python项目练习
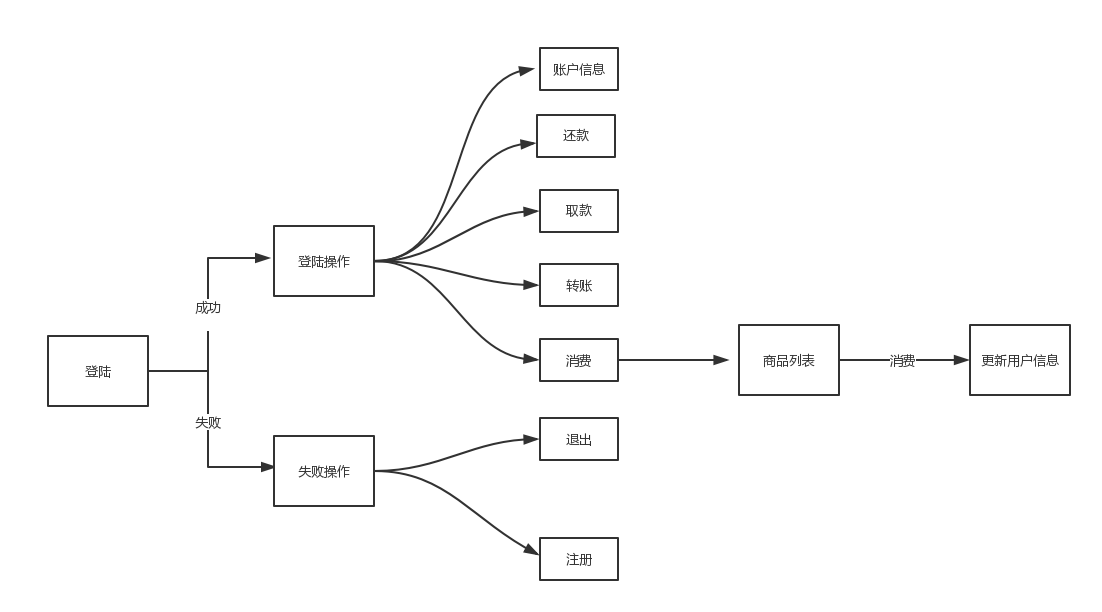
程序框图 (消费模块暂未写入)
bin:程序执行
- import os
- import sys
- base_dir = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)))
- print(base_dir)
- sys.path.append(base_dir)
- from core import main
- if __name__ == '__main__': #当作为脚本直接运行的时候,此时__name__等于__main__,当作为模块导入的时候,__name__为文件名但不带.py,故不运行if后语句。
- main.run()
atm.py
config:配置文件
- import os
- import sys
- import logging
- BASE_DIR = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)))
- DATABASE = {
- 'engine': 'file_storage', #support mysql,postgresql in the future
- 'name':'accounts',
- 'path': "%s/db" % BASE_DIR
- }
- LOG_LEVEL = logging.INFO
- LOG_TYPES = {
- 'transaction': 'transactions.log',
- 'access': 'access.log',
- '':'11111.log'
- }
- TRANSACTION_TYPE = {
- 'repay':{'action':'plus', 'interest':0},
- 'withdraw':{'action':'minus', 'interest':0.05},
- 'transfer':{'action':'minus', 'interest':0.05},
- 'consume':{'action':'minus', 'interest':0},
- }
settings
core:程序主要代码
- import json
- import time
- from core import db_handler
- from conf import settings
- def load_current_balance(account_id):
- '''
- return account balance and other basic info
- :param account_id:
- :return:
- '''
- db_path = db_handler.db_handler(settings.DATABASE)
- account_file = "%s/%s.json" %(db_path,account_id)
- with open(account_file) as f:
- acc_data = json.load(f)
- return acc_data
- def dump_account(account_data):
- '''
- after updated transaction or account data , dump it back to file db
- :param account_data:
- :return:
- '''
- db_path = db_handler.db_handler(settings.DATABASE)
- account_file = "%s/%s.json" %(db_path,account_data['id'])
- with open(account_file, 'w') as f:
- acc_data = json.dump(account_data,f)
- return True
accounts
- import os
- from core import db_handler
- from conf import settings
- from core import logger
- import json
- import time
- def acc_auth(account,password):
- '''
- account auth func
- :param account: credit account number
- :param password: credit card password
- :return: if passed the authentication , retun the account object, otherwise ,return None
- '''
- db_path = db_handler.db_handler(settings.DATABASE)
- account_file = "%s/%s.json" %(db_path,account)
- print(account_file) #base_dir + accounts + account.json
- if os.path.isfile(account_file): #判断文件名是否存在,存在执行下面语句
- with open(account_file,'r') as f:
- account_data = json.load(f)
- if account_data['password'] == password:
- exp_time_stamp = time.mktime(time.strptime(account_data['expire_date'], "%Y-%m-%d"))
- if time.time() >exp_time_stamp:
- print("\033[31;1mAccount [%s] has expired,please contact the back to get a new card!\033[0m" % account)
- else: #passed the authentication
- return account_data
- else:
- print("\033[31;1mAccount ID or password is incorrect!\033[0m")
- else:
- print("\033[31;1mAccount [%s] does not exist!\033[0m" % account)
- def acc_login(user_data,log_obj):
- '''
- account login func
- :user_data: user info data , only saves in memory
- :return:
- '''
- retry_count = 0
- while user_data['is_authenticated'] is not True and retry_count < 3 :
- account = input("\033[32;1maccount:\033[0m").strip()
- password = input("\033[32;1mpassword:\033[0m").strip()
- auth = acc_auth(account, password)
- if auth: #not None means passed the authentication
- user_data['is_authenticated'] = True
- user_data['account_id'] = account
- #print("welcome")
- return auth
- retry_count +=1
- else:
- log_obj.error("account [%s] too many login attempts" % account)
- exit()
登陆认证
- def file_db_handle(conn_params):
- '''
- parse the db file path
- :param conn_params: the db connection params set in settings
- :return:
- '''
- print('file db:',conn_params)
- db_path ='%s/%s' %(conn_params['path'],conn_params['name'])
- return db_path
- def mysql_db_handle(conn_parms):
- pass
- def db_handler(conn_parms):
- '''
- connect to db
- :param conn_parms: the db connection params set in settings
- :return:a
- '''
- if conn_parms['engine'] == 'file_storage':
- return file_db_handle(conn_parms)
- if conn_parms['engine'] == 'mysql':
- return mysql_db_handle(conn_parms)
数据存储路径
- import logging
- from conf import settings
- def logger(log_type):
- #create logger
- logger = logging.getLogger(log_type)
- logger.setLevel(settings.LOG_LEVEL)
- # create console handler and set level to debug
- ch = logging.StreamHandler()
- ch.setLevel(settings.LOG_LEVEL)
- # create file handler and set level to warning
- log_file = "%s/log/%s" %(settings.BASE_DIR, settings.LOG_TYPES[log_type])
- fh = logging.FileHandler(log_file)
- fh.setLevel(settings.LOG_LEVEL)
- # create formatter
- formatter = logging.Formatter('%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s')
- # add formatter to ch and fh
- ch.setFormatter(formatter)
- fh.setFormatter(formatter)
- # add ch and fh to logger
- logger.addHandler(ch)
- logger.addHandler(fh)
- return logger
日志
- from core import auth
- from core import accounts
- from core import logger
- from core import accounts
- from core import transaction
- import time
- #transaction logger
- trans_logger = logger.logger('transaction')
- #access logger
- access_logger = logger.logger('access')
- #temp account data ,only saves the data in memory
- user_data = {
- 'account_id':None,
- 'is_authenticated':False,
- 'account_data':None
- }
- def account_info(acc_data):
- print(user_data)
- def repay(acc_data):
- '''
- print current balance and let user repay the bill
- :return:
- '''
- account_data = accounts.load_current_balance(acc_data['account_id']) #获取用户id,就是要用实时的最新数据,为了安全
- #for k,v in account_data.items():
- # print(k,v )
- current_balance= ''' --------- BALANCE INFO --------
- Credit : %s
- Balance: %s''' %(account_data['credit'],account_data['balance'])
- print(current_balance)
- back_flag = False
- while not back_flag:
- repay_amount = input("\033[33;1mInput repay amount:\033[0m").strip()
- if len(repay_amount) >0 and repay_amount.isdigit():
- #print('ddd 00')
- new_balance = transaction.make_transaction(trans_logger,account_data,'repay', repay_amount)
- if new_balance:
- print('''\033[42;1mNew Balance:%s\033[0m''' %(new_balance['balance']))
- else:
- print('\033[31;1m[%s] is not a valid amount, only accept integer!\033[0m' % repay_amount)
- if repay_amount == 'b':
- back_flag = True
- def withdraw(acc_data):
- '''
- print current balance and let user do the withdraw action
- :param acc_data:
- :return:
- '''
- account_data = accounts.load_current_balance(acc_data['account_id'])
- current_balance= ''' --------- BALANCE INFO --------
- Credit : %s
- Balance: %s''' %(account_data['credit'],account_data['balance'])
- print(current_balance)
- back_flag = False
- while not back_flag:
- withdraw_amount = input("\033[33;1mInput withdraw amount:\033[0m").strip()
- if len(withdraw_amount) >0 and withdraw_amount.isdigit():
- new_balance = transaction.make_transaction(trans_logger,account_data,'withdraw', withdraw_amount) # new_balance就是 函数返回值 acount_data
- if new_balance:
- print('''\033[42;1mNew Balance:%s\033[0m''' %(new_balance['balance']))
- else:
- print('\033[31;1m[%s] is not a valid amount, only accept integer!\033[0m' % withdraw_amount)
- if withdraw_amount == 'b':
- back_flag = True
- def transfer(acc_data):
- pass
- def pay_check(acc_data):
- pass
- def logout(acc_data):
- pass
- def interactive(acc_data):
- '''
- interact with user
- :return:
- '''
- menu = u'''
- ------- Oldboy Bank ---------
- \033[32;1m1. 账户信息
- 2. 还款(功能已实现)
- 3. 取款(功能已实现)
- 4. 转账
- 5. 账单
- 6. 退出
- \033[0m'''
- menu_dic = {
- '': account_info,
- '': repay,
- '': withdraw,
- '': transfer,
- '': pay_check,
- '': logout,
- }
- exit_flag = False
- while not exit_flag:
- print(menu)
- user_option = input(">>:").strip()
- if user_option in menu_dic:
- menu_dic[user_option](acc_data) #比如选择了2 ,则运行 repay(acc_data),调用repay函数
- else:
- print("\033[31;1mOption does not exist!\033[0m")
- def run():
- '''
- this function will be called right a way when the program started, here handles the user interaction stuff
- :return:
- '''
- acc_data = auth.acc_login(user_data,access_logger) #userdata作为条件,access_logger作为日志信息传入
- if user_data['is_authenticated']:
- user_data['account_data'] = acc_data #acc_data 即是用户信息 1234.json
- interactive(user_data) #交互
主程序
- from conf import settings
- from core import accounts
- from core import logger
- #transaction logger
- def make_transaction(log_obj,account_data,tran_type,amount,**others):
- '''
- deal all the user transactions
- :param account_data: user account data
- :param tran_type: transaction type
- :param amount: transaction amount
- :param others: mainly for logging usage
- :return:
- '''
- amount = float(amount)
- if tran_type in settings.TRANSACTION_TYPE:
- interest = amount * settings.TRANSACTION_TYPE[tran_type]['interest']
- old_balance = account_data['balance']
- if settings.TRANSACTION_TYPE[tran_type]['action'] == 'plus':
- new_balance = old_balance + amount + interest
- elif settings.TRANSACTION_TYPE[tran_type]['action'] == 'minus':
- new_balance = old_balance - amount - interest
- #check credit
- if new_balance <0:
- print('''\033[31;1mYour credit [%s] is not enough for this transaction [-%s], your current balance is
- [%s]''' %(account_data['credit'],(amount + interest), old_balance ))
- return
- account_data['balance'] = new_balance
- accounts.dump_account(account_data) #save the new balance back to file
- log_obj.info("account:%s action:%s amount:%s interest:%s" %
- (account_data['id'], tran_type, amount,interest) )
- return account_data
- else:
- print("\033[31;1mTransaction type [%s] is not exist!\033[0m" % tran_type)
交易种类
db:用户信息存储
- {"id": "gkx", "password": "", "credit": 15000, "balance": 15000, "enroll_date": "2016-01-02", "expire_date": "2021-01-01", "pay_day": 22, "status": 0}
python项目练习的更多相关文章
- 给缺少Python项目实战经验的人
我们在学习过程中最容易犯的一个错误就是:看的多动手的少,特别是对于一些项目的开发学习就更少了! 没有一个完整的项目开发过程,是不会对整个开发流程以及理论知识有牢固的认知的,对于怎样将所学的理论知识应用 ...
- 正确地组织python项目的结构
统一的项目结构 写了不少python项目后, 越来越认识到python项目结构重要性. 不管项目是否要开源, 是否要提交pypi, 项目结构的一致性带来的好处还有很多: 多人合作开发大家都有个基本的g ...
- eclipse中建python项目并运行
1. Help → Install New Software 2.Enter http://pydev.org/updates 3.点击Click "Next" and " ...
- 使用 tox flake8 pytest 规范 python 项目
使用 tox flake8 pytest 规范 python 项目 python 中有些很好的工作来规范整个项目的开发,而其中使用较多的就是使用 tox . flake8 . pytest . tox ...
- 2013流行Python项目汇总
2013流行Python项目汇总 转自:http://www.kankanews.com/ICkengine/archives/102963.shtml Python作为程序员的宠儿,越来越得到人们的 ...
- python项目
python实战项目: http://www.the5fire.com/category/python实战/ python基础教程中的十个项目: python项目练习一:即时标记 python项目练习 ...
- Eclipse开发Python项目
最近倒腾python自带的开发工具idle,用的很不习惯,还是用Eclipse编写python项目方便(自动补齐,智能报错,调试方便),下面就说说怎么用Eclipse编写python代码吧~ 1.安装 ...
- 以正确的方式开源 Python 项目
以正确的方式开源 Python 项目 大多数Python开发者至少都写过一个像工具.脚本.库或框架等对其他人也有用的工具.我写这篇文章的目的是让现有Python代码的开源过程尽可能清 晰和无痛.我不是 ...
- 流行的Python项目汇总
年有哪些流行的Python项目呢?下面,我们一起来看下. 一.测试和调试 python_koans :Python Koans 算 “Ruby Koans” 的一部分,作为交互式教程,可以学习 TDD ...
- 创建成功的Python项目
创建成功的Python项目 前端开发工具技巧介绍—Sublime篇 SEO在网页制作中的应用 观察者模式 使用D3制作图表 英文原文:Create successful Python projects ...
随机推荐
- 动物管理员--zooKeeper-01
ZooKeeper集群角色介绍: 最典型集群模式:Master/Slave 模式(主备模式).在这种模式中,通常 Master 服务器作为主服务器提供写服务,其他的 Slave 服务器从服务器通过异步 ...
- 关于lazyload的实现原理
核心原理是: 1 设置一个定时器,计算每张图片是否会随着滚动条的滚动,而出现在视口(也就是浏览器中的 展现网站的空白部分 )中: 2 为<img>标签设置一个暂存图片URL的自定义属性(例 ...
- winfrom进程、线程、用户控件
一.进程 一个进程就是一个程序,利用进程可以在一个程序中打开另一个程序. 1.开启某个进程Process.Start("文件缩写名"); 注意:Process要解析命名空间. 2. ...
- Java 五大原则
1.单一职责 不论是在设计类,接口还是方法,单一职责都会处处体现,单一职责的定义:我们把职责定义为系统变化的原因.所有在定义类,接口,方法的时候.定义完以后再去想一想是不能多于一个的动机去改变这个类, ...
- 微信公众号开发流程,jssdk的使用以及签名算法的实现
一 开发流程 1 基本配置-登录自己的公众号 A:新型微信认证,认证过的企业号才可以进行自定义菜单中的连接跳转: B:开发基本配置里面进行开发者iD查询,密码查询和重置和ip白名单配置: C:公众号设 ...
- nginx与PHP配置
一.安装依赖包 yum -y install libxml2 libxml2-devel openssl openssl-devel curl curl-devel libjpeg li ...
- LeetCode #002# Add Two Numbers(js描述)
索引 思路1:基本加法规则 思路2:移花接木法... 问题描述:https://leetcode.com/problems/add-two-numbers/ 思路1:基本加法规则 根据小学学的基本加法 ...
- 基本数据类型大总结(int,str,list,dict,tuple)
python基本数据类型 int==>整数,主要用来进行数学运算 str==>字符串,可以保存单一数值 bool==>判断真假,true,false list==>存储大量数据 ...
- Ansible 的安装
On Fedora: $ sudo dnf install ansible On RHEL and CentOS: $ sudo yum install ansible On Ubuntu: $ su ...
- HTML基础(2)——边框
边框:(尺寸 样式 颜色) div{border:1px solid red;} 样式可能的值: dotted(点状边框,在大多数浏览器里呈现实线) dashed(虚线.在大多数浏览器中呈现为实线) ...
