P03-Python装饰器
本文总结自oldboy python教学视频。
一、前言
1.装饰器本质上就是函数,功能是装饰其他函数,为其他函数添加附加功能。
装饰器在装饰函数时必须遵循3个重要的原则:
(1)不能修改被装饰的函数的源代码
(2)不能修改被装饰的函数的调用方式
(3)不能修改表装饰函数的返回结果
2.实现装饰器的知识储备:
(1)函数即“变量”
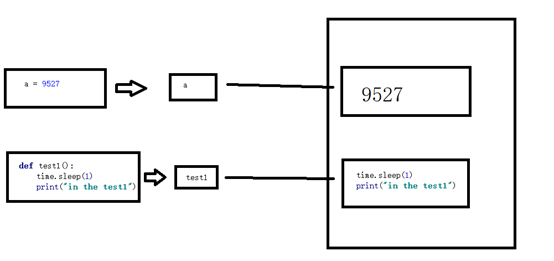
关于函数即变量,我的理解如下所示,即当定义一个函数时,相当于在内存中划一块内存空间,里面存放函数的函数体,而函数名指向这块空间——这跟普通的函数定义如 a = 9527 是一样的。如此一来,函数名便可以跟普通变量一样,作为参数传给其他函数,也能在函数中作为结果被返回。
(2)高阶函数
a.把一个函数名当做实参传给另一个函数(在不修改被装饰函数源代码的情况下为其添加功能)
或:
b.返回值中包含函数名(不修改函数的调用方式)
(3)嵌套函数
所谓嵌套函数,即在一个函数内定义另外一个函数(注意是定义,而不是调用)。
3.高阶函数 + 嵌套函数 => 装饰器
二、装饰器应用
1.被装饰函数没有参数
假设被装饰的函数为test1(),此时的test1()没有形参,默认返回NULL;装饰器timmer完成的附加功能是计时。
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
#Author:Suxy import time def timmer(func):
def wrapper():
start_time = time.time()
func()
stop_time = time.time()
print("the func run time is %s" %(stop_time - start_time))
return wrapper @timmer #test1 = timmer(test1),即test1 = wrapper
def test1():
time.sleep(1)
print("in the test1") test1()
输出:
C:\app\Anaconda3\python.exe E:/python_workspace/pure_python/day4/decorator.py
in the test1
the func run time is 1.0003414154052734
Process finished with exit code 0
注:在函数test1()的上面加上@timmer,作用相当于test1 = timmer(test1),又因为timmer函数中返回wrapper,所以有test1 = timmer(test1) = wrapper,因此最后一行代码在使用test()方式调用函数的时候,实际调用的是wrapper(),而wrapper中的变量func接收了timemr(test1)传进来的test1,所以实际调用时,先执行wrapper中附加的功能(计时),之后执行test1()本身的功能。
2.被装饰函数带有参数
装饰器不仅要能装饰无参函数,还得能装饰带参函数。这里以只带一个参数的函数test2(name)为例。此时若是不修改上面装饰器的任何代码便用来装饰test2(name),则会报错,具体如下:
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
#Author:Suxy import time def timmer(func):
def wrapper():
start_time = time.time()
func()
stop_time = time.time()
print("the func run time is %s" %(stop_time - start_time))
return wrapper @timmer #test1 = timmer(test1),即test1 = wrapper
def test1():
time.sleep(1)
print("in the test1") @timmer
def test2(name):
time.sleep(1)
print("in the test2, ", name) test1()
test2("suxy")
输出:
C:\app\Anaconda3\python.exe E:/python_workspace/pure_python/day4/decorator.py
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "E:/python_workspace/pure_python/day4/decorator.py", line 25, in <module>
test2("suxy")
TypeError: wrapper() takes 0 positional arguments but 1 was given
in the test1
the func run time is 1.000788688659668 Process finished with exit code 1
可见,此时装饰器timmer用于装饰test1()时没有问题,但是装饰test2()时报错了:wrapper()函数接受0个位置参数,但是在调用时却传了1个。
由第1步可知,在使用装饰器timmer装饰函数test2之后,调用test2(“suxy”)就相当于调用wrapper(“suxy”)函数,而当前的wrapper()函数是不接收参数的。
若需要timme装饰器能够同时装饰test1和test2函数,则需要对timmer装饰器进行修改——不过也不能简单地将timmer()中wrapper()函数的定义修改为wrapper(name),因为这样一来timmer装饰test1就会出错,此外,timmer装饰器有可能还要装饰其他的比如带有默认参数、关键字参数等的函数,因此,wrapper函数的定义应修改为wrapper(*args, **kwargs),并且wrapper中func的调用方式也得进行相应的修改func(*args, **kwargs),这样一来,无论被装饰的函数是无参函数、默认参数、关键字参数还是如*args列表参数、**kwargs字典参数,装饰器都能进行装饰。如下:
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
#Author:Suxy import time def timmer(func):
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
start_time = time.time()
func(*args, **kwargs)
stop_time = time.time()
print("the func run time is %s" %(stop_time - start_time))
return wrapper @timmer #test1 = timmer(test1),即test1 = wrapper
def test1():
time.sleep(1)
print("in the test1") @timmer
def test2(name):
time.sleep(1)
print("\nin the test2, ", name) test1()
test2("suxy")
输出:
C:\app\Anaconda3\python.exe E:/python_workspace/pure_python/day4/decorator.py
in the test1
the func run time is 1.000464916229248 in the test2, suxy
the func run time is 1.0004689693450928 Process finished with exit code 0
3.上面第2步所说的装饰器已经能够装饰一般的带参函数了,不过,若是被装饰函数具有返回值,则上面的装饰器就有问题了。如下(为缩减篇幅,暂将函数test1省略掉):
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
#Author:Suxy import time def timmer(func):
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
start_time = time.time()
func(*args, **kwargs)
stop_time = time.time()
print("the func run time is %s" %(stop_time - start_time))
return wrapper @timmer
def test2(name):
time.sleep(1)
print("\nin the test2, ", name)
return 9527 print(test2("suxy"))
输出:
C:\app\Anaconda3\python.exe E:/python_workspace/pure_python/day4/decorator.py in the test2, suxy
the func run time is 1.0003151893615723
None Process finished with exit code 0
可见,函数test2()中明明返回了9527,但是最后输出确是None,违反了装饰器不能修改被装饰函数的返回结果的原则。这是因为装饰器的wrapper中调用func(*args, **kwargs)函数(注: func(*args, **kwargs) = test2(*args, **kwargs))时,只是进行直接的调用,而没有将调用的结果返回。可以将装饰器代码修改为 return func(*args, **kwargs),或者先用res = func(*args, **kwargs)将函数执行结果保存到res中,最后再返回res。如下:
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
#Author:Suxy import time def timmer(func):
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
start_time = time.time()
res = func(*args, **kwargs)
stop_time = time.time()
print("the func run time is %s" %(stop_time - start_time))
return res
return wrapper @timmer
def test2(name):
time.sleep(1)
print("\nin the test2, ", name)
return 9527 print(test2("suxy"))
输出:
C:\app\Anaconda3\python.exe E:/python_workspace/pure_python/day4/decorator.py in the test2, suxy
the func run time is 1.0006110668182373 Process finished with exit code 0
4.到上一步,装饰器已经可以装饰绝大部分的函数了。但是目前的装饰器只能简单的接受一个参数,即被装饰函数的函数名,无法接受其他的参数。若是有其他复杂的需求,比如接受func_type字段,根据func_type的不同而做不同的输出,则目前的装饰器无法完成这个功能。
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
#Author:Suxy import time def before_timmer(func_type):
if func_type == "type1":
print("It is type 1")
elif func_type == "type2":
print("It is type 2")
else:
print("Another type") def timmer(func):
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
start_time = time.time()
res = func(*args, **kwargs)
stop_time = time.time()
print("the func run time is %s" % (stop_time - start_time))
return res
return wrapper
return timmer @before_timmer(func_type = "type2")
def test2(name):
time.sleep(1)
print("\nin the test2, ", name)
return 9527 test2("suxy")
输出:
C:\app\Anaconda3\python.exe E:/python_workspace/pure_python/day4/decorator.py
It is type 2 in the test2, suxy
the func run time is 1.0008769035339355 Process finished with exit code 0
仔细对比这里和3中装饰器代码的区别可以发现,这一步相当于又新建了一个装饰器before_timmer将原先的装饰器timmer包了起来,并将timmer函数作为结果返回,使得可以在before_timmer装饰器中先完成判断功能,再调用timmer计时功能。
此时对于test1()函数定义上的@before_timmer(func_type = "type1"),我的理解是:test2 = before_timmer(func_type = “type2”),又因为before_timmer中有return timmer,所以test2 = before_timmer(func_type = “type2”) = timmer(test2),同时由于timmer中有return wrapper,所以 test2 = before_timmer(func_type = “type2”) = timmer(test2) = wrapper,因此,当调用test2(“suxy”)时,还是最后还是相当于调用了wrapper(“suxy”)。
P03-Python装饰器的更多相关文章
- 关于python装饰器
关于python装饰器,不是系统的介绍,只是说一下某些问题 1 首先了解变量作用于非常重要 2 其次要了解闭包 def logger(func): def inner(*args, **kwargs) ...
- python装饰器通俗易懂的解释!
1.python装饰器 刚刚接触python的装饰器,简直懵逼了,直接不懂什么意思啊有木有,自己都忘了走了多少遍Debug,查了多少遍资料,猜有点点开始明白了.总结了一下解释得比较好的,通俗易懂的来说 ...
- Python 装饰器学习
Python装饰器学习(九步入门) 这是在Python学习小组上介绍的内容,现学现卖.多练习是好的学习方式. 第一步:最简单的函数,准备附加额外功能 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 # -*- c ...
- python 装饰器修改调整函数参数
简单记录一下利用python装饰器来调整函数的方法.现在有个需求:参数line范围为1-16,要求把9-16的范围转化为1-8,即9对应1,10对应2,...,16对应8. 下面是例子: def fo ...
- python 装饰器学习(decorator)
最近看到有个装饰器的例子,没看懂, #!/usr/bin/python class decorator(object): def __init__(self,f): print "initi ...
- Python装饰器详解
python中的装饰器是一个用得非常多的东西,我们可以把一些特定的方法.通用的方法写成一个个装饰器,这就为调用这些方法提供一个非常大的便利,如此提高我们代码的可读性以及简洁性,以及可扩展性. 在学习p ...
- 关于python装饰器(Decorators)最底层理解的一句话
一个decorator只是一个带有一个函数作为参数并返回一个替换函数的闭包. http://www.xxx.com/html/2016/pythonhexinbiancheng_0718/1044.h ...
- Python装饰器由浅入深
装饰器的功能在很多语言中都有,名字也不尽相同,其实它体现的是一种设计模式,强调的是开放封闭原则,更多的用于后期功能升级而不是编写新的代码.装饰器不光能装饰函数,也能装饰其他的对象,比如类,但通常,我们 ...
- Python装饰器与面向切面编程
今天来讨论一下装饰器.装饰器是一个很著名的设计模式,经常被用于有切面需求的场景,较为经典的有插入日志.性能测试.事务处理等.装饰器是解决这类问题的绝佳设计,有了装饰器,我们就可以抽离出大量函数中与函数 ...
- python装饰器方法
前几天向几位新同事介绍项目,被问起了@login_required的实现,我说这是django框架提供的装饰器方法,验证用户是否登录,只要这样用就行了,因为自己不熟,并没有做过多解释. 今天查看dja ...
随机推荐
- java高级工程师(二)
一.Java底层基础题 1.SpringMVC的原理以及返回数据如何渲染到jsp/html上? 答:Spring MVC的核心就是 DispatcherServlet , 一个请求经过 Dispatc ...
- Rotate image and fit show use canvas
Description In the field of image processing, We always to show image after modified the image raw d ...
- 将Oracle数据库设置为归档模式及非归档模式
一.将Oracle数据库设置为归档模式 1)sql>shutdown normal/immediate;2)sql>startup mount;3)sql>alter databas ...
- AES CFB/OFB/ECB/CBC/CTR优缺点
AES CFB/OFB/ECB/CBC/CTR优缺点 摘自:http://www.metsky.com/archives/418.html 发表时间:2010年05月11 分类: 网络日志 作者: 天 ...
- CentOS 7如何开放其它的端口,比如8080
CentOS 7如何开放其它的端口,比如8080 CentOS 7.0默认使用的是firewall作为防火墙,这里改为iptables防火墙. 1.关闭firewall: systemctl stop ...
- 用word2016 写CSDN 博客
目前大部分的博客作者在用Word写博客这件事情上都会遇到以下3个痛点: 1.所有博客平台关闭了文档发布接口,用户无法使用Word,Windows Live Writer等工具来发布博客.使用Word写 ...
- linux每天一小步---tail命令详解
1 命令功能 tail命令用于显示文件中末尾的内容(默认显示最后10行内容) 2 命令语法 tail [选项参数] [文件名1] [文件名2] 3 命令参数 -f 用于循环读取文件的内容,监视文件的 ...
- VS2017中对C++的单元测试
安装Visual Studio 2017 由于平时都是用codeblock,因此电脑中没有装VS系列的IDE,就从安装开始吧 最开始安装的时候没有注意什么都没选,安装完了以后根本没有c++的编译器和各 ...
- javaWeb项目中到底什么是单例,多例
你用杯子喝可乐,喝完了不刷,继续去倒果汁喝,就是单例.你用杯子喝可乐,直接扔了杯子,换个杯子去倒果汁喝,就是多例. 数据库连接池就是单例模式,有且仅有一个连接池管理者,管理多个连接池对象. 1. 什么 ...
- [C#]如何解决修改注册表受限问题(转)
在项目中添加一个Application Manifest File,名字默认为app.manifest,内容中应该有一行: <requestedExecutionLevellevel=" ...
