openGL学习----相机
0.参考:https://learnopengl-cn.github.io/01%20Getting%20started/09%20Camera/
0.0其实相机就是搞清楚cameraPos,cameraFornt,cameraUp的关系和用法,以及跟三个欧拉角的关系,以及如何跟鼠标、键盘的wasd键联系起来(也就是视角移动跟距离移动)实现跟用户的交互,然后生成LookAt矩阵就OK了,重点是理解跟4中的注意点
0.1我们介绍的摄像机系统是一个FPS风格的摄像机,它能够满足大多数情况需要,而且与欧拉角兼容,但是在创建不同的摄像机系统,比如飞行模拟摄像机,时就要当心。每个摄像机系统都有自己的优点和不足,所以确保对它们进行了详细研究。比如,这个FPS摄像机不允许俯仰角大于90度,而且我们使用了一个固定的上向量(0, 1, 0),这在需要考虑滚转角的时候就不能用了。
0.2鼠标控制方向,键盘控制距离,滚轮控制视角
1.当我们讨论摄像机/观察空间(Camera/View Space)的时候,是在讨论以摄像机的视角作为场景原点时场景中所有的顶点坐标(之前的原点是世界坐标系的原点):观察矩阵把所有的世界坐标变换为相对于摄像机位置与方向的观察坐标。要定义一个摄像机,我们需要它在世界空间中的位置、观察的方向、一个指向它右测的向量以及一个指向它上方的向量。细心的读者可能已经注意到我们实际上创建了一个三个单位轴相互垂直的、以摄像机的位置为原点的坐标系。
2.具体相机坐标系原理可参看资料。。。
3.这里只讲一下大致的观察矩阵的初始化api
相机坐标系转换就是生成一个观察矩阵,也就是著名的LookAt矩阵

3.1幸运的是,GLM已经提供了这些支持。我们要做的只是定义一个摄像机位置,一个目标位置和一个表示世界空间中的上向量的向量(我们计算右向量使用的那个上向量)。接着GLM就会创建一个LookAt矩阵,我们可以把它当作我们的观察矩阵:
glm::mat4 view;
view = glm::lookAt(glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 3.0f),
glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f),
glm::vec3(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f));
glm::LookAt函数需要一个位置、目标和上向量。
其实比较经典和完美的初始化方法是下面(上面只是简单情况下的写法):
view = glm::lookAt(cameraPos, cameraPos + cameraFront, cameraUp);
第一个参数是相机位置,是个点,是世界坐标系,因为还没有生成观察矩阵作用到坐标上,怎么可能是相机坐标系呢
第二个参数是看向的目标位置,也是个点,也是世界坐标系。例子中是相机前面的点,也就是说相机一直是朝着它前面的目标点,也就是z轴负方向看的。它只是一个点,并不是一个向量,仅仅是表明在第一个参数的情况下,相机朝向哪个点看的(他与第一个参数一起才构成了相机的朝向向量,也就是朝向哪个方向看的)。
一般情况下这个点是由相机的点跟方向向量相加而得。因为已知他的方向向量(详见下面代码)
第三个参数是一个向量表示相机的上向量,指向y轴,可以通过这个向量跟前两个参数,两次向量叉乘出三个互相正交的向量
4.有了观察矩阵也就是都转换到相机坐标系了。这时候可以有一些交互设计了,比如鼠标控制朝向方向,键盘wasd控制移动,但是有些注意点(以下为相机移动的重点,要重点理解)
4.0主要讲解鼠标控制的视角移动跟键盘wasd控制的距离移动,以及滚轮控制的缩放移动
4.1键盘的wasd键用来控制前后左右的移动,其原理就是控制相机的位置,也就是更改cameraPos的值,那具体向哪个方向移动呢?对啦,就是向相机的方向向量(cameraFront)所指的方向移动就好啦,w就是他的方向,s就是反向,a就是他和相机的cameraUp向量叉乘出来的方向,d就是a的反向。但是要注意相乘的向量必须是单位向量,不然移动距离不对

4.2关于移动速度:
目前我们的移动速度是个常量。理论上没什么问题,但是实际情况下根据处理器的能力不同,有些人可能会比其他人每秒绘制更多帧,也就是以更高的频率调用processInput函数。结果就是,根据配置的不同,有些人可能移动很快,而有些人会移动很慢。当你发布你的程序的时候,你必须确保它在所有硬件上移动速度都一样。
图形程序和游戏通常会跟踪一个时间差(Deltatime)变量,它储存了渲染上一帧所用的时间。我们把所有速度都去乘以deltaTime值。结果就是,如果我们的deltaTime很大,就意味着上一帧的渲染花费了更多时间,所以这一帧的速度需要变得更高来平衡渲染所花去的时间。使用这种方法时,无论你的电脑快还是慢,摄像机的速度都会相应平衡,这样每个用户的体验就都一样了。
4.3关于视角移动:
一共有3种欧拉角:俯仰角(Pitch)、偏航角(Yaw)和滚转角(Roll),下面的图片展示了它们的含义:
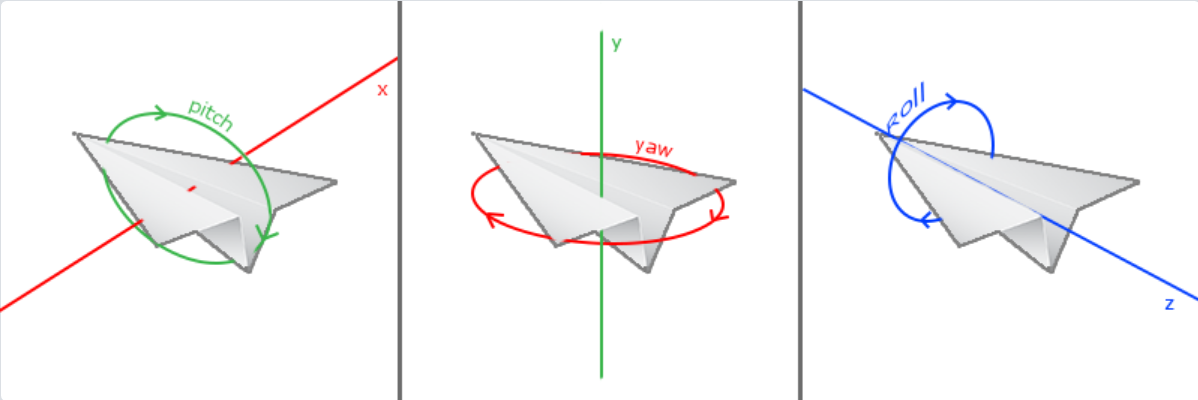
欧拉角与相机方向向量的关系:
direction.x = cos(glm::radians(pitch)) * cos(glm::radians(yaw));
direction.y = sin(glm::radians(pitch));
direction.z = cos(glm::radians(pitch)) * sin(glm::radians(yaw));
具体坐标系再具体分析,鼠标动一下,欧拉角响应加或者减一些,相机向量cameraFornt变一下,但是十分注意三个欧拉角的初始值,并不一定全是0,有可能是-90度
void mouse_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xpos, double ypos)
{
if (firstMouse)
{
lastX = xpos;
lastY = ypos;
firstMouse = false;
} float xoffset = xpos - lastX;
float yoffset = lastY - ypos; // reversed since y-coordinates go from bottom to top
lastX = xpos;
lastY = ypos; float sensitivity = 0.1f; // change this value to your liking
xoffset *= sensitivity;
yoffset *= sensitivity; yaw += xoffset;
pitch += yoffset; // make sure that when pitch is out of bounds, screen doesn't get flipped
if (pitch > 89.0f)
pitch = 89.0f;
if (pitch < -89.0f)
pitch = -89.0f; glm::vec3 front;
front.x = cos(glm::radians(yaw)) * cos(glm::radians(pitch));
front.y = sin(glm::radians(pitch));
front.z = sin(glm::radians(yaw)) * cos(glm::radians(pitch));
cameraFront = glm::normalize(front);
}
4.4还要注意一般不用翻滚角,且俯仰角的范围有限制,在正负89度之间,另外还有第一次捕捉鼠标位置时的问题
4.5鼠标滚轮的缩放移动
void scroll_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xoffset, double yoffset)
{
if(fov >= 1.0f && fov <= 45.0f)
fov -= yoffset;
if(fov <= 1.0f)
fov = 1.0f;
if(fov >= 45.0f)
fov = 45.0f;
}
//fov是init投影矩阵的视角参数
5.完整的一个代码
#include <glad/glad.h>
#include <GLFW/glfw3.h>
#include <stb_image.h> #include <glm/glm.hpp>
#include <glm/gtc/matrix_transform.hpp>
#include <glm/gtc/type_ptr.hpp> #include <learnopengl/shader_m.h> #include <iostream> void framebuffer_size_callback(GLFWwindow* window, int width, int height);
void mouse_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xpos, double ypos);
void scroll_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xoffset, double yoffset);
void processInput(GLFWwindow *window); // settings
const unsigned int SCR_WIDTH = ;
const unsigned int SCR_HEIGHT = ; // camera
glm::vec3 cameraPos = glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 3.0f);
glm::vec3 cameraFront = glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f);
glm::vec3 cameraUp = glm::vec3(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f); bool firstMouse = true;
float yaw = -90.0f; // yaw is initialized to -90.0 degrees since a yaw of 0.0 results in a direction vector pointing to the right so we initially rotate a bit to the left.
float pitch = 0.0f;
float lastX = 800.0f / 2.0;
float lastY = 600.0f / 2.0;
float fov = 45.0f; // timing
float deltaTime = 0.0f; // time between current frame and last frame
float lastFrame = 0.0f; int main()
{
// glfw: initialize and configure
// ------------------------------
glfwInit();
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MAJOR, );
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MINOR, );
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_OPENGL_PROFILE, GLFW_OPENGL_CORE_PROFILE); #ifdef __APPLE__
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_OPENGL_FORWARD_COMPAT, GL_TRUE); // uncomment this statement to fix compilation on OS X
#endif // glfw window creation
// --------------------
GLFWwindow* window = glfwCreateWindow(SCR_WIDTH, SCR_HEIGHT, "LearnOpenGL", NULL, NULL);
if (window == NULL)
{
std::cout << "Failed to create GLFW window" << std::endl;
glfwTerminate();
return -;
}
glfwMakeContextCurrent(window);
glfwSetFramebufferSizeCallback(window, framebuffer_size_callback);
glfwSetCursorPosCallback(window, mouse_callback);
glfwSetScrollCallback(window, scroll_callback); // tell GLFW to capture our mouse
glfwSetInputMode(window, GLFW_CURSOR, GLFW_CURSOR_DISABLED); // glad: load all OpenGL function pointers
// ---------------------------------------
if (!gladLoadGLLoader((GLADloadproc)glfwGetProcAddress))
{
std::cout << "Failed to initialize GLAD" << std::endl;
return -;
} // configure global opengl state
// -----------------------------
glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST); // build and compile our shader zprogram
// ------------------------------------
Shader ourShader("6.2.coordinate_systems.vs", "6.2.coordinate_systems.fs"); // set up vertex data (and buffer(s)) and configure vertex attributes
// ------------------------------------------------------------------
float vertices[] = {
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f, -0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f, -0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f
};
// world space positions of our cubes
glm::vec3 cubePositions[] = {
glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f),
glm::vec3(2.0f, 5.0f, -15.0f),
glm::vec3(-1.5f, -2.2f, -2.5f),
glm::vec3(-3.8f, -2.0f, -12.3f),
glm::vec3(2.4f, -0.4f, -3.5f),
glm::vec3(-1.7f, 3.0f, -7.5f),
glm::vec3(1.3f, -2.0f, -2.5f),
glm::vec3(1.5f, 2.0f, -2.5f),
glm::vec3(1.5f, 0.2f, -1.5f),
glm::vec3(-1.3f, 1.0f, -1.5f)
};
unsigned int VBO, VAO;
glGenVertexArrays(, &VAO);
glGenBuffers(, &VBO); glBindVertexArray(VAO); glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, VBO);
glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof(vertices), vertices, GL_STATIC_DRAW); // position attribute
glVertexAttribPointer(, , GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, * sizeof(float), (void*));
glEnableVertexAttribArray();
// texture coord attribute
glVertexAttribPointer(, , GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, * sizeof(float), (void*)( * sizeof(float)));
glEnableVertexAttribArray(); // load and create a texture
// -------------------------
unsigned int texture1, texture2;
// texture 1
// ---------
glGenTextures(, &texture1);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, texture1);
// set the texture wrapping parameters
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GL_REPEAT);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, GL_REPEAT);
// set texture filtering parameters
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
// load image, create texture and generate mipmaps
int width, height, nrChannels;
stbi_set_flip_vertically_on_load(true); // tell stb_image.h to flip loaded texture's on the y-axis.
unsigned char *data = stbi_load("resources/textures/container.jpg", &width, &height, &nrChannels, );
if (data)
{
glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, , GL_RGB, width, height, , GL_RGB, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, data);
glGenerateMipmap(GL_TEXTURE_2D);
}
else
{
std::cout << "Failed to load texture" << std::endl;
}
stbi_image_free(data);
// texture 2
// ---------
glGenTextures(, &texture2);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, texture2);
// set the texture wrapping parameters
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GL_REPEAT);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, GL_REPEAT);
// set texture filtering parameters
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
// load image, create texture and generate mipmaps
data = stbi_load("resources/textures/awesomeface.png", &width, &height, &nrChannels, );
if (data)
{
// note that the awesomeface.png has transparency and thus an alpha channel, so make sure to tell OpenGL the data type is of GL_RGBA
glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, , GL_RGB, width, height, , GL_RGBA, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, data);
glGenerateMipmap(GL_TEXTURE_2D);
}
else
{
std::cout << "Failed to load texture" << std::endl;
}
stbi_image_free(data); // tell opengl for each sampler to which texture unit it belongs to (only has to be done once)
// -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
ourShader.use();
ourShader.setInt("texture1", );
ourShader.setInt("texture2", ); // render loop
// -----------
while (!glfwWindowShouldClose(window))
{
// per-frame time logic
// --------------------
float currentFrame = glfwGetTime();
deltaTime = currentFrame - lastFrame;
lastFrame = currentFrame; // input
// -----
processInput(window); // render
// ------
glClearColor(0.2f, 0.3f, 0.3f, 1.0f);
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT); // bind textures on corresponding texture units
glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE0);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, texture1);
glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE1);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, texture2); // activate shader
ourShader.use(); // pass projection matrix to shader (note that in this case it could change every frame)
glm::mat4 projection = glm::perspective(glm::radians(fov), (float)SCR_WIDTH / (float)SCR_HEIGHT, 0.1f, 100.0f);
ourShader.setMat4("projection", projection); // camera/view transformation
glm::mat4 view = glm::lookAt(cameraPos, cameraPos + cameraFront, cameraUp);
ourShader.setMat4("view", view); // render boxes
glBindVertexArray(VAO);
for (unsigned int i = ; i < ; i++)
{
// calculate the model matrix for each object and pass it to shader before drawing
glm::mat4 model;
model = glm::translate(model, cubePositions[i]);
float angle = 20.0f * i;
model = glm::rotate(model, glm::radians(angle), glm::vec3(1.0f, 0.3f, 0.5f));
ourShader.setMat4("model", model); glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES, , );
} // glfw: swap buffers and poll IO events (keys pressed/released, mouse moved etc.)
// -------------------------------------------------------------------------------
glfwSwapBuffers(window);
glfwPollEvents();
} // optional: de-allocate all resources once they've outlived their purpose:
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------
glDeleteVertexArrays(, &VAO);
glDeleteBuffers(, &VBO); // glfw: terminate, clearing all previously allocated GLFW resources.
// ------------------------------------------------------------------
glfwTerminate();
return ;
} // process all input: query GLFW whether relevant keys are pressed/released this frame and react accordingly
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void processInput(GLFWwindow *window)
{
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_ESCAPE) == GLFW_PRESS)
glfwSetWindowShouldClose(window, true); float cameraSpeed = 2.5 * deltaTime;
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_W) == GLFW_PRESS)
cameraPos += cameraSpeed * cameraFront;
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_S) == GLFW_PRESS)
cameraPos -= cameraSpeed * cameraFront;
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_A) == GLFW_PRESS)
cameraPos -= glm::normalize(glm::cross(cameraFront, cameraUp)) * cameraSpeed;
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_D) == GLFW_PRESS)
cameraPos += glm::normalize(glm::cross(cameraFront, cameraUp)) * cameraSpeed;
} // glfw: whenever the window size changed (by OS or user resize) this callback function executes
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void framebuffer_size_callback(GLFWwindow* window, int width, int height)
{
// make sure the viewport matches the new window dimensions; note that width and
// height will be significantly larger than specified on retina displays.
glViewport(, , width, height);
} // glfw: whenever the mouse moves, this callback is called
// -------------------------------------------------------
void mouse_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xpos, double ypos)
{
if (firstMouse)
{
lastX = xpos;
lastY = ypos;
firstMouse = false;
} float xoffset = xpos - lastX;
float yoffset = lastY - ypos; // reversed since y-coordinates go from bottom to top
lastX = xpos;
lastY = ypos; float sensitivity = 0.1f; // change this value to your liking
xoffset *= sensitivity;
yoffset *= sensitivity; yaw += xoffset;
pitch += yoffset; // make sure that when pitch is out of bounds, screen doesn't get flipped
if (pitch > 89.0f)
pitch = 89.0f;
if (pitch < -89.0f)
pitch = -89.0f; glm::vec3 front;
front.x = cos(glm::radians(yaw)) * cos(glm::radians(pitch));
front.y = sin(glm::radians(pitch));
front.z = sin(glm::radians(yaw)) * cos(glm::radians(pitch));
cameraFront = glm::normalize(front);
} // glfw: whenever the mouse scroll wheel scrolls, this callback is called
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------
void scroll_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xoffset, double yoffset)
{
if (fov >= 1.0f && fov <= 45.0f)
fov -= yoffset;
if (fov <= 1.0f)
fov = 1.0f;
if (fov >= 45.0f)
fov = 45.0f;
}
openGL学习----相机的更多相关文章
- OpenGL学习进程(12)第九课:矩阵乘法实现3D变换
本节是OpenGL学习的第九个课时,下面将详细介绍OpenGL的多种3D变换和如何操作矩阵堆栈. (1)3D变换: OpenGL中绘制3D世界的空间变换包括:模型变换.视图变换.投影变换和视口 ...
- OpenGL学习之路(五)
1 引子 不知不觉我们已经进入到读书笔记(五)了,我们先对前四次读书笔记做一个总结.前四次读书笔记主要是学习了如何使用OpenGL来绘制几何图形(包括二维几何体和三维几何体),并学习了平移.旋转.缩放 ...
- OpenGL学习脚印:深度測试(depth testing)
写在前面 上一节我们使用AssImp载入了3d模型,效果已经令人激动了.可是绘制效率和场景真实感还存在不足,接下来我们还是要保持耐心,继续学习一些高级主题,等学完后面的高级主题,我们再次来改进我们载入 ...
- OpenGL学习进程(7)第五课:点、边和图形(二)边
本节是OpenGL学习的第五个课时,下面介绍OpenGL边的相关知识: (1)边的概念: 数学上的直线没有宽度,但OpenGL的直线则是有宽度的.同时,OpenGL的直线必须是有限长度,而不是像数学概 ...
- OpenGL学习笔记3——缓冲区对象
在GL中特别提出了缓冲区对象这一概念,是针对提高绘图效率的一个手段.由于GL的架构是基于客户——服务器模型建立的,因此默认所有的绘图数据均是存储在本地客户端,通过GL内核渲染处理以后再将数据发往GPU ...
- OpenGL学习进程(11)第八课:颜色绘制的详解
本节是OpenGL学习的第八个课时,下面将详细介绍OpenGL的颜色模式,颜色混合以及抗锯齿. (1)颜色模式: OpenGL支持两种颜色模式:一种是RGBA,一种是颜色索引模式. R ...
- OpenGL学习笔记:拾取与选择
转自:OpenGL学习笔记:拾取与选择 在开发OpenGL程序时,一个重要的问题就是互动,假设一个场景里面有很多元素,当用鼠标点击不同元素时,期待作出不同的反应,那么在OpenGL里面,是怎么知道我当 ...
- OpenGL学习之路(一)
1 引子 虽然是计算机科班出身,但从小对几何方面的东西就不太感冒,空间想象能力也较差,所以从本科到研究生,基本没接触过<计算机图形学>.为什么说基本没学过呢?因为好奇(尤其是惊叹于三维游戏 ...
- OpenGL学习之路(三)
1 引子 这些天公司一次次的软件发布节点忙的博主不可开交,另外还有其它的一些事也占用了很多时间.现在坐在电脑前,在很安静的环境下,与大家分享自己的OpenGL学习笔记和理解心得,感到格外舒服.这让我回 ...
随机推荐
- git 同步远程已删除的分支和删除本地多余的分支
使用git branch -a可以查看本地分支和远程分支情况 但远程分支(红色部分)删除后,发现本地并没有同步过来. 一. 同步本地的远程分支 查看本地分支和追踪情况: git remote show ...
- 深入理解 Java 虚拟机之学习笔记(3)
垃圾回收(Garbage Collection,GC ),GC的历史其实比Java久远,1960年诞生与MIT的Lisp是第一门真正使用内存动态分配和垃圾收集技术的语言.当Lisp还在胚胎时期时,人们 ...
- PowerBI与Visio
前言 如何在Power BI中使用Visio, 刚好最近微软推出了适用于Power BI 的 Visio自定义可视化对象预览,分享给大家. 我们先看一下效果: 通过自定义可视化对象,将Visio ...
- a排兵布阵
来源hdu1166 C国的死对头A国这段时间正在进行军事演习,所以C国间谍头子Derek和他手下Tidy又开始忙乎了.A国在海岸线沿直线布置了N个工兵营地,Derek和Tidy的任务就是要监视这些工兵 ...
- array_push() 与 $arr[]=$value 的使用场景
在只压入一个元素的时候使用 $arr[] = $value 当可以同时压入多个元素的时候推荐使用 array_push. 注:如果是压入一个元素,使用$arr[]=$value效率高,因为可以节省调用 ...
- Python Solve UnicodeEncodeError 'gbk' / 'ascii' / 'utf8' codec can't encode character '\x??' in position ? 解决有关Python编码的错误
在Python中,处理中文字符一直是很令人头痛的问题,一言不合就乱码,而且引起乱码的原因也不尽相同,有时候是python本身默认的编码器设置的不对,有时候是使用的IDE的解码器不对,还有的时候是终端t ...
- poj3278_kuagnbin带你飞专题一
Catch That Cow Time Limit: 2000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 88247 Accepted: 27640 ...
- mybatis13--2级缓存
验证内置的2级缓存 Ehcache缓存的配置 01.引入需要的ehcache 和mybatis-ehcache 两个jar包 02.在mapper文件中增加 <cache type=" ...
- java 三大框架 struct2部分 实现增删该查操作
1.三层架构 表现层:接收和处理请求. MVC模型:它是一个表现层模型. 业务层:处理程序业务需求. 持久层:对数据库操作的.2.MVC模型 M:Model ...
- Linux 命令 which whereis locate find
which: 查询某指令的完整路径 $ which [-a] command -a: 将所有在PATH目录中可以找到的指令均列出. 注意:只搜索PATH下的路径. whereis: 只搜索几个特定目录 ...
