Hdu 5444 Elven Postman dfs
Elven Postman
Time Limit: 1 Sec
Memory Limit: 256 MB
题目连接
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5444
Description
Elves are very peculiar creatures. As we all know, they can live for a very long time and their magical prowess are not something to be taken lightly. Also, they live on trees. However, there is something about them you may not know. Although delivering stuffs through magical teleportation is extremely convenient (much like emails). They still sometimes prefer other more “traditional” methods.
So, as a elven postman, it is crucial to understand how to deliver the mail to the correct room of the tree. The elven tree always branches into no more than two paths upon intersection, either in the east direction or the west. It coincidentally looks awfully like a binary tree we human computer scientist know. Not only that, when numbering the rooms, they always number the room number from the east-most position to the west. For rooms in the east are usually more preferable and more expensive due to they having the privilege to see the sunrise, which matters a lot in elven culture.
Anyways, the elves usually wrote down all the rooms in a sequence at the root of the tree so that the postman may know how to deliver the mail. The sequence is written as follows, it will go straight to visit the east-most room and write down every room it encountered along the way. After the first room is reached, it will then go to the next unvisited east-most room, writing down every unvisited room on the way as well until all rooms are visited.
Your task is to determine how to reach a certain room given the sequence written on the root.
For instance, the sequence 2, 1, 4, 3 would be written on the root of the following tree.
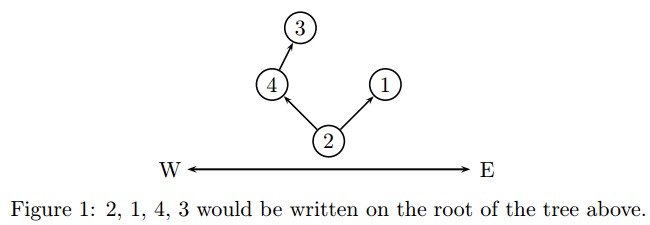
Input
First you are given an integer T(T≤10) indicating the number of test cases.
For each test case, there is a number n(n≤1000) on a line representing the number of rooms in this tree. n integers representing the sequence written at the root follow, respectively a1,...,an where a1,...,an∈{1,...,n}.
On the next line, there is a number q representing the number of mails to be sent. After that, there will be q integers x1,...,xq indicating the destination room number of each mail.
Output
For each query, output a sequence of move (E or W) the postman needs to make to deliver the mail. For that E means that the postman should move up the eastern branch and W the western one. If the destination is on the root, just output a blank line would suffice.
Note that for simplicity, we assume the postman always starts from the root regardless of the room he had just visited.
Sample Input
2
4
2 1 4 3
3
1 2 3
6
6 5 4 3 2 1
1
1
Sample Output
E
WE
EEEEE
HINT
题意
建树;编号是这棵树从右往左进行编号的,越往右边的编号越小
给你一个数组,然后问你走到一些点,究竟该怎么走
题解:
注意,树的形态是唯一的
我们可以处理每个节点能够放的点的大小的范围,然后就可以求出这棵树的样子了
回答就可以顺便再DFS建树的过程中处理出来
赛后听人说,这是先序遍历/中序遍历?
非计算机专业完全不懂= =
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <vector>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <queue>
#include <iomanip>
#include <string>
#include <ctime>
#include <list>
#include <bitset>
typedef unsigned char byte;
#define pb push_back
#define input_fast std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);std::cin.tie(0)
#define local freopen("in.txt","r",stdin)
#define pi acos(-1) using namespace std;
struct node
{
int L , R ;
string str;
}; const int maxn = 1e3 + ;
int n , p[maxn] , q , ctt = ;
vector<int>qq;
node c[maxn]; bool dfs(int u)
{
/* cout << "u is " << u << endl;
cout << "ctt is " << ctt << endl;
getch();*/
if(ctt == n + ) return true;
while()
{
if(c[u].L <= p[ctt] && p[ctt] <= c[u].R)
{
int x = p[ctt];
int y = u;
if(x < y)
{
c[x].str = c[u].str + 'E';
c[x].R = y;
c[x].L = c[u].L;
}
else
{
c[x].str = c[u].str + 'W';
c[x].L = y;
c[x].R = c[u].R;
}
ctt++;
if(ctt == n + ) return true;
if(dfs(x)) return true;
}
else
return false;
if(ctt == n + ) return true;
}
} void initiation()
{
qq.clear();
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i = ; i <= n ; ++ i) scanf("%d",p + i);
scanf("%d",&q);
for(int i = ; i <= q; ++ i)
{
int x;
scanf("%d",&x);
qq.push_back(x);
}
for(int i = ; i <= n ; ++ i)
{
c[i].str = "";
c[i].L = - , c[i].R = ;
}
ctt = ;
dfs(p[]);
} void solve()
{
for(int i = ; i < q ;++ i) cout << c[qq[i]].str << endl;
} int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
//freopen("out.txt","w",stdout);
int Case;
scanf("%d",&Case);
while(Case--)
{
initiation();
solve();
}
return ;
}
Hdu 5444 Elven Postman dfs的更多相关文章
- hdu 5444 Elven Postman
题目连接 http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5444 Elven Postman Description Elves are very peculia ...
- hdu 5444 Elven Postman(长春网路赛——平衡二叉树遍历)
题目链接:pid=5444http://">http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5444 Elven Postman Time Limi ...
- 2015 ACM/ICPC Asia Regional Changchun Online HDU 5444 Elven Postman【二叉排序树的建树和遍历查找】
Elven Postman Time Limit: 1500/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 131072/131072 K (Java/Others)T ...
- hdu 5444 Elven Postman 二叉树
Time Limit: 1500/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 131072/131072 K (Java/Others) Problem Descrip ...
- hdu 5444 Elven Postman(二叉树)——2015 ACM/ICPC Asia Regional Changchun Online
Problem Description Elves are very peculiar creatures. As we all know, they can live for a very long ...
- HDU 5444 Elven Postman (2015 ACM/ICPC Asia Regional Changchun Online)
Elven Postman Elves are very peculiar creatures. As we all know, they can live for a very long time ...
- HDU 5444 Elven Postman 二叉排序树
HDU 5444 题意:给你一棵树的先序遍历,中序遍历默认是1...n,然后q个查询,问根节点到该点的路径(题意挺难懂,还是我太傻逼) 思路:这他妈又是个大水题,可是我还是太傻逼.1000个点的树,居 ...
- hdu 5444 Elven Postman(根据先序遍历和中序遍历求后序遍历)2015 ACM/ICPC Asia Regional Changchun Online
很坑的一道题,读了半天才读懂题,手忙脚乱的写完(套上模板+修改模板),然后RE到死…… 题意: 题面上告诉了我们这是一棵二叉树,然后告诉了我们它的先序遍历,然后,没了……没了! 反复读题,终于在偶然间 ...
- HDU 5444 Elven Postman (二叉树,暴力搜索)
题意:给出一颗二叉树的先序遍历,默认的中序遍历是1..2.……n.给出q个询问,询问从根节点出发到某个点的路径. 析:本来以为是要建树的,一想,原来不用,其实它给的数是按顺序给的,只要搜结点就行,从根 ...
随机推荐
- 三个入侵的必备小工具-lcx.exe、nc.exe、sc.exe
lcx.exe的使用方法 以前抓肉鸡都是通过1433弱口令,然后.. 但是发现很多服务器开了1433,3389,但是终端是连不上的,因为服务器本身是在内网,只对外开放了1433端口,幸好有lcx. ...
- 在SQLite中使用索引优化查询速度
在进行多个表联合查询的时候,使用索引可以显著的提高速度,刚才用SQLite做了一下测试. 建立三个表: create table t1 (id integer primary key,num inte ...
- SQL列数据转换为字符串
行列转换,将列数据转换为字符串输出 ) SET @center_JZHW = ( SELECT DISTINCT STUFF( ( SELECT ',' + ce_code FROM ap_cente ...
- struts2关于package 的 namespace
namespace决定了action的访问路径,默认为"",可以接收所有路径的actionnamespace可以写为/ ,或者/xxx,或者/xxx/yyy,对应的action访问 ...
- linq .dbml转化成sql脚本
public String ConvertDBMLToSqlScript(System.Data.Linq.DataContext DBContext) { String DBCon ...
- ASP.NET的六种验证控件的使用
C# 中的验证控件分为一下六种 :1 CompareValidator:比较验证,两个字段的值是否相等,比如判断用户输入的密码和确认密码是否一致,则可以用改控件: 2 CustomValidator ...
- UVa 1572 (拓扑排序) Self-Assembly
题意: 有n种正放形,每种正方形的数量可视为无限多.已知边与边之间的结合规则,而且正方形可以任意旋转和反转,问这n中正方形是否可以拼成无限大的图案. 分析: 首先因为可以旋转和反转,所以可以保证在拼接 ...
- BZOJ3232: 圈地游戏
题解: 神题一道... 题解戳这里:http://hi.baidu.com/strongoier/item/0425f0e5814e010265db0095 分数规划可以看这里:http://blog ...
- apache开源项目--TIKA
Tika是一个内容抽取的工具集合(a toolkit for text extracting).它集成了POI, Pdfbox 并且为文本抽取工作提供了一个统一的界面.其次,Tika也提供了便利的扩展 ...
- innodb force recovery
innodb force recovery的6种设置: 1.innodb force recovery=1,即使发现了损坏页面也继续让服务器继续运行,这个选项对于备份或者转存当前数据尤为有用2.inn ...
