【转】JDBC学习笔记(3)——复习和练习
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/ysw-go/
复习部分
一、获取数据库连接
1)方式一

1 // 获取数据库连接
2 @Test
3 public void testGetConnection() throws Exception {
4 // 1.准备获取连接的四个字符串:user,jdbcurl,password,driverClass
5 String user = "root";
6 String password = "123456";
7 String jdbcUrl = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/atguigu";
8 String driverClass = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
9 Class.forName(driverClass);
10 Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(jdbcUrl, user,
11 password);
12 System.out.println(connection);
13 }

2)方式二:解耦合

1 public Connection getConnection() throws IOException,
2 ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
3 Properties properties = new Properties();
4 InputStream inputStream = JDBCTest.class.getClassLoader()
5 .getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties");
6 properties.load(inputStream);
7 String user = properties.getProperty("user");
8 String password = properties.getProperty("password");
9 String jdbcUrl = properties.getProperty("jdbcUrl");
10 String driverClass = properties.getProperty("driver");
11 Class.forName(driverClass);
12 Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(jdbcUrl, user,
13 password);
14 return connection;
15 }

二、Statement执行更新数据的操作
我们这里把更新数据的操作。用一个通用的update函数来表示

1 public void update() {
2 // 1.获取数据库连接
3 Connection connection = null;
4 Statement statement = null;
5 try {
6 connection=getConnection();
7 // 2.调用Connection对象的createStatement()方法获取
8 // Statement对象
9 statement=connection.createStatement();
10 // 3.准备SQL语句
11 String sql="insert into examstudent values(1,4,'412824195263214584','200523164754000','张峰','郑州',85)";
12 // 4.发送SQL语句:调用Statement对象的excuteUpdate(sql)方法
13 statement.executeUpdate(sql);
14
15 } catch (Exception e) {
16 e.printStackTrace();
17 }finally{
18 // 5.关闭数据库资源:由里向外关闭
19 releaseDB(null, statement, connection);
20 }
21 }

三、ResultSet执行查询操作

1 @Test
2 public void testResultSet(){
3 Connection connection=null;
4 Statement statement=null;
5 ResultSet resultSet=null;
6 try {
7 //1.获取数据库连接
8 connection=getConnection();
9 //2.Statement
10 statement=connection.createStatement();
11 //3.准备SQL
12 String sql="select * from customers";
13 //4.执行SQL,得到结果集
14 resultSet=statement.executeQuery(sql);
15 //5.处理结果集
16 while(resultSet.next()){
17 int id=resultSet.getInt(1);
18 String name=resultSet.getString(2);
19 String email=resultSet.getString(3);
20 Date birth=resultSet.getDate(4);
21 System.out.println(id);
22 System.out.println(name);
23 System.out.println(email);
24 System.out.println(birth);
25 System.out.println("----------");
26 }
27
28 } catch (Exception e) {
29 e.printStackTrace();
30 }finally{
31 releaseDB(resultSet, statement, connection);
32 }
33 }

四、工具类的使用JDBCTools
将获取连接、执行更新操作、释放资源封装在一个JDBCTools类中

1 package com.atguigu.jdbc;
2
3 import java.io.IOException;
4 import java.io.InputStream;
5 import java.sql.Connection;
6 import java.sql.DriverManager;
7 import java.sql.ResultSet;
8 import java.sql.SQLException;
9 import java.sql.Statement;
10 import java.util.Properties;
11
12 public class JDBCTools {
13 // 更新的方法:插入、删除、更新,但是不包含select
14 public static void update(String sql) {
15 // 1.获取数据库连接
16 Connection connection = null;
17 Statement statement = null;
18 try {
19 connection = getConnection();
20 // 2.调用Connection对象的createStatement()方法获取
21 // Statement对象
22 statement = connection.createStatement();
23 // 4.发送SQL语句:调用Statement对象的excuteUpdate(sql)方法
24 statement.executeUpdate(sql);
25
26 } catch (Exception e) {
27 e.printStackTrace();
28 } finally {
29 // 5.关闭数据库资源:由里向外关闭
30 release(null, statement, connection);
31 }
32 }
33
34 // 获取数据库连接
35 public static Connection getConnection() throws IOException,
36 ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
37 Properties properties = new Properties();
38 InputStream inputStream = JDBCTest.class.getClassLoader()
39 .getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties");
40 properties.load(inputStream);
41 String user = properties.getProperty("user");
42 String password = properties.getProperty("password");
43 String jdbcUrl = properties.getProperty("jdbcUrl");
44 String driverClass = properties.getProperty("driver");
45 Class.forName(driverClass);
46 Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(jdbcUrl, user,
47 password);
48 return connection;
49 }
50
51 // 释放数据库资源
52 public static void release(ResultSet rs, Statement statement,
53 Connection conn) {
54 if (rs != null) {
55 try {
56 rs.close();
57 } catch (Exception e) {
58 // TODO: handle exception
59 }
60 }
61 if (statement != null) {
62 try {
63 statement.close();
64
65 } catch (Exception e2) {
66 // TODO: handle exception
67 }
68 }
69 if (conn != null) {
70 try {
71 conn.close();
72 } catch (SQLException e) {
73 e.printStackTrace();
74 }
75 }
76 }
77 }

练习部分
我们的练习是这样的:
新建一个表:
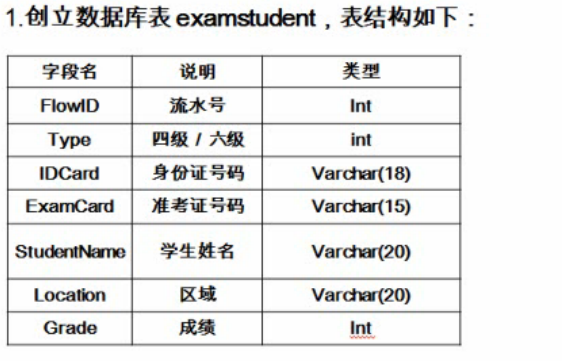
向表中插入数据:
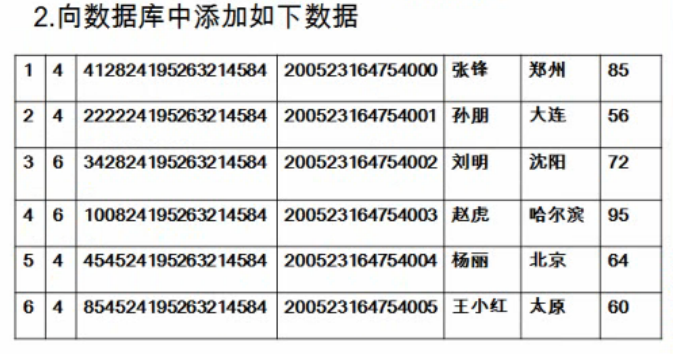
插入成功的话会出现这样的提示(我们从控制台获取要插入的数据):

第一步、用图形化界面SQLyog创建一个数据表examstudent
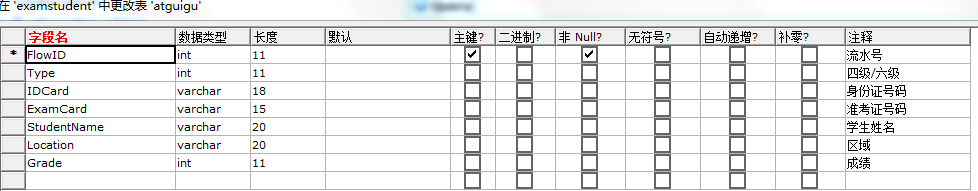
第二步、向数据表中插入数据
面向对象的思想去编程:将插入的数据封装在一个类Student中

1 package com.atguigu.jdbc;
2
3 public class Student {
4 // 流水号
5 private int flowId;
6 // 考试类型
7 private int type;
8 // 身份证号
9 private String idCard;
10 // 准考证号
11 private String examCard;
12 // 学生姓名
13 private String studentName;
14 // 学生地址
15 private String location;
16 // 考试成绩
17 private int grade;
18
19 public int getFlowId() {
20 return flowId;
21 }
22
23 public void setFlowId(int flowId) {
24 this.flowId = flowId;
25 }
26
27 public int getType() {
28 return type;
29 }
30
31 public void setType(int type) {
32 this.type = type;
33 }
34
35 public String getIdCard() {
36 return idCard;
37 }
38
39 public void setIdCard(String idCard) {
40 this.idCard = idCard;
41 }
42
43 public String getExamCard() {
44 return examCard;
45 }
46
47 public void setExamCard(String examCard) {
48 this.examCard = examCard;
49 }
50
51 public String getStudentName() {
52 return studentName;
53 }
54
55 public void setStudentName(String studentName) {
56 this.studentName = studentName;
57 }
58
59 public String getLocation() {
60 return location;
61 }
62
63 public void setLocation(String location) {
64 this.location = location;
65 }
66
67 public int getGrade() {
68 return grade;
69 }
70
71 public void setGrade(int grade) {
72 this.grade = grade;
73 }
74
75 public Student(int flowId, int type, String idCard, String examCard,
76 String studentName, String location, int grade) {
77 super();
78 this.flowId = flowId;
79 this.type = type;
80 this.idCard = idCard;
81 this.examCard = examCard;
82 this.studentName = studentName;
83 this.location = location;
84 this.grade = grade;
85 }
86
87 public Student() {
88
89 }
90
91 // 重写Student对象的toString函数
92 @Override
93 public String toString() {
94 return "Student [flowId=" + flowId + ", type=" + type + ", idCard="
95 + idCard + ", examCard=" + examCard + ", studentName="
96 + studentName + ", location=" + location + ", grade=" + grade
97 + "]";
98 }
99
100 }

从控制台获取输入信息作为插入student对象的相应的字段值,并插入到新创建的表中

1 package com.atguigu.jdbc;
2
3 import java.util.Scanner;
4
5 import org.junit.Test;
6
7 public class JDBCTestCase {
8
9 //单元测试
10 @Test
11 public void testAddNewStudent() {
12 Student student = getStudentFromConsole();
13 addNewStudent(student);
14 }
15
16 // 从控制台输入学生的信息
17 private Student getStudentFromConsole() {
18 Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
19 Student student = new Student();
20 System.out.print("FlowId:");
21 student.setFlowId(scanner.nextInt());
22 System.out.print("Type:");
23 student.setType(scanner.nextInt());
24 System.out.print("IdCard:");
25 student.setIdCard(scanner.next());
26 System.out.print("ExamCard:");
27 student.setExamCard(scanner.next());
28 System.out.print("StudentName:");
29 student.setStudentName(scanner.next());
30 System.out.print("Location:");
31 student.setLocation(scanner.next());
32 System.out.print("Grade:");
33 student.setGrade(scanner.nextInt());
34 return student;
35 }
36
37 public void addNewStudent(Student student) {
38 String sql = "insert into examstudent" + " values("
39 + student.getFlowId() + "," + student.getType() + ",'"
40 + student.getIdCard() + "','" + student.getExamCard() + "','"
41 + student.getStudentName() + "','" + student.getLocation()
42 + "'," + student.getGrade() + ")";
43 System.out.println(sql);
44 JDBCTools.update(sql);
45 }
46
47 }

第三步、进行数据的查询(按第三张图片中要求的形式进行查询)
1).从控制台输入一个整数,确定要查询的类型

1 /*
2 * 1.身份证查询。 2.用准考证查询 。 3,其他,重新输入
3 */
4 private int getSearchTypeFromConsole() {
5 System.out.println("请输入查询类型:1.身份证查询. 2.用准考证查询 ");
6 Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
7 int type = scanner.nextInt();
8 if (type != 1 && type != 2) {
9 System.out.println("输入有误,请重新输入!");
10 throw new RuntimeException();
11 }
12 return 0;
13 }

2).根据查询类型准备sql语句

1 // searchType:1或者2
2 private Student searchStudent(int searchType) {
3 String sql = "select * from examstudent where ";
4 Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
5 // 1.根据输入的searchType,提示用户输入信息
6 // 1.1若searchType=1,提示:请输入身份证号
7 // 1.2若searchType=2,提示:请输入准考证号
8 // 2/根据searchType确定SQL
9 if (searchType == 1) {
10 System.out.print("请输入准考证号:");
11 String examCard = scanner.next();
12 sql = sql + "examCard='" + examCard + "'";
13 } else {
14 System.out.print("请输入身份证号:");
15 String IdCard = scanner.next();
16 sql = sql + "IdCard='" + IdCard + "'";
17 }
18
19 // 3.执行查询
20 Student student = getStudent(sql);
21 // 4.若存在结果,将查询结果封装成一个Student对象
22 return student;
23 }

执行查询操作,将结果封装成一个Student对象

1 private Student getStudent(String sql) {
2 Student student = null;
3 Connection connection = null;
4 Statement statement = null;
5 ResultSet resultSet = null;
6 try {
7 connection = JDBCTools.getConnection();
8 statement = connection.createStatement();
9 resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);
10 if (resultSet.next()) {
11 student = new Student(resultSet.getInt(1), resultSet.getInt(2),
12 resultSet.getString(3), resultSet.getString(4),
13 resultSet.getString(5), resultSet.getString(6),
14 resultSet.getInt(7));
15 }
16 } catch (Exception e) {
17 e.printStackTrace();
18 } finally {
19 JDBCTools.release(resultSet, statement, connection);
20 }
21 return student;
22 }

打印查询结果:

1 /**
2 * 打印学生信息:若学生存在则打印具体信息,否则打印:查无此人
3 */
4 private void printStudent(Student student) {
5 if (student != null) {
6 System.out.println(student);
7 } else {
8 System.out.println("查无此人");
9 }
10 }

写一个测试方法测试一下:

1 @Test
2 public void testGetStudent() {
3 // 1.得到查询的类型
4 int searchType = getSearchTypeFromConsole();
5 // 2.具体查询信息
6 Student student = searchStudent(searchType);
7 // 3.打印学生信息
8 printStudent(student);
9 }

运行结果:
请输入查询类型:1.身份证查询. 2.用准考证查询 1 请输入身份证号:3 Student [flowId=1, type=2, idCard=3, examCard=4, studentName=lili, location=dalin, grade=85]
【转】JDBC学习笔记(3)——复习和练习的更多相关文章
- JDBC学习笔记(3)——复习和练习
复习和练习 复习部分 一.获取数据库连接 1)方式一 // 获取数据库连接 @Test public void testGetConnection() throws Exception { // 1. ...
- JDBC 学习笔记(十一)—— JDBC 的事务支持
1. 事务 在关系型数据库中,有一个很重要的概念,叫做事务(Transaction).它具有 ACID 四个特性: A(Atomicity):原子性,一个事务是一个不可分割的工作单位,事务中包括的诸操 ...
- JDBC 学习笔记(十)—— 使用 JDBC 搭建一个简易的 ORM 框架
1. 数据映射 当我们获取到 ResultSet 之后,显然这个不是我们想要的数据结构. 数据库中的每一个表,在 Java 代码中,一定会有一个类与之对应,例如: package com.gerrar ...
- JDBC 学习笔记(六)—— PreparedStatement
1. 引入 PreparedStatement PreparedStatement 通过 Connection.createPreparedStatement(String sql) 方法创建,主要用 ...
- JDBC学习笔记二
JDBC学习笔记二 4.execute()方法执行SQL语句 execute几乎可以执行任何SQL语句,当execute执行过SQL语句之后会返回一个布尔类型的值,代表是否返回了ResultSet对象 ...
- JDBC学习笔记一
JDBC学习笔记一 JDBC全称 Java Database Connectivity,即数据库连接,它是一种可以执行SQL语句的Java API. ODBC全称 Open Database Conn ...
- JDBC学习笔记(2)——Statement和ResultSet
Statement执行更新操作 Statement:Statement 是 Java 执行数据库操作的一个重要方法,用于在已经建立数据库连接的基础上,向数据库发送要执行的SQL语句.Statement ...
- JDBC学习笔记(1)——JDBC概述
JDBC JDBC API是一个Java API,可以访问任何类型表列数据,特别是存储在关系数据库中的数据.JDBC代表Java数据库连接. JDBC库中所包含的API任务通常与数据库使用: 连接到数 ...
- 【转】JDBC学习笔记(2)——Statement和ResultSet
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/ysw-go/ Statement执行更新操作 Statement:Statement 是 Java 执行数据库操作的一个重要方法,用于在已经建立数 ...
随机推荐
- 使用js在网页上记录鼠标划圈的小程序
Spin-Wheel 实现鼠标在网页上转圈时记录转动圈数的小程序,每转一圈记录一次,同时要是顺时针方向的. 问题分析与实现 这个小程序的难点在于如何知道鼠标完成了一个转圈的动作,而且人工使用鼠标划圈时 ...
- Java基础(下)(JVM、API)
Java基础(下) 第三部分:Java源程序的编辑 我们知道,计算机是不能直接理解源代码中的高级语言,只能直接理解机器语言,所以必须要把高级语言翻译成机器语言,计算机才能执行高级语言编写的程序. 翻译 ...
- android sdk 深入理解adb
adb 服务器-客户端程序包括3部分 1.客户端(client) 在开发机器上运行,可通过adb命令行呼叫客户端,ADT插件和DDMS同样需要adb客户端 2.服务端(server) 在开发机器上 ...
- 关于IE低版本兼容问题
1,元素浮动之后,能设置宽度的话就给元素加宽度.如果需要宽度是内容撑开,就给它里边的块元素加上浮动: 解决方案:给需要宽度由内容撑开的元素加上浮动 css样式: <style> .box{ ...
- 轻松理解JavaScript之AJAX
摘要 AJAX技术是网页构建的必备技能之一,本文希望能帮助大家轻松的学习这项技术 一.什么是ajax? ajax(异步javascript xml) 能够刷新局部网页数据而不是重新加载整个网页. 二. ...
- git 由http切换成git
项目中经常会遇到http 的git 协议为了安全切换成ssh 的git 协议. 这个时候,只要使用如下命令变更 remote 字符串就好了. git remote set-url origin git ...
- Selenium2 WebDriver环境搭建
1.下载Selenium Client Servers包 在Selenium官网上可以下载到最新的开源的包http://seleniumhq.org/download/,根据编写测试脚本所使用的语言下 ...
- eclipse和myeclipse设置默认编码格式为UTF-8
1:jsp页面设置默认为utf-8 以eclipse为例 2:java界面设置: Window->Preferences->General->Workspace 面板Text fil ...
- WebService客户端添加SOAPHeader信息
通过JAXBContext创建Marshaller对头信息进行解析为dom,获取WSBindingProvider,使用Headers.creat()创建soap的Header元素: 另外就是:将us ...
- oracle备份脚本
利用EXP导出全库,必须用SYSTEM或者DBA用户来导出. 具体脚本实现如下 全库导出(fullbackup): #!/bin/bash bname=`date +%Y%m%d` cd /backu ...
