列表:List<T>与HashSet和只读集合
一、概述
List<T> 是ArrayList类的等效泛型类。属System.Collections.Generic命名空间。
二、声明及初始化
1、List<T> mList=new List<T>([capacity]) :可带初始容量
List<string> mList=new List<string>();
2、List<T> mList=new List<T><IEnumerable<T> collection): 从指定集合(如数组)复制元素进行初始化。
List<string> mList0 = new List<string>(new []{ "a", "b", "c" });//数组
List<string> mList1 = new List<string>("a,b,c".Split(new char[] {','}));//将字符串转成List<string>
List<string> mList2 = new List<string> { "a", "b", "c" };//集合初始值设定项
三、常用属性和方法
1、添加元素
1、添加一个元素:
mList.Add("a");
2、添加一组元素
mList.AddRange(new [] { new Person("a", ), new Person("b", ), }
3、在Index处插入一个元素
mList.Insert(,"d");//以前占此及此位以后的元素都往后移动
4、在Index处插入一组元素:
mList.InsertRange(,new []{"E","f"});
2、删除元素
1、删除一个值:
mList.Remove("a");
2、删除索引处的元素:
mList.RemoveAt();
for (int i = mList.Count - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{ }
3、删除范围内的元素:
mList.RemoveRange(, );//index,count
4、清空所有元素:
mList.Clear();
5、删除与指定条件匹配的所有元素:
mList.RemoveAll(p => p.Length > );//bool Predicate<T>(T matach) 委托
注意:Remove()、Contais()、IndexOf、LastIndexOf()方法需要使用“相等”比较器。
List<T>中的元素实现了IEquatable接口则使用其Equals()方法,否则默认使用Object.Equals(object)。
3、访问列表元素以及遍历列表:
1、用索引的形式访问
mList[]
2、遍历
foreach (string s in mList)
{
Console.WriteLine(s);
} for (int i = ; i < mList.Count; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(s);
}
注意:Count属性:实际包含的元素数;Capacity:能够容纳的元素总数;TrimExcess()方法可将容量调整为实际容量。
4、判断元素存在:
1、判断整个元素是否存在该List中:
if (mList.Contains("d"))
{ }
2、判断是否存在于指定条件匹配的元素:
if (mList.Exists(p => p.Length > ))
{ }
3、判读是否List中每个元素都与指定条件匹配:
if (mList.TrueForAll(p => p.Length > ))
{}
5、搜索:
查找索引
1、查找列表中某个项的第一个索引:
mList.IndexOf(T,[index],[count]);
2、查找某元素在列表中最后一个匹配 项的索引:
mList.LastIndexOf(T,[index],[count]);
3、查找与指定条件匹配的元素在列表中第一个匹配项的索引:
mList.FindIndex([startIndex],[count],match);
4、查找与指定条件匹配的元素在列表中最后一个匹配项的索引:
mList.FindLastIndex(, , p => p.Length > );
查找元素:
1、查找与指定条件匹配的元素,返回第一个匹配元素:
string find= mList.Find( p => p.Length > );
2、查找与指定条件匹配的元素,返回最后一个匹配元素:
string find= mList.FindLast( p => p.Length > );
3、查找并返回与指定条件匹配的元素列表:
List<string> finds= mList.FindAll( p => p.Length > );
6、排序:
委托签名:
int Comparison<T>(T x, T y);
1、使用Comparision<T>委托进行元素排序:
mList.Sort((x, y) =>
{
int result = x[].CompareTo(y[]);
if (result == ) { return x[].CompareTo(y[]); }
return result;
});
2、顺序翻转
mList.Reverse()//index,count
注意:Sort方法还可以利用ICompable和Icomparer接口排序。
7、转换:
1、将一定范围内的元素从List<T>复制到兼容的一维数组中。
mList.CopyTo([index],array,[arrryIndex],[count]);
2、将List<T>中的元素复制到新数组中。
string[] arr=mList.ToArray();
3、创建源List<T>的元素范围的浅表副本。
List(string) range= mList.GetRange(inex,count);
4、将当前List<T>的元素转换成另一种类型,返回转换后元素的列表
List<char> chars=mList.ConvertAll(p=>p[]);
List<Racer> RacerList=PList.ConvertAll(Person,Racer)(p=>new Racer(p.FirstName+" " +p.LastName));
Converter委托签名:
TOutput Converter<in TInput,out TOutput>(TInput input);
5、将List<string>转成用逗号分隔的字符串
string aa= String.Join(",",mList)
8、去掉重复项(Distinct)
需要引用using System.Linq;
1、默认比较器:
mList.Distinct().ToList();
2、自定义比较器
mList.Distinct(new MyComparer()).ToList();
public class MyComparer : System.Collections.Generic.IEqualityComparer<string>
{
public bool Equals(string x, string y)
{
return x.ToUpper()==y.ToUpper();
} public int GetHashCode(string obj)
{
return obj.ToUpper().GetHashCode();
}
}
9、只读集合
List的AsReadOnly()方法返回ReadOnlyCollection,所有修改方法抛出NotSupportedException异常。
System.Collections.ObjectModel.ReadOnlyCollection readOnlyList= mList.AsReadOnly();
四:HashSet<T>
用来存储集合,基于Hash,可理解为没有Value的Dictionary<TKey,TValue);
1、HashSet<T>不能使用索引访问,不能存储重复数据,元素T必须实现了Equals和GetHashCode方法;
2、HashSet<T>的检索性能比List<T>好得多。如Contains(),Remove();
3、HashSet<T>是专门用来和集合运算(取并集、交集等),所以提供了UnionWith(),InterSetWith()等方法。
常用方法
Add、IsSubsetOf、IsSupersetOf、Overlaps、UnionWith
var companyTeams = new HashSet<string> { "Ferrari", "McLaren", "Mercedes" };//公司队
var traditionalTeams = new HashSet<string> { "Ferrari", "McLaren" };//传统队
var privateTeams = new HashSet<string> { "Red Bull", "Toro Rosso", "Force India", "Sauber" };//私有队
//Add方法,将一个元素添加到集中,成功返回true失败返回false
if (privateTeams.Add("Williams"))//返回true
Console.WriteLine("Williams Add Success.privateTeams count:{0}", privateTeams.Count);
if (!companyTeams.Add("McLaren"))//返回false
Console.WriteLine("McLaren Add Failure.companyTeams count:{0}", companyTeams.Count);
//IsSubset,确认(traditionalTeams)对象是否为指定集(companyTeams)的子集
if (traditionalTeams.IsSubsetOf(companyTeams))//traditionalTeams是companyTeams的子集,返回true
Console.WriteLine("traditionalTeams is sub of companyTeams.");
//IsSuperset,确认(companyTeams)对象是否为指定集(traditionalTeams)的超集(父集)
if (companyTeams.IsSupersetOf(traditionalTeams))//companyTeams是traditionalTeams的父集,返回true
Console.WriteLine("companyTeams is a superset of traditionalTeams");
//Overlaps,确认对象(privateTeams)和指定集(traditionalTeams)是否存在共同元素
traditionalTeams.Add("Williams");
if (privateTeams.Overlaps(traditionalTeams))//privateTeams和traditionalTeams都包含有Williams的元素,返回true
Console.WriteLine("At least one team is the same with the traditionalTeams and privateTeams.");
//UnionWith,将指定对象元素添加到当前对象(allTeams)中,因为对象类型为SortedSet,所以是元素是唯一有序的
var allTeams = new SortedSet<string>();
allTeams.UnionWith(companyTeams);
allTeams.UnionWith(traditionalTeams);
allTeams.UnionWith(privateTeams);
foreach (var item in allTeams)
{
Console.Write(item);
}
HashSet和SortedSet的区别
共同点:
1. 都是集,都具有集的特征,包含的元素不能有重复
不同点:
1. HashSet的元素是无序的,SortedSet的元素是有序的
五、链表 LinkedList
链表是一串存储数据的链式数据结构,它的每个成员都有额外的两个空间来关联它的上一个成员和下一个成员。所以,链表对于插入和删除操作效率会高于ArrayList,因为它存储了上一个成员和下一个成员的指针,进行插入和删除只需要改变当前LinkedListNode的Previous和Next的指向即可。
链表的内存表视图
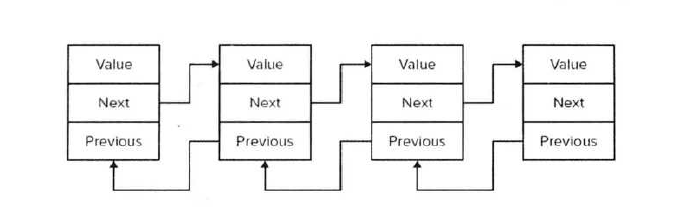
实例:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
LinkedList<Document> linkedlist = new LinkedList<Document>();
//添加节点
linkedlist.AddFirst(new Document(""));
linkedlist.AddFirst(new Document(""));
Display(linkedlist); //title:2 title:1 Document doc = new Document("");
linkedlist.AddLast(doc);
Document doc1 = new Document("");
linkedlist.AddLast(doc1);
Display(linkedlist); //title:2 title:1 title:3 title:4
//查找节点
LinkedListNode<Document> findnode = linkedlist.FindLast(doc);
Display(findnode.Value); //title:3 //插入节点
linkedlist.AddBefore(findnode, new Document(""));
Display(linkedlist); //title:2 title:1 title:5 title:3 title:4 linkedlist.AddAfter(findnode, new Document(""));
Display(linkedlist); //title:2 title:1 title:5 title:3 title:6 title:4 linkedlist.AddAfter(findnode.Previous, new Document(""));
Display(linkedlist); //title:2 title:1 title:5 title:7 title:3 title:6 title:4 linkedlist.AddAfter(findnode.Next, new Document(""));
Display(linkedlist); //title:2 title:1 title:5 title:7 title:3 title:6 title:8 title:4 //移除节点
linkedlist.Remove(findnode);
Display(linkedlist); //title:2 title:1 title:5 title:7 title:6 title:8 title:4 linkedlist.Remove(doc1);
Display(linkedlist); //title:2 title:1 title:5 title:7 title:6 title:8 linkedlist.RemoveFirst();
Display(linkedlist); //title:1 title:5 title:7 title:6 title:8 linkedlist.RemoveLast();
Display(linkedlist); //title:1 title:5 title:7 title:6
} private static void Display<T>(LinkedList<T> linkedlist)
{
foreach (var item in linkedlist)
{
Console.Write(item + " ");
}
} private static void Display<T>(T doc)
{
Console.Write(doc);
} public class Document
{
public string title { get; private set; }
public Document(string title)
{
this.title = title;
} public override string ToString()
{
return string.Format("title:{0}", title);
}
}
列表:List<T>与HashSet和只读集合的更多相关文章
- 使用ReadOnlyCollection创建只读集合
转载:http://www.cnblogs.com/abatei/archive/2008/02/04/1064102.html 使用泛型创建只读集合 问题 您希望类中的一个集合里的信息可以被外界访问 ...
- linq中查询列表的使用及iqueryable和list集合之间的转换
linq中查询列表的使用及iqueryable和list集合之间的转换 比如要查询一个货架集合,但是只需要其id和name即可,可以用以下方法:先写一个model类:CatalogModel(注意该类 ...
- WPF 只读集合在 XAML 中的绑定(WPF:Binding for readonly collection in xaml)
问题背景 某一天,我想做一个签到打卡的日历.基于 Calendar,想实现这个目标,于是找到了它的 SelectedDates 属性,用于标记签到过的日期. 问题来了. 基于MVVM模式,想将其在xa ...
- python基础--列表、元祖、字典、集合
列表(List) 1.列表特点 列表是可变的!! list 是一种有序的序列,可以添加.删除其中的元素,并且可以通过下标(索引)访问 数据 2.简单的常用操作 A.通过下表访问元素 print(lis ...
- python基础知识之列表、元祖、字典、集合、字符串。
1.可变类型之列表 列表用 [ ]来定义是可变的,可以通过索引值来去查询里面的字段可以可以追加,删除等 names='zhangyang guyun xiangpeng xuliangwei' nam ...
- java9新特性-12-集合工厂方法:快速创建只读集合
1.官方Feature 269: Convenience Factory Methods for Collections 2.产生背景 要创建一个只读.不可改变的集合,必须构造和分配它,然后添加元素, ...
- .NET重思(三)-数组列表与数组的区别,栈集合和队列结合的区别
数组列表和数组十分相似,区别在于数组列表的容量是可以动态变化的,而数组的容量是固定的.数组即Array类,数组列表即ArrayList类,两者十分相似.不过,Array类在System命名空间下,Ar ...
- 干货!Python中字符串、列表、元祖、字典,集合之间的转换
一.字符串的转化 1.字符串转换成列表 字符串转换成list 的时候,str可以作为迭代对象,直接放入:也可以使用split对字符串进行切割.然后返回list s = '1a1b1c' print(l ...
- python列表,字典,元组常用方法和集合
python 目录 一.列表 列表格式 1.添加 列表取数(按照下标取,下标从0开始) 获取长度 append添加(直接添加) extend添加(分别添加) insert()insert(index, ...
随机推荐
- PTA (Advanced Level) 1014 Waiting in Line
Waiting in Line Suppose a bank has N windows open for service. There is a yellow line in front of th ...
- Netty(1):第一个netty程序
为什么选择Netty netty是业界最流行的NIO框架之一,它的健壮型,功能,性能,可定制性和可扩展性都是首屈一指的,Hadoop的RPC框架Avro就使用了netty作为底层的通信框架,此外net ...
- 关于Hall定理的学习
基本定义 \(Hall\) 定理是二分图匹配的相关定理 用于判断二分图是否存在完美匹配 存在完美匹配的二分图即满足最大匹配数为 \(min(|X|,|Y|)\) 的二分图,也就是至少有一边的点全部被匹 ...
- Logback学习笔记
Logback介绍 Logback 分为三个模块:Core.Classic 和 Access.Core模块是其他两个模块的基础. Classic模块扩展了core模块. Classic模块相当于log ...
- 动态页面技术之JSP
1.什么是JSP技术 JSP全名为Java Server Pages,中文名叫java服务器页面,其根本是一个简化的Servlet设计,它是由Sun Microsystems公司倡导.许多公司参与一起 ...
- mysql update/delete in 子查询改写
#子查询(不支持) limit ,); #改写 limit ,) t ; #子查询(不支持) delete from `user` where id in ( ) ); #改写 delete from ...
- groovy和java的主要区别
1.Default imports,默认情况下,导入下面的包: java.io. * java.lang.* java.math.BigDecimal中 java.math.BigInteger中 j ...
- 【数据库】10.0 MySQL常用语句(一)
显示数据库语句: SHOW DATABASES 只是显示数据库的名字 显示数据库创建语句: SHOW CREATE DATABASE db_name 数据库删除语句: DROP DATABASE ...
- 解决react不能往setState中传key作为参数的办法(文章最后实现了传递key做参数的办法)
读者朋友可以直接看最后一个分割线下面的那部分!利用方括号语法来动态的访问对象的属性,实现当参数为属性名的传递; 有时候我们需要每次单独设置众多state中的一个,但是,都是进行相同的操作,这时候如果每 ...
- arcgis 3种方法快速制作tpk文件(转)
来自:http://blog.csdn.net/arcgis_mobile/article/details/8048549 tpk是ArcGIS10.1推出的一种新的数据文件类型,主要是用于将切片文件 ...
