V-rep学习笔记:转动关节2
Torque or force mode: in this mode, the joint is simulated by the dynamics module, if and only if it is dynamically enabled. When dynamically enabled, a joint can be free or controlled in Force/torque, in velocity or in position.
The differentiation comes from the fact that a joint that operates in force/torque mode will be handled by the physics engine. And the physics engine will perform by default 10 times more calculation steps than the simulation loop: the simulation loop runs at 20Hz (in simulation time), while the physics engine runs at 200Hz (also in simulation time). That default behaviour can entirely be configured if required。If the joint is not in force/torque mode: if the joint is not in force/torque mode, then you can directly (and instantaneously) set its position via the simSetJointPosition API function.
建立如下图所示的旋转模型:
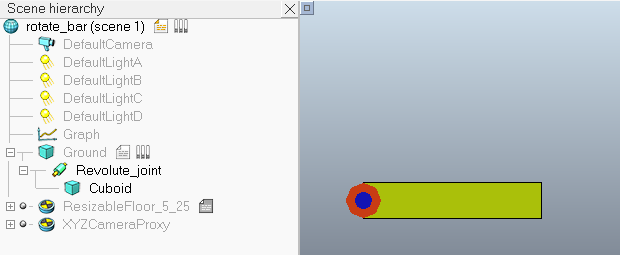
在转动关节的Joint Dynamic Properties对话框中勾选Control loop enable选项可以进行关节的位置控制(默认使用内置的PID控制器)。Target position为设定的目标位置(角度),Upper velocity limit为关节运动过程中允许的最大角速度,如果超过这个角速度则被限制为该值。
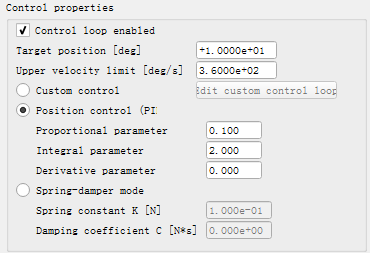
PID控制器将比例、积分、微分通过线性组合构成控制量,动态方程为:
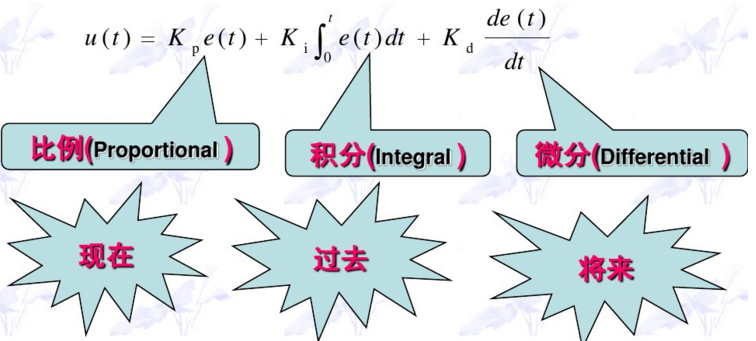
PID控制器的离散化表达式为:
$$u(k)=K_pe(k)+K_iTe(k)+\frac{K_d}{T}[e(k)-e(k-1)]$$
式中,T为采样周期,k为采样序号,Kp为比例系数,Ki为积分系数,Kd为微分系数
比例控制能提高系统的动态响应速度,迅速反应误差,从而减小误差,但比例控制不能消除稳态误差。$K_p$的加大,会引起系统的不稳定;积分控制的作用是消除稳态误差,因为系统只要存在误差,积分作用就不断地积累,输出控制量,直到偏差为零,积分作用才会停止。但积分作用太强会使系统超调加大,甚至使系统出现振荡。微分作用可以在产生误差之前一发现有产生误差的趋势就开始调节,提前进行控制,所以及时性更好,可以最大限度地减少动态误差。但微分作用只能作为比例和积分控制的一种补充,不能起主导作用,微分作用太强也会使系统出现不稳定,微分作用只能在P和I调好后再由小往大调,一点一点试着加上去。
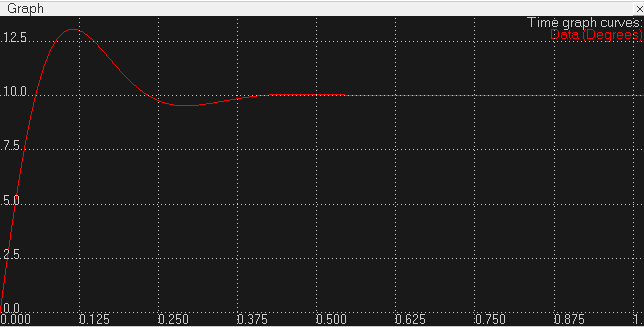
下面设10°为期望位置,PID参数设为0.1, 2, 0,仿真1s关节角度曲线如下图所示:
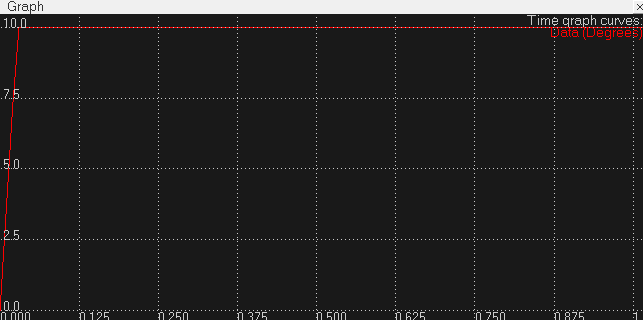
可以试着改变参数看看不同的效果,下图是使用默认参数0.1,0,0,即只使用比例控制的结果。可以看出增大积分项确实会引起超调
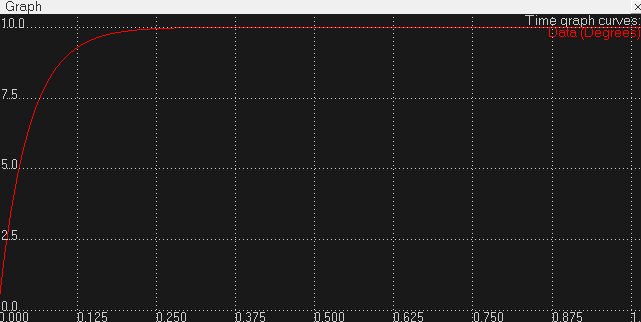
将比例系数设为1后结果如下图,可以看出到达目标位置的时间比Kp=0.1时要快很多,可以看出增大比例系数可以加快响应速度。
如果勾选Custom control选项,关节就会按照joint control callback script中用户编写的控制规律进行控制。This allows the user to write very specific joint controllers, that will be executed at each physics engine simulation step.
callback script脚本通常用于一些底层控制,VREP中分为3种:
- the contact callback script: the contact callback script lets you handle in a customized way each dynamic contact generated by the physics engine when two respondable objects collide.
- joint control callback scripts: a joint control callback script lets you write customized low-level controllers for joints that are dynamically enabled.
- the general callback script: each scene can have a general callback script that will be in charge of handling multi-purpose callback calls.
这些脚本有如下特点:
- a callback script always runs non-threaded.
- a callback script might be called more than once for each simulation step.
- a callback script handles low-level control items that the user wishes to customize. They should execute as quickly as possible, to avoid slowing down a simulation (this is particularly true for the contact callback script).
Joint control callback scripts, which are simulation scripts, can be enabled via the joint dynamics properties dialog. When enabled for a given joint (that must be dynamically enabled), then the physics engine will call the callback script with appropriate arguments, allowing the user to customize the control loop of the related joint in order to write low-level control algorithms for specific joints. The joint control callback script might be called quite often, normally 10 times per simulation step for a given joint (remember that the physics engine time step, by default, is 10 times smaller that the simulation time step). For that reason, keep things simple, in order to avoid slowing down the simulation. Following represents a simple PID joint control callback script:
打开关节控制脚本,默认进行PID控制,我们可以根据需要进行修改。代码中pidCumulativeErrorForIntegralParam变量用于存储积分项的累加值,如果是第一次调用控制脚本(init值为true)则将其初始化为0;dynStepSize与上面公式中的采样周期T意义相同;用于计算控制量的误差errorValue=targetPos-currentPos,那么与PID参数相乘后得到的控制量ctrl为位置量,如果要控制速度来使关节达到目标位置,则应施加的速度控制量为:velocityToApply=ctrl/dynStepSize
-- This example script performs a PID control
-- Be very careful when calling V-REP API functions from here:
-- 1. This routine gets called often, so it might slow down simulation (this is called at each dynamic simulation step, by default 10x more often than a child script)
-- 2. Some API functions are not meant to be called from here -- Following data is handed over from V-REP:
init,revolute,cyclic,jointHandle,passCnt,totalPasses,currentPos,targetPos,errorValue,effort,dynStepSize,lowLimit,highLimit,targetVel,maxForceTorque,velUpperLimit=... -- init: true when this callback is called for the first time (if the joint is dynamically reset during the simulation, this might be true more often)
-- revolute: true if the joint is revolute
-- cyclic: true if the joint is revolute and cyclic (i.e. no lower/upper limits)
-- passCnt: the current dynamics calculation pass. 0-9 by default. See next item for details.
-- totalPasses: the number of dynamics calculation passes for each "regular" simulation pass. 10 by default (i.e. 10*5ms=50ms which is the default simulation time step)
-- currentPos: the current position of the joint
-- targetPos: the desired position of the joint
-- errorValue: targetPos-currentPos (with revolute cyclic joints we take the shortest cyclic distance)
-- effort: the last force or torque that acted on this joint along/around its axis. With Bullet, torques from joint limits are not taken into account
-- dynStepSize: the step size used for the dynamics calculations (by default 5ms)
-- lowLimit: the joint lower limit
-- highLimit: the joint upper limit
-- targetVel: the joint target velocity (as set in the user interface)
-- maxForceTorque: the joint maximum force/torque (as set in the user interface)
-- velUpperLimit: the joint velocity upper limit (as set in the user interface) -- The control happens here:
-- 1. PID parameter def:
if not PID_P then
PID_P=0.1
PID_I=
PID_D=
end
-- 2. Clear some values when the dynamic joint calls this the first time (this can happen several times, if the joint is reset dynamically):
if init then
pidCumulativeErrorForIntegralParam=
end
-- 3. Proportional part:
ctrl=errorValue*PID_P
-- 4. Integral part:
if PID_I~= then
pidCumulativeErrorForIntegralParam=pidCumulativeErrorForIntegralParam+errorValue*dynStepSize
else
pidCumulativeErrorForIntegralParam=
end
ctrl=ctrl+pidCumulativeErrorForIntegralParam*PID_I
-- 5. Derivative part:
if not init then
ctrl=ctrl+(errorValue-pidLastErrorForDerivativeParam)*PID_D/dynStepSize
end
pidLastErrorForDerivativeParam=errorValue
-- 6. Calculate the velocity needed to reach the position in one dynamic time step:
velocityToApply=ctrl/dynStepSize
if (velocityToApply>velUpperLimit) then
velocityToApply=velUpperLimit
end
if (velocityToApply<-velUpperLimit) then
velocityToApply=-velUpperLimit
end
forceOrTorqueToApply=maxForceTorque -- Following data must be returned to V-REP:
return forceOrTorqueToApply,velocityToApply -- forceOrTorqueToApply: the maximum force/torque that the joint will be able to exert
-- velocityToApply: the velocity to apply to the joint.
注意Lua函数可以接受可变数目的参数,在函数参数列表中使用三点(...)表示函数有可变的参数。
V-rep学习笔记:转动关节2的更多相关文章
- R语言与机器学习学习笔记
人工神经网络(ANN),简称神经网络,是一种模仿生物神经网络的结构和功能的数学模型或计算模型.神经网络由大量的人工神经元联结进行计算.大多数情况下人工神经网络能在外界信息的基础上改变内部结构,是一种自 ...
- 蒟蒻的长链剖分学习笔记(例题:HOTEL加强版、重建计划)
长链剖分学习笔记 说到树的链剖,大多数人都会首先想到重链剖分.的确,目前重链剖分在OI中有更加多样化的应用,但它大多时候是替代不了长链剖分的. 重链剖分是把size最大的儿子当成重儿子,顾名思义长链剖 ...
- KD-Tree 学习笔记
这是一篇又长又烂的学习笔记,请做好及时退出的准备. KD-Tree 的复杂度大概是 \(O(n^{1-\frac{1}{k}})\) \(k\) 是维度 由于网上找不到靠谱的证明,咕了. 会证明之后再 ...
- 「学习笔记」FFT 快速傅里叶变换
目录 「学习笔记」FFT 快速傅里叶变换 啥是 FFT 呀?它可以干什么? 必备芝士 点值表示 复数 傅立叶正变换 傅里叶逆变换 FFT 的代码实现 还会有的 NTT 和三模数 NTT... 「学习笔 ...
- CF1147F Zigzag Game & 稳定婚姻问题学习笔记
CF1147F Zigzag Game 这题太神仙了,不得不记录一下. 我网络流做不动了,DS做不动了,DP做不动了,特别自闭.于是博弈论之神(就是随手切3500博弈的那种) \(\color{bla ...
- DirectX Graphics Infrastructure(DXGI):最佳范例 学习笔记
今天要学习的这篇文章写的算是比较早的了,大概在DX11时代就写好了,当时龙书11版看得很潦草,并没有注意这篇文章,现在看12,觉得是跳不过去的一篇文章,地址如下: https://msdn.micro ...
- Sass学习笔记之入门篇
Sass又名SCSS,是CSS预处理器之一,,它能用来清晰地.结构化地描述文件样式,有着比普通 CSS 更加强大的功能. Sass 能够提供更简洁.更优雅的语法,同时提供多种功能来创建可维护和管理的样 ...
- react-native学习笔记--史上最详细Windows版本搭建安装React Native环境配置
参考:http://www.lcode.org/react-native/ React native中文网:http://reactnative.cn/docs/0.23/android-setup. ...
- swift学习笔记5——其它部分(自动引用计数、错误处理、泛型...)
之前学习swift时的个人笔记,根据github:the-swift-programming-language-in-chinese学习.总结,将重要的内容提取,加以理解后整理为学习笔记,方便以后查询 ...
- Oracle学习笔记三 SQL命令
SQL简介 SQL 支持下列类别的命令: 1.数据定义语言(DDL) 2.数据操纵语言(DML) 3.事务控制语言(TCL) 4.数据控制语言(DCL)
随机推荐
- WaitForMultipleObjects返回0xffffffff
DWORD ret; ; HANDLE handle[THREAD_NUM]; ; i < THREAD_NUM; i++) handle[i] = (HANDLE)_beginthreadex ...
- day17--JQuery实例
1.表格选择框--全选,反选,取消 <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta c ...
- 用HTML+CSS画出一个同心圆
参加web前端校招的同学们经常会遇到这样的面试题:用HTML+CSS画出一个同心圆. 例如: 这道题主要考验的是基础盒模型布局能力和倒圆角属性的巧用. 1.html代码 <body> &l ...
- Ubuntu18.04更换国内源
Ubuntu18.04更换国内源 Ubuntu本身的源使用的是国内的源,下载速度比较慢,不像CentOS一样yum安装的时候对镜像站点进项选择, 所以选择了更换成国内的源. 以下内容整合自网络 备份/ ...
- POJ 2250 Compromise【LCS】+输出路径
题目链接:https://vjudge.net/problem/POJ-2250 题目大意:给出n组case,每组case由两部分组成,分别包含若干个单词,都以“#”当结束标志,要求输出最长子序列. ...
- Angular 个人深究(五)【外部包引用 Leaflet 简单实用】
Leaflet 使用 最近在Angular项目中,用到了地图,由于种种原因放弃了百度地图api使用,最后选择了leaflet,简单介绍一下. 介绍: Leaflet 是一个为移动设备设计的交互式地图的 ...
- python数据分析---第04章 NumPy基础:数组和矢量计算
NumPy(Numerical Python的简称)是Python数值计算最重要的基础包.大多数提供科学计算的包都是用NumPy的数组作为构建基础. NumPy的部分功能如下: ndarray,一个具 ...
- vue 之 加载 iframe 的处理
vue中加载 iframe 会出现跨域问题.以及iframe的高度自适应问题,以下是本人的解决办法: getGoodsContentHtml---- 你的iframe页面的地址, 如不同域的情况下 ...
- flask第九篇——url_for【2】
上一节说的是没有参数的url_for,如果没有参数,可以直接url_for('函数名')那如果我们构造的函数是: @app.route('/login/<page_id>/')def ...
- loj#2054. 「TJOI / HEOI2016」树
题目链接 loj#2054. 「TJOI / HEOI2016」树 题解 每次标记覆盖整棵字数,子树维护对于标记深度取max dfs序+线段树维护一下 代码 #include<cstdio> ...
