python函数(一)调用函数
在python中内置了很多函数或者类,比如:int,str,list,tuple,等。当然也可以自建函数,这个放在后文讨论。原理如下:
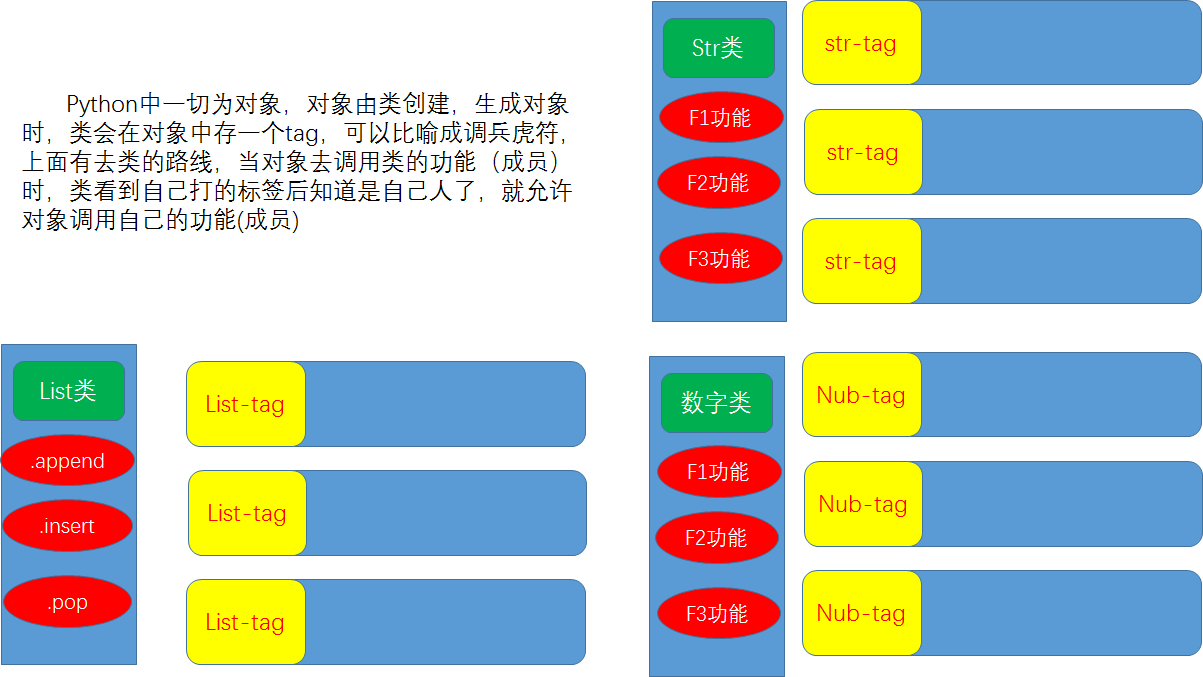
其实python中的类和方法非常非常多,这里只是以点带面,提供一个学习的方法。
(一)int
使用举例
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- age = -19 #其实是执行了一个__init__的过程。
print (type(age)) #打印age的类型
age = int(age)
re = age.__float__() #将age的类型变成浮点类型,注,本来是int类型。
print(type(re)) #打印re的类型
reslutd = age.__abs__() #绝对值.(-19)=19。 <===>...reslutd=abs(age)
reslut = reslutd.__divmod__(3) #divmod得出商和余数,19/4。在写扉页的时候会用到。<===>...reslutd=divmod(age)
reslut_fan = reslutd.__rdivmod__(4) #反向求商和余数。4/19
print(reslutd,reslut_fan,reslut) #结果
'''
<class 'int'>
<class 'float'>
19 (0, 4) (6, 1)
'''
按住Ctrl,点击int,可以在builtins模块中看到int成员,其中int成员里大部分都是带下划线的,这一类的功能大多是通过内置方法就可以直接执行(例子参考上面abs,divmod和下文中add),请看:
def __abs__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" abs(self) """
pass
#取绝对值 def __add__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self+value. """
pass
#相加,print(1+1)其实就是调用了“int”中内置的__add__这个函数,所以可以直接执行。但过程依然是:创建对象,调用方法,得到结果。 def __and__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self&value. """
pass
#融合
def __bool__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" self != 0 """
pass
#变成波尔类型 def __pow__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return pow(self, value, mod). """
pass
#取指数 .... def bit_length(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
int.bit_length() -> int Number of bits necessary to represent self in binary.
>>> bin(37)
'0b100101'
>>> (37).bit_length()
6
"""
return 0
#返回用最少多少位可以表示当前数字
#举例:
a= 59
result = a.bit_length()
print(result)
#结果
6
int成员
(二)str
先来个例题
#字符串。str如‘张洪震’‘zhang’。举例:
name = 'zhang'
name = str('zhang') #str执行时其本质是执行的.__init__方法.按住Ctrl,点击“str” ,查看有哪些成员
print(type(name)) #tpye.快速获取类
print(dir(name)) #dir.快速获取这个类里面有哪些成员
a = name.__contains__('ang') #a<=>b,a和b其实是一样的。
b = 'zh' in name
print(a,b) #结果:
'''
<class 'str'>
['__add__', '__class__', '__contains__', '__delattr__', '__dir__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__getitem__', '__getnewargs__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__init__', '__iter__', '__le__', '__len__', '__lt__', '__mod__', '__mul__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__rmod__', '__rmul__', '__setattr__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', 'capitalize', 'casefold', 'center', 'count', 'encode', 'endswith', 'expandtabs', 'find', 'format', 'format_map', 'index', 'isalnum', 'isalpha', 'isdecimal', 'isdigit', 'isidentifier', 'islower', 'isnumeric', 'isprintable', 'isspace', 'istitle', 'isupper', 'join', 'ljust', 'lower', 'lstrip', 'maketrans', 'partition', 'replace', 'rfind', 'rindex', 'rjust', 'rpartition', 'rsplit', 'rstrip', 'split', 'splitlines', 'startswith', 'strip', 'swapcase', 'title', 'translate', 'upper', 'zfill']
True True
来看下其他的成员:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- a = 'abc'
def capitalize(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
S.capitalize() -> str
#让第一个字母大写
"""
return ""
a1 = a.capitalize()
print(a1)
#结果
#Abc def center(self, width, fillchar=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
#width宽度;fillchar=None,填充字符,默认为空格
"""
S.center(width[, fillchar]) -> str
Return S centered in a string of length width. Padding is
done using the specified fill character (default is a space默认为空格)
"""
return ""
a2 = a.center(10) #让a这个字符串宽度为10.且abc位于中央。
print(a2)
# abc
a3 = a.center(10,'@') #以@为填充符。
print(a3)
#@@@abc@@@@ def count(self, sub, start=None, end=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
#统计子序列出现的次数。
#sub附属的,起始位置,结束为止
S.count(sub[, start[, end]]) -> int Return the number of non-overlapping occurrences of substring sub in
string S[start:end]. Optional arguments start and end are
interpreted as in slice notation.
"""
return 0
a4 = a.count('a',0,2) #计算从0-2之间有几个a。
print(a4)
# def encode(self, encoding='utf-8', errors='strict'): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
#转码,encoding是编码方式;默认转成utf-8。errors是错误处理方式。
S.encode(encoding='utf-8', errors='strict') -> bytes
"""
return b"" #返回为b"",就是以b开头。
A = '张洪震'
a5 = A.encode('gbk',errors='ignore') #转成gbk编码,忽略错误。注:其实内部还是从utf-8转为Unicode,再从Unicode转为gbk。
print(a5)
#b'\xd5\xc5\xba\xe9\xd5\xf0' def endswith(self, suffix, start=None, end=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
S.endswith(suffix[, start[, end]]) -> bool
#suffix后缀,
suffix can also be a tuple of strings to try.#后缀也可以是一个元组。
"""
return False #返回正误
a6 = a.endswith('c',0,3) #这里注意一下,是0<=suffix position.<3,
#a6 = a.endswith('c',0,2),这样写会报错。
print(a6)
#True def startswith(self, prefix, start=None, end=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
S.startswith(prefix[, start[, end]]) -> bool
Return True if S starts with the specified prefix, False otherwise.
With optional start, test S beginning at that position.
With optional end, stop comparing S at that position.
prefix can also be a tuple of strings to try.
判断是否是以“。。”开头,可以指定开头和结尾的位置,
"""
return False def expandtabs(self, tabsize=8): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
S.expandtabs(tabsize=8) -> str
Return a copy#副本of S where all tab characters are expanded using spaces.
If tabsize is not given, a tab size of 8 characters is assumed.
#返回一个用空格代替tab键的副本。
"""
return ""
B = 'zhan g'
b7 = B.expandtabs()
print(b7)
#zhan g def find(self, sub, start=None, end=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
#查找出sub所在的位置。
S.find(sub[, start[, end]]) -> int
Return -1 on failure.#如果失败的话返回-1.
"""
return 0
a8 =a.find('c',0,3) #在0-2的位置找c。
a9 =a.index('b') #index和find都是找,index找不到的话会直接报错。
print(a8,a9)
#2 1 def format(*args, **kwargs): # known special case of str.format
"""
S.format(*args, **kwargs) -> str
Return a formatted version of S, using substitutions from args and kwargs.
返回一个格式化的字符串,用替换的来自于传参。
The substitutions are identified by braces ('{' and '}').
被替换的东西用{}来定义
"""
pass
C ='zhen,{0},{1}'
a10 = C.format('是四个字母','对') #传参为“是四个字母”
print(a10)
#zhen,是四个字母,对
D ='zhen,{dd},{ddd}'
a10 = D.format(dd='是四个字母',ddd='对') #做一个动态对应
print(a10)
#zhen,是四个字母,对 #以is开头的大都是判断,举一个例子
def isalnum(self): # 判断是否是文字数字
return False def join(self, iterable): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
#主要用来做拼接
S.join(iterable) -> str
Return a string which is the concatenation of the strings in the
iterable.
The separator between elements is S.元素之间的分隔符是S.。
"""
return ""
E=['ni hao','zhang','chi le ma'] #定义一个列表
a11= ",".join(E) #让“E”中的字符串以“,”为分割符相连。
print(a11)
#ni hao,zhang,chi le ma def ljust(self, width, fillchar=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
S.ljust(width[, fillchar]) -> str
左对齐。参数为宽度,填充字段.默认为空
"""
return "" def rjust(self, width, fillchar=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
S.rjust(width[, fillchar]) -> str
右对齐。参数为宽度,填充字段,默认为空
"""
return ""
F = 'abc'
a12=F.ljust(7,'#') #让F的宽度为7个字符,如果不够7个,那么在字符串的右边填充上“#”把字符串“挤”至左对齐。
print(a12)
a13=F.rjust(6,'$') #让F的宽度为6个字符,如果不够6个,那么在字符串的左边填充上“#”把字符串“挤”至右对齐。
print(a13)
#结果
'''
abc####
$$$abc
''' def lower(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
S.lower() -> str
Return a copy of the string S converted to lowercase.
返回一个字符串的小写副本。
"""
return ""
def upper(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
S.upper() -> str
大写
Return a copy of S converted to uppercase.
"""
return "" def strip(self, chars=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
S.strip([chars]) -> str
Return a copy of the string S with leading and trailing whitespace removed.
If chars is given and not None, remove characters in chars instead.
删除开头和结尾空格,如果给定字符或不是空的,那么删除给定字符
"""
return ""
def lstrip(self, chars=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
S.lstrip([chars]) -> str
Return a copy of the string S with leading whitespace removed.
If chars is given and not None, remove characters in chars instead.
返回一个去掉字符串的开头空格的副本
如果给定字符而不是空的,则删除给定字符。
"""
return ""
a14=a.lstrip('a')
print(a14)
def rstrip(self, chars=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
S.rstrip([chars]) -> str
Return a copy of the string S with trailing whitespace removed.
If chars is given and not None, remove characters in chars instead.
返回一个去掉字符串的结尾空格的副本
如果给定字符而不是空的,则删除给定字符。
"""
return ""
a15=a.rstrip('c')
print(a15) def partition(self, sep): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
S.partition(sep) -> (head, sep, tail)
Search for the separator sep in S, and return the part before it,
the separator itself, and the part after it. If the separator is not
found, return S and two empty strings.
在字符串中搜索分隔符,并返回它前面的部分、分隔符本身和后面的部分。如果找不到分隔符,返回s和两个空字符串。
"""
pass
a16= a.partition('b') #以b为分隔符
print(a16)
#('a', 'b', 'c')
a17= a.partition('d') #以d为分割符
print(a17)
#('abc', '', '') def replace(self, old, new, count=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
S.replace(old, new[, count]) -> str
old replaced by new. If the optional argument count is
given, only the first count occurrences are replaced.
"""
return ""
h='aaaaaaa'
h1= h.replace('a','b',3) #用b替换a,个数为3
h2=h.replace('a','',2)
print(h1,h2)
#bbbaaaa 99aaaaa def split(self, sep=None, maxsplit=-1): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
S.split(sep=None, maxsplit=-1) -> list of strings
分割。
"""
i='zhang hong z hen'
i1=i.split('h',2) #指定h为分隔符,i中有3个h,指定最大为2个,所以,只有两个作为分割符了
i2=i.split() #没有指定,则以空格为分割符并删除空格
print(i1,i2)
#['z', 'ang ', 'ong z hen'] ['zhang', 'hong', 'z', 'hen'] def swapcase(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
S.swapcase() -> str
Return a copy of S with uppercase characters converted to lowercase
and vice versa.
如果是大写,那么给它换成小写,反之亦然。
"""
return "" def title(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
S.title() -> str Return a titlecased version of S, i.e. words start with title case
characters, all remaining cased characters have lower case.
"""
return ""
str其他成员
通过上面可以看出其实python的解释很清晰简洁,真的难懂的话可以通过翻译软件翻译出来,一般情况下是可以看懂的。
(三)list列表
如:['zhang']、[11,'hong','zhen']
class list(object):
"""
list() -> new empty list
list(iterable) -> new list initialized from iterable's items
"""
def append(self, p_object): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" L.append(object) -> None -- append object to end """ #从列表末尾加入元素
pass def clear(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" L.clear() -> None -- remove all items from L """ #清除所有
pass def copy(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" L.copy() -> list -- a shallow copy of L """ #浅拷贝
return [] def count(self, value): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" L.count(value) -> integer -- return number of occurrences of value """
#计数
return 0 def extend(self, iterable): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" L.extend(iterable) -> None -- extend list by appending elements from the iterable """
#扩展,将新列表元素加到老列表中 pass def index(self, value, start=None, stop=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
L.index(value, [start, [stop]]) -> integer -- return first index of value.
Raises ValueError if the value is not present. #下标,也就是索引号
"""
return 0 def insert(self, index, p_object): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" L.insert(index, object) -- insert object before index """ #指定位置插入元素
pass def pop(self, index=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
L.pop([index]) -> item -- remove and return item at index (default last).
Raises IndexError if list is empty or index is out of range. #移除,参数为指定位置
"""
pass def remove(self, value): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
L.remove(value) -> None -- remove first occurrence of value.
Raises ValueError if the value is not present. #移除,参数为指定的值
"""
pass def reverse(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" L.reverse() -- reverse *IN PLACE* """ #反转,即倒序。
pass def sort(self, key=None, reverse=False): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" L.sort(key=None, reverse=False) -> None -- stable sort *IN PLACE* """ #排序。
pass
list成员
(四)tuple元组
如:(11,22,)('zhang',[11,22,33],)
class tuple(object):
"""
tuple() -> empty tuple
tuple(iterable) -> tuple initialized from iterable's items If the argument is a tuple, the return value is the same object.
"""
def count(self, value): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" T.count(value) -> integer -- return number of occurrences of value """#计数
return 0 def index(self, value, start=None, stop=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
T.index(value, [start, [stop]]) -> integer -- return first index of value.#返回一个索引
Raises ValueError if the value is not present.
"""
return 0
#例:
a=(('zhang'),[11,22,33],)
re=a.index('zhang')
print(type(a),re) #<class 'tuple'> 0
tuple成员
(五)dict字典
如:{'张':'shuai','host':'Cmelo.com','123':'abc'}
使用:
name1=[11,22,33,44,55,66,77,88,99]
name2=[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]
dict['k1']=name1 #<=>dic=dict(k1=name1)
dict['k2']=name2 #<=>dic2=dict(k2=name2)
dict
dd={'张':'shuai','host':'Cmelo.com','':'abc'}
class dict(object):
"""
dict() -> new empty dictionary
dict(mapping) -> new dictionary initialized from a mapping object's
(key, value) pairs
dict(iterable) -> new dictionary initialized as if via:
d = {}
for k, v in iterable:
d[k] = v
dict(**kwargs) -> new dictionary initialized with the name=value pairs
in the keyword argument list. For example: dict(one=1, two=2)
"""
def clear(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" D.clear() -> None. Remove all items from D. """
pass
def copy(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" D.copy() -> a shallow copy of D """
pass
@staticmethod # known case
def fromkeys(*args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Returns a new dict with keys from iterable and values equal to value. """
pass
def get(self, k, d=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" D.get(k[,d]) -> D[k] if k in D, else d. d defaults to None. 如果key在D中就是key,否则就是设置的d。d默认是空"""
pass
#例
dd={'张':'shuai','host':'Cmelo.com','':'abc'}
kk= dd.get('li','sorry,meiyouzhaodao')
print(kk)
#sorry,meiyouzhaodao
def items(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" D.items() -> a set-like object providing a view on D's items 输出所有的字典对儿"""
pass
def keys(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" D.keys() -> a set-like object providing a view on D's keys 输出所有的key值"""
pass
def values(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" D.values() -> an object providing a view on D's values 输出所有的value值。"""
pass
def pop(self, k, d=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
D.pop(k[,d]) -> v, remove specified key and return the corresponding value.给定k值,删除相应的value
If key is not found, d is returned if given, otherwise KeyError is raised如果key没有找到,如果给了d的话d会输出。否则,报错,
"""
pass
#例:
dd={'张':'shuai','host':'Cmelo.com','':'abc'}
aa= dd.pop('li','sorry,meiyouzhaodao')
bb=dd.pop()
print(aa,bb)
#sorry,meiyouzhaodao
#bb=dd.pop()
#TypeError: pop expected at least 1 arguments, got 0
def popitem(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
D.popitem() -> (k, v), remove and return some (key, value) pair as a
2-tuple; but raise KeyError if D is empty. #随机删除一个对儿,如果参数是空的话会报错
"""
pass
def setdefault(self, k, d=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" D.setdefault(k[,d]) -> D.get(k,d), also set D[k]=d if k not in D 给设置一个默认值"""
pass
def update(self, E=None, **F): # known special case of dict.update
"""
D.update([E, ]**F) -> None. Update D from dict/iterable E and F.
If E is present and has a .keys() method, then does: for k in E: D[k] = E[k]
If E is present and lacks a .keys() method, then does: for k, v in E: D[k] = v
In either case, this is followed by: for k in F: D[k] = F[k]
"""
pass
def __contains__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" True if D has a key k, else False. """
pass
def __delitem__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Delete self[key]. """
pass
def __eq__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self==value. """
pass
def __getattribute__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return getattr(self, name). """
pass
def __getitem__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__getitem__(y) <==> x[y] """
pass
def __ge__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self>=value. """
pass
def __gt__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self>value. """
pass
def __init__(self, seq=None, **kwargs): # known special case of dict.__init__
"""
dict() -> new empty dictionary
dict(mapping) -> new dictionary initialized from a mapping object's
(key, value) pairs
dict(iterable) -> new dictionary initialized as if via:
d = {}
for k, v in iterable:
d[k] = v
dict(**kwargs) -> new dictionary initialized with the name=value pairs
in the keyword argument list. For example: dict(one=1, two=2)
# (copied from class doc)
"""
pass
def __iter__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Implement iter(self). """
pass
def __len__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return len(self). """
pass
def __le__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self<=value. """
pass
def __lt__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self<value. """
pass
@staticmethod # known case of __new__
def __new__(*args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Create and return a new object. See help(type) for accurate signature. """
pass
def __ne__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self!=value. """
pass
def __repr__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return repr(self). """
pass
def __setitem__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Set self[key] to value. """
pass
def __sizeof__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" D.__sizeof__() -> size of D in memory, in bytes """
pass
__hash__ = None
dict成员
python函数(一)调用函数的更多相关文章
- python中如何调用函数交换两个变量的值
python中如何调用函数交换两个变量的值 所有代码来在python3.7.1版本实现 以下实例通过用户输入两个变量,并相互交换: 方法一: def swap(a,b): # 创建临时变量,并交换 ...
- javascript学习笔记(二):定义函数、调用函数、参数、返回值、局部和全局变量
定义函数.调用函数.参数.返回值 关键字function定义函数,格式如下: function 函数名(){ 函数体 } 调用函数.参数.返回值的规则和c语言规则类似. <!DOCTYPE ht ...
- python可变参数调用函数的问题
已使用python实现的一些想法,近期使用python这种出现的要求,它定义了一个函数,第一种是一般的参数,第二个参数是默认,并有可变参数.在第一项研究中python时间,不知道keyword可变参数 ...
- 『Python』为什么调用函数会令引用计数+2
一.问题描述 Python中的垃圾回收是以引用计数为主,分代收集为辅,引用计数的缺陷是循环引用的问题.在Python中,如果一个对象的引用数为0,Python虚拟机就会回收这个对象的内存. sys.g ...
- Python 获取被调用函数名称,所处模块,被调用代码行
获取被调用函数名称,所处模块,被调用代码行 by:授客 QQ:1033553122 module2.py: #!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- _ ...
- python函数之调用函数
调用函数 python中内置了许多函数,我们可以直接调用,但需要注意的是参数的个数和类型一定要和函数一致,有时候不一致时,可以进行数据类型转换 1.abs()函数[求绝对值的函数,只接受一个参数] # ...
- Python基础笔记:函数:调用函数、定义函数、函数的参数、递归函数
一.定义一个求二元一次方程的根的函数 #Sublime Text import math def ee(a,b,c): delta=b*b-4*a*c if delta<0: return 'n ...
- python 获取当前调用函数名等log信息
import sys funcName = sys._getframe().f_back.f_code.co_name #获取调用函数名 lineNumber = sys._getframe().f_ ...
- Python 通过字符串调用函数、接近属性
需求:传入的是函数名.属性名,想通过字符串调用函数,接近属性. 通过字符串接近.变动属性 变量:model_name, field_name # 获取 model model = AppConfig. ...
- 总结javascript中的全局变量和局部变量的区别以及声明函数和调用函数的区别
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head lang="en"> <meta charset="utf-8&quo ...
随机推荐
- appium获取APP控件信息
uiautomatorviewer.bat 该文件位于SDK安装目录tools下,如笔者在“C:\Program Files (x86)\Android\android-sdk\tools”下,双击u ...
- 微信录音文件上传到服务器以及amr转化成MP3格式,linux上转换简单方法
微信公众号音频接口开发 根据业务需求,我们可能需要将微信录音保存到服务器,而通过微信上传语音接口上传到微信服务器的语音文件的有效期只有3天,所以需要将文件下载到我们自己的服务器. 上传语音接口 wx. ...
- 滴水穿石-01JAVA和C#的区别
排名不分先后,想到哪写到哪 1:数组的定义格式不同 java定义: 方式1: ] ; 方式2: ] ; C#中只有方式1 java有两种,C#只有一种 2:继承的实现关键字不同,同时java中实现接口 ...
- IDEA窗口重置
- Ubuntu16.04安装配置和使用ctags
Ubuntu16.04安装配置和使用ctags by ChrisZZ ctags可以用于在vim中的函数定义跳转.在ubuntu16.04下默认提供的ctags是很老很旧的ctags,快要发霉的版本( ...
- js模板引擎art-Template(以前的artTemplate)
使用js.jquery动态生成html会非常麻烦.现在的模板引擎可以很简单的解决这个问题.比如腾讯出的art-Template 官网:http://aui.github.io/art-template ...
- Give root password for maintenance(or type control -D to continue)
2017-09-30 18:12:08 1:错误如图,本来开机准备用一下虚拟机,就出现一个这,为啥记录一下呢,因为网上好多不是很靠谱. 原因可能是之前关闭虚拟机的时候不小心出现异常了: 2:解决办法: ...
- ExceptionLess的webAPI调用
引用 <package id="bootstrap" version="3.0.0" targetFramework="net461" ...
- Codeforces 177G2 Fibonacci Strings KMP 矩阵
原文链接https://www.cnblogs.com/zhouzhendong/p/CF117G2.html 题目传送门 - CF177G2 题意 定义斐波那契字符串如下: $s_1="a ...
- CodeForces 516A Drazil and Factorial 动态规划
原文链接http://www.cnblogs.com/zhouzhendong/p/8990592.html 题目传送门 - CodeForces 516A 题意 对于一个正整数$x$,$f(x)=x ...
