Flask系列之源码分析(二)
应用技术点
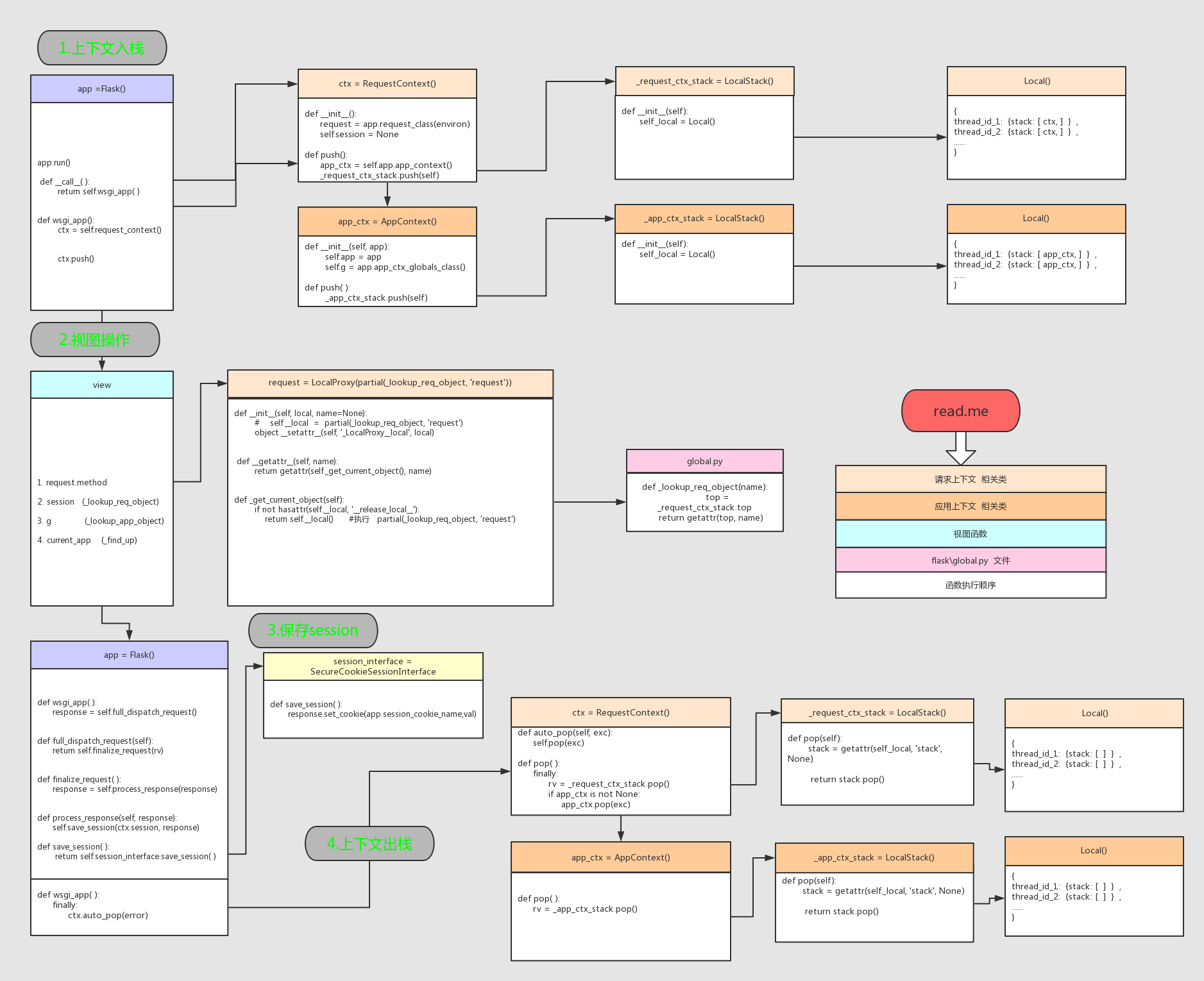
flask源码上下文管理
1、综述过程
将请求对象压入栈
1.请求进入
__call__ ---> wsgi_app ---> ctx = self.request_context(environ)
初始化请求对象
2.通过ctx.puth()建立2个请求堆栈(采用threading.local)
--app_ctx(app,g)
--ctx(request,session)
3._implicit_app_ctx_stack初始化
4._request_ctx_stack初始化
从栈中将请求对象调取出来
1.经过层层建立到达视图函数
--request
--session
--current_app
--g
2.以上四个对象通过localProxy(采用threading.local),调用
--_lookup_app_object
--_find_app
--_lookup_app
3.以上三个方法调用
_lookup_req_object ----> _implicit_app_ctx_stack
_find_app和_lookup_app ----> _request_ctx_stack
2、将请求对象压入栈
1.请求进入
__call__ ---> wsgi_app ---> ctx = self.request_context(environ)
初始化请求对象
wsgi_app源码
# Flask 类
def wsgi_app(self, environ, start_response): ctx = self.request_context(environ)
ctx.push() error = None
try:
try:
# 4 执行视图函数
response = self.full_dispatch_request()
except Exception as e:
# 异常处理试图报错,包含信号2345报错执行,got_request_exception信号
error = e
response = self.handle_exception(e)
except:
error = sys.exc_info()[1]
raise
# 将处理的内容,返回给用户浏览器
return response(environ, start_response)
finally:
if self.should_ignore_error(error):
error = None # 9、结束
ctx.auto_pop(error)
self.request_context(environ)
# Flask类
def request_context(self, environ):
return RequestContext(self, environ)
RequestContext(self, environ)
# RequestContest类
def __init__(self, app, environ, request=None):
self.app = app
# 初始化request请求对象
if request is None:
request = app.request_class(environ) self.request = request self.url_adapter = app.create_url_adapter(self.request)
self.flashes = None self.session = None
2.通过ctx.puth()建立2个请求堆栈(采用threading.local)
# RequestContext类
def push(self):
top = _request_ctx_stack.top
if top is not None and top.preserved:
top.pop(top._preserved_exc) # Before we push the request context we have to ensure that there
# is an application context.
app_ctx = _app_ctx_stack.top
if app_ctx is None or app_ctx.app != self.app:
# app_ctx = AppContext(self.app) --> _implictit_app_ctx_stack(app,g)
app_ctx = self.app.app_context()
app_ctx.push()
self._implicit_app_ctx_stack.append(app_ctx)
else:
self._implicit_app_ctx_stack.append(None) if hasattr(sys, 'exc_clear'):
sys.exc_clear() '''
请求相关数据,加到local中
'''
_request_ctx_stack.push(self) # Open the session at the moment that the request context is
# available. This allows a custom open_session method to use the
# request context (e.g. code that access database information
# stored on `g` instead of the appcontext). self.session = self.app.open_session(self.request)
if self.session is None:
self.session = self.app.make_null_session()
3._implicit_app_ctx_stack 调用
--app_ctx(app,g) --> self._implicit_app_ctx_stack.append(app_ctx)堆栈
top = _request_ctx_stack.top
_request_ctx_stack = LocalStack()
class LocalStack(object):
def __init__(self):
self._local = Local()
def __release_local__(self):
self._local.__release_local__()
def _get__ident_func__(self):
return self._local.__ident_func__
def _set__ident_func__(self, value):
object.__setattr__(self._local, '__ident_func__', value)
__ident_func__ = property(_get__ident_func__, _set__ident_func__)
del _get__ident_func__, _set__ident_func__
def __call__(self):
def _lookup():
rv = self.top
if rv is None:
raise RuntimeError('object unbound')
return rv
return LocalProxy(_lookup)
def push(self, obj):
"""Pushes a new item to the stack"""
rv = getattr(self._local, 'stack', None)
if rv is None:
self._local.stack = rv = []
rv.append(obj)
return rv
def pop(self):
"""Removes the topmost item from the stack, will return the
old value or `None` if the stack was already empty.
"""
stack = getattr(self._local, 'stack', None)
if stack is None:
return None
elif len(stack) == 1:
release_local(self._local)
return stack[-1]
else:
return stack.pop()
@property
def top(self):
"""The topmost item on the stack. If the stack is empty,
`None` is returned.
"""
try:
return self._local.stack[-1]
except (AttributeError, IndexError):
return None
app_ctx = self.app.app_context()
# Flask类
def app_context(self):
return AppContext(self)
AppContext(self)
# AppContext类,初始化
def __init__(self, app):
self.app = app # 等于Flask对象
self.url_adapter = app.create_url_adapter(None)
self.g = app.app_ctx_globals_class() # Flask系统全局变量 # Like request context, app contexts can be pushed multiple times
# but there a basic "refcount" is enough to track them.
self._refcnt = 0
4._request_ctx_stack调用
--_request_ctx_stack.push(self) (请求相关)(堆栈)
def push(self, obj):
"""Pushes a new item to the stack"""
rv = getattr(self._local, 'stack', None)
if rv is None:
self._local.stack = rv = []
rv.append(obj)
return rv
self._local
class Local(object):
__slots__ = ('__storage__', '__ident_func__') def __init__(self):
object.__setattr__(self, '__storage__', {})
object.__setattr__(self, '__ident_func__', get_ident) def __iter__(self):
return iter(self.__storage__.items()) def __call__(self, proxy):
"""Create a proxy for a name."""
return LocalProxy(self, proxy) def __release_local__(self):
self.__storage__.pop(self.__ident_func__(), None) def __getattr__(self, name):
try:
return self.__storage__[self.__ident_func__()][name]
except KeyError:
raise AttributeError(name) def __setattr__(self, name, value):
ident = self.__ident_func__()
storage = self.__storage__
try:
storage[ident][name] = value
except KeyError:
storage[ident] = {name: value} def __delattr__(self, name):
try:
del self.__storage__[self.__ident_func__()][name]
except KeyError:
raise AttributeError(name)
3、从栈中将请求对象调取出来
--request --->_lookup_req_object
--session --->_lookup_req_object
--current_app--->_find_app
--g--->_lookup_app_object
current_app = LocalProxy(_find_app)
request = LocalProxy(partial(_lookup_req_object, 'request'))
session = LocalProxy(partial(_lookup_req_object, 'session'))
g = LocalProxy(partial(_lookup_app_object, 'g'))
LocalProxy
@implements_bool
class LocalProxy(object): __slots__ = ('__local', '__dict__', '__name__', '__wrapped__') def __init__(self, local, name=None):
object.__setattr__(self, '_LocalProxy__local', local)
object.__setattr__(self, '__name__', name)
if callable(local) and not hasattr(local, '__release_local__'):
# "local" is a callable that is not an instance of Local or
# LocalManager: mark it as a wrapped function.
object.__setattr__(self, '__wrapped__', local) def _get_current_object(self):
if not hasattr(self.__local, '__release_local__'):
return self.__local()
try:
return getattr(self.__local, self.__name__)
except AttributeError:
raise RuntimeError('no object bound to %s' % self.__name__)
2.以上四个对象通过localProxy(采用threading.local),调用
--_lookup_app_object
def _lookup_req_object(name):
top = _request_ctx_stack.top
if top is None:
raise RuntimeError(_request_ctx_err_msg)
return getattr(top, name)
--_find_app
def _find_app():
top = _app_ctx_stack.top
if top is None:
raise RuntimeError(_app_ctx_err_msg)
return top.app
--_lookup_app
def _lookup_app_object(name):
top = _app_ctx_stack.top
if top is None:
raise RuntimeError(_app_ctx_err_msg)
return getattr(top, name)
3.以上三个方法调用
_lookup_req_object ----> _implicit_app_ctx_stack
_find_app和_lookup_app ----> _request_ctx_stack
4.上下文出栈流程
session的保存方式:
wsgi_app()-->full_dispatch_request-->self.dispatch_request()
wsgi_app()
def wsgi_app(self, environ, start_response):
try:
try:
# 4 执行视图函数
response = self.full_dispatch_request()
except Exception as e:
# 异常处理试图报错,包含信号2345报错执行,got_request_exception信号
error = e
response = self.handle_exception(e)
except:
error = sys.exc_info()[1]
raise
# 将处理的内容,返回给用户浏览器
return response(environ, start_response)
finally:
if self.should_ignore_error(error):
error = None # 9、结束
ctx.auto_pop(error)
full_dispatch_request
# Flask类
def full_dispatch_request(self):
"""Dispatches the request and on top of that performs request
pre and postprocessing as well as HTTP exception catching and
error handling. .. versionadded:: 0.7
""" self.try_trigger_before_first_request_functions()
try: request_started.send(self) rv = self.preprocess_request()
if rv is None:
# 触发执行视图函数,使用session
rv = self.dispatch_request()
except Exception as e:
rv = self.handle_user_exception(e) return self.finalize_request(rv)
finalize_request(self, rv, from_error_handler=False):
# Flask类
def finalize_request(self, rv, from_error_handler=False):
response = self.make_response(rv)
try:
'''8、'''
response = self.process_response(response)
request_finished.send(self, response=response)
except Exception:
if not from_error_handler:
raise
self.logger.exception('Request finalizing failed with an '
'error while handling an error')
return response
self.process_response(response)
# Flask类
def process_response(self, response):
ctx = _request_ctx_stack.top
bp = ctx.request.blueprint
funcs = ctx._after_request_functions
if bp is not None and bp in self.after_request_funcs:
funcs = chain(funcs, reversed(self.after_request_funcs[bp]))
if None in self.after_request_funcs:
funcs = chain(funcs, reversed(self.after_request_funcs[None]))
# 执行 after_request装饰器
for handler in funcs:
response = handler(response)
# 将内存中的session持久化到:数据库、....
if not self.session_interface.is_null_session(ctx.session):
self.save_session(ctx.session, response)
return response
self.save_session(ctx.session, response)
# Flask类
def save_session(self, session, response):
return self.session_interface.save_session(self, session, response)
上下文的出栈方式:
wsgi_app()-->ctx.auto_pop(error)-->
auto_pop
# RequestContext类
def auto_pop(self, exc):
if self.request.environ.get('flask._preserve_context') or \
(exc is not None and self.app.preserve_context_on_exception):
self.preserved = True
self._preserved_exc = exc
else:
self.pop(exc)
self.pop(exc)
#RequestContext类
def pop(self, exc=_sentinel):
app_ctx = self._implicit_app_ctx_stack.pop() try:
clear_request = False
if not self._implicit_app_ctx_stack:
self.preserved = False
self._preserved_exc = None
if exc is _sentinel:
exc = sys.exc_info()[1]
self.app.do_teardown_request(exc) # If this interpreter supports clearing the exception information
# we do that now. This will only go into effect on Python 2.x,
# on 3.x it disappears automatically at the end of the exception
# stack.
if hasattr(sys, 'exc_clear'):
sys.exc_clear() request_close = getattr(self.request, 'close', None)
if request_close is not None:
request_close()
clear_request = True
finally:
rv = _request_ctx_stack.pop() # get rid of circular dependencies at the end of the request
# so that we don't require the GC to be active.
if clear_request:
rv.request.environ['werkzeug.request'] = None # Get rid of the app as well if necessary.
if app_ctx is not None:
app_ctx.pop(exc) assert rv is self, 'Popped wrong request context. ' \
'(%r instead of %r)' % (rv, self)
rv = _request_ctx_stack.pop()
# LocalStack类
def pop(self):
stack = getattr(self._local, 'stack', None)
if stack is None:
return None
elif len(stack) == 1:
release_local(self._local)
return stack[-1]
else:
return stack.pop()
app_ctx.pop(exc)
#AppContext类
def pop(self, exc=_sentinel):
try:
self._refcnt -= 1
if self._refcnt <= 0:
if exc is _sentinel:
exc = sys.exc_info()[1]
self.app.do_teardown_appcontext(exc)
finally:
rv = _app_ctx_stack.pop()
assert rv is self, 'Popped wrong app context. (%r instead of %r)' \
% (rv, self)
# 信号执行8 appcontext_popped
appcontext_popped.send(self.app)
完成
Flask系列之源码分析(二)的更多相关文章
- Flask系列之源码分析(一)
目录: 涉及知识点 Flask框架原理 简单示例 路由系统原理源码分析 请求流程简单源码分析 响应流程简单源码分析 session简单源码分析 涉及知识点 1.装饰器 闭包思想 def wapper( ...
- 框架-springmvc源码分析(二)
框架-springmvc源码分析(二) 参考: http://www.cnblogs.com/leftthen/p/5207787.html http://www.cnblogs.com/leftth ...
- Fresco 源码分析(二) Fresco客户端与服务端交互(1) 解决遗留的Q1问题
4.2 Fresco客户端与服务端的交互(一) 解决Q1问题 从这篇博客开始,我们开始讨论客户端与服务端是如何交互的,这个交互的入口,我们从Q1问题入手(博客按照这样的问题入手,是因为当时我也是从这里 ...
- Tomcat源码分析二:先看看Tomcat的整体架构
Tomcat源码分析二:先看看Tomcat的整体架构 Tomcat架构图 我们先来看一张比较经典的Tomcat架构图: 从这张图中,我们可以看出Tomcat中含有Server.Service.Conn ...
- 十、Spring之BeanFactory源码分析(二)
Spring之BeanFactory源码分析(二) 前言 在前面我们简单的分析了BeanFactory的结构,ListableBeanFactory,HierarchicalBeanFactory,A ...
- Vue源码分析(二) : Vue实例挂载
Vue源码分析(二) : Vue实例挂载 author: @TiffanysBear 实例挂载主要是 $mount 方法的实现,在 src/platforms/web/entry-runtime-wi ...
- 多线程之美8一 AbstractQueuedSynchronizer源码分析<二>
目录 AQS的源码分析 该篇主要分析AQS的ConditionObject,是AQS的内部类,实现等待通知机制. 1.条件队列 条件队列与AQS中的同步队列有所不同,结构图如下: 两者区别: 1.链表 ...
- Flask源码分析二:路由内部实现原理
前言 Flask是目前为止我最喜欢的一个Python Web框架了,为了更好的掌握其内部实现机制,这两天准备学习下Flask的源码,将由浅入深跟大家分享下,其中Flask版本为1.1.1. 上次了解了 ...
- ABP源码分析二:ABP中配置的注册和初始化
一般来说,ASP.NET Web应用程序的第一个执行的方法是Global.asax下定义的Start方法.执行这个方法前HttpApplication 实例必须存在,也就是说其构造函数的执行必然是完成 ...
随机推荐
- 如何使用matlab中的胞元数组
胞元数组(cell Arry)的基本组分是胞元(cell),每个胞元本身在数组中是平等的,只能以下标区分.胞元可以存放任何类型.任何大小的数组,如任意维数值数组.字符串数组.符号对象等,而且同一个胞元 ...
- Html解析
相关解析组件: HtmlAgilityPack CsQuery Winista.Text.HtmlParser
- php学习十三:其他关键字
在php中,其实不止在php中,在其他语言中我们也会常常接触到一些关键字,整理了一下php当中的一下关键字,可能有些不全,希望大家指出来,多多交流,一起进步. 1.final 特性:1.使用final ...
- 开始iOS 7中自动布局教程(一)
本文转载至 http://www.cocoachina.com/industry/20131203/7462.html 到目前为止,如果你的设计相当的复杂,那么你必须编写大量的代码来适应这样的布局.你 ...
- JS AJAX传递List数组到后台(对象)
今天在写代码的时候,碰到的问题,百度了一下,发现原来AJAX传递List数据是可以的,之前还一直用JSON序列化(new Array()数组设置)进行传值的. var _list = {}; //等价 ...
- 图片上传Security Error
jQuery.Uploadify v3.2.js 现在得到的一个原因是跨域 http://www.xuebuyuan.com/848255.html 最近项目中要用文件上传控件,我就想到了Upload ...
- C++面向对象类的实例题目十二
题目描述: 写一个程序计算正方体.球体和圆柱体的表面积和体积 程序代码: #include<iostream> #define PAI 3.1415 using namespace std ...
- 【jdk源码学习】HashMap
package com.emsn.crazyjdk.java.util; /** * “人”类,重写了equals和hashcode方法...,以id来区分不同的人,你懂的... * * @autho ...
- change事件的兼容性问题
当input的value被修改时,在没有失去焦点的情况下,无法触发change事件,但是可以触发propertychange事件. 但是propertychange事件存在兼容性问题: IE9以下支持 ...
- sencha touch 入门系列 (八)sencha touch类系统讲解(下)
接着上一讲,我们通过一组代码来讲解一下st的类的一些属性: Ext.define("MyConfig",{ config:{ website:"http://127.0. ...