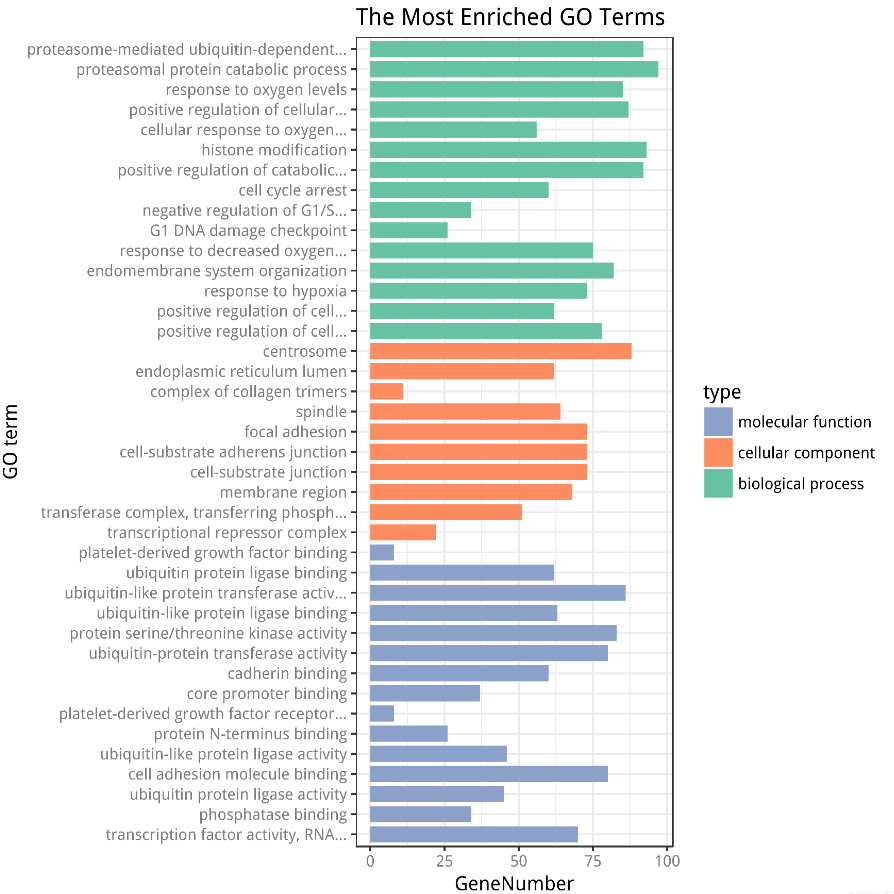
GO富集分析柱状图
- target_gene_id <- unique(read.delim("miRNA-gene interactions.txt")$EntrezID)
- # BiocInstaller::biocLite("clusterProfiler")
- # BiocInstaller::biocLite("org.Hs.eg.db")
- display_number = c(, , )
- ## GO enrichment with clusterProfiler
- library(clusterProfiler)
- ego_MF <- enrichGO(OrgDb="org.Hs.eg.db",
- gene = target_gene_id,
- pvalueCutoff = 0.05,
- ont = "MF",
- readable=TRUE)
- ego_result_MF <- as.data.frame(ego_MF)[:display_number[], ]
- # ego_result_MF <- ego_result_MF[order(ego_result_MF$Count),]
- ego_CC <- enrichGO(OrgDb="org.Hs.eg.db",
- gene = target_gene_id,
- pvalueCutoff = 0.05,
- ont = "CC",
- readable=TRUE)
- ego_result_CC <- as.data.frame(ego_CC)[:display_number[], ]
- # ego_result_CC <- ego_result_CC[order(ego_result_CC$Count),]
- ego_BP <- enrichGO(OrgDb="org.Hs.eg.db",
- gene = target_gene_id,
- pvalueCutoff = 0.05,
- ont = "BP",
- readable=TRUE)
- ego_result_BP <- na.omit(as.data.frame(ego_BP)[:display_number[], ])
- # ego_result_BP <- ego_result_BP[order(ego_result_BP$Count),]
- go_enrich_df <- data.frame(ID=c(ego_result_BP$ID, ego_result_CC$ID, ego_result_MF$ID),
- Description=c(ego_result_BP$Description, ego_result_CC$Description, ego_result_MF$Description),
- GeneNumber=c(ego_result_BP$Count, ego_result_CC$Count, ego_result_MF$Count),
- type=factor(c(rep("biological process", display_number[]), rep("cellular component", display_number[]),
- rep("molecular function", display_number[])), levels=c("molecular function", "cellular component", "biological process")))
- ## numbers as data on x axis
- go_enrich_df$number <- factor(rev(:nrow(go_enrich_df)))
- ## shorten the names of GO terms
- shorten_names <- function(x, n_word=, n_char=){
- if (length(strsplit(x, " ")[[]]) > n_word || (nchar(x) > ))
- {
- if (nchar(x) > ) x <- substr(x, , )
- x <- paste(paste(strsplit(x, " ")[[]][:min(length(strsplit(x," ")[[]]), n_word)],
- collapse=" "), "...", sep="")
- return(x)
- }
- else
- {
- return(x)
- }
- }
- labels=(sapply(
- levels(go_enrich_df$Description)[as.numeric(go_enrich_df$Description)],
- shorten_names))
- names(labels) = rev(:nrow(go_enrich_df))
- ## colors for bar // green, blue, orange
- CPCOLS <- c("#8DA1CB", "#FD8D62", "#66C3A5")
- library(ggplot2)
- p <- ggplot(data=go_enrich_df, aes(x=number, y=GeneNumber, fill=type)) +
- geom_bar(stat="identity", width=0.8) + coord_flip() +
- scale_fill_manual(values = CPCOLS) + theme_bw() +
- scale_x_discrete(labels=labels) +
- xlab("GO term") +
- theme(axis.text=element_text(face = "bold", color="gray50")) +
- labs(title = "The Most Enriched GO Terms")
- p
- pdf("go_enrichment_of_miRNA_targets.pdf")
- p
- dev.off()
- svg("go_enrichment_of_miRNA_targets.svg")
- p
- dev.off()
GO富集分析柱状图的更多相关文章
- 基因探针富集分析(GSEA)& GO & pathway
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_4c1f21000100utyx.html GO是Gene Ontology的简称,是生物学家为了衡量基因的功能而而发起的一个项目,从分子 ...
- GO富集分析示例【华为云技术分享】
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,遵循CC 4.0 BY-SA版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接和本声明. 本文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/devcloud/article/detai ...
- DAVID 进行 GO/KEGG 功能富集分析
何为功能富集分析? 功能富集分析是将基因或者蛋白列表分成多个部分,即将一堆基因进行分类,而这里的分类标准往往是按照基因的功能来限定的.换句话说,就是把一个基因列表中,具有相似功能的基因放到一起,并和生 ...
- 利用GSEA对基因表达数据做富集分析
image Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) is a computational method that determines whether an a p ...
- R: 修改镜像、bioconductor安装及go基因富集分析
1.安装bioconductor及go分析涉及的相关包 source("http://bioconductor.org/biocLite.R") options(BioC_mirr ...
- GO富集分析
GO的主要用途之一是对基因组进行富集分析.例如,给定一组在特定条件下上调的基因,富集分析将使用该基因组的注释发现哪些GO术语被过度表示(或未充分表示). 富集分析工具 用户可以直接从GOC网站的 ...
- OS Tools-GO富集分析工具的使用与解读详细教程
我们的云平台上的GO富集分析工具,需要输入的文件表格和参数很简单,但很多同学都不明白其中的原理与结果解读,这个帖子就跟大家详细解释~ 一.GO富集介绍: Gene Ontology(简称G ...
- webgestalt 通路富集分析
http://www.webgestalt.org/ 通路富集分析 参考 http://www.sci666.com.cn/9596.html
- GSEA 基因集富集分析
http://software.broadinstitute.org/gsea/index.jsp GSEA(Gene Set Enrichment Analysis)是一种生物信息学的计算方法,用于 ...
随机推荐
- Selenium2+python自动化
一.打开网站1.第一步:从selenium里面导入webdriver模块2.打开Firefox浏览器(Ie和Chrome对应下面的)3.打开百度网址二.设置休眠1.由于打开百度网址后,页面加载需要几秒 ...
- 【[SHOI2012]随机树】
感觉第一问就非常神仙,还有第二问怎么被我当成组合数学题来做了 首先是第一问 期望具有线性性,于是深度平均值的期望等于深度和的期望值的平均 设\(dp_x\)表示具有\(x\)个叶子节点的树的深度和的期 ...
- RedHat(小红帽)下 yum用不了的解决办法
由于RedHat是商业版的,通常由于没有注册,导致yum程序无法使用(linux下面,yum是个安装软件的“神器”).此时可用CentOS的地址进行替换.下面将一步步说明如何处理: 一.删除RedHa ...
- Linux下一种简单易行的cpu benchmark方法
用Linux自带的bc计算器计算pi值的一种benchmark手段 其实很简单,就是一行命令. time echo “scale=5000; 4*a(1)” | bc -l -q time是计时程 ...
- iOS的AssetsLibrary框架访问所有相片
该框架下有几个类,ALAssetsLibrary,ALAssetsGroup,ALAsset,ALAssetsFilter,ALAssetRepresentation. ALAssetsLibrary ...
- Java Runnable和Thread区别
Thread是多个线程分别完成自己的任务,Runnable是多个线程共同完成1个任务.在实际开发中,一个多线程的操作很少使用Thread类,而是通过Runnable接口完成,好处有: 1. 避免点继承 ...
- lwip 2.0.3 DNS 域名解析 使用
1. 在 lwipopts.h 中 #define LWIP_DNS 1 /* 使能 DNS 服务器的功能 ,2018年1月8日21:16:20,suozhang */ #define LWIP_ ...
- G1 GC日志:Application time: 0.8766273 seconds
启动日志一直循环: 1.159: Application time: 0.8766273 seconds 1.160: Total time for which application threads ...
- java 网站源码 六套模版 兼容手机平板PC freemaker 静态引擎 在线编辑模版
官网 http://www.fhadmin.org/ 系统介绍: 1.网站后台采用主流的 SSM 框架 jsp JSTL,网站后台采用freemaker静态化模版引擎生成html 2.因为是生成的ht ...
- C++快速开发样本工程的建立--建立工程
因为QT建立工程清晰整洁,便于作为样板工程原型.采用QT 5.8.0 64位版本建立工程. 1.建立工程 打开VS2015 新建->新建项目->QT GUI Application -&g ...
