在树莓派上实现numpy的conv2d卷积神经网络做图像分类,加载pytorch的模型参数,推理mnist手写数字识别,并使用多进程加速
这几天又在玩树莓派,先是搞了个物联网,又在尝试在树莓派上搞一些简单的神经网络,这次搞得是卷积识别mnist手写数字识别
训练代码在电脑上,cpu就能训练,很快的:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
from torchvision import datasets, transforms
import numpy as np # 设置随机种子
torch.manual_seed(42) # 定义数据预处理
transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(),
# transforms.Normalize((0.1307,), (0.3081,))
]) # 加载训练数据集
train_dataset = datasets.MNIST('data', train=True, download=True, transform=transform)
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=64, shuffle=True) # 构建卷积神经网络模型
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 10, kernel_size=5)
self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(2)
self.fc = nn.Linear(10 * 12 * 12, 10) def forward(self, x):
x = self.pool(torch.relu(self.conv1(x)))
x = x.view(-1, 10 * 12 * 12)
x = self.fc(x)
return x model = Net() # 定义损失函数和优化器
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.01, momentum=0.5) # 训练模型
def train(model, device, train_loader, optimizer, criterion, epochs):
model.train()
for epoch in range(epochs):
for batch_idx, (data, target) in enumerate(train_loader):
data, target = data.to(device), target.to(device)
optimizer.zero_grad()
output = model(data)
loss = criterion(output, target)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if batch_idx % 100 == 0:
print(f'Train Epoch: {epoch+1} [{batch_idx * len(data)}/{len(train_loader.dataset)} '
f'({100. * batch_idx / len(train_loader):.0f}%)]\tLoss: {loss.item():.6f}') # 在GPU上训练(如果可用),否则使用CPU
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
model.to(device) # 训练模型
train(model, device, train_loader, optimizer, criterion, epochs=5) # 保存模型为NumPy数据
model_state = model.state_dict()
numpy_model_state = {key: value.cpu().numpy() for key, value in model_state.items()}
np.savez('model.npz', **numpy_model_state)
print("Model saved as model.npz")
然后需要自己在dataset里导出一些图片:我保存在了mnist_pi文件夹下,“_”后面的是标签,主要是在pc端导出保存到树莓派下
树莓派推理端的代码,需要numpy手动重新搭建网络,并且需要手动实现conv2d卷积神经网络和maxpool2d最大池化,然后加载那些保存的矩阵参数,做矩阵乘法和加法
import numpy as np
import os
from PIL import Image def conv2d(input, weight, bias, stride=1, padding=0):
batch_size, in_channels, in_height, in_width = input.shape
out_channels, in_channels, kernel_size, _ = weight.shape # 计算输出特征图的大小
out_height = (in_height + 2 * padding - kernel_size) // stride + 1
out_width = (in_width + 2 * padding - kernel_size) // stride + 1 # 添加padding
padded_input = np.pad(input, ((0, 0), (0, 0), (padding, padding), (padding, padding)), mode='constant') # 初始化输出特征图
output = np.zeros((batch_size, out_channels, out_height, out_width)) # 执行卷积操作
for b in range(batch_size):
for c_out in range(out_channels):
for h_out in range(out_height):
for w_out in range(out_width):
h_start = h_out * stride
h_end = h_start + kernel_size
w_start = w_out * stride
w_end = w_start + kernel_size # 提取对应位置的输入图像区域
input_region = padded_input[b, :, h_start:h_end, w_start:w_end] # 计算卷积结果
x = input_region * weight[c_out]
bia = bias[c_out]
conv_result = np.sum(x, axis=(0,1, 2)) + bia # 将卷积结果存储到输出特征图中
output[b, c_out, h_out, w_out] = conv_result return output def max_pool2d(input, kernel_size, stride=None, padding=0):
batch_size, channels, in_height, in_width = input.shape if stride is None:
stride = kernel_size out_height = (in_height - kernel_size + 2 * padding) // stride + 1
out_width = (in_width - kernel_size + 2 * padding) // stride + 1 padded_input = np.pad(input, ((0, 0), (0, 0), (padding, padding), (padding, padding)), mode='constant') output = np.zeros((batch_size, channels, out_height, out_width)) for b in range(batch_size):
for c in range(channels):
for h_out in range(out_height):
for w_out in range(out_width):
h_start = h_out * stride
h_end = h_start + kernel_size
w_start = w_out * stride
w_end = w_start + kernel_size input_region = padded_input[b, c, h_start:h_end, w_start:w_end] output[b, c, h_out, w_out] = np.max(input_region) return output # 加载保存的模型数据
model_data = np.load('model.npz') # 提取模型参数
conv_weight = model_data['conv1.weight']
conv_bias = model_data['conv1.bias']
fc_weight = model_data['fc.weight']
fc_bias = model_data['fc.bias'] # 进行推理
def inference(images):
# 执行卷积操作
conv_output = conv2d(images, conv_weight, conv_bias, stride=1, padding=0)
conv_output = np.maximum(conv_output, 0) # ReLU激活函数
#maxpool2d
pool = max_pool2d(conv_output,2)
# 执行全连接操作
flattened = pool.reshape(pool.shape[0], -1)
fc_output = np.dot(flattened, fc_weight.T) + fc_bias
fc_output = np.maximum(fc_output, 0) # ReLU激活函数 # 获取预测结果
predictions = np.argmax(fc_output, axis=1) return predictions folder_path = './mnist_pi' # 替换为图片所在的文件夹路径
def infer_images_in_folder(folder_path):
for file_name in os.listdir(folder_path):
file_path = os.path.join(folder_path, file_name)
if os.path.isfile(file_path) and file_name.endswith(('.jpg', '.jpeg', '.png')):
image = Image.open(file_path)
label = file_name.split(".")[0].split("_")[1]
image = np.array(image)/255.0
image = np.expand_dims(image,axis=0)
image = np.expand_dims(image,axis=0)
print("file_path:",file_path,"img size:",image.shape,"label:",label)
predicted_class = inference(image)
print('Predicted class:', predicted_class) infer_images_in_folder(folder_path)
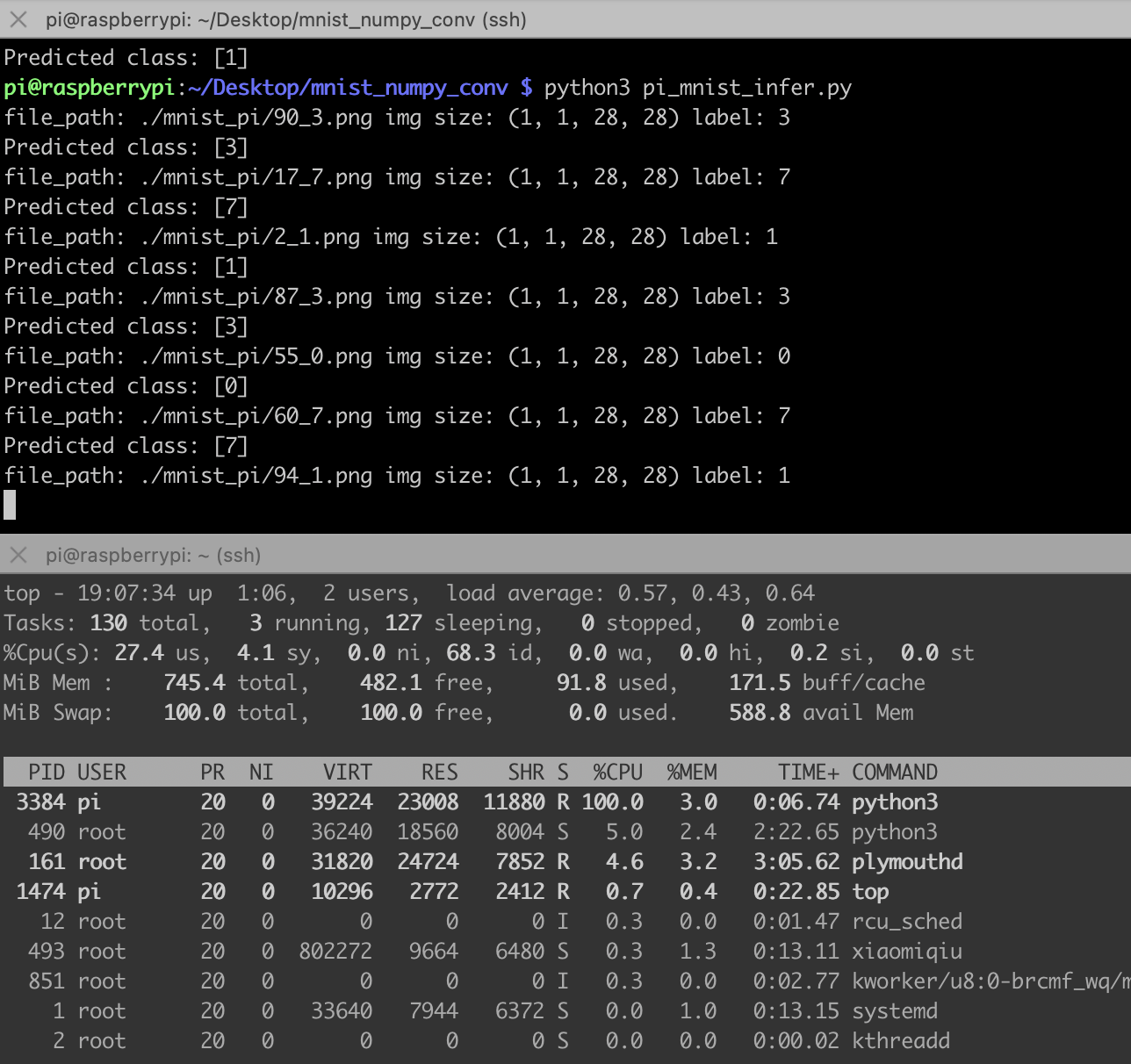
这代码完全就是numpy推理,不需要安装pytorch,树莓派也装不动pytorch,太重了,下面是推理结果,比之前的MLP网络慢很多,主要是手动实现的卷积网络全靠循环实现。
那我们给它加加速吧,下面是一个多线程加速程序:
import numpy as np
import os
from PIL import Image
from multiprocessing import Pool def conv2d(input, weight, bias, stride=1, padding=0):
batch_size, in_channels, in_height, in_width = input.shape
out_channels, in_channels, kernel_size, _ = weight.shape # 计算输出特征图的大小
out_height = (in_height + 2 * padding - kernel_size) // stride + 1
out_width = (in_width + 2 * padding - kernel_size) // stride + 1 # 添加padding
padded_input = np.pad(input, ((0, 0), (0, 0), (padding, padding), (padding, padding)), mode='constant') # 初始化输出特征图
output = np.zeros((batch_size, out_channels, out_height, out_width)) # 执行卷积操作
for b in range(batch_size):
for c_out in range(out_channels):
for h_out in range(out_height):
for w_out in range(out_width):
h_start = h_out * stride
h_end = h_start + kernel_size
w_start = w_out * stride
w_end = w_start + kernel_size # 提取对应位置的输入图像区域
input_region = padded_input[b, :, h_start:h_end, w_start:w_end] # 计算卷积结果
x = input_region * weight[c_out]
bia = bias[c_out]
conv_result = np.sum(x, axis=(0,1, 2)) + bia # 将卷积结果存储到输出特征图中
output[b, c_out, h_out, w_out] = conv_result return output def max_pool2d(input, kernel_size, stride=None, padding=0):
batch_size, channels, in_height, in_width = input.shape if stride is None:
stride = kernel_size out_height = (in_height - kernel_size + 2 * padding) // stride + 1
out_width = (in_width - kernel_size + 2 * padding) // stride + 1 padded_input = np.pad(input, ((0, 0), (0, 0), (padding, padding), (padding, padding)), mode='constant') output = np.zeros((batch_size, channels, out_height, out_width)) for b in range(batch_size):
for c in range(channels):
for h_out in range(out_height):
for w_out in range(out_width):
h_start = h_out * stride
h_end = h_start + kernel_size
w_start = w_out * stride
w_end = w_start + kernel_size input_region = padded_input[b, c, h_start:h_end, w_start:w_end] output[b, c, h_out, w_out] = np.max(input_region) return output # 加载保存的模型数据
model_data = np.load('model.npz') # 提取模型参数
conv_weight = model_data['conv1.weight']
conv_bias = model_data['conv1.bias']
fc_weight = model_data['fc.weight']
fc_bias = model_data['fc.bias'] # 进行推理
def inference(images):
# 执行卷积操作
conv_output = conv2d(images, conv_weight, conv_bias, stride=1, padding=0)
conv_output = np.maximum(conv_output, 0) # ReLU激活函数
# maxpool2d
pool = max_pool2d(conv_output, 2)
# 执行全连接操作
flattened = pool.reshape(pool.shape[0], -1)
fc_output = np.dot(flattened, fc_weight.T) + fc_bias
fc_output = np.maximum(fc_output, 0) # ReLU激活函数 # 获取预测结果
predictions = np.argmax(fc_output, axis=1) return predictions labels = []
preds = []
def infer_image(file_path):
image = Image.open(file_path)
label = file_path.split("/")[-1].split(".")[0].split("_")[1]
image = np.array(image) / 255.0
image = np.expand_dims(image, axis=0)
image = np.expand_dims(image, axis=0)
print("file_path:", file_path, "img size:", image.shape, "label:", label)
predicted_class = inference(image)
print('Predicted class:', predicted_class) folder_path = './mnist_pi' # 替换为图片所在的文件夹路径
pool = Pool(processes=4) # 设置进程数为2,可以根据需要进行调整 def infer_images_in_folder(folder_path):
for file_name in os.listdir(folder_path):
file_path = os.path.join(folder_path, file_name)
if os.path.isfile(file_path) and file_name.endswith(('.jpg', '.jpeg', '.png')):
pool.apply_async(infer_image, args=(file_path,)) pool.close()
pool.join() infer_images_in_folder(folder_path)
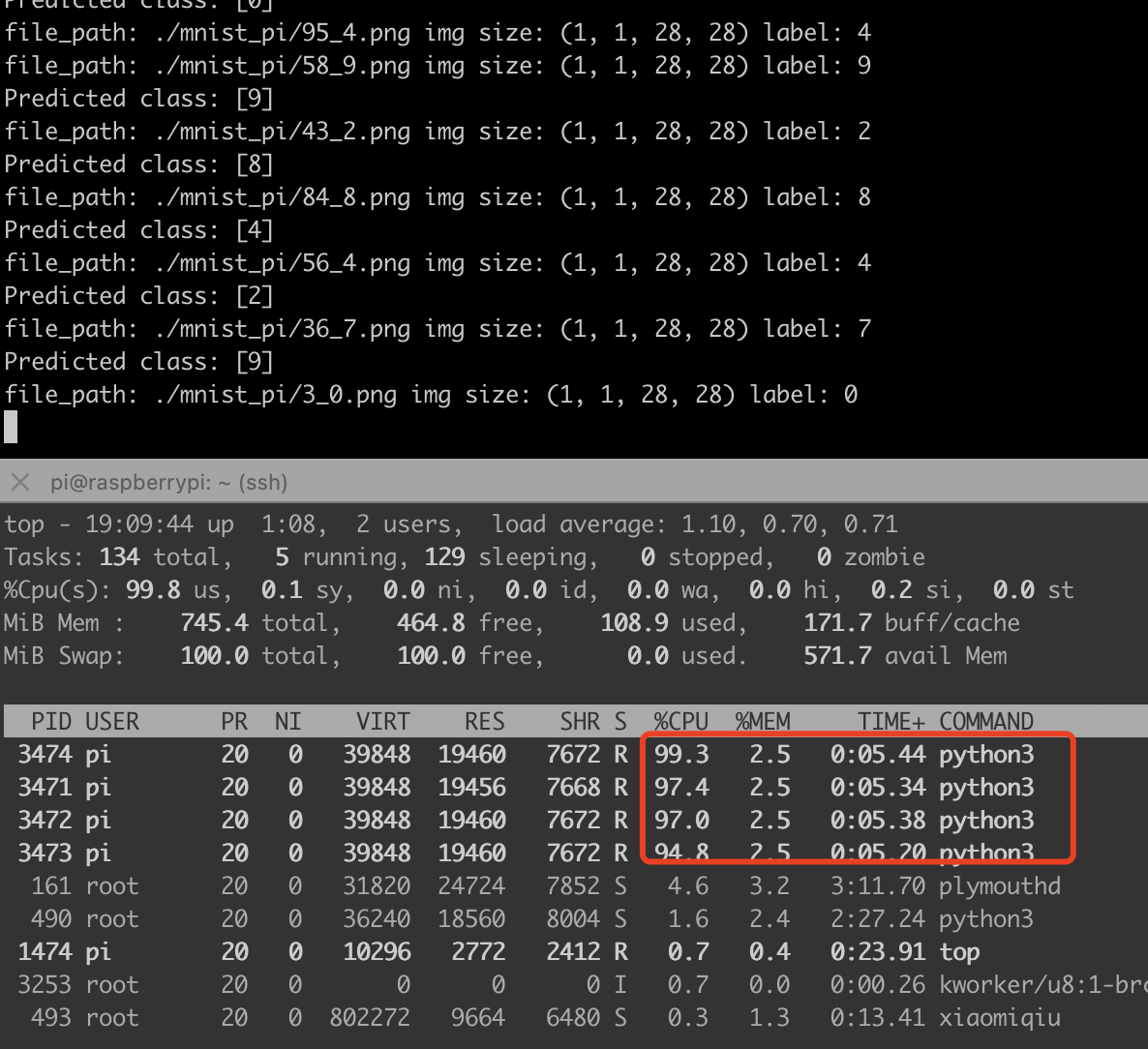
下图可以看出来,我的树莓派3b+,cpu直接拉满,速度提升4倍:
在树莓派上实现numpy的conv2d卷积神经网络做图像分类,加载pytorch的模型参数,推理mnist手写数字识别,并使用多进程加速的更多相关文章
- MNIST手写数字识别:卷积神经网络
代码 import torch from torchvision import datasets from torch.utils.data import DataLoader import torc ...
- 【深度学习系列】手写数字识别卷积神经--卷积神经网络CNN原理详解(一)
上篇文章我们给出了用paddlepaddle来做手写数字识别的示例,并对网络结构进行到了调整,提高了识别的精度.有的同学表示不是很理解原理,为什么传统的机器学习算法,简单的神经网络(如多层感知机)都可 ...
- 【TensorFlow-windows】(四) CNN(卷积神经网络)进行手写数字识别(mnist)
主要内容: 1.基于CNN的mnist手写数字识别(详细代码注释) 2.该实现中的函数总结 平台: 1.windows 10 64位 2.Anaconda3-4.2.0-Windows-x86_64. ...
- 手写数字识别 卷积神经网络 Pytorch框架实现
MNIST 手写数字识别 卷积神经网络 Pytorch框架 谨此纪念刚入门的我在卷积神经网络上面的摸爬滚打 说明 下面代码是使用pytorch来实现的LeNet,可以正常运行测试,自己添加了一些注释, ...
- 手写数字识别 ----在已经训练好的数据上根据28*28的图片获取识别概率(基于Tensorflow,Python)
通过: 手写数字识别 ----卷积神经网络模型官方案例详解(基于Tensorflow,Python) 手写数字识别 ----Softmax回归模型官方案例详解(基于Tensorflow,Pytho ...
- 手写数字识别 ----卷积神经网络模型官方案例注释(基于Tensorflow,Python)
# 手写数字识别 ----卷积神经网络模型 import os import tensorflow as tf #部分注释来源于 # http://www.cnblogs.com/rgvb178/p/ ...
- 第三节,TensorFlow 使用CNN实现手写数字识别(卷积函数tf.nn.convd介绍)
上一节,我们已经讲解了使用全连接网络实现手写数字识别,其正确率大概能达到98%,这一节我们使用卷积神经网络来实现手写数字识别, 其准确率可以超过99%,程序主要包括以下几块内容 [1]: 导入数据,即 ...
- 卷积神经网络CNN 手写数字识别
1. 知识点准备 在了解 CNN 网络神经之前有两个概念要理解,第一是二维图像上卷积的概念,第二是 pooling 的概念. a. 卷积 关于卷积的概念和细节可以参考这里,卷积运算有两个非常重要特性, ...
- 手写数字识别——基于LeNet-5卷积网络模型
在<手写数字识别——利用Keras高层API快速搭建并优化网络模型>一文中,我们搭建了全连接层网络,准确率达到0.98,但是这种网络的参数量达到了近24万个.本文将搭建LeNet-5网络, ...
- 利用卷积神经网络实现MNIST手写数据识别
代码: import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.utils.data as Data import torchvision # 数据库模块 im ...
随机推荐
- 获取了文心一言的内测及与其ChatGPT、GPT-4 对比结果
百度在3月16日召开了关于文心一言(知识增强大语言模型)的发布会,但是会上并没现场展示demo.如果要测试的文心一言 也要获取邀请码,才能进行测试的. 我这边通过预约得到了邀请码,大概是在3月17日晚 ...
- while与do-while的区别是什么,怎么用?
前言 在上一篇文章中,壹哥给大家讲解了循环的概念,并重点给大家讲解了for循环的使用.但在Java中,除了for循环之外,还有while.do-while.foreach等循环形式.今天壹哥就再用一篇 ...
- CSAPP-Attack Lab
目录 Code Injection Attacks Level 1 Level 2 Level_3 Return-Oriented Programming Level_4 Level_5 获取栈顶地址 ...
- Go语言:一文看懂什么是DI依赖注入(dependency injection)设计模式
前言: 本文主要介绍的是Goalng中关于 DI 的部分,前一部分会先通过典型的面向对象语言Java引入DI这个概念 仅供初学者理解使用,文章如有纰漏敬请指出 本文涉及到的知识面较为零散,其中包含面向 ...
- jQ的事件
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8&quo ...
- ECC(SM2) 简介及 C# 和 js 实现【加密知多少系列】
〇.简介 椭圆曲线密码学(Elliptic curve cryptography:ECC),一种建立公开密钥加密的演算法,基于椭圆曲线数学.利用有限域上椭圆曲线的点构成的 Abel 群离散对数难解性, ...
- 开发轻量级REST API样板 基于Node.js、MongoDB 通过Mongoose驱动
ZY.Node.Mongodb https://gitee.com/Z568_568/node.mongodb.git https://github.com/ZHYI-source/ZY.Node.M ...
- 二进制安装Kubernetes(k8s) v1.22.10 IPv4/IPv6双栈
二进制安装Kubernetes(k8s) v1.22.10 IPv4/IPv6双栈 Kubernetes 开源不易,帮忙点个star,谢谢了 介绍 kubernetes二进制安装 后续尽可能第一时间更 ...
- 自建kms2种方法,亲测有效
你还在用网上那种坑爹的Ghost盗版系统吗?内置各种辣鸡.流氓软件,新系统?纯净版Ghost系统?不存在的~ 在开始自建KMS服务器之前,我觉得很有必要给大家分享一个神站,没错就是MSDN! 地址:h ...
- 详解Redis三大集群模式,轻松实现高可用!
1. Redis集群简介 1.1 什么是Redis集群 Redis集群是一种通过将多个Redis节点连接在一起以实现高可用性.数据分片和负载均衡的技术.它允许Redis在不同节点上同时提供服务,提高整 ...
