VLAN、Trunk,以太通道及DHCP
VLAN、Trunk,以太通道及DHCP
1 案例1:Vlan的划分
1.1 问题
VLAN(虚拟局域网)是对连接到的第二层交换机端口的网络用户的逻辑分段,不受网络用户的物理位置限制而根据用户需求进行网络分段。一个VLAN可以在一个交换机或者跨交换机实现。VLAN可以根据网络用户的位置、作用、部门或者根据网络用户所使用的应用程序和协议来进行分组。基于交换机的虚拟局域网能够为局域网解决冲突域、广播域、带宽问题。
- 按企业部门规划vlan
1.2 方案
在交换机上创建vlan2、vlan3,参照如下网络拓扑如图-1所示:

图-1
1.3 步骤
实现此案例需要按照如下步骤进行。
步骤一:客户端与交换机相连
1)为了使同vlan在交换机上可以通信,需要给同vlan客户端配置同网段IP地址,如图-2、图-3所示
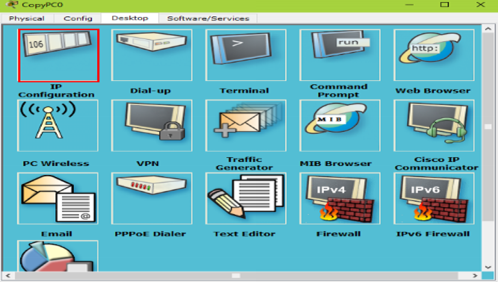
图-2
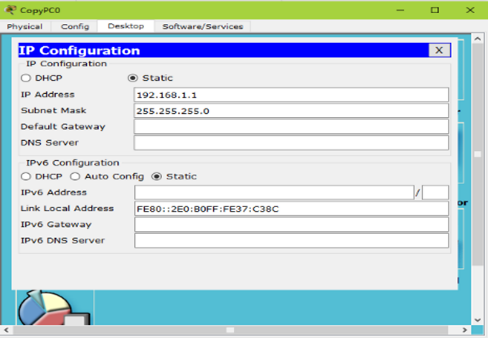
图-3
分别配置为192.168.1.1、192.169.1.2;192.168.2.1、192.168.2.2;192.168.3.1、192.168.3.2;
2)在交换机上创建vlan2 和vlan3并将指定的接口划分到相对应的vlan下
- Switch >enable
- Switch#configure terminal
- Switch(config)#vlan 2
- Switch(config-vlan)#exit
- Switch(config)#vlan 3
- Switch(config-vlan)#exit
- Switch(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/3
- Switch(config-if)#switchport access vlan 2
- Switch(config-if)#exit
- Switch(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/4
- Switch(config-if)#switchport access vlan 2
- Switch(config-if)#exit
- Switch(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/5
- Switch(config-if)#switchport access vlan 3
- Switch(config-if)#exit
- Switch(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/6
- Switch(config-if)#switchport access vlan 3
3)在交换机上查看vlan信息,可以看到创建的vlan以及vlan下的接口
- Switch>enable
- Switch#show vlan
- VLAN Name Status Ports
- ---- -------------------------------- --------- -------------------------------
- 1 default active Fa0/1, Fa0/2, Fa0/7, Fa0/8
- Fa0/9, Fa0/10, Fa0/11, Fa0/12
- Fa0/13, Fa0/14, Fa0/15, Fa0/16
- Fa0/17, Fa0/18, Fa0/19, Fa0/20
- Fa0/21, Fa0/22, Fa0/23, Fa0/24
- 2 VLAN0002 active Fa0/3, Fa0/4
- 3 VLAN0003 active Fa0/5, Fa0/6
- 1002 fddi-default act/unsup
- 1003 token-ring-default act/unsup
- 1004 fddinet-default act/unsup
- 1005 trnet-default act/unsup
- VLAN Type SAID MTU Parent RingNo BridgeNo Stp BrdgMode Trans1 Trans2
- ---- ----- ---------- ----- ------ ------ -------- ---- -------- ------ ------
- 1 enet 100001 1500 - - - - - 0 0
- 2 enet 100002 1500 - - - - - 0 0
- 3 enet 100003 1500 - - - - - 0 0
- 1002 fddi 101002 1500 - - - - - 0 0
- 1003 tr 101003 1500 - - - - - 0 0
- 1004 fdnet 101004 1500 - - - ieee - 0 0
- 1005 trnet 101005 1500 - - - ibm - 0 0
- Remote SPAN VLANs
- ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- Primary Secondary Type Ports
- ------- --------- ----------------- ------------------------------------------
4)在客户端测试网络的连通性
在192.168.1.0/24的客户机上测试1.0网段的连通性
- PC1>ping 192.168.1.2
- Pinging 192.168.1.2 with 32 bytes of data:
- Reply from 192.168.1.2: bytes=32 time=11ms TTL=128
- Reply from 192.168.1.2: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=128
- Reply from 192.168.1.2: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=128
- Reply from 192.168.1.2: bytes=32 time=4ms TTL=128
- Ping statistics for 192.168.1.2:
- Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
- Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
- Minimum = 1ms, Maximum = 11ms, Average = 4ms
5)在192.168.2.0/24的客户机上测试2.0网段的连通性
- PC>ping 192.168.2.2
- Pinging 192.168.2.2 with 32 bytes of data:
- Reply from 192.168.2.2: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=128
- Reply from 192.168.2.2: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=128
- Reply from 192.168.2.2: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=128
- Reply from 192.168.2.2: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=128
- Ping statistics for 192.168.2.2:
- Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
- Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
- Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 1ms, Average = 0ms
6)在192.168.3.0/24的客户机上测试3.0网段的连通性
- PC>ping 192.168.3.2
- Pinging 192.168.3.2 with 32 bytes of data:
- Reply from 192.168.3.2: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=128
- Reply from 192.168.3.2: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=128
- Reply from 192.168.3.2: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=128
- Reply from 192.168.3.2: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=128
- Ping statistics for 192.168.3.2:
- Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
- Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
- Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 1ms, Average = 0ms
2 案例2:配置trunk中继链路
2.1 问题
在两台交换机上分别创建vlan2、vlan3,参照如下网络拓扑图-4将端口加入到指定的vlan并配置IP址,实现跨交换机的同vlan主机的通信。

图-4
2.2 方案
分别在sw1和sw2上创建vlan2和vlan3并把相应的接口划分到对应的vlan并为客户端配置IP地址,IP地址具有唯一性所以同一局域网络中不能存在相同的IP,另所有的接口默认为vlan1,所以不配置trunk中继链路vlan1也是可以跨交换机通信的。
2.3 步骤
实现此案例需要按照如下步骤进行
步骤一:为客户端配置IP,分别为交换机sw1和sw2创建vlan并把相应的接口划到相对应的vlan下
1)参照图-4为客户端分别配置相对应网段的IP
2)为交换机创建vlan2、vlan3 并把相应的接口划到vlan下
- Switch >enable
- Switch#configure terminal
- Switch(config)#hostname SW1
- SW1 (config)#Switch(config-vlan)#exit
- SW1 (config)#vlan 3
- SW1 (config-vlan)#exit
- SW1 (config)#interface fastEthernet 0/3
- SW1 (config-if)#switchport access vlan 2
- SW1 (config-if)#exit
- SW1 (config)#interface fastEthernet 0/4
- SW1 (config-if)#switchport access vlan 2
- SW1 (config-if)#exit
- SW1 (config)#interface fastEthernet 0/5
- SW1 (config-if)#switchport access vlan 3
- SW1 (config-if)#exit
- SW1 (config)#interface fastEthernet 0/6
- SW1 (config-if)#switchport access vlan 3
- Switch >enable
- Switch#configure terminal
- Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
- Switch(config)#hostname SW2
- SW2 (config)#Switch(config-vlan)#exit
- SW2 (config)#vlan 3
- SW2 (config-vlan)#exit
- SW2 (config)#interface fastEthernet 0/3
- SW2(config-if)#switchport access vlan 2
- SW2 (config-if)#exit
- SW2 (config)#interface fastEthernet 0/4
- SW2 (config-if)#switchport access vlan 2
- SW2 (config-if)#exit
- SW2 (config)#interface fastEthernet 0/5
- SW2 (config-if)#switchport access vlan 3
- SW2 (config-if)#exit
- SW2 (config)#interface fastEthernet 0/6
- SW2 (config-if)#switchport access vlan 3
3)分别查看SW1和SW2交换机上的vlan信息
- SW1#show vlan
- VLAN Name Status Ports
- ---- -------------------------------- --------- -------------------------------
- 1 default active Fa0/1, Fa0/2, Fa0/8, Fa0/9
- Fa0/10, Fa0/11, Fa0/12, Fa0/13
- Fa0/14, Fa0/15, Fa0/16, Fa0/17
- Fa0/18, Fa0/19, Fa0/20, Fa0/21
- Fa0/22, Fa0/23, Fa0/24
- 2 VLAN0002 active Fa0/3, Fa0/4
- 3 VLAN0003 active Fa0/5, Fa0/6
- 1002 fddi-default act/unsup
- 1003 token-ring-default act/unsup
- 1004 fddinet-default act/unsup
- 1005 trnet-default act/unsup
- VLAN Type SAID MTU Parent RingNo BridgeNo Stp BrdgMode Trans1 Trans2
- ---- ----- ---------- ----- ------ ------ -------- ---- -------- ------ ------
- 1 enet 100001 1500 - - - - - 0 0
- 2 enet 100002 1500 - - - - - 0 0
- 3 enet 100003 1500 - - - - - 0 0
- 1002 fddi 101002 1500 - - - - - 0 0
- 1003 tr 101003 1500 - - - - - 0 0
- 1004 fdnet 101004 1500 - - - ieee - 0 0
- 1005 trnet 101005 1500 - - - ibm - 0 0
- Remote SPAN VLANs
- ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- Primary Secondary Type Ports
- ------- --------- ----------------- ------------------------------------------
- SW1#
- SW2#show vlan
- VLAN Name Status Ports
- ---- -------------------------------- --------- -------------------------------
- 1 default active Fa0/1, Fa0/2, Fa0/8, Fa0/9
- Fa0/10, Fa0/11, Fa0/12, Fa0/13
- Fa0/14, Fa0/15, Fa0/16, Fa0/17
- Fa0/18, Fa0/19, Fa0/20, Fa0/21
- Fa0/22, Fa0/23, Fa0/24
- 2 VLAN0002 active Fa0/3, Fa0/4
- 3 VLAN0003 active Fa0/5, Fa0/6
- 1002 fddi-default act/unsup
- 1003 token-ring-default act/unsup
- 1004 fddinet-default act/unsup
- 1005 trnet-default act/unsup
- VLAN Type SAID MTU Parent RingNo BridgeNo Stp BrdgMode Trans1 Trans2
- ---- ----- ---------- ----- ------ ------ -------- ---- -------- ------ ------
- 1 enet 100001 1500 - - - - - 0 0
- 2 enet 100002 1500 - - - - - 0 0
- 3 enet 100003 1500 - - - - - 0 0
- 1002 fddi 101002 1500 - - - - - 0 0
- 1003 tr 101003 1500 - - - - - 0 0
- 1004 fdnet 101004 1500 - - - ieee - 0 0
- 1005 trnet 101005 1500 - - - ibm - 0 0
- Remote SPAN VLANs
- ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- Primary Secondary Type Ports
- ------- --------- ----------------- ------------------------------------------
- SW2#
步骤二:为交换机配置trunk中继链接路
1)分别进入两台交换机相连接的f0/7接口配置trunk中继链路
- SW1>enable
- SW1#configure terminal
- SW1(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/7
- SW1(config-if)#switchport mode trunk
- SW2#enable
- SW2#configure terminal
- SW2(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/7
- SW2(config-if)#switchport mode trunk
- SW2(config-if)#
2)测试2.0网段和3.0网段跨交换机通信
- PC>ping 192.168.2.3
- Pinging 192.168.2.3 with 32 bytes of data:
- Reply from 192.168.2.3: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=128
- Reply from 192.168.2.3: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=128
- Reply from 192.168.2.3: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=128
- Reply from 192.168.2.3: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=128
- Ping statistics for 192.168.2.3:
- Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
- Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
- Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 1ms, Average = 0ms
- PC>ping 192.168.3.3
- Pinging 192.168.3.3 with 32 bytes of data:
- Reply from 192.168.3.3: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=128
- Reply from 192.168.3.3: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=128
- Reply from 192.168.3.3: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=128
- Reply from 192.168.3.3: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=128
- Ping statistics for 192.168.3.3:
- Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
- Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
- Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 1ms, Average = 0ms
3 案例3:以太通道配置
3.1 问题
企业需要增加带宽和网络可用性,以太通道可以同时满足这两个条件,而又无需购买新设备。
3.2 方案
在某些环境下,为了在现有条件下增加带宽而不增加额外的设备,以太通道是可用技术之一。以太通道为交换机提供了端口捆绑的技术,允许两个交换机之间通过两个或多个端口并行连接,同时传输数据,以提供更高的带宽。
企业网络模拟拓扑环境如图-5所示:

图-5
3.3 步骤
实现此案例需要按照如下步骤进行。
步骤一:在交换机A上分别配置以太通道
太通道的配置模式与Trunk类似,也有开启、企望等。同样的,在生产环境下都是强制设置以太通道处于on的状态,而不是让它们自动协商。
- sw1(config)# interface range fastEthernet 0/7 – 9
- Switch(config-if-range)#switchport mode trunk
- sw1(config-if-range)#channel-group 1 mode on
- sw1(config-if-range)#
步骤二:在交换机B上分别配置以太通道
- sw2(config)# interface range fastEthernet 0/7 – 9
- Switch(config-if-range)#switchport mode trunk
- sw2(config-if-range)#channel-group 1 mode on
- sw2(config-if-range)#
步骤三:在交换机A上查看以太通通道配置
- sw1# show etherchannel 1 summary
- Flags: D - down P - in port-channel
- I - stand-alone s - suspended
- H - Hot-standby (LACP only)
- R - Layer3 S - Layer2
- U - in use f - failed to allocate aggregator
- u - unsuitable for bundling
- w - waiting to be aggregated
- d - default port
- Number of channel-groups in use: 1
- Number of aggregators: 1
- Group Port-channel Protocol Ports
- ------+-------------+-----------+---------------------------------
- 1 Po1(SU) - Fa0/7(P) Fa0/8(P) Fa0/9(P)
根据输出最后一行小括号中的提示,可以获知以太通道是二层的(S)、正在被使用的(U),端口Fa0/7、Fa0/8和Fa09在以太通道中(P)。
步骤四:创建以太通道后,系统会增加一个名称为Port-channel 1的端口,可以通过show running-config命令查看到其信息
- sw2#show running-config
- Building configuration...
- Current configuration : 1308 bytes
- !
- version 12.2
- no service timestamps log datetime msec
- no service timestamps debug datetime msec
- no service password-encryption
- !
- hostname tarena-sw2
- !
- !
- .. ..
- interface Port-channel 1 //以太通道信息
- switchport mode trunk
- !
- .. ..
4 案例4:DHCP服务配置
4.1 问题
大型企业网络客户机数量较多,客记机IP地址配置如果都为静态配置存在如下问题:
- 增加网络管理员工作量
- 静态手动配置容易输入错误
- 静态手动配置容易冲突
4.2 方案
在路由器上配置DHCP服务为客户端自动分配IP地址如图-6所示:
图-6
- VLAN 1:192.168.1.0/24
- 网关192.168.1.254
- 首选DNS为202.106.0.20
- 预留IP地址打印服务器:192.168.1.1
- 预留IP地址文件服务器:192.168.1.100
4.3 步骤
实现此案例需要按照如下步骤进行。
步骤一:路由器R1配置DHCP服务
1)配置路由器接口IP
- R1(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/0
- R1(config-if)#ip address 192.168.1.254 255.255.255.0
- R1(config-if)#no shutdown
2)DHCP服务配置
- R1(config)#ip dhcp pool vlan11)
- R1(dhcp-config)#network 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0
- R1(dhcp-config)#default-router 192.168.1.254
- R1(dhcp-config)#dns-server 202.106.0.20
- R1(config)#ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.1.1
- R1(config)#ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.1.100
3)设置主机A的IP配置为自动获取如图-7所示:
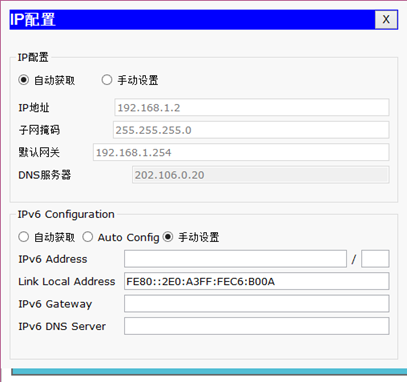
图-7
VLAN、Trunk,以太通道及DHCP的更多相关文章
- Cisco基础(一):Vlan的划分、配置trunk中继链路、以太通道配置、DHCP服务配置
一.Vlan的划分 目标: VLAN(虚拟局域网)是对连接到的第二层交换机端口的网络用户的逻辑分段,不受网络用户的物理位置限制而根据用户需求进行网络分段.一个VLAN可以在 一个交换机或者跨交换机实现 ...
- 2.1-VLAN/TRUNK/VTP
2.1-VLAN/TRUNK/VTP 注意:配置VLAN时要退出VLAN配置模式才会执行 如果VLAN被删除或者shutdown,那么属于这个vlan的接口将被阻塞(灯一直是橙色,变不了绿色) ...
- 配置网卡为vlan trunk
http://www.microhowto.info/tutorials/802.1q.html Configure an Ethernet interface as a VLAN trunk hos ...
- vlan trunk配置
vlan trunk配置 Trunk:中继干道 作用:一条链路能承载多个vlan的流量,并对不同vlan的流量进行不同标记 trunk能够使vlan跨越交换机 PT配置 配置vlan:两台交换机同样的 ...
- CCNA 之 八 交换基础 VLAN TRUNK VTP
交换基础 主要知识点: 二层交换基础 Vlan的概念 Trunk的概念 VTP 二层交换基本配置 首先来看下园区网分层结构 交换机的主要功能: Address learning 学习MAC地址 会维护 ...
- 虚拟机 vlan trunk 特性
1. 功能 1)允许不同vlan的network下的虚拟机之间通信.一般情况下,虚拟机只能在相同vlan的网络下通信. 2)允许虚拟机发送vlan报文. 2. 组网图 虚拟机出来的tap设备连接到tb ...
- vtp——vlan trunk protcal
server模式——服务器模式,在该模式下可以建立vlan,删除vlan,该模式下的vlan可以下发到其他的交换机 client模式——客户端模式,被动模式.交换机可以接受从server模式下传来的v ...
- 实验13:VLAN/TRUNK/VTP/
实验10-1: 划分VLAN Ø 实验目的通过本实验,读者可以掌握如下技能:(1) 熟悉VLAN 的创建(2) 把交换机接口划分到特定VLAN Ø 实验拓扑 实验步骤要配置VLAN,首先要 ...
- vlan trunk vtp端口聚合
第一步:端口聚合(两端都需要做相同的操作) 第二步:在服务器端配置为服务器模式 第四步:在服务器端添加vlan 第五步:在两端分别将不同的端口添加到不同的vlan
随机推荐
- Java集合04——fail-fast&fail-safe 详解
在前几个回合中,我们已经详细了解过了 Java 集合中的List.Set 和 Map,对这部分内容感兴趣的朋友可以关注我的公众号「Java面典」了解.今天我们将为各位介绍集合的失败机制--fail-f ...
- 数据结构 - Collection接口
简介 Collection继承自Iterable,Collection接口是Java集合两大分支中的一支,Queue.List.Set都是Collection的扩展:集合大类分为了Collection ...
- RabbitMQ消息发布和消费的确认机制
前言 新公司项目使用的消息队列是RabbitMQ,之前其实没有在实际项目上用过RabbitMQ,所以对它的了解都谈不上入门.趁着周末休息的时间也猛补习了一波,写了两个窗体应用,一个消息发布端和消息消费 ...
- vue-element框架通过blob进行后端token权限验证下载
在项目中,后端要求下载时要进行后端的权限验证,发现a链接进行直接下载无法满足这个需求,只能通过blob对象来进行下载操作,翻阅大量资料最后实现该功能.以下是我个人的理解,如有不足,请各位大佬多指教 / ...
- Swift 4.0 高级-自定义操作符
在Swift语言中,常见的操作符有+.-.*./.>.<.==.&&.||等等,如果不喜欢,你也可以定义自己喜欢的操作符. 操作符类型 中置运算符(infix operat ...
- 软件版本管理工具-SVN
一.SVN简介 Subversion(svn)是一款开发源代码的版本控制系统. repository(源代码库):源代码统一存放的地方 Checkout(检出):当你手上没有源代码的时候,你需要从re ...
- POJ1780 欧拉路+手写栈解决爆战问题
题目链接:http://poj.org/problem?id=1780 本题中给出一个位数n,要求给出一个10^n+n-1位数的数,要求每个n位的数都要在里面出现,一个n位的数一共有10^n种,我们容 ...
- jvm:内存结构(堆、方法区、程序计数器、本地方法栈、虚拟机栈)
1.jvm内存结构 静态编译:把java源文件编译成字节码文件class,这个时候class文件以静态方式存在. 类加载器:把java字节码文件加载到内存中 方法区:将字节码放到方法区作为元数据(简单 ...
- Java进阶之心态
不管什么时候学习都是一个积累的过程,量变才能引起质变.一口吃一个胖子是不存在的,成长的路上没有捷径,只有学到的知识才是我们走向远方道路的基石!
- Linux基础篇学习——文件目录常用管理命令mkdir,cat,more,less,ln,file,cp,find,split,mv
mkdir 创建目录 -p 递归创建目录 -v 显示创建信息 [root@zycentos7 ~]# mkdir -p {mylinux/{bin,conf,lib,logs,webapps/{doc ...
