文件I/O流、文件、FileInputStreaam、FileOutputStream、FileReader、FileWriter的介绍和使用
一、文件:保存数据的地方
1、文件流:文件在程序中是以流的形式类操作的

类比:

流:数据在数据源(文件)和程序(内存)之间经历的路径
输入流:数据从数据源(文件)到程序(内存)的路径
输出流:数据从程序(内存)到数据源(文件)的路径
2、常用的文件操作和方法
1)、相关方法:
new File(String pathname)1/根据路径构建一个File对象
new File(File parent,String child)//根据父目录文件+子路径构建
new File(String parent,String child)//根据父目录+子路径构建
createNewFile创建新文件

创建文件的三个方式案例:
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException; public class fileCreate {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String filePath1 = "C:\\Users\\wenman\\Desktop\\test\\news1.txt";
//创建第一个txt文件new File(String pathname)1/根据路径构建一个File对象
File file1 = new File(filePath1);
try {
file1.createNewFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("New1/txt创建成功!!");
//创建一个txt,new File(String parent,String child)//根据父目录+子路径构建
String filePath2 = "C:\\Users\\wenman\\Desktop\\test";
String filePathChild = "\\news2.txt";
File file2 = new File(filePath2, filePathChild);
try {
file2.createNewFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("news2.txt文件创建成功!"); //创建一个文件夹和txt,new File(File parent,String child)//根据父目录文件+子路径构建
File file = new File("C:\\Users\\wenman\\Desktop\\test");
String filePath3 = "\\news3.txt"; File file3 = new File(file, filePath3);
try {
file3.createNewFile();
System.out.println("文件file3创建成功!");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} }
}
2)、获取文件的相关信息:
File file = new File( "e: \ lnews1.txt");
//调用相应的方法,得到对应信息
System.out.println("文件名字="+ file.getName());
//getName、getAbsolutePath、getParent、length、exists、isFile、isDirectory
System.out.println("文件绝对路径=" + file.getAbsolutepath());
System.out.println("文件父级目录=" + file.getParent());
System.out.println("文件大小(字节)=" + file.length();//
{
①ASCII码中,一个英文字母(不分大小写)占一个字节的空间,一个中文汉字占两个字节的空间。一个二进制数字序列,在计算机中作为一个数字单元,一般为8位二进制数,换算为十进制。最小值0,最大值255。
②UTF-8编码中,一个英文字符等于一个字节,一个中文(含繁体)等于三个字节。
③Unicode编码中,一个英文等于两个字节,一个中文(含繁体)等于两个字节。
符号:英文标点占一个字节,中文标点占两个字节。举例:英文句号“.”占1个字节的大小,中文句号“。”占2个字节的大小。
④UTF-16编码中,一个英文字母字符或一个汉字字符存储都需要2个字节(Unicode扩展区的一些汉字存储需要4个字节)。
⑤UTF-32编码中,世界上任何字符的存储都需要4个字节。
}
System.out.printLn("文件是否存在=" + file.exists());//T
System.out.println("是不是一个文件=" + file.isFile());//T
System.out.println("是不是一个目录= + file.isDirectory();//F
3)、目录的操作和文件删除
mkdir创建一级目录、mkdirs创建多级目录、delete删除空目录或文件(如果不是空需要删除其中内容)

二、IO流原理及流的分类
Java IO流的原理:
1. I/O是Input/Output的缩写, I/O技术是非常实用的技术,用于处理数据传输。
如读/写文件,网络通讯等。
2. Java程序中,对于数据的输入/输出操作以”流(stream)" 的方式进行。
3. java.io包下提供了各种"流”类和接口,用以获取不同种类的数据,并通过方
法输入或输出数据
4.输入input: 读取外部数据(磁盘、 光盘等存储设备的数据)到程序(内存)中。
5.输出output: 将程序(内存)数据输出到磁盘、光盘等存储设备中

流的分类:
按操作数据单位不同分为:字节流(8 bit)二进制文件,字符流(按字符)文本文件
按数据流的流向不同分为:输入流,输出流
按流的角色的不同分为:节点流,处理流/包装流

1) Java的IO流共涉及40多个类,实际上非常规则,都是从如上4个抽象基类派生的。
2)由这四个类派生出来的子类名称都是以其父类名作为子类名后缀。
IO流体系图: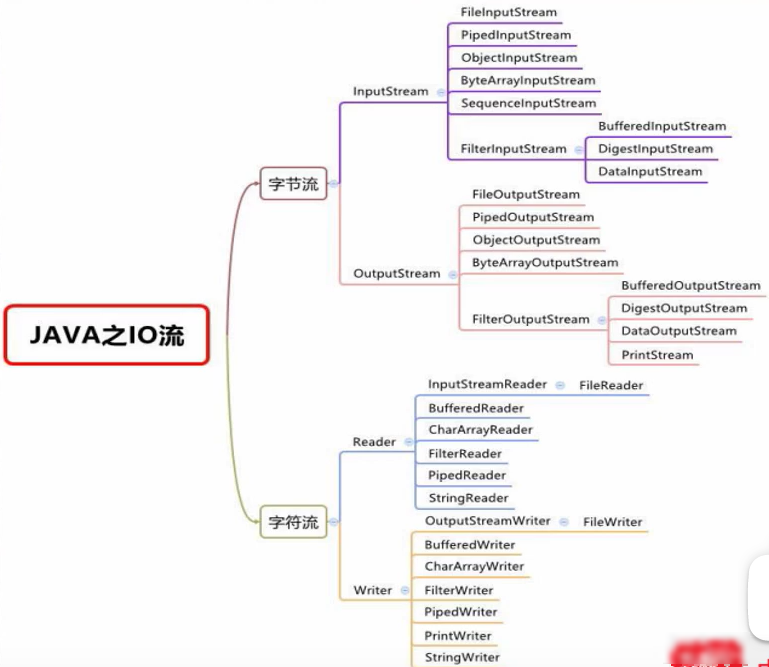
文件VS流(文件和流的比较):

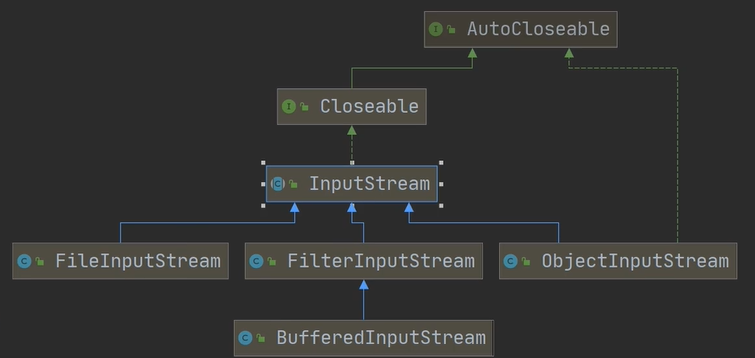
字节输入流:InputStream
InputStream抽象类是所有字节输入类的超类:
InputStream常用的子类:
1. FilelnputStream:文件输入流
2. BufferedInputStream:缓冲字节输入流
3. ObjectInputStream: 对象字节输入流
继承实现图:
字节流输入代码演示
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test; import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException; public class FileInputStream_ { @Test
public void readFile(){
//文件路径
String filePath1 = "C:\\Users\\wenman\\Desktop\\test\\news1.txt";
//创建文件对象
// File file = new File(filePath1);
//创建流对象
FileInputStream inputStream =null;
int fileData = 0;
try {
inputStream = new FileInputStream(filePath1);
//按照字节读取文件read()每次只能读取一个字节
while ((fileData=inputStream.read() )!=-1 ){
//将返回结果转化成char类型输出
System.out.print((char) fileData);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
@Test
public void readFile1(){
//文件路径
String filePath1 = "C:\\Users\\wenman\\Desktop\\test\\news1.txt";
//创建文件对象
File file = new File(filePath1);
//定义流对象
FileInputStream inputStream =null;
//创建byte[]数组,用于接收返回的字节
byte[] bytes = new byte[100];
String Data = null;
int fileData = 0;
try {
//创建流对象
inputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
//读取文件中的内容:read(bytes)按照字节数组的方式读取,如果没有内容返回-1
//如果长度不够返回实际的字节长度
while ((fileData=inputStream.read(bytes)) != -1){
System.out.println(new String(bytes));
System.out.println(new String(bytes, 0, fileData));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
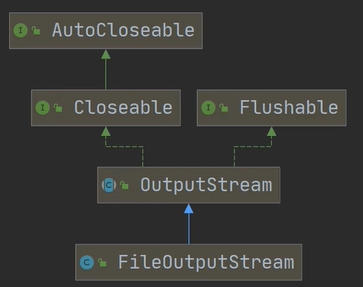
输出流:继承实现图
输出流代码演示:
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test; import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException; public class fileOutputStream_ {
@Test
public void write(){
//定义文件路径
String filePath1 = "C:\\Users\\wenman\\Desktop\\test\\news2.txt";
//定义一个输出流
FileOutputStream OutputStream = null;
String s= "hellt tttt"; try {
//1. new FiLeOutputStream(fiLePath) 创建方式,当写入内容时,会覆盖原来的内容
//2. new FiLe0utputStream(fiLePath, true) 创建方式,当写入内容时,是追加到文件后面
//3.当当前文件不存在时,会创建该文件并输出内容到文件
// OutputStream = new FileOutputStream(filePath1,true);
OutputStream = new FileOutputStream(filePath1);
OutputStream.write(s.getBytes());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
OutputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
三、FileReader和FileWriter介绍
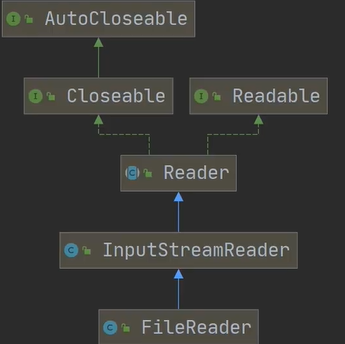
FileReader和FileWriter是字符流,即按照字符来操作:
FileReader相关方法:
继承实现图:
1) new FileReader(File/String)
2) read:每次读取单个字符,返回该字符,如果到文件末尾返回-1
3) read(char[]):批量读取多个字符到数组,返回读取到的字符数,如果到文件末尾返回-1
相关APl:
1) new String(char[]):将char[]转换成String
2) new String(char[I]off,len):将char[]的指定部分转换成String
代码实例:
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException; public class Reader_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//定义一个文件的路径
String filePath1 = "C:\\Users\\wenman\\Desktop\\test\\news3.txt";
//创建一个字符输入流
FileReader fileReader = null;
//创建一个字符数组,保存读取的内容
char[] chars = new char[100];
int dateLine = 0;
try {
fileReader= new FileReader(filePath1);
while ((dateLine=fileReader.read(chars))!=-1 ){//循环读取,返回实际读取的字符数,如果没有读取到返回-1
// System.out.println(new String(chars));
System.out.println(new String(chars,0,dateLine));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}finally {
try {
fileReader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} }
FileWriter常用方法
继承实现图:
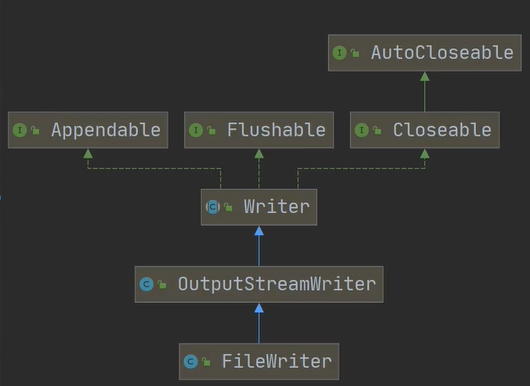
1) new FileWriter(File/String):覆盖模式,相当于流的指针在首端
2) new FileWriter(File/String,true):追加模式,相当于流的指针在尾端
3) write(int):写入单个字符
4) write(char[):写入指定数组
5) write(char[,off.len):写入指定数组的指定部分
6) write (string) :写入整个字符串
7) write(string,off,len):写入字符串的指定部分
相关API: String类: toCharArray:将String转换成char[]
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test; import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException; public class Writer_ {
@Test
public void write1() {
//定义文件地址
String filePath1 = "C:\\Users\\wenman\\Desktop\\test\\note.txt";
String txt = "海阔凭鱼跃,天空任鸟飞!!";
//定义一个输出流
FileWriter fileWriter = null; try {
fileWriter = new FileWriter(filePath1);//默认覆盖原有内容重新将内容写进去
fileWriter.write(txt);
fileWriter.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
fileWriter.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} }
@Test
public void write2() {
//定义文件地址
String filePath1 = "C:\\Users\\wenman\\Desktop\\test\\note.txt";
String txt = "海阔凭鱼跃,天空任鸟飞!!";
//定义一个输出流
FileWriter fileWriter = null;
char[] chars = {'q','w','e'}; try {
fileWriter = new FileWriter(filePath1,true);//在文件末尾添加内容 // 1) write(int):写入单个字符
fileWriter.write("Z");
// 2) write(char[]):写入指定数组
fileWriter.write(chars);
// 3) write(char[],off.len):写入指定数组的指定部分
fileWriter.write(chars,0,2);
// 4) write (string) :写入整个字符串
fileWriter.write(txt);
// 5) write(string,off,len):写入字符串的指定部分
fileWriter.write(txt,3,6); fileWriter.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
fileWriter.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} }
}
注意:
FileWriter使用后,必须要关闭(close)或刷新(flush), 否则写入不到指定的文件!
文件I/O流、文件、FileInputStreaam、FileOutputStream、FileReader、FileWriter的介绍和使用的更多相关文章
- 节点流(文件流) FileInputStream & FileOutputStream & FileReader & FileWriter
节点流(文件流) FileInputStream(字节流)处理视频类的 FileOutputStream(字节流) FileReader(字符流)处理文本文件 ...
- Java基础知识强化之IO流笔记37:FileReader/FileWriter(转换流的子类)复制文本文件案例
1. 转换流的简化写法: 由于我们常见的操作都是使用本地默认编码,所以,不用指定编码.而转换流的名称有点长,所以,Java就提供了其子类供我们使用:FileReader / FileWriterOut ...
- c#中文件与二进制流文件的转换
将文件转换成二进制方法: /// <summary> /// 将文件转换成二进制 /// </summary> /// <param name=&quo ...
- java IO操作:FileInputStream,FileOutputStream,FileReader,FileWriter实例
FileInputStream <span style="font-family:Verdana;">import java.io.File; import java. ...
- 文件和IO流
摘要:本文主要介绍了Java的文件处理以及常用的IO流操作. 文件操作 概念 File是数据源(保存数据的地方)的一种,可以表示一个文件,也可以表示一个文件目录. File类只能对文件和文件夹进行创建 ...
- JavaIO流文件的操作总结
IO流的分类 1.根据数据的流向: 输入流:用来读数据,如从外界设备读数据到内存中: 输出流:用来写数据,如从内存输出数据到外界存储设备: 2.根据数据流的格式: 字节流:一般用于声音或者秃瓢等二进制 ...
- Java——文件操作字符流和字节流的区别
转:http://blog.csdn.net/joephoenix/articles/2283165.aspx java的IO流分两种流 字节流 InputStream OutputStream 字符 ...
- java 流 文件 IO
Java 流(Stream).文件(File)和IO Java.io 包几乎包含了所有操作输入.输出需要的类.所有这些流类代表了输入源和输出目标. Java.io 包中的流支持很多种格式,比如:基本类 ...
- 文件I/O:文件流→序列化
★文件流 文件操作是最简单最直接也是最容易想到的一种方式,我们说的文件操作不仅仅是通过FileInputStream/FileOutputStream这么“裸”的方式直接把数据写入到本地文件(像我以前 ...
- 文件(2)--IO流
IO流 输入流和输出流 Java中的IO流根据功能划分为:输入流和输出流.输入流:用于读取数据.输出流:用于写出数据.输入输出的参照方向是根据我们的程序的. 字节流和字符流 Java中的IO流根据处理 ...
随机推荐
- MATLAB 设置示波器颜色和行列
设置颜色 设置行列和图例 放大缩小显示
- PHP 中的闭包函数和匿名函数
闭包函数 闭包函数通常作为函数中的函数使用. <?php $foo = function($s) { echo $s; }; $foo('hello'); <?php function t ...
- SCryptPasswordEncoder 单向加密 --- 心得
1.前言 * BCryptPasswordEncoder相关知识:* 用户表的密码通常使用MD5等不可逆算法加密后存储,为防止彩虹表破解更会先使用一个特定的字符串(如域名)加密,然后再使用一个随机的s ...
- Centos6.8安装并配置VNC
一般服务器都会在IDC或云端,为了可以看到服务器的图形化界面,需要安装配置VNC,本例为Centos6.8上安装配置VNC. [root@hostname ~]#yum install -y tige ...
- SGU140. Integer Sequences
https://codeforces.com/problemsets/acmsguru/problem/99999/140 n元同余方程的求解 对于任意二元我们可以替换成kgcd(a,b),不断迭代下 ...
- netty系列之:一口多用,使用同一端口运行不同协议
目录 简介 SocksPortUnificationServerHandler 自定义PortUnificationServerHandler 总结 简介 在之前的文章中,我们介绍了在同一个netty ...
- 带你自定义实现Spring事件驱动模型
Spring 事件驱动模型概念 Spring 事件驱动模型就是观察者模式很经典的一个应用,我们可以通过Spring 事件驱动模型来完成代码的解耦. 三角色 Spring 事件驱动模型或者说观察者模式需 ...
- Selenium_python自动化跨浏览器执行测试
Selenium_python自动化跨浏览器执行测试(简单多线程案例) 转:https://www.cnblogs.com/dong-c/p/8976746.html 跨浏览器测试是功能测试的一个分 ...
- 【刷题-PAT】A1112 Stucked Keyboard (20 分)
1112 Stucked Keyboard (20 分) On a broken keyboard, some of the keys are always stucked. So when you ...
- Qt之QFileDialog
widget.h: #ifndef WIDGET_H #define WIDGET_H #include <QWidget> #include<QString> class W ...
