3分钟看完Java 8——史上最强Java 8新特性总结之第四篇 其他新特性
目录
· 初步理解
· 应用模式
· 优先级问题
· Optional
· 基本用法
· CompletableFuture与Stream API
· 旧API
· 创建
· 操作
· 格式化与解析
· 时区
默认方法和静态方法
初步理解
1. 面临问题:Java 8以前,当已设计的接口被其他框架、库使用后,如果向接口添加新方法,将导致这些框架和库无法编译。
2. 解决方法:Java 8可在接口中使用静态方法和默认方法。
应用模式
1. 合并接口与辅助工具类:比如接口java.util.Collection与其辅助工具类java.util.Collections,接口支持静态方法后,可将辅助工具类的方法加入到接口。
2. 可选方法:比如JDK中的java.util.Iterator,接口提供一个默认的remove()实现,这样实体类就无需在自己的实现中显式地提供一个空方法。
interface Iterator<T> {
boolean hasNext();
T next();
default void remove() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
}
3. 行为多继承
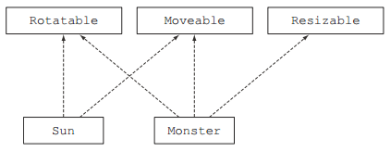
a) Rotatable.java
public interface Rotatable {
void setRotationAngle(int angleInDegrees);
int getRotationAngle();
default void rotateBy(int angleInDegrees) {
setRotationAngle((getRotationAngle() + angleInDegrees) % 360);
}
}
b) Moveable.java
public interface Moveable {
int getX();
int getY();
void setX(int x);
void setY(int y);
default void moveHorizontally(int distance) {
setX(getX() + distance);
}
default void moveVertically(int distance) {
setY(getY() + distance);
}
}
c) Resizable.java
public interface Resizable {
int getWidth();
int getHeight();
void setWidth(int width);
void setHeight(int height);
void setAbsoluteSize(int width, int height);
default void setRelativeSize(int wFactor, int hFactor) {
setAbsoluteSize(getWidth() / wFactor, getHeight() / hFactor);
}
}
d) Monster.java
public class Monster implements Rotatable, Moveable, Resizable {
@Override
public int getX() {
return 0;
}
@Override
public int getY() {
return 0;
}
@Override
public void setX(int x) {
}
@Override
public void setY(int y) {
}
@Override
public int getWidth() {
return 0;
}
@Override
public int getHeight() {
return 0;
}
@Override
public void setWidth(int width) {
}
@Override
public void setHeight(int height) {
}
@Override
public void setAbsoluteSize(int width, int height) {
}
@Override
public void setRotationAngle(int angleInDegrees) {
}
@Override
public int getRotationAngle() {
return 0;
}
}
e) Sun.java
public class Sun implements Moveable, Rotatable {
@Override
public int getX() {
return 0;
}
@Override
public int getY() {
return 0;
}
@Override
public void setX(int x) {
}
@Override
public void setY(int y) {
}
@Override
public void setRotationAngle(int angleInDegrees) {
}
@Override
public int getRotationAngle() {
return 0;
}
}
优先级问题
1. 方法执行优先级规则:
a) 距离当前类越近的方法优先级越高;
b) 显示方法近于隐式方法;
c) 距离相等时,非默认方法优先于默认方法。
2. 举例
a) hello()方法优先级:B > A。
i. A.java
public interface A {
default void hello() {
System.out.println("Hello from A");
}
}
ii. B.java
public interface B extends A {
default void hello() {
System.out.println("Hello from B");
}
}
iii. C.java
public class C implements B, A {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new C().hello(); // Hello from B
}
}
b) hello()方法优先级:B > A。
i. A.java
public interface A {
default void hello() {
System.out.println("Hello from A");
}
}
ii. B.java
public interface B extends A {
default void hello() {
System.out.println("Hello from B");
}
}
iii. D.java
public class D implements A{
}
iv. C.java
public class C extends D implements B, A {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new C().hello(); // Hello from B
}
}
c) hello()方法优先级:D > B > A。
i. A.java
public interface A {
default void hello() {
System.out.println("Hello from A");
}
}
ii. B.java
public interface B extends A {
default void hello() {
System.out.println("Hello from B");
}
}
iii. D.java
public class D implements A {
@Override
public void hello() {
System.out.println("Hello from D");
}
}
iv. C.java
public class C extends D implements B, A {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new C().hello(); // Hello from D
}
}
d) hello()方法优先级:C > B = A,由于A、B优先级相等,有冲突,所以必须在C中Override hello()方法,否则将报错class C inherits unrelated defaults for hello() from types B and A。
i. A.java
public interface A {
default void hello() {
System.out.println("Hello from A");
}
}
ii. B.java
public interface B {
default void hello() {
System.out.println("Hello from B");
}
}
iii. C.java
public class C implements B, A {
@Override
public void hello() {
B.super.hello();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new C().hello(); // Hello from B
}
}
Optional
1. Optional目的:解决null带来的以下问题。
a) 错误:NullPointerException。
b) 代码膨胀:代码充斥着深度嵌套的null检查,可读性变差。
c) 毫无意义:null自身没有任何语义,它代表在静态类型语言中以一种错误的方式对缺失变量值的建模。
d) 破坏了Java的哲学:Java一直试图避免让程序员意识到指针的存在,唯一的例外是null指针。
e) 类型缺陷:null并不属于任何类型,它可以被赋值给任意引用类型的变量。这导致当这个变量被传递到系统中的另一个部分后,将无法获知null变量最初的赋值到底是什么类型。
2. java.util.Optional类的方法
|
方法 |
描述 |
|
empty |
返回空Optional实例 |
|
filter |
如果值存在并且满足提供的Predicate,则返回包含该值的Optional对象;否则返回空Optional对象 |
|
flatMap |
如果值存在,就对该值执行提供的mapping函数,返回Optional类型的值,否则返回一个空Optional对象 |
|
get |
如果值存在,将该值用Optional封装返回,否则抛出NoSuchElementException异常 |
|
ifPresent |
如果值存在,则执行使用该值的方法调用,否则什么也不做 |
|
isPresent |
如果值存在,则返回true,否则返回false |
|
map |
如果值存在,则对该值执行提供的mapping函数 |
|
of |
将指定值用Optional封装后返回,如果该值为null,则抛出NullPointerException异常 |
|
ofNullable |
将指定值用Optional封装后返回,如果该值为null,则返回空Optional对象 |
|
orElse |
如果有值,则将其返回,否则返回一个默认值 |
|
orElseGet |
如果有值,则将其返回,否则返回由指定Supplier接口生成的值 |
|
orElseThrow |
如果有值,则将其返回,否则抛出指定的Supplier接口生成的异常 |
3.举例
a) 使用Optional前
i. Person.java
public class Person {
private Car car;
public Car getCar() {
return car;
}
}
ii. Car.java
public class Car {
private Insurance insurance;
public Insurance getInsurance() {
return insurance;
}
}
iii. Insurance.java
public class Insurance {
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
iv. Test.java
public class Test {
public static String getCarInsuranceName(Person person) {
if (person != null) {
Car car = person.getCar();
if (car != null) {
Insurance insurance = car.getInsurance();
if (insurance != null) {
return insurance.getName();
}
}
}
return "Unknown";
}
}
b) 使用Optional后
i. Person.java
import java.util.Optional;
public class Person {
// 可能为null
private Car car;
public Optional<Car> getCar() {
// 使用Optional封装car,允许car为null
return Optional.ofNullable(car);
}
}
ii. Car.java
import java.util.Optional;
public class Car {
// 可能为null
private Insurance insurance;
public Optional<Insurance> getInsurance() {
return Optional.ofNullable(insurance);
}
}
iii. Insurance.java
public class Insurance {
// 不可能为null
private String name;
// 不可能为null,所以不使用Optional
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
iv. Test.java
import java.util.Optional;
public class Test {
public static String getCarInsuranceName(Person person) {
Optional<Person> optPerson = Optional.ofNullable(person);
// 由于Person::getCar返回类型是Optional<Car>,
// 所以optPerson.map(Person::getCar)返回类型是Optional<Optional<Car>>,
// 因此导致map(Car::getInsurance)报错
// Optional<String> name = optPerson.map(Person::getCar)
// .map(Car::getInsurance)
// .map(Insurance::getName);
// 使用flatMap扁平化,从而避免上述报错
return optPerson.flatMap(Person::getCar)
.flatMap(Car::getInsurance)
.map(Insurance::getName)
.orElse("Unknown"); // 如果Optional结果值为空,则使用默认值
}
}
c) 使用filter()方法判断Predicate
// 不使用Optional
Insurance insurance = null;
if(insurance != null && "CambridgeInsurance".equals(insurance.getName())){
System.out.println("ok");
}
// 使用Optional
Optional<Insurance> optInsurance = Optional.ofNullable(null);
optInsurance.filter(ins -> "CambridgeInsurance".equals(ins.getName()))
.ifPresent(ins -> System.out.println("ok"));
CompletableFuture
基本用法
1. java.util.concurrent.Future接口
a) 起始:Java 5。
b) 使用方法:通常需要将耗时操作封装在一个Callable对象中,再将它提交给ExecutorService执行,最后通过Future获取执行结果。
2. java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture类
a) 起始:Java 8。
b) 优点:比Future更加直观,功能更强大。
3. 举例
a) Future
i. Shop.java
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class Shop {
public double getPrice(String product) {
return calculatePrice(product);
}
public Future<Double> getPriceAsync(String product) {
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
Future<Double> future = executor.submit(new Callable<Double>() {
public Double call() {
return getPrice(product);
}
});
return future;
}
private double calculatePrice(String product) {
delay();
return Math.random() * 1000;
}
private static void delay() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
ii. Test.java
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Future<Double> future = new Shop().getPriceAsync("Candy");
Double price = future.get();
System.out.println(price);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
b) CompletableFuture方法一
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class Shop {
public double getPrice(String product) {
return calculatePrice(product);
}
public Future<Double> getPriceAsync(String product) {
CompletableFuture<Double> future = new CompletableFuture<>();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
double price = getPrice(product);
future.complete(price); // 如果价格计算正常结束,完成Future操作并设置商品价格
} catch (Exception ex) {
future.completeExceptionally(ex); // 否则就抛出导致失败的异常,完成这次Future操作
}
}).start();
return future;
}
private double calculatePrice(String product) {
delay();
return Math.random() * 1000;
}
private static void delay() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
c) CompletableFuture方法二
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class Shop {
public double getPrice(String product) {
return calculatePrice(product);
}
public Future<Double> getPriceAsync(String product) {
return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> calculatePrice(product));
}
private double calculatePrice(String product) {
delay();
return Math.random() * 1000;
}
private static void delay() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
CompletableFuture与Stream API
1. 并行流与顺序流+CompletableFuture都可以实现流的并行处理,如何选取?
a) 灵活
i. 并行流:线程数由ForkJoinPool的全局属性决定。
ii. 顺序流+CompletableFuture:自由创建线程池,灵活控制线程数。
b) 场景
i. 并行流:更适合计算密集型并且没有I/O的操作,因为实现简单,同时效率更高(如果所有的线程都是计算密集型,则没有必要创建比CPU核数更多的线程)。
ii. 顺序流+CompletableFuture:更适合并行工作单元涉及I/O等待(包括网络连接等待)的操作,该场景不使用并行流的另一个原因是处理流的流水线中如果发生I/O等待,流的延迟特性会让我们很难判断到底什么时候触发了等待。该场景线程数用以下公式计算(出自《Java并发编程实战》):
NCPU为CPU核数,可通过Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors()获取。
UCPU为期望的CPU利用率(应介于0和1之间)。
W/C是等待时间与计算时间的比率。
2. 举例
a) Shop.java
public class Shop {
private String name;
public Shop(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public double getPrice(String product) {
return calculatePrice(product);
}
private double calculatePrice(String product) {
delay();
return Math.random() * 1000;
}
private static void delay() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
b) Test.java
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.*; import static java.util.stream.Collectors.toList; public class Test { // 顺序流
public static List<String> findPrices1(List<Shop> shops, String product) {
return shops.stream()
.map(shop -> String.format("%s price is %.2f", shop.getName(), shop.getPrice(product)))
.collect(toList());
} // 并行流
public static List<String> findPrices2(List<Shop> shops, String product) {
return shops.parallelStream()
.map(shop -> String.format("%s price is %.2f", shop.getName(), shop.getPrice(product)))
.collect(toList());
} // 顺序流+CompletableFuture
public static List<String> findPrices3(List<Shop> shops, String product) {
// 创建一个线程池,线程池中线程的数目为100和商店数目二者中较小的一个值
Executor executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(Math.min(shops.size(), 100),
new ThreadFactory() {
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
Thread t = new Thread(r);
t.setDaemon(true); // 使用守护线程——这种方式不会阻止程序的关停
return t;
}
});
List<CompletableFuture<String>> priceFutures = shops.stream()
.map(shop -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> String.format("%s price is %.2f", shop.getName(), shop.getPrice(product)), executor))
.collect(toList());
return priceFutures.stream()
.map(CompletableFuture::join) // 等待所有异步操作结束
.collect(toList());
} public static void printPrices(List<String> prices) {
prices.stream().forEach(System.out::println);
} public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Shop> shops = Arrays.asList(new Shop("BestPrice"),
new Shop("LetsSaveBig"),
new Shop("MyFavoriteShop"),
new Shop("BuyItAll"));
String product = "Candy";
List<String> prices1 = findPrices1(shops, product);
printPrices(prices1);
List<String> prices2 = findPrices2(shops, product);
printPrices(prices2);
List<String> prices3 = findPrices3(shops, product);
printPrices(prices3);
} }
新日期和时间API
旧API
1. java.util.Date
a) 起始:Java 1.0。
b) 缺点:只能以毫秒精度表示时间;易用性差,比如年份从1900开始,月份从0开始。
// 2014年3月18日
System.out.println(new Date(114, 2, 18));
2.java.util.Calendar
a) 起始:Java 1.1。
b) 缺点:易用性差,比如月份从0开始;Date和Calendar如何选择问题;格式化类DateFormat只能用于Date。
创建
1. java.time.LocalDate
a) 只存储年、月、日,不存储时区。
b) 不可变,线程安全。
2. java.time.LocalTime
a) 只存储时、分、秒,不存储时区。
b) 不可变,线程安全。
3. java.time.LocalDateTime
a) 只存储年、月、日、时、分、秒,不存储时区。
b) 不可变,线程安全。
c) LocalDate和LocalTime的合体。
4. java.time.Instant
a) Unix时间戳秒数,即与UTC时区1970-01-01 00:00:00的秒数和纳秒差值。
b) 内部存储秒数和纳秒(1 ns = 10^-9 s)两个字段。
c) 面向机器设计的类,方便机器处理。
5. java.time.temporal.ChronoField
a) 实现了java.time.temporal.TemporalFieldl接口的枚举,提供了访问java.time.temporal.Temporal接口实现类的标准字段。
b) LocalDate、LocalTime、LocalDateTime和Instant实现了Temporal接口。
c) 注意:由于Instant是面向机器的,通过ChronoField获取Instant字段时,只支持秒、毫秒(1,000毫秒=1秒)、微秒(1,000,000微秒=1秒)和纳秒(1,000,000,000纳秒=1秒)。
6. java.time.Duration
a) 表示一个时间段的持续时长。
b) 内部存储持续时长的秒和纳秒。
7. java.time.Period
a) 表示一个时间段的持续时长。
b) 内部存储持续时长的年、月、日。
8. Duration和Period的通用方法
|
方法 |
静态方法 |
描述 |
|
between |
Y |
创建两个时间点之间的间隔时长 |
|
from |
Y |
由一个临时时间点创建间隔时长 |
|
of |
Y |
由组成部分创建时长的实例 |
|
parse |
Y |
由字符串创建时长的实例 |
|
addTo |
N |
创建该时长的副本,并将其叠加到某个指定的Temporal对象 |
|
get |
N |
读取该时长的状态 |
|
isNegative |
N |
检查该时长是否为负值,不包含零 |
|
isZero |
N |
检查该时长的时长是否为零 |
|
minus |
N |
通过减去一定的时间创建该时长的副本 |
|
multipliedBy |
N |
将时长的值乘以某个标量创建该时长的副本 |
|
negated |
N |
以忽略某个时长的方式创建该时长的副本 |
|
plus |
N |
以增加某个指定时长的方式创建该时长的副本 |
|
subtractFrom |
N |
从指定的Temporal对象中减去该时长 |
9. 举例
a) java.time.LocalDate
// 创建
LocalDate today = LocalDate.now();
LocalDate d = LocalDate.parse("2014-03-18");
LocalDate date = LocalDate.of(2014, 3, 18); // 2014-03-18
// 直接获取字段
int year = date.getYear(); //
Month month = date.getMonth(); // MARCH
int day = date.getDayOfMonth(); //
DayOfWeek dow = date.getDayOfWeek(); // TUESDAY
int len = date.lengthOfMonth(); // 31 (3月总天数)
boolean leap = date.isLeapYear(); // false
// 通过ChronoField获取字段
int year = date.get(ChronoField.YEAR); //
int month = date.get(ChronoField.MONTH_OF_YEAR); //
int day = date.get(ChronoField.DAY_OF_MONTH); //
b) java.time.LocalTime
// 创建
LocalTime t = LocalTime.parse("13:45:20");
LocalTime time = LocalTime.of(13, 45, 20); // 13:45:20
// 直接获取字段
int hour = time.getHour(); //
int minute = time.getMinute(); //
int second = time.getSecond(); //
c) java.time.LocalDateTime
// 创建2014-03-18T13:45:20的4种方法
LocalDateTime dt1 = LocalDateTime.of(2014, Month.MARCH, 18, 13, 45, 20);
LocalDateTime dt2 = LocalDateTime.of(date, time);
LocalDateTime dt3 = date.atTime(13, 45, 20);
LocalDateTime dt4 = date.atTime(time);
// 提取
LocalDate date1 = dt1.toLocalDate(); // 2014-03-18
LocalTime time1 = dt1.toLocalTime(); // 13:45:20
d) java.time.Instant
// 创建1970-01-01T00:00:03Z的4种方法
Object o1 = Instant.ofEpochSecond(3);
Object o2 = Instant.ofEpochSecond(3, 0);
Object o3 = Instant.ofEpochSecond(2, 1_000_000_000); // 2秒之后再加上100万纳秒(1秒)
Object o4 = Instant.ofEpochSecond(4, -1_000_000_000); // 4秒之前的100万纳秒(1秒)
// Exception in thread "main" java.time.temporal.UnsupportedTemporalTypeException: Unsupported field: DayOfMonth
int day = Instant.now().get(ChronoField.DAY_OF_MONTH);
e) java.time.Duration
// 创建3秒持续时长的5种方法
Duration d1 = Duration.between(LocalTime.parse("00:00:00"), LocalTime.parse("00:00:03"));
Duration d2 = Duration.between(LocalDateTime.parse("1970-01-01T00:00:00"), LocalDateTime.parse("1970-01-01T00:00:03"));
Duration d3 = Duration.between(Instant.ofEpochSecond(0), Instant.ofEpochSecond(3));
Duration d4 = Duration.ofSeconds(3);
Duration d5 = Duration.of(3, ChronoUnit.SECONDS);
f) java.time.Period
// 创建10天持续时长的3种方法
Period p1 = Period.between(LocalDate.of(2014, 3, 8), LocalDate.of(2014, 3, 18));
Period p2 = Period.ofDays(10);
Period p3 = Period.of(0, 0, 10);
操作
1. 操作相关方法
a) with*()方法:创建某字段为新值的新Temporal对象。
b) plus*()方法:创建加上某个时长的新Temporal对象。
c) minus*()方法:创建减去某个时长的新Temporal对象。
d) java.time.temporal.TemporalAdjuster.*方法:高级日期时间操作方法
|
方法 |
描述 |
|
dayOfWeekInMonth |
创建一个新日期,它的值为同一个月中每一周的第几天 |
|
firstDayOfMonth |
创建一个新日期,它的值为当月的第一天 |
|
firstDayOfNextMonth |
创建一个新日期,它的值为下月的第一天 |
|
firstDayOfNextYear |
创建一个新日期,它的值为明年的第一天 |
|
firstDayOfYear |
创建一个新日期,它的值为当年的第一天 |
|
firstInMonth |
创建一个新日期,它的值为同一个月中,第一个符合星期几要求的值 |
|
lastDayOfMonth |
创建一个新日期,它的值为下月的最后一天 |
|
lastDayOfNextMonth |
创建一个新日期,它的值为下月的最后一天 |
|
lastDayOfNextYear |
创建一个新日期,它的值为明年的最后一天 |
|
lastDayOfYear |
创建一个新日期,它的值为今年的最后一天 |
|
lastInMonth |
创建一个新日期,它的值为同一个月中,最后一个符合星期几要求的值 |
|
next previous |
创建一个新日期,并将其值设置为日期调整后或调整前,第一个符合指定星期几要求的日期 |
|
nextOrSame previousOrSame |
创建一个新日期,并将其值设置为日期调整后或调整前,第一个符合指定星期几要求的日期,如果该日期已经符合要求,直接返回该对象 |
2. 举例
a) with*()方法
LocalDate date1 = LocalDate.of(2014, 3, 18); // 2014-03-18
LocalDate date2 = date1.withYear(2011); // 2011-03-18
LocalDate date3 = date2.withDayOfMonth(25); // 2011-03-25
LocalDate date4 = date3.with(ChronoField.MONTH_OF_YEAR, 9); // 2011-09-25
b) plus*()方法和minus*()方法
LocalDate date1 = LocalDate.of(2014, 3, 18); // 2014-03-18
LocalDate date2 = date1.plusWeeks(1); // 2014-03-25
LocalDate date3 = date2.minusYears(3); // 2011-03-25
LocalDate date4 = date3.plus(6, ChronoUnit.MONTHS); // 2011-09-25
c) TemporalAdjuster.*方法
import static java.time.temporal.TemporalAdjusters.*;
LocalDate date1 = LocalDate.of(2014, 3, 18); // 2014-03-18
LocalDate date2 = date1.with(nextOrSame(DayOfWeek.SUNDAY)); // 2014-03-23
LocalDate date3 = date2.with(lastDayOfMonth()); // 2014-03-31
d) 自定义TemporalAdjuster:计算下一个工作日(仅跳过周六日)
TemporalAdjuster nextWorkingDay = TemporalAdjusters.ofDateAdjuster(
temporal -> {
DayOfWeek dow = DayOfWeek.of(temporal.get(ChronoField.DAY_OF_WEEK));
int dayToAdd = 1;
if (dow == DayOfWeek.FRIDAY) dayToAdd = 3;
if (dow == DayOfWeek.SATURDAY) dayToAdd = 2;
return temporal.plus(dayToAdd, ChronoUnit.DAYS);
});
date = date.with(nextWorkingDay); // 2014-03-19
格式化与解析
1. java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter
a) 用于格式化和解析。
b) 线程安全。
2. 举例
a) 使用内置格式格式化与解析
// 格式化
LocalDate date = LocalDate.of(2014, 3, 18);
String s1 = date.format(DateTimeFormatter.BASIC_ISO_DATE); //
String s2 = date.format(DateTimeFormatter.ISO_LOCAL_DATE); // 2014-03-18
// 解析
LocalDate date1 = LocalDate.parse("20140318", DateTimeFormatter.BASIC_ISO_DATE);
LocalDate date2 = LocalDate.parse("2014-03-18", DateTimeFormatter.ISO_LOCAL_DATE);
b) 使用模式自定义格式式化与解析
DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy年MM月dd日");
// 格式化
LocalDate date1 = LocalDate.of(2014, 3, 18);
String formattedDate = date1.format(formatter);
// 解析
LocalDate date2 = LocalDate.parse(formattedDate, formatter);
c) 更复杂方式自定义格式式化与解析
DateTimeFormatter formatter = new DateTimeFormatterBuilder()
.appendValue(ChronoField.YEAR, 4, 10, SignStyle.EXCEEDS_PAD)
.appendLiteral("年")
.appendValue(ChronoField.MONTH_OF_YEAR, 2)
.appendLiteral("月")
.appendValue(ChronoField.DAY_OF_MONTH, 2)
.appendLiteral("日")
.parseCaseInsensitive()
.toFormatter();
// 格式化
LocalDate date1 = LocalDate.of(2014, 3, 18);
String formattedDate = date1.format(formatter);
// 解析
LocalDate date2 = LocalDate.parse(formattedDate, formatter);
时区
1. java.time.ZoneId类:替换java.util.TimeZone的新时区类。
2. 举例
a) 获取时区
// 北京时间
ZoneId beijingZone = ZoneId.of("Asia/Shanghai");
// 默认时区
ZoneId zoneId = TimeZone.getDefault().toZoneId();
b) 设置时区
LocalDate date = LocalDate.of(2014, Month.MARCH, 18);
ZonedDateTime zdt1 = date.atStartOfDay(beijingZone);
LocalDateTime dateTime = LocalDateTime.of(2014, Month.MARCH, 18, 13, 45);
ZonedDateTime zdt2 = dateTime.atZone(beijingZone);
Instant instant = Instant.now();
ZonedDateTime zdt3 = instant.atZone(beijingZone);
作者:netoxi
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/netoxi
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,未经同意须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文连接。欢迎指正与交流。
3分钟看完Java 8——史上最强Java 8新特性总结之第四篇 其他新特性的更多相关文章
- 3分钟看完Java 8——史上最强Java 8新特性总结之第二篇 Stream API
目录 · 概况 · 切片(Slicing) · 映射(Mapping) · 匹配(Matching) · 查找(Finding) · 归约(Reducing) · 排序(Sorting) · 数值流( ...
- 3分钟看完Java 8——史上最强Java 8新特性总结之第三篇 函数式编程技巧
目录 · 改写设计模式 · 策略模式(Strategy Pattern) · 模板方法模式(Template Method Pattern) · 观察者模式(Observer Pattern) · 责 ...
- 3分钟看完Java 8——史上最强Java 8新特性总结之第一篇 函数式编程基础
目录 · 行为参数化 · Lambda表达式 · 概况 · 函数式接口 · 类型推断 · 使用外层变量 · 方法引用 · 复合Lambda表达式 行为参数化 1. 理解函数式编程要先理解行为参数化. ...
- 史上最强Java NIO入门:担心从入门到放弃的,请读这篇!
本文原题“<NIO 入门>,作者为“Gregory M. Travis”,他是<JDK 1.4 Tutorial>等书籍的作者. 1.引言 Java NIO是Java 1.4版 ...
- 金九银十,史上最强 Java 面试题整理。
以下会重新整理所有 Java 系列面试题答案.及各大互联网公司的面试经验,会从以下几个方面汇总,本文会长期更新. Java 面试篇 史上最全 Java 面试题,带全部答案 史上最全 69 道 Spri ...
- 史上最强Java开发环境搭建
在项目产品开发中,开发环境搭建是软件开发的首要阶段,也是必须阶段,只有开发环境搭建好了,方可进行开发,良好的开发环境搭建,为后续的开发工作带来极大便利. 对于大公司来说,软件开发环境搭建工作一般是由运 ...
- c#代码 天气接口 一分钟搞懂你的博客为什么没人看 看完python这段爬虫代码,java流泪了c#沉默了 图片二进制转换与存入数据库相关 C#7.0--引用返回值和引用局部变量 JS直接调用C#后台方法(ajax调用) Linq To Json SqlServer 递归查询
天气预报的程序.程序并不难. 看到这个需求第一个想法就是只要找到合适天气预报接口一切都是小意思,说干就干,立马跟学生沟通价格. 不过谈报价的过程中,差点没让我一口老血喷键盘上,话说我们程序猿的人 ...
- 一文深入了解史上最强的Java堆内缓存框架Caffeine
它提供了一个近乎最佳的命中率.从性能上秒杀其他一堆进程内缓存框架,Spring5更是为了它放弃了使用多年的GuavaCache 缓存,在我们的日常开发中用的非常多,是我们应对各种性能问题支持高并发的一 ...
- Java算法面试题(史上最强、持续更新、吐血推荐)
文章很长,建议收藏起来,慢慢读! 疯狂创客圈为小伙伴奉上以下珍贵的学习资源: 疯狂创客圈 经典图书 : <Netty Zookeeper Redis 高并发实战> 面试必备 + 大厂必备 ...
随机推荐
- 201621123002《JAVA程序设计》第二周学习总结
1.本周学习总结 1.重点String类 2.Java的数据类型 3.Java中的引用类,包装类 for(类型 元素变量名(任取):遍历对象(数组名)) 2.书面作业 1.String-使用Eclip ...
- Eclipse Python 开发环境搭建 pydev 插件
已安装: python 3.6 JDK Eclispe 在 Eclipse 中安装 pydev Pydev 的下载网址 http://www.pydev.org/download.html 安装完成后 ...
- redis主从复制详述
一.主从复制详述 原理其实很简单,master启动会生成一个run id,首次同步时会发送给slave,slave同步命令会带上run id以及offset,显然,slave启动(初次,重启)内存中没 ...
- selenium_unittest基本框架
from selenium import webdriver import unittest import time #创建类引入unitest.testcase用例库 class BaiDu_tes ...
- 去掉input[type="number"]的默认样式
input::-webkit-outer-spin-button,input::-webkit-inner-spin-button{ -webkit-appearance: none !importa ...
- Visual Studio 2017 调试器的工作进程(msvsmon.exe)意外退出 调试将终止
开发环境: Windows 10 in Parallels Desktop Visual Studio 15.6 场景还原: 使用 Visual Studio 15.6 (即 Visual Studi ...
- 7.ASP.NET MVC 5.0中的Routing【路由】
大家好,这一篇向大家介绍ASP.NET MVC路由机制.[PS:上一篇-->6. ASP.NET MVC 5.0中的HTML Helpers[HTML帮助类] ] 路由是一个模式匹配系统,它确保 ...
- 深圳scala-meetup-20180902(3)- Using heterogeneous Monads in for-comprehension with Monad Transformer
scala中的Option类型是个很好用的数据结构,用None来替代java的null可以大大降低代码的复杂性,它还是一个更容易解释的状态表达形式,比如在读取数据时我们用Some(Row)来代表读取的 ...
- Tomcat 在 Linux 上的安装和配置
一.文件上传 先上传tomcat安装文件到Linux服务器 二.解压安装 使用以下命令解压安装包 .tar.gz 解压成功会生成一个文件夹 tomcat服务器运行时是需要JDK支持的,所以必须先安装好 ...
- Java 代码需要使用转义符的地方
1.正则表达式特殊字符 Java 代码中使用到正则表达式里的特殊字符需要使用转义符 \ 进行转义 . ? * + ! ^ $ [ ] ( ) \ 因为反斜线 \ 也是特殊字符,所以转义需双反斜线 \\ ...
