『高性能模型』深度可分离卷积和MobileNet_v1
论文原址:MobileNets v1
TensorFlow实现:mobilenet_v1.py
TensorFlow预训练模型:mobilenet_v1.md
一、深度可分离卷积
标准的卷积过程可以看上图,一个2×2的卷积核在卷积时,对应图像区域中的所有通道均被同时考虑,问题在于,为什么一定要同时考虑图像区域和通道?我们为什么不能把通道和空间区域分开考虑?
深度可分离卷积提出了一种新的思路:对于不同的输入channel采取不同的卷积核进行卷积,它将普通的卷积操作分解为两个过程。
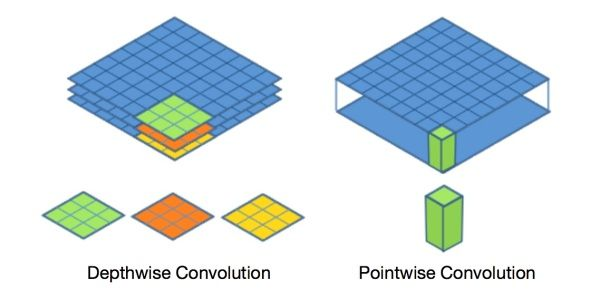
卷积过程
假设有 的输入,同时有
个
的卷积。如果设置
且
,那么普通卷积输出为
。

Depthwise 过程
Depthwise是指将 的输入分为
组,然后每一组做
卷积。这样相当于收集了每个Channel的空间特征,即Depthwise特征。

Pointwise 过程
Pointwise是指对 的输入做
个普通的
卷积。这样相当于收集了每个点的特征,即Pointwise特征。Depthwise+Pointwise最终输出也是
。
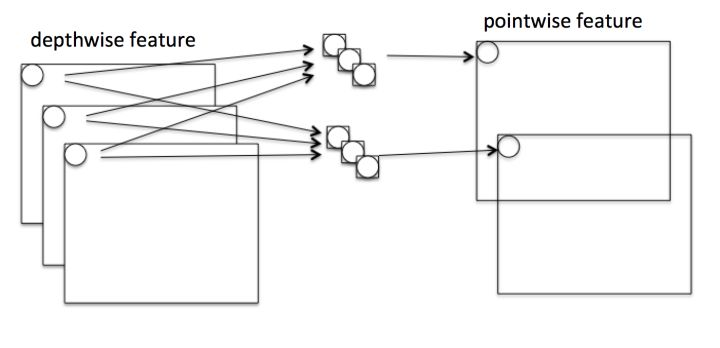
二、优势与创新
Depthwise+Pointwise可以近似看作一个卷积层:
- 普通卷积:3x3 Conv+BN+ReLU
- Mobilenet卷积:3x3 Depthwise Conv+BN+ReLU 和 1x1 Pointwise Conv+BN+ReLU
计算加速
参数量降低
假设输入通道数为3,要求输出通道数为256,两种做法:
1.直接接一个3×3×256的卷积核,参数量为:3×3×3×256 = 6,912
2.DW操作,分两步完成,参数量为:3×3×3 + 3×1×1×256 = 795(3个特征层*(3*3的卷积核)),卷积深度参数通常取为1
乘法运算次数降低
对比一下不同卷积的乘法次数:
- 普通卷积计算量为:
- Depthwise计算量为:
- Pointwise计算量为:
通过Depthwise+Pointwise的拆分,相当于将普通卷积的计算量压缩为:
通道区域分离
深度可分离卷积将以往普通卷积操作同时考虑通道和区域改变(卷积先只考虑区域,然后再考虑通道),实现了通道和区域的分离。
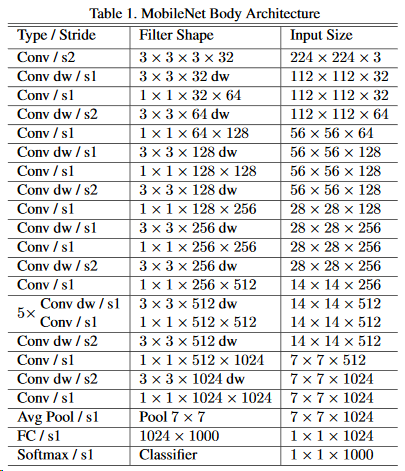
三、Mobilenet v1
Mobilenet v1利用深度可分离卷积进行加速,其架构如下,
还可以对所有卷积层 数量统一乘以缩小因子
(其中
)以压缩网络。这样Depthwise+Pointwise总计算量可以进一降低为:
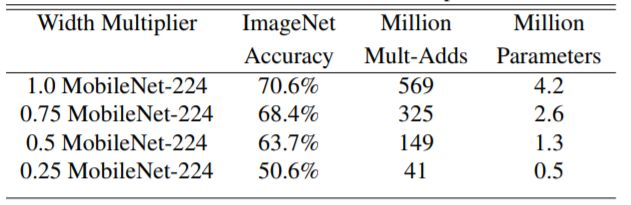
当然,压缩网络计算量肯定是有代价的。下图展示了 不同时Mobilenet v1在ImageNet上的性能。可以看到即使
时Mobilenet v1在ImageNet上依然有63.7%的准确度。
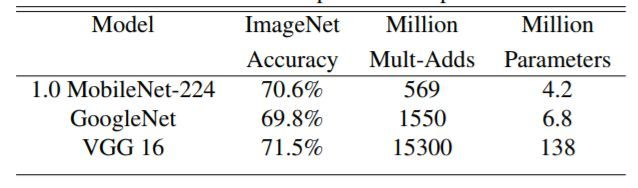
下图展示Mobilenet v1 与GoogleNet和VGG16的在输入分辨率
情况下,准确度差距非常小,但是计算量和参数量都小很多。同时原文也给出了以Mobilenet v1提取特征的SSD/Faster R-CNN在COCO数据集上的性能。
结构实现一探
在实现代码中(链接见本文开头),作者使用具名元组存储了网络结构信息,
Conv = namedtuple('Conv', ['kernel', 'stride', 'depth'])
DepthSepConv = namedtuple('DepthSepConv', ['kernel', 'stride', 'depth'])
# MOBILENETV1_CONV_DEFS specifies the MobileNet body
MOBILENETV1_CONV_DEFS = [
Conv(kernel=[3, 3], stride=2, depth=32),
DepthSepConv(kernel=[3, 3], stride=1, depth=64),
DepthSepConv(kernel=[3, 3], stride=2, depth=128),
DepthSepConv(kernel=[3, 3], stride=1, depth=128),
DepthSepConv(kernel=[3, 3], stride=2, depth=256),
DepthSepConv(kernel=[3, 3], stride=1, depth=256),
DepthSepConv(kernel=[3, 3], stride=2, depth=512),
DepthSepConv(kernel=[3, 3], stride=1, depth=512),
DepthSepConv(kernel=[3, 3], stride=1, depth=512),
DepthSepConv(kernel=[3, 3], stride=1, depth=512),
DepthSepConv(kernel=[3, 3], stride=1, depth=512),
DepthSepConv(kernel=[3, 3], stride=1, depth=512),
DepthSepConv(kernel=[3, 3], stride=2, depth=1024),
DepthSepConv(kernel=[3, 3], stride=1, depth=1024)
]
然后,在生成结构中迭代这个具名元组列表,根据信息生成网路结构,这仅仅给出深度可分离层的实现部分,
elif isinstance(conv_def, DepthSepConv):
end_point = end_point_base + '_depthwise' # By passing filters=None
# separable_conv2d produces only a depthwise convolution layer
if use_explicit_padding:
net = _fixed_padding(net, conv_def.kernel, layer_rate)
net = slim.separable_conv2d(net, None, conv_def.kernel, # <---Depthwise
depth_multiplier=1,
stride=layer_stride,
rate=layer_rate,
scope=end_point) end_points[end_point] = net
if end_point == final_endpoint:
return net, end_points
end_point = end_point_base + '_pointwise'
net = slim.conv2d(net, depth(conv_def.depth), [1, 1], # <---Pointwise
stride=1,
scope=end_point)
四、相关框架实现
TensorFlow 分步执行
顺便一提,tf的实现可以接收rate参数,即可以采用空洞卷积的方式进行操作。
1、depthwise_conv2d 分离卷积部分
我们定义一张4*4的双通道图片
import tensorflow as tf img1 = tf.constant(value=[[[[1],[2],[3],[4]],
[[1],[2],[3],[4]],
[[1],[2],[3],[4]],
[[1],[2],[3],[4]]]],dtype=tf.float32) img2 = tf.constant(value=[[[[1],[1],[1],[1]],
[[1],[1],[1],[1]],
[[1],[1],[1],[1]],
[[1],[1],[1],[1]]]],dtype=tf.float32) img = tf.concat(values=[img1,img2],axis=3) img
<tf.Tensor 'concat_1:0' shape=(1, 4, 4, 2) dtype=float32>
使用3*3的卷积核,输入channel为2,输出channel为2(卷积核数目为2),
filter1 = tf.constant(value=0, shape=[3,3,1,1],dtype=tf.float32)
filter2 = tf.constant(value=1, shape=[3,3,1,1],dtype=tf.float32)
filter3 = tf.constant(value=2, shape=[3,3,1,1],dtype=tf.float32)
filter4 = tf.constant(value=3, shape=[3,3,1,1],dtype=tf.float32)
filter_out1 = tf.concat(values=[filter1,filter2],axis=2)
filter_out2 = tf.concat(values=[filter3,filter4],axis=2)
filter = tf.concat(values=[filter_out1,filter_out2],axis=3) filter
<tf.Tensor 'concat_4:0' shape=(3, 3, 2, 2) dtype=float32>
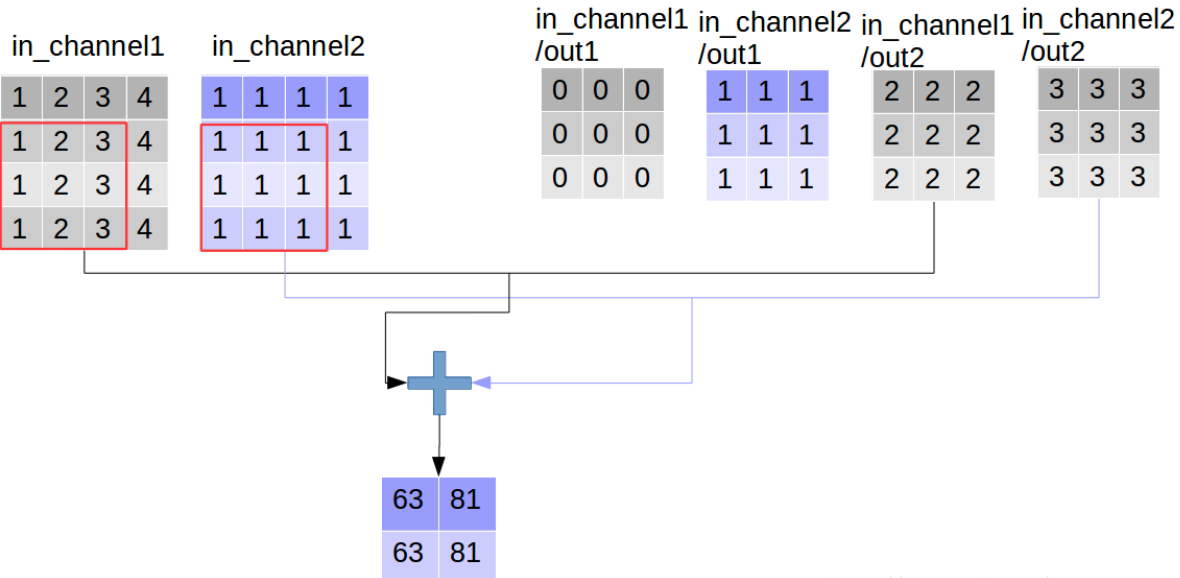
同时执行卷积操作,和深度可分离卷积操作,
out_img_conv = tf.nn.conv2d(input=img, filter=filter,
strides=[1,1,1,1], padding='VALID')
out_img_depthwise = tf.nn.depthwise_conv2d(input=img,
filter=filter, strides=[1,1,1,1],
rate=[1,1], padding='VALID') with tf.Session() as sess:
res1 = sess.run(out_img_conv)
res2 = sess.run(out_img_depthwise)
print(res1, '\n', res1.shape)
print(res2, '\n', res2.shape)
[[[[ 9. 63.]
[ 9. 81.]] [[ 9. 63.]
[ 9. 81.]]]]
(1, 2, 2, 2) # 《---------- [[[[ 0. 36. 9. 27.]
[ 0. 54. 9. 27.]] [[ 0. 36. 9. 27.]
[ 0. 54. 9. 27.]]]]
(1, 2, 2, 4)# 《----------
对比输出shape,depthwise_conv2d输出的channel数目为in_channel * 卷积核数目,每一个卷积核对应通道都会对对应的channel进行一次卷积,所以输出通道数更多,
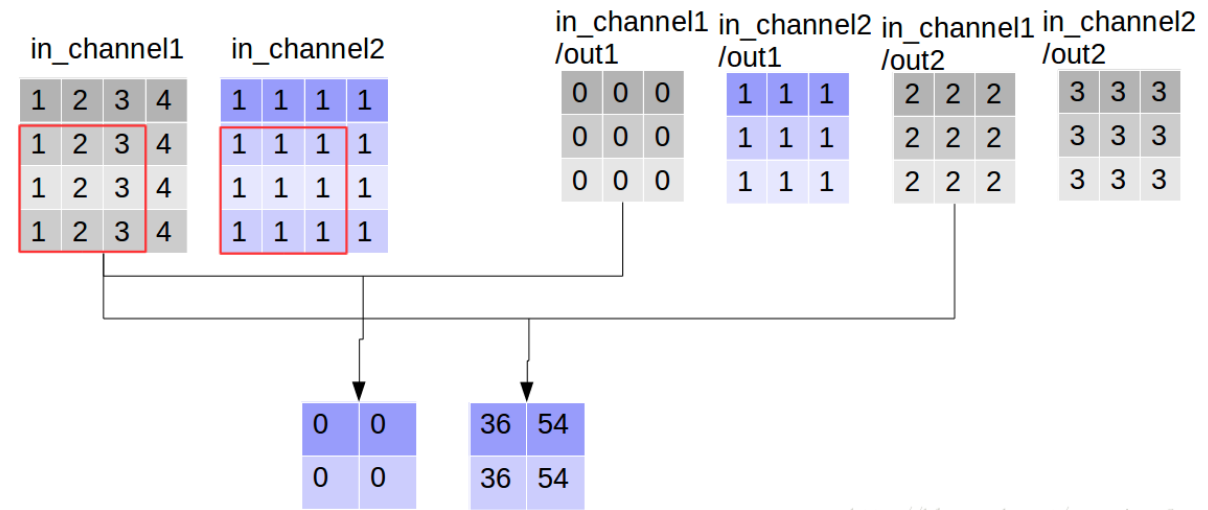
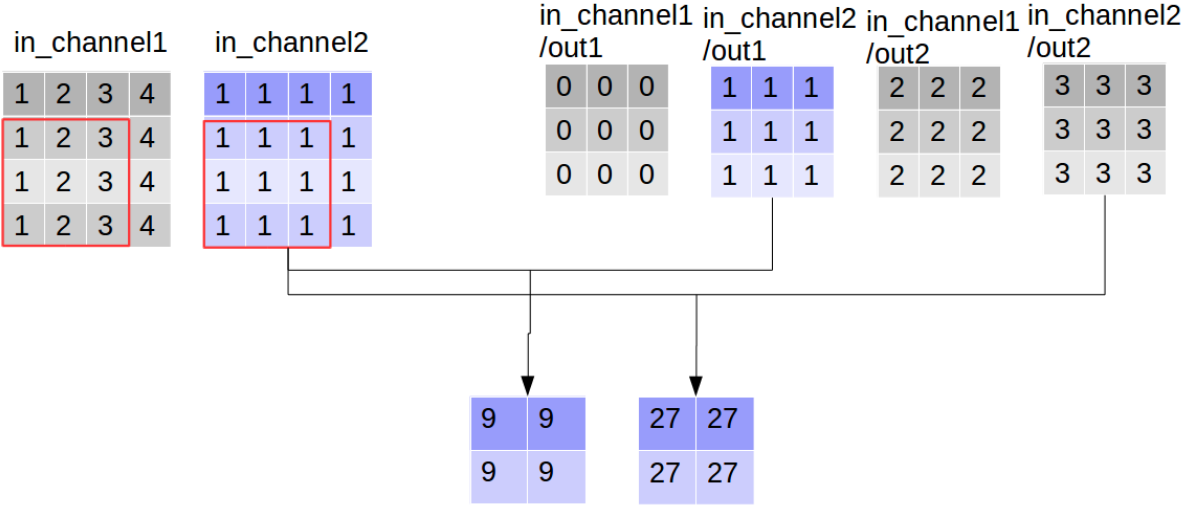
看到这里大家可能会误解深度可分离卷积的输出通道数大于普通卷积,其实这只是“分离”部分,后面还有组合的步骤,而普通卷积只不过直接完成了组合:通过对应点相加,将四个卷积中间结果合并为卷积核个数(这里是2)
2、合并特征
合并过程如下,可分离卷积中的合并过程变成可学习的了,使用一个1*1的普通卷积进行特征合并,
point_filter = tf.constant(value=1, shape=[1,1,4,4],dtype=tf.float32)
out_img_s = tf.nn.conv2d(input=out_img_depthwise, filter=point_filter, strides=[1,1,1,1], padding='VALID')
with tf.Session() as sess:
res3 = sess.run(out_img_s)
print(res3, '\n', res3.shape)
[[[[ 72. 72. 72. 72.]
[ 90. 90. 90. 90.]] [[ 72. 72. 72. 72.]
[ 90. 90. 90. 90.]]]]
(1, 2, 2, 4)
TensorFlow 一步执行
out_img_se = tf.nn.separable_conv2d(input=img,
depthwise_filter=filter,
pointwise_filter=point_filter,
strides=[1,1,1,1], rate=[1,1], padding='VALID') with tf.Session() as sess:
print(sess.run(out_img_se))
[[[[ 72. 72. 72. 72.]
[ 90. 90. 90. 90.]][[ 72. 72. 72. 72.]
[ 90. 90. 90. 90.]]]]
(1, 2, 2, 4)
slim 库API介绍
def separable_convolution2d(
inputs,
num_outputs,
kernel_size,
depth_multiplier=1,
stride=1,
padding='SAME',
data_format=DATA_FORMAT_NHWC,
rate=1,
activation_fn=nn.relu,
normalizer_fn=None,
normalizer_params=None,
weights_initializer=initializers.xavier_initializer(),
pointwise_initializer=None,
weights_regularizer=None,
biases_initializer=init_ops.zeros_initializer(),
biases_regularizer=None,
reuse=None,
variables_collections=None,
outputs_collections=None,
trainable=True,
scope=None): """一个2维的可分离卷积,可以选择是否增加BN层。
这个操作首先执行逐通道的卷积(每个通道分别执行卷积),创建一个称为depthwise_weights的变量。如果num_outputs
不为空,它将增加一个pointwise的卷积(混合通道间的信息),创建一个称为pointwise_weights的变量。如果
normalizer_fn为空,它将给结果加上一个偏置,并且创建一个为biases的变量,如果不为空,那么归一化函数将被调用。
最后再调用一个激活函数然后得到最终的结果。 Args:
inputs: 一个形状为[batch_size, height, width, channels]的tensor
num_outputs: pointwise 卷积的卷积核个数,如果为空,将跳过pointwise卷积的步骤.
kernel_size: 卷积核的尺寸:[kernel_height, kernel_width],如果两个的值相同,则可以为一个整数。
depth_multiplier: 卷积乘子,即每个输入通道经过卷积后的输出通道数。总共的输出通道数将为:
num_filters_in * depth_multiplier。
stride:卷积步长,[stride_height, stride_width],如果两个值相同的话,为一个整数值。
padding: 填充方式,'VALID' 或者 'SAME'.
data_format:数据格式, `NHWC` (默认) 和 `NCHW`
rate: 空洞卷积的膨胀率:[rate_height, rate_width],如果两个值相同的话,可以为整数值。如果这两个值
任意一个大于1,那么stride的值必须为1.
activation_fn: 激活函数,默认为ReLU。如果设置为None,将跳过。
normalizer_fn: 归一化函数,用来替代biase。如果归一化函数不为空,那么biases_initializer
和biases_regularizer将被忽略。 biases将不会被创建。如果设为None,将不会有归一化。
normalizer_params: 归一化函数的参数。
weights_initializer: depthwise卷积的权重初始化器
pointwise_initializer: pointwise卷积的权重初始化器。如果设为None,将使用weights_initializer。
weights_regularizer: (可选)权重正则化器。
biases_initializer: 偏置初始化器,如果为None,将跳过偏置。
biases_regularizer: (可选)偏置正则化器。
reuse: 网络层和它的变量是否可以被重用,为了重用,网络层的scope必须被提供。
variables_collections: (可选)所有变量的collection列表,或者是一个关键字为变量值为collection的字典。
outputs_collections: 输出被添加的collection.
trainable: 变量是否可以被训练
scope: (可选)变量的命名空间。
Returns:
代表这个操作的输出的一个tensor"""
『高性能模型』深度可分离卷积和MobileNet_v1的更多相关文章
- 『高性能模型』HetConv: HeterogeneousKernel-BasedConvolutionsforDeepCNNs
论文地址:HetConv 一.现有网络加速技术 1.卷积加速技术 作者对已有的新型卷积划分如下:标准卷积.Depthwise 卷积.Pointwise 卷积.群卷积(相关介绍见『高性能模型』深度可分离 ...
- 『高性能模型』轻量级网络ShuffleNet_v1及v2
项目实现:GitHub 参考博客:CNN模型之ShuffleNet v1论文:ShuffleNet: An Extremely Efficient Convolutional Neural Netwo ...
- 『高性能模型』轻量级网络MobileNet_v2
论文地址:MobileNetV2: Inverted Residuals and Linear Bottlenecks 前文链接:『高性能模型』深度可分离卷积和MobileNet_v1 一.Mobil ...
- 『高性能模型』卷积复杂度以及Inception系列
转载自知乎:卷积神经网络的复杂度分析 之前的Inception学习博客: 『TensorFlow』读书笔记_Inception_V3_上 『TensorFlow』读书笔记_Inception_V3_下 ...
- 『高性能模型』Roofline Model与深度学习模型的性能分析
转载自知乎:Roofline Model与深度学习模型的性能分析 在真实世界中,任何模型(例如 VGG / MobileNet 等)都必须依赖于具体的计算平台(例如CPU / GPU / ASIC 等 ...
- Github 恶搞教程(一起『玩坏』自己的 Github 吧)
最近在伯乐在线读到一篇趣文,<如何在 Github『正确』做贡献>,里面各种能人恶搞 Github 的『Public contributions』,下面截取几个小伙伴的战绩: 顺藤摸瓜,发 ...
- 2017-2018-2 165X 『Java程序设计』课程每周成绩公布
2017-2018-2 165X 『Java程序设计』课程 每周成绩公布 本博客将跟随教学进度不定期更新,每次更新后将在课程群公布.如对成绩有疑问,请于公布成绩后的1天之内联系助教,进行审核确认. - ...
- 20172325『Java程序设计』课程 结对编程练习_四则运算第三周阶段总结
20172325『Java程序设计』课程 结对编程练习_四则运算第三周阶段总结 结对伙伴 学号:20172306 姓名:刘辰 在这次项目的完成过程中刘辰同学付出了很多,在代码的实践上完成的很出色,在技 ...
- 2017-2018-2 1723 『Java程序设计』课程 结对编程练习-四则运算-准备阶段
2017-2018-2 1723 『Java程序设计』课程 结对编程练习-四则运算-准备阶段 在一个人孤身奋斗了将近半个学期以后,终于迎来的我们的第一次团队协作共同编码,也就是,我们的第一个结对编程练 ...
随机推荐
- Apache ab并发负载压力测试(python+django+mysql+apache)
如标题,大家都知道秒杀中存在高并发使库存骤然为0,但在我们个人PC或小区域内是模拟不出这样的情景 现在利用 Apache ab并发负载压力测试 1,数据库建入库存字段并映射模型 2,view编写脚本 ...
- Linux 安装python3.7.0
我这里使用的时centos7-mini,centos系统本身默认安装有python2.x,版本x根据不同版本系统有所不同,可通过 python --V 或 python --version 查看系统自 ...
- 20165330 2017-2018-2 《Java程序设计》第7周学习总结
课本知识总结 第十一章 JDBC与MySQL数据库 安装XAMPP软件及启动MySQL 下载链接:XAMPP 安装步骤:参考教程xampp新手学习指引(windows示例) 启动MySQL:打开系统c ...
- Python静态方法(staticmethod)和类方法(classmthod)
Python静态方法(staticmethod)和类方法(classmthod)翻了翻之前的笔记,也刚好看到一篇不错的blog,关于静态方法和类方法的,方便以后查阅,就写在这里了,废话不多说,直接上代 ...
- Linux下安装whl文件
直接使用pip安装: [root@mycentos ~]# pip install *.whl
- 揭开yield关键字的神秘面纱
写在前言 经常会看见,python函数中带有yield关键字,那么yield是什么,有什么作用? 答案:可以理解yield是一个生成器: 作用:遇到yield关键字,函数会直接返回yield值,相当于 ...
- Vue系列之 => 命名视图实现经典布局
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <meta name ...
- Oracle表空间迁移Move Tablespace
move一个表到另外一个表空间时,索引不会跟着一起move,而且会失效.(LOB类型例外) move分为: *普通表move *分区表move *LONG,LOB大字段类型move来进行测试和说明. ...
- photoshop cc 安装失败 2%
photoshop cc 安装失败 2% C盘--Program Files---Common Files--Adobe--caps ,把这个文件夹中的文件全部删除,然后再安装 C:\Pr ...
- 常用git命令总结 初始化git库操作 git 子模块
查看 git status 查看状态 Gitk 界面各个版本查看 添加 Git add filename 添加指定文件 Git add . 操作未暂存的文件 Git add -A 操作所有文件 包括删 ...
