CTR学习笔记&代码实现3-深度ctr模型 FNN->PNN->DeepFM
这一节我们总结FM三兄弟FNN/PNN/DeepFM,由远及近,从最初把FM得到的隐向量和权重作为神经网络输入的FNN,到把向量内/外积从预训练直接迁移到神经网络中的PNN,再到参考wide&Deep框架把人工特征交互替换成FM的DeepFM,我们终于来到了2017年。。。
以下代码针对Dense输入感觉更容易理解模型结构,针对spare输入的代码和完整代码
https://github.com/DSXiangLi/CTR
FNN
FNN算是把FM和深度学习最早的尝试之一。可以从两个角度去理解FNN:从之前Embedding+MLP的角看,FNN使用FM预训练的隐向量作为第一层可以加快模型收敛。从FM的角度来看,FM局限于二阶特征交互信息,想要学到更高阶的特征交互,在FM基础上叠加全联接层就是FNN。
补充一下Embedding直接拼接作为输入为啥收敛的这么慢,一个是参数太多一层Embedding就要N*K个参数再加上后面的全联接层,另外就是每次gradient descent只会更新和稀疏离散输入里面非0特征对应的Embedding。
模型
先看下FM的公式,FNN提取了以下的\(W,V\)来作为神经网络第一层的输入
FNN的模型结构比较简单。输入特征N维, FM隐向量维度是K
- 预训练FM模型提取最终的隐向量\(V = [v_1,v_2,...,v_n] \in R^{N*k} \,\, v_i \in R^{1*K}\)和权重\(w= [w_1,w2,...,w_n] w \in R^{1*N}\)
- FNN模型用\(V\)和\(W\)来初始化神经网络的第一层.模型输入是由特征离散化后的one-hot矩阵拼接而成(x),每个离散特征(i)的one-hot输入都映射到它的低维embedding上\(z_i = [w_i, v_i] *x[start_i:end_i]\), 第一层是由\([z_1,z_2,...z_n]\)
- 两个常规的全联接层到最终给出CTR的预测。
模型结构如下

FNN几个能想到的问题有
- 非端到端的模型,一点都不优雅有没有
- 最终FNN的表现会一定程度受到预训练FM表现的限制,神经网络的最大信息量<=FM隐向量和权重所含信息量,当然这不代表FNN会比FM差因为FM对信息的提取只用了内积
- 从Wide&Deep角度,模型对低阶信息的提炼会比较有限
- 单纯的全联接层对于进一步提炼隐向量上的信息可能不够高效
代码实现
这里用了tf.contrib.framework.load_variable去读了之前FM模型的embedding和weight。感觉也可以直接把FM的variable写出来,然后FNN里用params再传进去也是可以的。
@tf_estimator_model
def model_fn(features, labels, mode, params):
feature_columns= build_features()
input = tf.feature_column.input_layer(features, feature_columns)
with tf.variable_scope('init_fm_embedding'):
# method1: load from checkpoint directly
embeddings = tf.Variable( tf.contrib.framework.load_variable(
'./checkpoint/FM',
'fm_interaction/v'
) )
weight = tf.Variable( tf.contrib.framework.load_variable(
'./checkpoint/FM',
'linear/w'
) )
dense = tf.add(tf.matmul(input, embeddings), tf.matmul(input, weight))
add_layer_summary('input', dense)
with tf.variable_scope( 'Dense' ):
for i, unit in enumerate( params['hidden_units'] ):
dense = tf.layers.dense( dense, units=unit, activation='relu', name='dense{}'.format( i ) )
dense = tf.layers.batch_normalization( dense, center=True, scale=True, trainable=True,
training=(mode == tf.estimator.ModeKeys.TRAIN) )
dense = tf.layers.dropout( dense, rate=params['dropout_rate'],
training=(mode == tf.estimator.ModeKeys.TRAIN) )
add_layer_summary( dense.name, dense )
with tf.variable_scope('output'):
y = tf.layers.dense(dense, units= 1, name = 'output')
tf.summary.histogram(y.name, y)
return y
PNN
PNN的目标在paper最开始就点明了以比MLPs更有效的方式来挖掘信息。在前一篇我们就说过MLP理论上可以提炼任意信息,但也因为它太过general导致最终模型能学到模式受数据量的限制会非常有限,PNN借鉴了FM的思路来帮助MLP学到更多特征交互信息。
模型
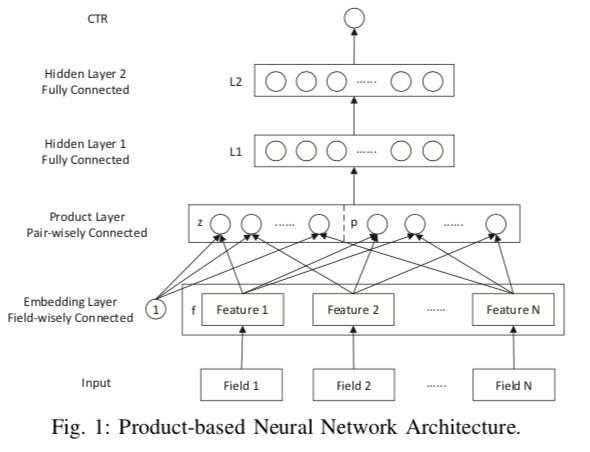
PNN给出了三种挖掘特征交互信息的方式IPNN采用向量内积,OPNN采用向量外积,concat在一起就是PNN。模型结构如下
- Input层
输入是N个离散特征one-hot处理后拼接而成的高维稀疏矩阵,每个特征映射到相同维度(k)的低维embddding上 - Product层
- Z是线性部分,和‘1’相乘也就是直接把N个K维Embedding拼接得到N*K的稠密矩阵copy过来
- p是特征交互部分
- IPNN是两两特征做内积\((1*k)*(k*1)\)得到的scaler拼接成p,维度是\(O(N^2)\)
- OPNN是两两特征做外积\((k*1)*(1*k)\)得到\(K^2\)的矩阵拼接成p,维度是\(O(K^2N^2)\)
- PNN就是[IPNN,OPNN]
之后跟全连接层。可以发现去掉全联接层把权重都设为1,把线性部分对接到最初的离散输入那IPNN就退化成了FM。
Product层的优化
以上IPNN和OPNN的计算都有维度过高,计算复杂度过高的问题,作者进行了相应的优化。
- OPNN: \(O(N^2K^2) \to O(K^2)\)
原始的OPNN,p中的每个元素都是向量外积的矩阵\(p_{i,j} \in R^{k*k}\),优化后作者对所有K*K矩阵进行了sum_pooling,也等同于先对隐向量求和\(R^{N*K} \to R^{1*K}\)再做外积\(p = \sum_{i=1}^N\sum_{j=1}^N f_if_j^T=f_{\sum}(f_{\sum})^T \, \, f_{\sum}=\sum_{i=1}^Nf_i\) - IPNN: \(O(N^2) \to O(N*K)\)
IPNN的优化又一次用到了FM的思想,内积产生的\(p \in R^{N^2}\)是对称矩阵,因此在之后全联接层的权重\(w_p\)也一定是对称矩阵。所以用矩阵分解来进行降维,假定每个神经元对应的权重\(w_p^n = \theta^n{\theta^n}^T \text{where } \theta^n \in R^N\)
\(w_p^n \odot p = \sum_{i=1}^N\sum_{j=1}^N\theta^n_i\theta^n_j<f_i,f_j>=<\sum_{i=1}^N\delta_i^n,\sum_{i=1}^N\delta_i^n>\)
PNN的几个可能可以吐槽的地方
- 和FNN一样对低阶特征的提炼比较有限
- OPNN的部分如果不优化维度太高,在我尝试的训练集上基本是没啥用。优化后这个sum_pooling究竟还保留了什么信息,我是没太琢磨明白
代码实现
@tf_estimator_model
def model_fn(features, labels, mode, params):
dense_feature= build_features()
dense = tf.feature_column.input_layer(features, dense_feature) # lz linear concat of embedding
feature_size = len( dense_feature )
embedding_size = dense_feature[0].variable_shape.as_list()[-1]
embedding_matrix = tf.reshape( dense, [-1, feature_size, embedding_size] ) # batch * feature_size *emb_size
with tf.variable_scope('IPNN'):
# use matrix multiplication to perform inner product of embedding
inner_product = tf.matmul(embedding_matrix, tf.transpose(embedding_matrix, perm=[0,2,1])) # batch * feature_size * feature_size
inner_product = tf.reshape(inner_product, [-1, feature_size * feature_size ])# batch * (feature_size * feature_size)
add_layer_summary(inner_product.name, inner_product)
with tf.variable_scope('OPNN'):
outer_collection = []
for i in range(feature_size):
for j in range(i+1, feature_size):
vi = tf.gather(embedding_matrix, indices = i, axis=1, batch_dims=0, name = 'vi') # batch * embedding_size
vj = tf.gather(embedding_matrix, indices = j, axis=1, batch_dims= 0, name='vj') # batch * embedding_size
outer_collection.append(tf.reshape(tf.einsum('ai,aj->aij',vi,vj), [-1, embedding_size * embedding_size])) # batch * (emb * emb)
outer_product = tf.concat(outer_collection, axis=1)
add_layer_summary( outer_product.name, outer_product )
with tf.variable_scope('fc1'):
if params['model_type'] == 'IPNN':
dense = tf.concat([dense, inner_product], axis=1)
elif params['model_type'] == 'OPNN':
dense = tf.concat([dense, outer_product], axis=1)
elif params['model_type'] == 'PNN':
dense = tf.concat([dense, inner_product, outer_product], axis=1)
add_layer_summary( dense.name, dense )
with tf.variable_scope('Dense'):
for i, unit in enumerate( params['hidden_units'] ):
dense = tf.layers.dense( dense, units=unit, activation='relu', name='dense{}'.format( i ) )
dense = tf.layers.batch_normalization( dense, center=True, scale=True, trainable=True,
training=(mode == tf.estimator.ModeKeys.TRAIN) )
dense = tf.layers.dropout( dense, rate=params['dropout_rate'],
training=(mode == tf.estimator.ModeKeys.TRAIN) )
add_layer_summary( dense.name, dense)
with tf.variable_scope('output'):
y = tf.layers.dense(dense, units=1, name = 'output')
add_layer_summary( 'output', y )
return y
DeepFM
DeepFM是对Wide&Deep的Wide侧进行了改进。之前的Wide是一个LR,输入是离散特征和交互特征,交互特征会依赖人工特征工程来做cross。DeepFM则是用FM来代替了交互特征的部分,和Wide&Deep相比不再依赖特征工程,同时cross-column的剔除可以降低输入的维度。
和PNN/FNN相比,DeepFM能更多提取到到低阶特征。而且上述这些模型间直接并不互斥,比如把DeepFM的FMLayer共享到Deep部分其实就是IPNN。
模型
Wide部分就是一个FM,输入是N个one-hot的离散特征,每个离散特征对应到等长的低维(k)embedding上,最终输出的就是之前FM模型的output。并且因为这里不需要像IPNN一样输出隐向量,因此可以使用FM降低复杂度的trick。

Deep部分和Wide部分共享N*K的Embedding输入层,然后跟两个全联接层
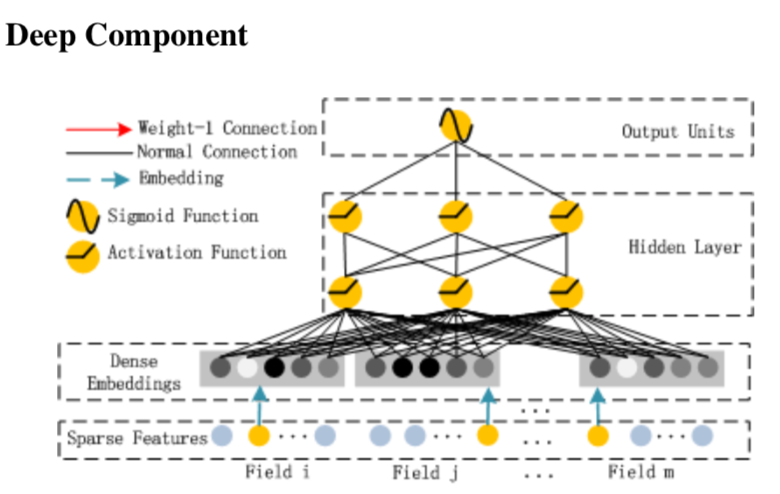
Deep和Wide联合训练,模型最终的输出是FM部分和Deep部分权重为1的简单加和。联合训练共享Embedding也保证了二阶特征交互学到的Embedding会和高阶信息学到的Embedding的一致性。
代码实现
@tf_estimator_model
def model_fn(features, labels, mode, params):
dense_feature, sparse_feature = build_features()
dense = tf.feature_column.input_layer(features, dense_feature)
sparse = tf.feature_column.input_layer(features, sparse_feature)
with tf.variable_scope('FM_component'):
with tf.variable_scope( 'Linear' ):
linear_output = tf.layers.dense(sparse, units=1)
add_layer_summary( 'linear_output', linear_output )
with tf.variable_scope('second_order'):
# reshape (batch_size, n_feature * emb_size) -> (batch_size, n_feature, emb_size)
emb_size = dense_feature[0].variable_shape.as_list()[0] # all feature has same emb dimension
embedding_matrix = tf.reshape(dense, (-1, len(dense_feature), emb_size))
add_layer_summary( 'embedding_matrix', embedding_matrix )
# Compared to FM embedding here is flatten(x * v) not v
sum_square = tf.pow( tf.reduce_sum( embedding_matrix, axis=1 ), 2 )
square_sum = tf.reduce_sum( tf.pow(embedding_matrix,2), axis=1 )
fm_output = tf.reduce_sum(tf.subtract( sum_square, square_sum) * 0.5, axis=1, keepdims=True)
add_layer_summary('fm_output', fm_output)
with tf.variable_scope('Deep_component'):
for i, unit in enumerate(params['hidden_units']):
dense = tf.layers.dense(dense, units = unit, activation ='relu', name = 'dense{}'.format(i))
dense = tf.layers.batch_normalization(dense, center=True, scale = True, trainable=True,
training=(mode ==tf.estimator.ModeKeys.TRAIN))
dense = tf.layers.dropout( dense, rate=params['dropout_rate'], training = (mode==tf.estimator.ModeKeys.TRAIN))
add_layer_summary( dense.name, dense )
with tf.variable_scope('output'):
y = dense + fm_output + linear_output
add_layer_summary( 'output', y )
return y
CTR学习笔记&代码实现系列
https://github.com/DSXiangLi/CTR
CTR学习笔记&代码实现1-深度学习的前奏LR->FFM
CTR学习笔记&代码实现2-深度ctr模型 MLP->Wide&Deep
资料
- Huifeng Guo et all. "DeepFM: A Factorization-Machine based Neural Network for CTR Prediction," In IJCAI,2017.
- Qu Y, Cai H, Ren K, et al. Product-based neural networks for user response prediction,2016 IEEE
- Weinan Zhang, Tianming Du, and Jun Wang. Deep learning over multi-field categorical data - - A case study on user response
- https://daiwk.github.io/posts/dl-dl-ctr-models.html
- https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/86181485
CTR学习笔记&代码实现3-深度ctr模型 FNN->PNN->DeepFM的更多相关文章
- CTR学习笔记&代码实现5-深度ctr模型 DeepCrossing -> DCN
之前总结了PNN,NFM,AFM这类两两向量乘积的方式,这一节我们换新的思路来看特征交互.DeepCrossing是最早在CTR模型中使用ResNet的前辈,DCN在ResNet上进一步创新,为高阶特 ...
- CTR学习笔记&代码实现4-深度ctr模型 NFM/AFM
这一节我们总结FM另外两个远亲NFM,AFM.NFM和AFM都是针对Wide&Deep 中Deep部分的改造.上一章PNN用到了向量内积外积来提取特征交互信息,总共向量乘积就这几种,这不NFM ...
- CTR学习笔记&代码实现6-深度ctr模型 后浪 xDeepFM/FiBiNET
xDeepFM用改良的DCN替代了DeepFM的FM部分来学习组合特征信息,而FiBiNET则是应用SENET加入了特征权重比NFM,AFM更进了一步.在看两个model前建议对DeepFM, Dee ...
- CTR学习笔记&代码实现2-深度ctr模型 MLP->Wide&Deep
背景 这一篇我们从基础的深度ctr模型谈起.我很喜欢Wide&Deep的框架感觉之后很多改进都可以纳入这个框架中.Wide负责样本中出现的频繁项挖掘,Deep负责样本中未出现的特征泛化.而后续 ...
- CTR学习笔记&代码实现1-深度学习的前奏LR->FFM
CTR学习笔记系列的第一篇,总结在深度模型称王之前经典LR,FM, FFM模型,这些经典模型后续也作为组件用于各个深度模型.模型分别用自定义Keras Layer和estimator来实现,哈哈一个是 ...
- GIS案例学习笔记-明暗等高线提取地理模型构建
GIS案例学习笔记-明暗等高线提取地理模型构建 联系方式:谢老师,135-4855-4328,xiexiaokui#qq.com 目的:针对数字高程模型,通过地形分析,建立明暗等高线提取模型,生成具有 ...
- 【PyTorch深度学习】学习笔记之PyTorch与深度学习
第1章 PyTorch与深度学习 深度学习的应用 接近人类水平的图像分类 接近人类水平的语音识别 机器翻译 自动驾驶汽车 Siri.Google语音和Alexa在最近几年更加准确 日本农民的黄瓜智能分 ...
- [原创]java WEB学习笔记44:Filter 简介,模型,创建,工作原理,相关API,过滤器的部署及映射的方式,Demo
本博客为原创:综合 尚硅谷(http://www.atguigu.com)的系统教程(深表感谢)和 网络上的现有资源(博客,文档,图书等),资源的出处我会标明 本博客的目的:①总结自己的学习过程,相当 ...
- cips2016+学习笔记︱简述常见的语言表示模型(词嵌入、句表示、篇章表示)
在cips2016出来之前,笔者也总结过种类繁多,类似词向量的内容,自然语言处理︱简述四大类文本分析中的"词向量"(文本词特征提取)事实证明,笔者当时所写的基本跟CIPS2016一 ...
随机推荐
- Linux基本操作 ------ 文件处理命令
显示目录文件 ls //显示当前目录下文件 ls /home //显示home文件夹下文件 ls -a //显示当前目录下所有文件,包括隐藏文件 ls -l //显示当前目录下文件的详细信息 ls - ...
- Hive数据倾斜的原因及主要解决方法
数据倾斜产生的原因 数据倾斜的原因很大部分是join倾斜和聚合倾斜两大类 Hive倾斜之group by聚合倾斜 原因: 分组的维度过少,每个维度的值过多,导致处理某值的reduce耗时很久: 对一些 ...
- [vijos1725&bzoj2875]随机数生成器<矩阵乘法&快速幂&快速乘>
题目链接:https://vijos.org/p/1725 http://www.lydsy.com/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=2875 这题是前几年的noi的题,时间比较 ...
- RecyclerView 的 Item 的单击事件
RecyclerView 的每个Item的点击事件并没有像 ListView 一样封装在组件中,需要 Item 的单击事件时就需要自己去实现,在 Adapter 中为RecyclerView 添加单击 ...
- java web利用mvc结构实现简单聊天室功能
简单聊天室采用各种内部对象不适用数据库实现. 一个聊天室要实现的基本功能是: 1.用户登录进入聊天室, 2.用户发言 3.用户可以看见别人发言 刚才算是简单的需求分析了,现在就应该是进 ...
- java数据库 DBHelper
package com.dangdang.msg.dbutil; import com.dangdang.msg.configure.*; import com.mysql.jdbc.Connecti ...
- IOS部分APP使用burpsuite抓不到包原因
曾经在ios12的时候,iphone通过安装burpsuite的ca证书并开启授权,还可以抓到包,升级到ios13后部分app又回到以前连上代理就断网的情况. 分析:ios(13)+burpsuite ...
- PTA数据结构与算法题目集(中文) 7-10
PTA数据结构与算法题目集(中文) 7-10 7-10 公路村村通 (30 分) 现有村落间道路的统计数据表中,列出了有可能建设成标准公路的若干条道路的成本,求使每个村落都有公路连通所需要的最低 ...
- PXE基础装机环境
PXE基础装机环境 案例1:PXE基础装机环境 案例2:配置并验证DHC ...
- Thinkphp getLastSql函数用法
如何判断一个更新操作是否成功: $Model = D('Blog'); $data['id'] = 10; $data['name'] = 'update name'; $result = $Mode ...
