;
this.sal = sal;
this.id = id;
}
}
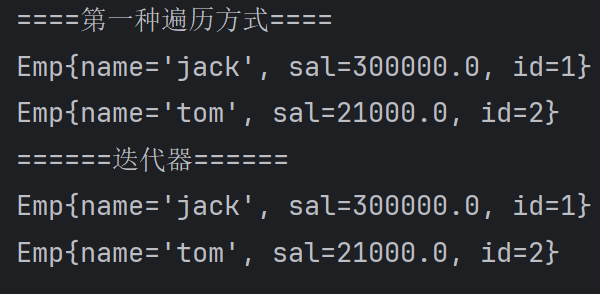
542,总结-开发中如何选择集合实现类(记住)

545,Collections工具类
package com.hspedu.list_; import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletionService; @SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public class Map_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建 ArrayList 集合, 用于测试
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add("tom");
list.add("smith");
list.add("king");
list.add("milan");
list.add("tom"); //reverse(List): 反转 List 中元素的顺序
Collections.reverse(list);
System.out.println("list=" + list);
//shuffle(List): 对 List 集合元素进行随机排序
Collections.shuffle(list);
System.out.println("list=" + list);
//sort(List): 根据元素的自然顺序对指定 List 集合元素按升序排序
Collections.sort(list);
System.out.println("sort排序后");
System.out.println("list=" + list);
//sort(List, Comparator): 根据指定的 Comparator 产生的顺序对 List 集合元素进行排序
//我们希望按照 字符串的长度大小排序
Collections.sort(list, new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
return ((String)o1).length() - ((String)o2).length();
}
});
System.out.println("字符串长度大小排序=" + list);
// swap(List, int, int): 将指定 list 集合中的 i 处元素和 j 处元素进行交换
Collections.swap(list, 0, 1);
System.out.println("交换后的情况");
System.out.println("list=" + list); //Object max(Collection): 根据元素的自然顺序, 返回给定集合中的最大元素
System.out.println("自然顺序最大元素=" + Collections.max(list));
//Object max(Collection, Comparator): 根据 Comparator 指定的顺序, 返回给定集合中的最大元素
//比如, 我们要返回长度最大的元素
Object maxObject = Collections.max(list, new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
return ((String)o1).length() - ((String)o2).length();
}
});
System.out.println("长度最大的元素=" + maxObject);
//Object min(Collection)
//Object min(Collection, Comparator)
//上面的两个方法, 参考 max 即可 //int frequency(Collection, Object): 返回指定集合中指定元素的出现次数
System.out.println("tom出现的次数=" + Collections.frequency(list, "tom")); //void copy(List dest,List src): 将 src 中的内容复制到 dest 中
ArrayList dest = new ArrayList();
//为了完成一个完整拷贝, 我们需要先给 dest 赋值, 大小和 list.size()一样,因为dest初始长度是0
for(int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
dest.add("");
}
//拷贝
Collections.copy(dest, list);
System.out.println("dest=" + dest); //boolean replaceAll(List list, Object oldVal, Object newVal): 使用新值替换 List 对象的所有旧值
//如果 list 中, 有 tom 就替换成 汤姆
Collections.replaceAll(list, "tom", "汤姆");
System.out.println("list替换后=" + list); }
}

547,集合家庭作业1

package com.hspedu.list_; import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletionService; @SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public class Map_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList();
arrayList.add(new News("新冠确诊病例超千万,数百万印度教信徒赴恒河\"圣浴\"引民众担忧"));
arrayList.add(new News("男子突然想起2个月前钓的鱼还在网兜里,捞起一看赶紧放生")); int size = arrayList.size();
for (int i = size - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
//System.out.println(arrayList.get(i));
News news = (News) arrayList.get(i);
System.out.println(processTitle(news.getTitle()));
}
}
//专门写一个方法,处理现实新闻标题
public static String processTitle(String title) {
if (title == null) {
return "";
}
if(title.length() > 15) {
return title.substring(0,15) + "...";
}else {
return title;
}
}
} class News {
private String title;
private String content; public News(String title) {
this.title = title;
} public String getTitle() {
return title;
} public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
} public String getContent() {
return content;
} public void setContent(String content) {
this.content = content;
} @Override
public String toString() {
return "News{" +
"title='" + title + '\'' +
'}';
}
}

548,集合家庭作业2

package com.hspedu.list_; import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletionService; @SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public class Map_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList();
Car car = new Car("宝马", 400000);
Car car2 = new Car("宾利", 5000000);
arrayList.add(car);
arrayList.add(car2);
System.out.println(arrayList);
arrayList.remove(car);
System.out.println(arrayList);
System.out.println(arrayList.contains(car));//F
System.out.println(arrayList.size());//1
System.out.println(arrayList.isEmpty());//F
arrayList.addAll(arrayList);//2个宾利
System.out.println(arrayList);
System.out.println(arrayList.containsAll(arrayList));
//arrayList.removeAll(arrayList);//相当于清空
System.out.println("----遍历----");
for (Object o : arrayList) {
System.out.println(o);
}
Iterator iterator = arrayList.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
Object next = iterator.next();
System.out.println(next);
} }
}
class Car {
private String name;
private double price; public Car(String name, double price) {
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
} public String getName() {
return name;
} public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
} public double getPrice() {
return price;
} public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
} @Override
public String toString() {
return "Car{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
'}';
}
}
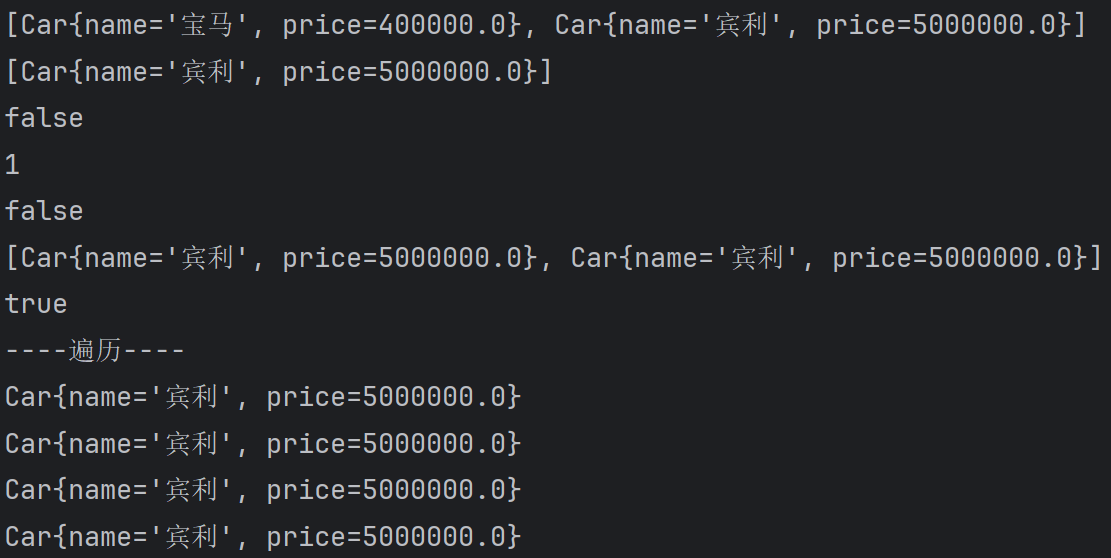
549,集合家庭作业3
package com.hspedu.list_; import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletionService; @SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public class Map_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
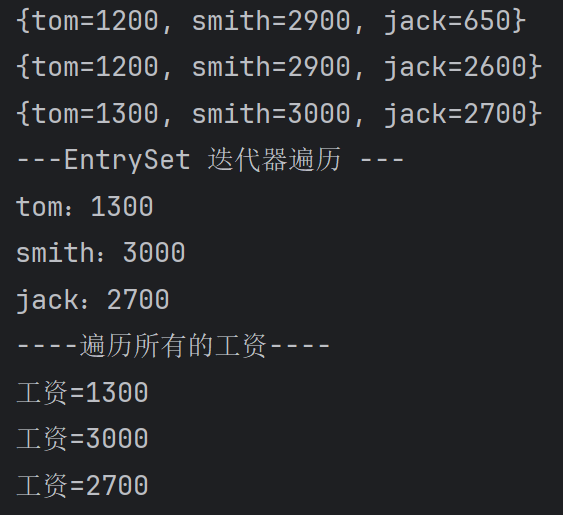
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("jack", 650);
map.put("tom", 1200);
map.put("smith", 2900);
System.out.println(map); map.put("jack", 2600);//替换
System.out.println(map); //为所有员工工资加薪100元
//先取出key,用keySet
Set keySet = map.keySet();
for(Object key : keySet) {
//通过key更新value
map.put(key, (Integer)map.get(key) + 100);
}
System.out.println(map); //遍历 EntrySet
System.out.println("---EntrySet 迭代器遍历 ---");
Set entrySet = map.entrySet();
Iterator iterator = entrySet.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry)iterator.next();
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + ":" + entry.getValue());
} System.out.println("----遍历所有的工资----");
Collection values = map.values();
for (Object value : values) {
System.out.println("工资=" + value);
} }
}
Java基础 韩顺平老师的 集合 的部分笔记的更多相关文章
- java韩顺平老师视频有需要可以留言
java韩顺平老师视频有需要可以留言
- 韩顺平老师java视频全套-java视频教程下载
解压压缩包会有一个种子文件.直接迅雷下载即可,包含了韩顺平老师的java入门视频,jdbc,jsp,servlet,oracle,hibermate,spring,SHH框架,struct,linux ...
- Linux基础指令--韩顺平老师课程笔记
一.vi和vim编辑器 ①.三种模式 所有的 Linux 系统都会内建 vi 文本编辑器.vim 具有程序编辑的能力,可以看做是 vi 的增强版本,可以主动的以字体颜色辨别语法的正确性,方便程序设计. ...
- java基础(十四)集合(一)
这里有我之前上课总结的一些知识点以及代码大部分是老师讲的笔记 个人认为是非常好的,,也是比较经典的内容,真诚的希望这些对于那些想学习的人有所帮助! 由于代码是分模块的上传非常的不便.也比较多,讲的也是 ...
- java基础(十六)集合(三)
这里有我之前上课总结的一些知识点以及代码大部分是老师讲的笔记 个人认为是非常好的,,也是比较经典的内容,真诚的希望这些对于那些想学习的人有所帮助! 由于代码是分模块的上传非常的不便.也比较多,讲的也是 ...
- java基础(十五)集合(二)
这里有我之前上课总结的一些知识点以及代码大部分是老师讲的笔记 个人认为是非常好的,,也是比较经典的内容,真诚的希望这些对于那些想学习的人有所帮助! 由于代码是分模块的上传非常的不便.也比较多,讲的也是 ...
- JAVA基础部分复习(二、集合类型)
对于这些常用的集合,建议还是需要先了解一下底层实现原理,这样在不同的使用场景下才能选择更好的方案. Set介绍以及对比,常用方法: package cn.review.day02; import ja ...
- Java基础(十三):集合
一.Java 集合框架: 早在Java 2中之前,Java就提供了特设类.比如:Dictionary, Vector, Stack, 和Properties这些类用来存储和操作对象组.虽然这些类都非常 ...
- java基础笔试题二(集合关系)
知识点:java集合继承关系(Collection,Map) 1.集合框架体系图 2.java的集合层次 来自博客(http://blog.csdn.net/stubbornaccepted/arti ...
- JAVA基础知识总结15(集合容器)
集合框架:用于存储数据的容器. 1:对象封装数据,对象多了也需要存储.集合用于存储对象. 2:对象的个数确定可以使用数组,但是不确定怎么办?可以用集合.因为集合是可变长度的. 集合和数组的区别: 1: ...
随机推荐
- 13年过去了,Spring官方竟然真的支持Bean的异步初始化了!
你好呀,我是歪歪. 两年前我曾经发布过这样的一篇文章<我是真没想到,这个面试题居然从11年前就开始讨论了,而官方今年才表态.> 文章主要就是由这个面试题引起: Spring 在启动期间会做 ...
- CeiT:商汤提出结合CNN优势的高效ViT模型 | 2021 arxiv
论文提出CeiT混合网络,结合了CNN在提取低维特征方面的局部性优势以及Transformer在建立长距离依赖关系方面的优势.CeiT在ImageNet和各种下游任务中达到了SOTA,收敛速度更快,而 ...
- JS / jQuery 刷新页面的方法
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8&quo ...
- MQ的相关概念
MQ的相关概念 什么是MQ MQ(message queue),从字面意思上看,本质是个队列,FIFO 先入先出,只不过队列中存放的内容是 message 而已,还是一种跨进程的通信机制,用于上下 ...
- Qt工具栏的使用
参考视频:黑马科技:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1XW411x7NU?p=19 对话框通常会是一个顶层窗口,出现在程序最上层,用于实现短期任务或者简洁的用户交互. ...
- react props进阶 children属性
children属性,表示组件标签的子节点,当组件标签有子节点时,props就会有该属性,与与普通的props一样,其值可以使任意类型. # 父组件 class App extends React.C ...
- AGC055
AGC055 第一次打AGC,好难受. T1 看了一眼题解,没看懂--但是还是做出来了. T2 感觉比 T1 简单,构造很好猜. 其他的没时间思考,T1 花了我 2h30min,难受. A.ABC I ...
- 算法学习笔记(10): BSGS算法及其扩展算法
BSGS算法及其扩展算法 BSGS算法 所谓 Baby Step, Giant Step 算法,也就是暴力算法的优化 用于求出已知 \(a, b, p\), 且 \(p\) 为质数 时 \(a^x \ ...
- JVM垃圾回收器(详解)
引言 垃圾回收(GC,Garbage Collection) 在笔者上一篇文章中(JVM内存模型),介绍了JVM内存模型以及JVM运行时的数据区,堆是JVM内存区域里面最大的一块区域,用于存放实例数据 ...
- 判断一个数n是不是快乐数
引言 题目:编写一个算法来判断一个数n是不是快乐数 来源:网友分享的面试算法题 题目描述 [快乐数定义] 对于一个正整数,每一次将该数替换为它每个位置上的数字的平方和. 然后重复这个过程直到这个数变为 ...
