学习spring第二天
Spring第二天笔记
1. 使用注解配置Spring入门
1.1. 说在前面
学习基于注解的IoC配置,大家脑海里首先得有一个认知,即注解配置和xml配置要实现的功能都是一样的,都是要降低程序间的耦合。只是配置的形式不一样。
关于实际的开发中到底使用xml还是注解,每家公司有着不同的使用习惯。所以这两种配置方式我们都需要掌握。
基于注解配置的方式也已经逐渐代替xml。所以我们必须要掌握使用注解的方式配置Spring。
1.2. 配置步骤
注意:Eclipse需要先安装了STS插件,或者使用STS开发工具创建项目。
1.2.1. 第一步:拷贝必备jar包到工程的lib目录。
注意:在基于注解的配置中,我们还要多拷贝一个aop的jar包。如下图:

|
1.2.2. 第二步:在类的根路径下创建一个任意名称的xml文件(不能是中文)
|
注意:基于注解整合时,Spring配置文件导入约束时需要多导入一个context名称空间下的约束
|
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd "> </beans> |
1.2.3. 第二步:创建一个服务类
创建一个测试的服务类,并且加入使用@Component注解,声明该类允许注入到Spring容器
|
package com.zj.spring.service; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; //1.使用注解配置,需要将启动是就创建对象的类表示为组件类 @Component public class CustomerService { public void save(){ System.out.println("-保存数据-"); } } |
1.2.4. 第四步在spring的配置文件加入扫描注解
|
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!-- 声明扫描包以及子包的类。如果发现有组件注解的类,就创建对象,并加入到容器 --> <context:component-scan base-package="cn.zj.spring"></context:component-scan> </beans> |
1.2.5. 第五步:测试调用代码
|
package com.zj.spring.test; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import com.zj.spring.service.CustomerService; public class CustomerServiceTest { public static void main(String[] args) { //CustomerService cs=new CustomerService(); ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:applicationContext.xml"); CustomerService customerService = context.getBean("customerService",CustomerService.class); customerService.save(); context.close(); } } |
--测试结果,如果可以调用服务方法,测试成功

|
1.2.6. 设置注解扫描的组件的名称
默认情况下, 被注解@Component 扫描的类的名称就是当前类名的首字母小写名称,开发者可以自定义组件的名称
|
/* 使用注解方式配置IOC @Component 说明当前类被Spring管理,Spring框架启动的时候就会创建此类的对象 设置当前Bean的名称 默认当前Bean的名称就是简单类名的 首字母小写 customerService value 属性可以自定义组件的名称 等价于 <bean id/name="bean名称"> @Component(value="service") 简写,可以省略value @Component("service") */ @Component("service") public class CustomerService { public void save() { System.out.println("-保存数据-"); } } |
2. Spring常用注解说明
2.1. 用于对象的注解-IOC相关注解
我们将用于被扫描创建对象的注解,统称为组件注解。
组件包括:@Component,@Controller,@Service,@Repository。
组件注解的功能都是标识类为注解的组件类,启动Spring框架的程序时,声明将这些组件类注入到Spring容器里面。意味着,只有加了这四个注解任何一个注解的类,在程序启动的时候,Spring就通过配置文件指定的路径将该路径下的所有带组件注解的类创建对象并且放在容器里面。
功能类似原来配置文件的<bean>标签
问题:明明一个@Component注解就可以满足了扫描的需要,为什么要有四个呢?
答:其实Spring第一版注解的实现(spring 2.5),就是使用一个@Component。从3.0以后,作者认为根据分层的需要,把它拆成了四个。为了可以让开发人员,可见即可得,一看到注解,立即知道类的性质。所以分成了四个
@Controller:用于声明表示层的组件注解
@Service:用于声明服务层的组件注解
@Repository:用于声明持久层的组件注解
@Component:用于声明三层以外的组件注解
问题:那么,这四个注解交换使用会报错吗。如:持久层,我放@Service标记。
答:处理@Controller在SpringMVC里面有强制的要求,SpringMVC的表示层必须使用@Controller组件注解。其他情况,用乱了是不会报错的,不过我们必须不能用乱。不遵守规范,不然别人无法跟你一起开发了。
2.1.1. @Scope用于设置对象的生命周期注解
Xml配置需要配置对象的作用范围
|
<bean id="someBean" class="..." scope="作用范围"></bean> |
如果使用注解配置bean,那么bean的作用范围也需要使用注解配置
@Scope("作用范围")
|
singleton |
单例 ,在Spring IoC容器中仅存在一个Bean实例 (默认的scope) |
|
prototype |
多例 ,每次从容器中调用Bean时,都返回一个新的实例,即每次调用getBean()时 ,相当于执行new XxxBean(): |
|
request |
用于web开发,将Bean放入request范围 ,request.setAttribute("xxx") , 在同一个request 获得同一个Bean |
|
session |
用于web开发,将Bean 放入Session范围,在同一个Session 获得同一个Bean |
|
package cn.zj.spring.controller; import javax.annotation.Resource; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import cn.zj.spring.service.CustomerService; @Controller("customerController") @Scope("prototype") public class CustomerController { //直接字段注入,不需要setter方法 //@Resource //按照类型注入 @Resource(name="customerService")//类型+id private CustomerService customerService; public void save() { //调用服务的save方法 customerService.save(); } } |
在开发中主要使用 scope="singleton"、 scope="prototype"
对于MVC中的Action/Controller使用prototype类型,其他使用singleton
2.1.2. @PostConstruct @PreDestroy初始化和销毁方法注解
在xml配置中可以配置对象的初始化方法和销毁方法
|
<bean id="someBean" class="cn.zj.spring.domain.SomeBean" init-method="init" destroy-method="destory"></bean> |
如果使用注解配置bean,那么bean的作用范围也需要使用注解配置
|
@PostConstruct // 相当于<bean init-method="init" /> public void init() { System.out.println("初始化方法执行了"); } @PreDestroy// 相当于<bean destroy-method="destory" /> public void destory() { System.out.println("销毁方法执行了"); } |
2.2. 用于依赖注入的注解
回顾:XML配置文件使用<property name=”” ref=””>实现注入的。通过注入注解也可以实现。
Spring提供了两套注解可以解决依对象依赖注入的方案
1,@Autowired +@Qualifier():是Spring定义的标签
2,@Resouce:是J2EE的规范
2.2.1. @Autowired注解
@Autowired注解:用于给引用注入容器的对象。
- @Autowired标签贴在字段或者setter方法上
- 默认情况下@Autowired标签必须要能找到对应的对象,否则报错。不过,可使用required=false来避免该问题:@Autowired(required=false)
- @Autowired找bean的方式:
(1) 首先按照依赖对象的类型找,如果找到则使用setter方法或者字段直接注入;
(2) 如果在Spring上下文中找到多个匹配的类型,再按照名字去找,如果没有匹配则报错;
(3) 可以通过使用@Qualifier("otherBean")标签来规定依赖对象按照bean的id+类型去找
使用@Autowired注入的三种情况
2.2.1.1. 在字段上面注入
|
package cn.zj.spring.controller; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import cn.zj.spring.service.CustomerService; //表示层使用@Controller //如果组件注解不声明对象名,默认使用默认命名法, //所谓的默认命名就是,将类的首字符小写作为类的对象名 //组件注解 //属性 value:作用用于指定该类对象的自定义对象名 @Controller("customerController") public class CustomerController { //直接字段注入,不需要setter方法 @Autowired private CustomerService customerService; /*public void setCustomerService(CustomerService customerService) { this.customerService = customerService; }*/ public void save() { //调用服务的save方法 customerService.save(); } } |
2.2.1.2. 在方法上面注入
|
package cn.zj.spring.controller; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import cn.zj.spring.service.CustomerService; //表示层使用@Controller //如果组件注解不声明对象名,默认使用默认命名法, //所谓的默认命名就是,将类的首字符小写作为类的对象名 //组件注解 //属性 value:作用用于指定该类对象的自定义对象名 @Controller(value="customerController") public class CustomerController { private CustomerService customerService=null; //注意,如果将@Autowired方法方法上面,意思就是将对象注入到该的方法的参数 //意味着:Spring会自动根据参数的CustomerService类型匹配容器中对应的对象给它 //注意:能够使用@Autowired注解的方法是必须有参数的 @Autowired public void setCustomerService(CustomerService customerService) { //问题:加了@Autowired的方法在启动的时候是否执行了? //答:如果该方法没有执行,那么this.customerService的对象从哪里来呢? //加了@Autowired在启动项目的时候是必须自动执行的 System.out.println("-setCustomerService已经被执行-"); this.customerService = customerService; } public void save(){ System.out.println("-保存客户-CustomerAction"); customerService.save(); } } |
2.2.1.3. 在构造方法上面注入
|
package cn.zj.spring.controller; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import cn.zj.spring.service.CustomService; @Controller public class CustomController { private CustomService service; /* * 方式三 : 构造器注入 * 使用注解的IOC创建bean的情况下 * 默认bean中有什么样的构造器,spring就调用那个构造器去创建对应的bean对象 * 并且会自动注入 构造器中对应类型参数的对象 * * 问题: 如果构造函数的参数类型对应的bean有多个,会抛出异常 * org.springframework.beans.factory.NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException 不是唯一的bean异常 * 解决方案: 在参数前面 使用 @Qualifier("service1") 注解 * 从多个bean 获取指定 id 对应的bean即可 */ public CustomController(@Qualifier("service1") CustomService service) { this.service = service; } public void save() { service.save(); } } |
2.2.2. @Qualifier注解
@Qualifier注解:用于指定注入的对象名,使用@Autowired注入对象时,@Autowired没有指定对象名的属性,只能通过@Qualifier字段容器中对象名
属性
value:指定注入Spring容器中对应对象名的对象给引用。
|
@Controller("customerController") public class CustomerController { //直接字段注入,不需要setter方法 @Autowired @Qualifier(value="customerService") private CustomerService customerService; public void save() { //调用服务的save方法 customerService.save(); } } |
2.2.3. @Resource注解
@Resource注解是Spring框架支持Sun官方制定的JSR-250标准注入对象的实现。
JSR-250就是Sun公司制定,对注入的对象的标准。
@Resource 功能等同 @Autowired + @Qualifier ,等同配置文件标签 <proprty name=”...” ref=”...”>
@Resource注解:用于给引用注入容器的对象,可以通过name属性指定对象名
注意事项:@Resource只能使用字段和setter方法,不能注入构造方法
|
package cn.zj.spring.controller; import javax.annotation.Resource; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import cn.zj.spring.service.CustomerService; @Controller("customerController") public class CustomerController { //直接字段注入,不需要setter方法 //@Resource //按照类型注入 @Resource(name="customerService")//类型+id private CustomerService customerService; public void save() { //调用服务的save方法 customerService.save(); } } |
2.2.4. 依赖注入注解所在的包的位置
除了@Resource注解是Java官方的标准,内置在JDK里面以外,Spring内置实现的注解声明放在spring-beans-5.0.5.RELEASE.jar里面。如下图所示:
2.2.5. @Value注解
<value>
//value只能设置,标量类型=基础数据类型+包装类+String
@Value注解:注入基本数据类型以及它们的包装类和String类型数据的,支持${}注入Properties文件的键值对,等同 <proprty name=”...” value=”${Key}”>。
属性:
value:注入基本数据类型和String类型数据的
2.2.5.1. 案例代码
|
package cn.zj.spring.dao.impl; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; import cn.zj.spring.dao.UserDao; import cn.zj.spring.pojo.User; @Repository public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao { /** * @Value(value="") * 可以从Spring容器读取 .properties 配置文件内容 * value :配置文件的对应的key -->使用 ${key} 获取 * 程序运行中自动将 properties 对应key的获取出来设置给字段 * */ //等价 <property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driverClassName}"> @Value("${jdbc.driverClassName}") private String driverClassName; @Value("${jdbc.url}") private String url; @Value("${jdbc.username}") private String username; @Value("${jdbc.password}") private String password; //@Value("${jdbc.maxActive}") @Value("100") //开发者也手动赋值 private String maxActive; @Override public void insert(User user) { System.out.println(driverClassName); System.out.println(url); System.out.println(username); System.out.println(password); System.out.println(maxActive); } } |
3. 模拟注册功能(使用注解方式)
3.1. DAO层代码
|
//@Component("userDao") @Repository("userDao") public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao { @Override public void insert(User user) { System.out.println("注册的Dao方法执行"); } } |
3.2. Service层代码
|
@Service("userService") public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService { /*@Autowired @Qualifier("userDao")*/ @Resource(name="userDao") private UserDao dao; @Override public void register(User user) { dao.insert(user); } //因为要用 public void setDao(UserDao dao) { this.dao = dao; } } |
3.3. 表现层代码
|
@Controller public class UserController { /*@Autowired @Qualifier("userService")*/ @Resource(name="userService") private UserService service; public void register(User user) { service.register(user); } } |
3.4. 测试代码
|
public class UserServletTest { @Test public void testSpring() throws Exception { //创建用户对象:模拟接受用户参数,封装对象的过程 User user = new User(); user.setUsername("张三"); user.setPassword("admin"); UserController controller = context.getBean("userController",CustomerController.class); //执行注册操作 controller.register(user); } } |
3.5. applicationContext.xml
配置文件(只需要配置一个包扫描即可)
|
<!-- 配置包扫描 cn.zj.spring : 此包以及子包全部被扫描 --> <context:component-scan base-package="cn.zj.spring"/> |
4. 纯注解配置
4.1. 问题
我们发现,之所以我们现在离不开xml配置文件,是因为我们有一句很关键的配置:
<!-- 告知spring框架在,读取配置文件,创建容器时,扫描注解,依据注解创建对象,并存入容器中 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="cn.zj.spring"></context:component-scan>
如果他要也能用注解配置,那么我们就可以脱离xml文件了。
通过@Configuration注解和@ComponentScan注解
|
替换XML配置文件的 @Configuration注解 |
@Configuration配置类注解,在纯注解配置中,类加了该注解,就意味着该类是Spring的配置类。该类的功能就是用于替代原来的XML配置文件。 作用: 用于指定当前类是一个spring配置类,当创建容器时会从该类上加载注解。获取容器时需要使用AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(有@Configuration注解的类.class)。 |
|
@ComponentScan注解 |
@ComponentScan注解扫描类,作用就是配置扫描Spring组件类的路径。功能等同原来配置文件的 --作用: 用于指定spring在初始化容器时要扫描的包。作用和在spring的xml配置文件中的: <context:component-scan base-package="cn.zj.spring"/>是一样的。 --属性: basePackages:用于指定要扫描的包。和该注解中的value属性作用一样。 |
|
@PropertySource注解 |
作用: 用于加载.properties文件中的配置。例如我们配置数据源时,可以把连接数据库的信息写到properties配置文件中,就可以使用此注解指定properties配置文件的位置。 属性: value[]:用于指定properties文件位置。如果是在类路径下,需要写上classpath: |
|
@Bean注解 |
作用: 该注解只能写在方法上,使用此方法创建一个对象,并且放入spring容器。它就相当于我们之前在xml配置中介绍的<bean标签> 属性: name:给当前@Bean注解方法创建的对象指定一个名称(即bean的id)。 |
|
@Import注解 |
作用: 用于导入其他配置类,在引入其他配置类时,可以不用再写@Configuration注解。当然,写上也没问题。 <import > 属性: value[]:用于指定其他配置类的字节码。 |
4.2. 示例代码
4.2.1. 简单入门
4.2.1.1. 说明
需求:通过一个简单的入门示例,实现创建一个配置类使用@Configuration注解和@ComponentScan注解替换xml文件。
4.2.1.2. 配置步骤
4.2.1.2.1. 第一步:创建一个Java项目
创建一个Java项目,导入必须的jar包以及编写好需要的类结构。代码目录如下:

|
4.2.1.2.2. 第三步:编写配置类代码
--通过该配置类的代码替换掉Spring配置文件
|
package cn.zj.spring.config; import javax.sql.DataSource; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource; import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource; /* * @Configuration * 说明把当前类当做成Spring框架的配置文件 * @ComponentScan * 配置注解包扫描的位置 * @PropertySource("classpath:db.properties") * 读取.peroperties 后缀的配置文件 */ @Configuration //@ComponentScan(basePackages= {"cn.zj.spring.action","cn.zj.spring.service","cn.zj.spring.dao"}) @ComponentScan("cn.zj.spring") @PropertySource("classpath:db.properties") public class SpringConfig { /** * @Value(value="") * 可以从Spring容器读取 .properties 配置文件内容 * value :配置文件的对应的key -->使用 ${key} 获取 * 程序运行中自动将 properties 对应key的获取出来设置给字段 * */ //等价 <property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driverClassName}"> @Value("${jdbc.driverClassName}") private String driverClassName; @Value("${jdbc.url}") private String url; @Value("${jdbc.username}") private String username; @Value("${jdbc.password}") private String password; @Value("${jdbc.maxActive}") private Integer maxActive; //<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource" //init-method="init" destroy-method="close"> @Bean(name="dataSource",initMethod="init",destroyMethod="close") public DataSource getDataSource() { DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource(); dataSource.setDriverClassName(driverClassName); dataSource.setUrl(url); dataSource.setUsername(username); dataSource.setPassword(password); dataSource.setMaxActive(maxActive); return dataSource; } } |
4.2.1.2.3. 第四步:编写测试代码
|
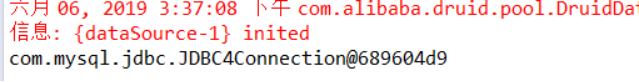
package cn.zj.spring.test; import java.sql.Connection; import javax.sql.DataSource; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext; import cn.zj.spring.config.SpringConfig; public class SpringTest { @Test public void testName() throws Exception { // 1.读取 xml 配置文件,启动框架,创建Spring容器对象 //ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); // 1. 读取SpringConfig 类配置文件,启动动框架,创建Spring容器对象 ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class); //2. 获取 连接池对象 DataSource dataSource = context.getBean("dataSource", DataSource.class); //2.1获取数据库连接对象 Connection conn = dataSource.getConnection(); System.out.println(conn); } } |
--测试结果,输出组件类调用方法的输出值。配置成功
|
5. Spring的测试
5.1. 传统的测试
存在问题:
1,每个测试都要重新启动Spring容器,启动容器的开销大,测试效率低下。
2,不应该是测试代码管理Spring容器,应该是Spring容器在管理测试代码。

|
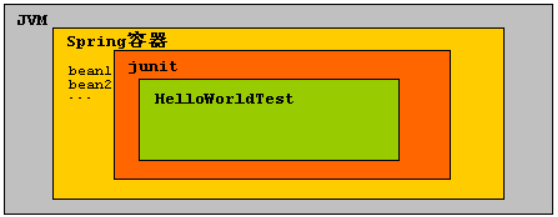
5.2. 正确使用Spring的测试
|
5.3. 如何使用Spring测试
5.3.1. 导入spring测试的jar包

|
Spring测试必须保证Eclipse的单元测试的最低版本是 4.12版本,如果使用的Eclipse版本很低,那么单元测试版本可能低于4.12,那么需要开发者手动导入单元测试的jar包
如果使用Spring方式测试,必须使用两个注解
@RunWith注解
表示先启动Spring容器,把junit运行在Spring容器中
@ContextConfiguration注解
从哪里加载资源文件,默认从src(源目录)下面加载
5.3.2. 案例代码
|
package cn.zj.spring.test; import static org.junit.Assert.*; import javax.annotation.Resource; import javax.swing.Spring; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext; import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner; import cn.zj.spring.config.SpringConfig; import cn.zj.spring.service.CustomerService; //表示先启动Spring容器,把junit运行在Spring容器中 @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) //表示从哪里加载资源文件,默认从src(源目录)下面加载 @ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext.xml") public class CustomerServiceTest { @Resource ApplicationContext context; @Test public void testSpring() throws Exception { //1.获取Spring容器对象 //AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context=new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(“applicationContext.xml”); //2.获取CustomerController对象 CustomerService controller = context.getBean("customerService",CustomerService.class); //执行保存方法 controller.save(); } } |
5.3.3. 纯注解方式的配置
@ContextConfiguration()
classes 属性: 读取spring的纯java配置文件
|
package cn.zj.spring.test; import static org.junit.Assert.*; import javax.annotation.Resource; import javax.swing.Spring; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext; import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner; import cn.zj.spring.config.SpringConfig; import cn.zj.spring.service.CustomerService; @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @ContextConfiguration(classes=Spring.class) public class CustomerServiceTest { @Resource ApplicationContext context; @Test public void testSpring() throws Exception { //1.获取Spring容器对象 //AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context=new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class); //2.获取CustomerController对象 CustomerService controller = context.getBean("customerService",CustomerService.class); //执行保存方法 controller.save(); } } |
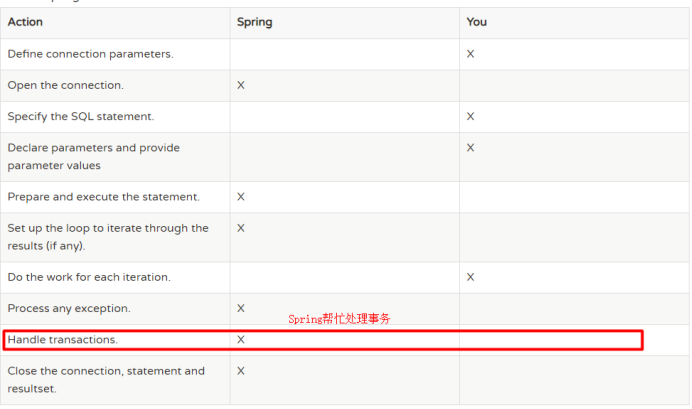
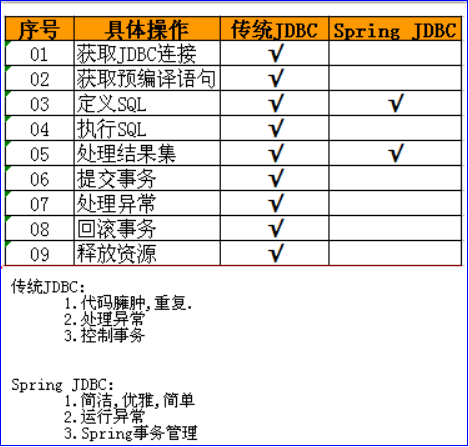
6. Spring的JDBC操作
Spring对象也支持JDBC,对JDBC只进行了薄薄的一层封装
问题: Java开发已经有JDBC,为什么Spring还要支持JDBC操作呢?
最重要的原因: Spring操作JDBC能自动管理事务
|
|
6.1. 操作步骤
|
1,创建数据库 spring_jdbc |
|
2.创建数据表 t_user |
|
CREATE TABLE `t_user` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `name` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL, `email` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; |
|
3.创建对应的domain对象 |
|
public class User { private Integer id; private String name; private String email; public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getEmail() { return email; } public void setEmail(String email) { this.email = email; } @Override public String toString() { return "User [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", email=" + email + "]"; } public User(Integer id, String name, String email) { super(); this.id = id; this.name = name; this.email = email; } public User() { super(); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } } |
|
4.创建DAO层 |
|
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao { @Override public void save(User user) { } @Override public void delete(Integer id) { } @Override public void update(User user) { } @Override public User findById(Integer id) { return null; } @Override public List<User> list() { return null; } } |
|
5.创建Service层 |
|
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService { private UserDao dao; @Override public void save(User user) { dao.save(user); } @Override public void delete(Integer id) { dao.delete(id); } @Override public void update(User id) { dao.update(id); } @Override public User findById(Integer id) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return dao.findById(id); } @Override public List<User> list() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return dao.list(); } public void setDao(UserDao dao) { this.dao = dao; } } |
|
6.测试代码 |
|
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext.xml") public class UserServiceTest { @Resource private UserService service; @Test public void testSave() { User user = new User(null, "乔峰", "qf@qq.com"); service.save(user); } @Test public void testDelete() { service.delete(3); } @Test public void testUpdate() { User user = new User(2, "段誉", "123123sdfsdf@qq.com"); service.update(user); } @Test public void testFindById() { User user = service.findById(1); System.out.println(user); } @Test public void testList() { List<User> users = service.list(); System.out.println(users); } } |
|
ApplicationContext.xml配置 |
|
<!-- 引入 db.properties配置文件 --> <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:db.properties"/> <!-- 配置Druid连接池 : DataSource 数据源 --> <bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource" init-method="init" destroy-method="close" > <!-- setter方法注入属性值 --> <property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driverClassName}"/> <property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/> <property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/> <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/> <!-- 最大连接数 --> <property name="maxActive" value="${jdbc.maxActive}"/> </bean> <!-- 配置DAO层 --> <bean id="userDao" class="cn.zj.spring.dao.impl.UserDaoImpl2"> <!-- setter方法注入数据源:连接池 --> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> </bean> <!-- 配置Service层 --> <bean id="userSercice" class="cn.zj.spring.service.impl.UserServiceImpl"> <!-- 注入dao --> <property name="dao" ref="userDao"/> </bean> |
6.2. 快速生成一个类有多个测试方法的单元测试类
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.2.1. JDBCTemplate模板类
Spring为各大框架提供对应的模板类可以直接操作数据库
|
如果使用JDBC就使用JDBCTemplate类(将数据库的基本操作方法已经封装好了,直接调用即可) |
|
导入相关jar包 mysql-connector-java-5.x.jar:MySQL驱动包 spring-jdbc-5.0.5.RELEASE.jar:支持JDBC spring-tx-5.0.5.RELEASE.jar: 支持事务 druid1.9.jar 连接池 |
|
DAO层代码 |
|
// 引入JDBCTemplate 模板类 private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; //使用setter方式注入数据源即可 public void setDataSource(DataSource dataSource) { this.jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate(dataSource); } @Override public void save(User user) { this.jdbcTemplate.update("insert into t_user (name,email) values (?,?)", user.getName(),user.getEmail()); } @Override public void delete(Integer id) { this.jdbcTemplate.update("delete from t_user where id = ?",id); } @Override public void update(User user) { this.jdbcTemplate.update("update t_user set name = ?,email = ? where id = ?", user.getName(),user.getEmail(),user.getId()); } @Override public User findById(Integer id) { String sql = "select * from t_user where id = ?"; User user = this.jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql,new Object[] {id}, new RowMapper<User>() { @Override public User mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws SQLException { User user = new User(); user.setName(rs.getString("name")); user.setEmail(rs.getString("email")); user.setId(id); return user; } }); return user; } @Override public List<User> list() { String sql = "select * from t_user"; List<User> users = this.jdbcTemplate.query(sql,new RowMapper<User>(){ @Override public User mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws SQLException { User user = new User(); user.setName(rs.getString("name")); user.setEmail(rs.getString("email")); user.setId(rs.getInt("id")); return user; } }); return users; } |
6.2.2. DAOSupport
问题: 每个DAO层的实现类都写上述同样的代码,100个DAO写100次,代码重复99次
Spring考虑到这点:专门为各种持久化操作抽取了 Support父类,开发者自己的到只需要继承对应的Support类即可
|
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao { // 引入JDBCTemplate 模板类 private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; //使用setter方式注入数据源即可 public void setDataSource(DataSource dataSource) { this.jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate(dataSource); } } |

|
|
JdbcDaoSupport类的结构 public abstract class JdbcDaoSupport extends DaoSupport { @Nullable private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; /** * Set the JDBC DataSource to be used by this DAO. */ public final void setDataSource(DataSource dataSource) { if (this.jdbcTemplate == null || dataSource != this.jdbcTemplate.getDataSource()) { this.jdbcTemplate = createJdbcTemplate(dataSource); initTemplateConfig(); } } @Nullable public final JdbcTemplate getJdbcTemplate() { return this.jdbcTemplate; } } |
|
让自己的类继承自JdbcDaoSupport类就解决上上述代码重复问题 |
|
public class UserDaoImpl2 extends JdbcDaoSupport implements UserDao {} |
7. 小结
Spring的IOC和DI 的配置 可以使用XML配置,也可以注解配置
今日内容
注解配置
- 注解配置IOC (控制反正,将对象的创建权交给Spring)-重点
(1) @Component 通用IOC 组件,试用任意Spring对象管理
(2) @Controller 主要在表现层使用
(3) @Service 业务层使用
(4) @Repository DAO层使用
(5) 必须在xml中配置包扫描的位置
(6) <context:component-scan base-package=”cn.zj.spring”>
- 注解配置ID (依赖注入)注入对象的属性(值,集合,引用)-重点
(1) @Autowired + @Qualifier Spring 框架提供
(2) @Resource JavaEE 官方的规范
- Spring纯注解配置-重点
(1) 纯注解配置替代xml配置,但是所有配置依然存在,只是配置方式变换成在类上面贴注解的形式(未来的趋势)--SpringBoot(纯注解)
- Spring测试-(理解)
(1) 为了更方便的开发Spring程序
- SpringJDBC-(理解)
(1) 优点 :主要能够让Spring自动控制事务
(2) JdbcTemplate 模板类 进行数据表的增删改查
(3) JdbcDaoSupport
① 优点: 将jdbcTemplate模板类的创建进行封装
② 缺点:只能在xml配置对应DAO类
学习spring第二天的更多相关文章
- 深入浅出学习Spring框架(四):IoC和AOP的应用——事务配置
在前文 深入浅出学习Spring框架(一):通过Demo阐述IoC和DI的优势所在. 深入浅出学习Spring框架(三):AOP 详解 分别介绍了Spring的核心功能——IoC和AOP,光讲知识远远 ...
- Spring第二天
Spring第二天 整体课程安排(3天+2天): 第一天:Spring框架入门.IoC控制反转的配置管理.Spring Web集成.Spring Junit集成. 第二天:Spring AOP面向切面 ...
- 【转】Spring学习---Spring IoC容器的核心原理
[原文] Spring的两个核心概念:IoC和AOP的雏形,Spring的历史变迁和如今的生态帝国. IoC和DI的基本概念 IoC(控制反转,英文含义:Inverse of Control)是Spr ...
- 学习Spring——依赖注入
前言: 又开始动笔开了“学习Spring”系列的头…… 其实一开始写“学习SpringMVC”的几篇文章是出于想系统的了解下Spring以及SpringMVC,因为平时在公司中虽然每天都在使用Spri ...
- RabbitMQ学习总结 第二篇:快速入门HelloWorld
目录 RabbitMQ学习总结 第一篇:理论篇 RabbitMQ学习总结 第二篇:快速入门HelloWorld RabbitMQ学习总结 第三篇:工作队列Work Queue RabbitMQ学习总结 ...
- 菜鸟学习Spring——60s配置XML方法实现简单AOP
一.概述. 上一篇博客讲述了用注解的形式实现AOP现在讲述另外一种AOP实现的方式利用XML来实现AOP. 二.代码演示. 准备工作参照上一篇博客<菜鸟学习Spring--60s使用annota ...
- 学习KnockOut第二篇之Counter
学习KnockOut第二篇之Counter 欲看此 ...
- 跟着刚哥学习Spring框架--创建HelloWorld项目(一)
1.Spring框架简介 Spring是一个开源框架,Spring是在2003年兴起的一个轻量级的开源框架,由Rod johnson创建.主要对JavaBean的生命周期进行管理的轻量级框架,Spri ...
- Spring第二篇和第三篇的补充【JavaConfig配置、c名称空间、装载集合、JavaConfig与XML组合】
前言 在写完Spring第二和第三篇后,去读了Spring In Action这本书-发现有知识点要补充,知识点跨越了第二和第三篇,因此专门再开一篇博文来写- 通过java代码配置bean 由于Spr ...
随机推荐
- 基础语法-选择结构switch
基础语法-选择结构switch 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 一.Switch语句特点 switch语句选择的类型在jdk1.6只支持四种:byte,short,i ...
- sourcetree安装以及跳过sourcetree注册登录 - git仓库管理工具桌面版
腾讯软件下载:https://pc.qq.com/detail/17/detail_23237.html 官网下载:https://www.sourcetreeapp.com/ 下载完直接安装 ...
- TypeScript 文件引入 Html (ts import html webpack)
我们的目标是把html引入ts文件,webpack打包时就能把html打进js文件,减少文件加载啦 1 安装 text-loader npm install text-loader --save-de ...
- bzoj 3876: [Ahoi2014]支线剧情
就是加一个1的下界就好了. #include<bits/stdc++.h> #define N 100005 #define LL long long #define inf 0x3f3f ...
- bzoj 4300绝世好题
呵呵呵呵 #include<bits/stdc++.h> #define INF 0x7fffffff #define LL long long #define N 100005 usin ...
- react-native-tab-view 导航栏切换插件讲解
首先引入插件 yarn add react-native-tab-view 如果用的原生环境要安装另外几个插件 yarn add react-native-reanimated react-nativ ...
- 读书笔记 - javascript 高级程序设计 - 第一章 简介
第一章 简介 诞生时间 1995 最初用途 客服端验证 第一版标准 注意是标准 1997年 Ecma-262 一个完整的js实现由三部分组成 ECMAScript DOM 文档对象模型 BO ...
- 什么是控制反转IOC
1.IOC 是什么 IOC- Inversion of Control , 即“控制反转” ,不是一个技术,而是一个设计思想,在java 开发中,IOC意味着将你设计好的Java 对象交个容器控制,而 ...
- 最短路问题--P4779 单源最短路(标准版)Dijkstra堆优化
题目背景 2018 年7月 19 日,某位同学在 NOI Day 1 T1 归程 一题里非常熟练地使用了一个广为人知的算法求最短路. 最终,他因此没能与理想的大学达成契约. 小 F 衷心祝愿大家不再重 ...
- HashMap的fast-fail和ConcurrentHashMap的fail-safe实例
声明:迁移自本人CSDN博客https://blog.csdn.net/u013365635 Java HashMap遍历过程中如果元素被修改会导致遍历失败,ConcurrentHashMap则不会有 ...