应用监控CAT之cat-client源码阅读(一)
CAT 由大众点评开发的,基于 Java 的实时应用监控平台,包括实时应用监控,业务监控。对于及时发现线上问题非常有用。(不知道大家有没有在用)
应用自然是最初级的,用完之后,还想了解下其背后的原理,所以有了源码阅读一说。
今天来看看 cat-client 模块,重在调用方。
打开文件,首先看一下使用说明,背景,资料。ok,进入正题。
先大致看一下目录结构:
接下来,从样例开始着手,在这里从单元测试开始干活。
public class CatTest {
@Test
public void test() {
Transaction trans = Cat.newTransaction("logTransaction", "logTransaction");
Cat.newEvent("logEvent", "logEvent");
Cat.newTrace("logTrace", "logTrace");
Cat.newHeartbeat("logHeartbeat", "logHeartbeat");
Throwable cause = new Throwable();
Cat.logError(cause);
Cat.logError("message", cause);
Cat.logTrace("logTrace", "<trace>");
Cat.logTrace("logTrace", "<trace>", Trace.SUCCESS, "data");
Cat.logMetric("logMetric", "test", "test");
Cat.logMetricForCount("logMetricForCount");
Cat.logMetricForCount("logMetricForCount", 4);
Cat.logMetricForDuration("logMetricForDuration", 100);
Cat.logMetricForSum("logMetricForSum", 100);
Cat.logMetricForSum("logMetricForSum", 100, 100);
Cat.logEvent("RemoteLink", "Call", Message.SUCCESS, "Cat-0a010680-384736-2061");
Cat.logEvent("EventType", "EventName");
Cat.logHeartbeat("logHeartbeat", "logHeartbeat", Message.SUCCESS, null);
trans.setStatus(Transaction.SUCCESS);
// trans.setStatus(cause);
trans.complete();
Assert.assertEquals(true, Cat.isInitialized());
}
}
看得出来,cat把其主要功能都列举在了这个单元测试里。大概功能就是,记录event,trace,error,metrics.
不过,咱们只讨论下其中个别类型的处理就O了。
先来看第一个创建事务的方法:
Cat.newTransaction("logTransaction", "logTransaction");
// 进入方法查看,1. 先获取生产者; 2. 创建一个事务
public static Transaction newTransaction(String type, String name) {
return Cat.getProducer().newTransaction(type, name);
}
// 查看获取生产者的方法,检查是否已初始化,如果没有初始化则进行初始化,深度咱们就先到这里
public static MessageProducer getProducer() {
checkAndInitialize();
return s_instance.m_producer;
}
// 2. 创建一个事务,1.先获取上下文如果没有则新建; 2. 如果可以记录消息,则立马创建一个默认事务DefaultTransaction; 3. 开启执行,返回事务实例,供下文调用;
@Override
public Transaction newTransaction(String type, String name) {
// this enable CAT client logging cat message without explicit setup
if (!m_manager.hasContext()) {
m_manager.setup();
}
if (m_manager.isMessageEnabled()) {
DefaultTransaction transaction = new DefaultTransaction(type, name, m_manager);
m_manager.start(transaction, false);
return transaction;
} else {
return NullMessage.TRANSACTION;
}
}
// 2.1. 如何获取当前上下文,
@Override
public void setup() {
Context ctx;
if (m_domain != null) {
ctx = new Context(m_domain.getId(), m_hostName, m_domain.getIp());
} else {
ctx = new Context("Unknown", m_hostName, "");
}
m_context.set(ctx);
}
// 2.2. 检查是否已初始化上下文
@Override
public boolean hasContext() {
return m_context.get() != null;
}
// 2.3. 上下文怎么保证线程安全,使用 ThreadLocal 线程变量
private ThreadLocal<Context> m_context = new ThreadLocal<Context>();
// 2.4. 开启一个事务,1. 获取上下文; 2. 开启上下文事务; 3. 如果是tag类型的事务,则将其放入 m_taggedTransactions; 配置有误,只提示一次警告
@Override
public void start(Transaction transaction, boolean forked) {
Context ctx = getContext();
if (ctx != null) {
ctx.start(transaction, forked);
if (transaction instanceof TaggedTransaction) {
TaggedTransaction tt = (TaggedTransaction) transaction;
m_taggedTransactions.put(tt.getTag(), tt);
}
} else if (m_firstMessage) {
m_firstMessage = false;
m_logger.warn("CAT client is not enabled because it's not initialized yet");
}
}
// 2.4.1. 获取上下文
private Context getContext() {
if (Cat.isInitialized()) {
Context ctx = m_context.get();
if (ctx != null) {
return ctx;
} else {
if (m_domain != null) {
ctx = new Context(m_domain.getId(), m_hostName, m_domain.getIp());
} else {
ctx = new Context("Unknown", m_hostName, "");
}
m_context.set(ctx);
return ctx;
}
}
return null;
}
// 2.4.2. 开启事务,1. 如果stack为空就把事务设置到m_tree上,否则处理子节点; 2. 把事务压入栈中;
public void start(Transaction transaction, boolean forked) {
if (!m_stack.isEmpty()) {
// Do NOT make strong reference from parent transaction to forked transaction.
// Instead, we create a "soft" reference to forked transaction later, via linkAsRunAway()
// By doing so, there is no need for synchronization between parent and child threads.
// Both threads can complete() anytime despite the other thread.
if (!(transaction instanceof ForkedTransaction)) {
Transaction parent = m_stack.peek();
addTransactionChild(transaction, parent);
}
} else {
m_tree.setMessage(transaction);
}
if (!forked) {
m_stack.push(transaction);
}
}
// 2.4.3. 上下文结构
public Context(String domain, String hostName, String ipAddress) {
m_tree = new DefaultMessageTree(); // 创建一个消息树
m_stack = new Stack<Transaction>(); // 存放栈信息
Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();
String groupName = thread.getThreadGroup().getName();
m_tree.setThreadGroupName(groupName);
m_tree.setThreadId(String.valueOf(thread.getId()));
m_tree.setThreadName(thread.getName());
m_tree.setDomain(domain);
m_tree.setHostName(hostName);
m_tree.setIpAddress(ipAddress);
m_length = 1;
m_knownExceptions = new HashSet<Throwable>();
}
// DefaultModuleInitializer
@Override
public void execute(ModuleContext ctx, Module... modules) {
Set<Module> all = new LinkedHashSet<Module>();
info(ctx, "Initializing top level modules:");
for (Module module : modules) {
info(ctx, " " + module.getClass().getName());
}
try {
expandAll(ctx, modules, all);
for (Module module : all) {
if (!module.isInitialized()) {
executeModule(ctx, module, m_index++);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Error when initializing modules! Exception: " + e, e);
}
}
// 调用executeModule方法,初始化数据
private synchronized void executeModule(ModuleContext ctx, Module module, int index) throws Exception {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
// set flat to avoid re-entrance
module.setInitialized(true);
info(ctx, index + " ------ " + module.getClass().getName());
// execute itself after its dependencies
module.initialize(ctx);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
info(ctx, index + " ------ " + module.getClass().getName() + " DONE in " + (end - start) + " ms.");
}
// cat初始化
// this should be called during application initialization time
public static void initialize(File configFile) {
PlexusContainer container = ContainerLoader.getDefaultContainer();
initialize(container, configFile);
}
public static void initialize(PlexusContainer container, File configFile) {
ModuleContext ctx = new DefaultModuleContext(container);
// 该方法会去 components.xml中查找 org.unidal.initialization.Module 的实现类,
Module module = ctx.lookup(Module.class, CatClientModule.ID);
if (!module.isInitialized()) {
ModuleInitializer initializer = ctx.lookup(ModuleInitializer.class);
ctx.setAttribute("cat-client-config-file", configFile);
initializer.execute(ctx, module);
}
}
// components.xml 中配置的 Module, 加载入 CatClientModule
<component>
<role>org.unidal.initialization.Module</role>
<role-hint>cat-client</role-hint>
<implementation>com.dianping.cat.CatClientModule</implementation>
</component>
// plexus.xml 中 配置日志输出
<plexus>
<components>
<component>
<role>org.codehaus.plexus.logging.LoggerManager</role>
<implementation>org.unidal.lookup.logger.TimedConsoleLoggerManager</implementation>
<configuration>
<dateFormat>MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS</dateFormat>
<showClass>true</showClass>
<logFilePattern>cat_{0,date,yyyyMMdd}.log</logFilePattern>
<baseDirRef>CAT_HOME</baseDirRef>
<defaultBaseDir>/data/applogs/cat</defaultBaseDir>
</configuration>
</component>
</components>
</plexus>
// logEvent 举个例子,event处理过程
Cat.logEvent("RemoteLink", "Call", Message.SUCCESS, "Cat-0a010680-384736-2061");
// 进入方法
public static void logEvent(String type, String name, String status, String nameValuePairs) {
Cat.getProducer().logEvent(type, name, status, nameValuePairs);
}
// DefaultMessageProducer, logEvent
@Override
public void logEvent(String type, String name, String status, String nameValuePairs) {
Event event = newEvent(type, name);
if (nameValuePairs != null && nameValuePairs.length() > 0) {
event.addData(nameValuePairs);
}
event.setStatus(status);
event.complete();
}
// DefaultEvent, complete 方法
@Override
public void complete() {
setCompleted(true);
if (m_manager != null) {
m_manager.add(this);
}
}
// DefaultMessageManager, add方法,添加到上下文中
@Override
public void add(Message message) {
Context ctx = getContext();
if (ctx != null) {
ctx.add(message);
}
}
// DefaultMessageManager, 最终添加方法
public void add(Message message) {
if (m_stack.isEmpty()) {
MessageTree tree = m_tree.copy();
tree.setMessage(message);
flush(tree);
} else {
Transaction parent = m_stack.peek();
addTransactionChild(message, parent);
}
}
// DefaultMessageManager, 发送刷写数据
public void flush(MessageTree tree) {
if (tree.getMessageId() == null) {
tree.setMessageId(nextMessageId());
}
MessageSender sender = m_transportManager.getSender();
if (sender != null && isMessageEnabled()) {
sender.send(tree);
reset();
} else {
m_throttleTimes++;
if (m_throttleTimes % 10000 == 0 || m_throttleTimes == 1) {
m_logger.info("Cat Message is throttled! Times:" + m_throttleTimes);
}
}
}
// TcpSocketSender, 发送数据
// 先插入 BlockingQueue<MessageTree> m_queue 阻塞队列中,如果插入失败,则进行日志队列检查
@Override
public void send(MessageTree tree) {
if (isAtomicMessage(tree)) {
boolean result = m_atomicTrees.offer(tree, m_manager.getSample());
if (!result) {
logQueueFullInfo(tree);
}
} else {
boolean result = m_queue.offer(tree, m_manager.getSample());
if (!result) {
logQueueFullInfo(tree);
}
}
}
// 日志队列检查
private void logQueueFullInfo(MessageTree tree) {
if (m_statistics != null) {
m_statistics.onOverflowed(tree);
}
int count = m_errors.incrementAndGet();
if (count % 1000 == 0 || count == 1) {
m_logger.error("Message queue is full in tcp socket sender! Count: " + count);
}
tree = null;
}
// 如果队列不为空,则插入到上一节点之后
private void addTransactionChild(Message message, Transaction transaction) {
long treePeriod = trimToHour(m_tree.getMessage().getTimestamp());
long messagePeriod = trimToHour(message.getTimestamp() - 10 * 1000L); // 10 seconds extra time allowed
if (treePeriod < messagePeriod || m_length >= m_configManager.getMaxMessageLength()) {
m_validator.truncateAndFlush(this, message.getTimestamp());
}
transaction.addChild(message);
m_length++;
}
// DefaultTransaction, addChild, 添加子节点,完成添加操作
@Override
public DefaultTransaction addChild(Message message) {
if (m_children == null) {
m_children = new ArrayList<Message>();
}
if (message != null) {
m_children.add(message);
} else {
Cat.logError(new Exception("null child message"));
}
return this;
}
// Transaction 的 complete 实现,最终的提交
trans.complete();
// 进入方法,如果已经结束,则认为是异常情况
@Override
public void complete() {
try {
if (isCompleted()) {
// complete() was called more than once
DefaultEvent event = new DefaultEvent("cat", "BadInstrument"); event.setStatus("TransactionAlreadyCompleted");
event.complete();
addChild(event);
} else {
m_durationInMicro = (System.nanoTime() - m_durationStart) / 1000L; setCompleted(true); // 防止下次再进入 if (m_manager != null) {
m_manager.end(this);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
// ignore
}
}
// DefaultMessageManager, end 方法
@Override
public void end(Transaction transaction) {
Context ctx = getContext(); if (ctx != null && transaction.isStandalone()) {
if (ctx.end(this, transaction)) {
m_context.remove();
}
}
}
// DefaultMessageManager, end transaction 进行校验
public boolean end(DefaultMessageManager manager, Transaction transaction) {
if (!m_stack.isEmpty()) {
Transaction current = m_stack.pop(); if (transaction == current) {
m_validator.validate(m_stack.isEmpty() ? null : m_stack.peek(), current);
} else {
while (transaction != current && !m_stack.empty()) {
m_validator.validate(m_stack.peek(), current); current = m_stack.pop();
}
} if (m_stack.isEmpty()) {
MessageTree tree = m_tree.copy(); m_tree.setMessageId(null);
m_tree.setMessage(null); if (m_totalDurationInMicros > 0) {
adjustForTruncatedTransaction((Transaction) tree.getMessage());
} manager.flush(tree);
return true;
}
} return false;
}
// 验证事务的正确性,对嵌套的 transaction 进行验证
public void validate(Transaction parent, Transaction transaction) {
if (transaction.isStandalone()) {
List<Message> children = transaction.getChildren();
int len = children.size(); for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
Message message = children.get(i); if (message instanceof Transaction) {
validate(transaction, (Transaction) message);
}
} if (!transaction.isCompleted() && transaction instanceof DefaultTransaction) {
// missing transaction end, log a BadInstrument event so that
// developer can fix the code
markAsNotCompleted((DefaultTransaction) transaction);
}
} else if (!transaction.isCompleted()) {
if (transaction instanceof DefaultForkedTransaction) {
// link it as run away message since the forked transaction is not completed yet
linkAsRunAway((DefaultForkedTransaction) transaction);
} else if (transaction instanceof DefaultTaggedTransaction) {
// link it as run away message since the forked transaction is not completed yet
markAsRunAway(parent, (DefaultTaggedTransaction) transaction);
}
}
}
// 适应事务时间段
private void adjustForTruncatedTransaction(Transaction root) {
DefaultEvent next = new DefaultEvent("TruncatedTransaction", "TotalDuration");
long actualDurationInMicros = m_totalDurationInMicros + root.getDurationInMicros(); next.addData(String.valueOf(actualDurationInMicros));
next.setStatus(Message.SUCCESS);
root.addChild(next); m_totalDurationInMicros = 0;
}
// 发送最后的数据
public void flush(MessageTree tree) {
if (tree.getMessageId() == null) {
tree.setMessageId(nextMessageId());
} MessageSender sender = m_transportManager.getSender(); if (sender != null && isMessageEnabled()) {
sender.send(tree); reset();
} else {
m_throttleTimes++; if (m_throttleTimes % 10000 == 0 || m_throttleTimes == 1) {
m_logger.info("Cat Message is throttled! Times:" + m_throttleTimes);
}
}
}
// 可以记录的前提是,所有条件均满足
@Override
public boolean isMessageEnabled() {
return m_domain != null && m_domain.isEnabled() && m_context.get() != null && m_configManager.isCatEnabled();
}
// 发送messageTree到 LinkedBlockingQueue<MessageTree> m_tree
@Override
public void send(MessageTree tree) {
if (isAtomicMessage(tree)) {
boolean result = m_atomicTrees.offer(tree, m_manager.getSample()); if (!result) {
logQueueFullInfo(tree);
}
} else {
boolean result = m_queue.offer(tree, m_manager.getSample()); if (!result) {
logQueueFullInfo(tree);
}
}
}
// 发送数据完成后,需要将原来的数据清空还原,以便下次可用
@Override
public void reset() {
// destroy current thread local data
Context ctx = m_context.get(); if (ctx != null) {
if (ctx.m_totalDurationInMicros == 0) {
ctx.m_stack.clear();
ctx.m_knownExceptions.clear();
m_context.remove();
} else {
ctx.m_knownExceptions.clear();
}
}
}
// 上下文的移除,其他链表结构各自移除
public void remove() {
ThreadLocalMap m = getMap(Thread.currentThread());
if (m != null)
m.remove(this);
}
// 为保证上下文绝对移除,再次操作
@Override
public void end(Transaction transaction) {
Context ctx = getContext(); if (ctx != null && transaction.isStandalone()) {
if (ctx.end(this, transaction)) {
m_context.remove();
}
}
}
// 写入队列后,由 TcpSocketSender 线程进行轮询发送到cat后台
@Override
public void run() {
m_active = true; while (m_active) {
ChannelFuture channel = m_manager.channel(); if (channel != null && checkWritable(channel)) {
try {
MessageTree tree = m_queue.poll(); if (tree != null) {
sendInternal(tree);
tree.setMessage(null);
} } catch (Throwable t) {
m_logger.error("Error when sending message over TCP socket!", t);
}
} else {
long current = System.currentTimeMillis();
long oldTimestamp = current - HOUR; while (true) {
try {
MessageTree tree = m_queue.peek(); if (tree != null && tree.getMessage().getTimestamp() < oldTimestamp) {
MessageTree discradTree = m_queue.poll(); if (discradTree != null) {
m_statistics.onOverflowed(discradTree);
}
} else {
break;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
m_logger.error(e.getMessage(), e);
break;
}
} try {
Thread.sleep(5);
} catch (Exception e) {
// ignore it
m_active = false;
}
}
}
}
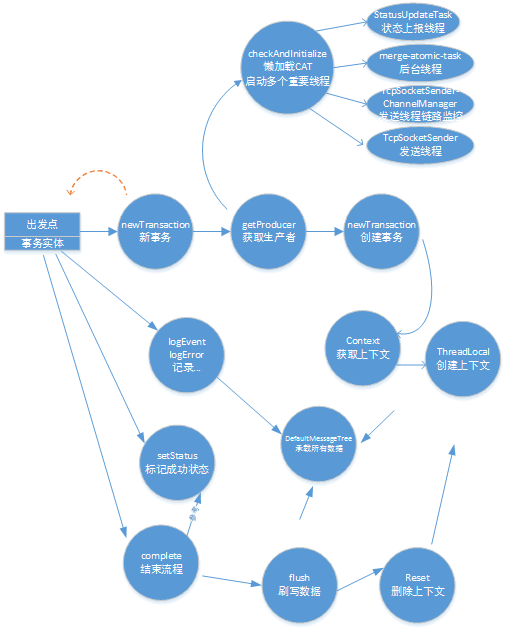
如此,整个cat埋点的过程就搞定了。关键技术就是:
1. ThreadLocal 用于保存上下文埋点,保证线程安全。
2. LinkedBlockingQueue 用于保存消息树,作为生产线程与消费线的沟通桥梁!
3. AtomicInteger 用于计数,保证准确性。
4. 心跳线和用于发送本机的状态到cat后台。
5. 懒加载,单例模式的使用。
等等,来个图:
应用监控CAT之cat-client源码阅读(一)的更多相关文章
- 【原】Spark中Client源码分析(二)
继续前一篇的内容.前一篇内容为: Spark中Client源码分析(一)http://www.cnblogs.com/yourarebest/p/5313006.html DriverClient中的 ...
- ZooKeeper源码阅读——client(二)
原创技术文章,转载请注明:转自http://newliferen.github.io/ 如何连接ZooKeeper集群 要想了解ZooKeeper客户端实现原理,首先需要关注一下客户端的使用方式, ...
- Rpc框架dubbo-client(v2.6.3) 源码阅读(二)
接上一篇 dubbo-server 之后,再来看一下 dubbo-client 是如何工作的. dubbo提供者服务示例, 其结构是这样的!dubbo://192.168.11.6:20880/com ...
- InfluxDB源码阅读之httpd服务
操作系统 : CentOS7.3.1611_x64 go语言版本:1.8.3 linux/amd64 InfluxDB版本:1.1.0 服务模块介绍 源码路径: github.com/influxda ...
- Pytorch版本yolov3源码阅读
目录 Pytorch版本yolov3源码阅读 1. 阅读test.py 1.1 参数解读 1.2 data文件解析 1.3 cfg文件解析 1.4 根据cfg文件创建模块 1.5 YOLOLayer ...
- Redis源码阅读(一)事件机制
Redis源码阅读(一)事件机制 Redis作为一款NoSQL非关系内存数据库,具有很高的读写性能,且原生支持的数据类型丰富,被广泛的作为缓存.分布式数据库.消息队列等应用.此外Redis还有许多高可 ...
- Kubernetes 学习(九)Kubernetes 源码阅读之正式篇------核心组件之 Scheduler
0. 前言 继续上一篇博客阅读 Kubernetes 源码,参照<k8s 源码阅读>首先学习 Kubernetes 的一些核心组件,首先是 kube-scheduler 本文严重参考原文: ...
- Spring源码阅读 之 配置的读取,解析
在上文中我们已经知道了Spring如何从我们给定的位置加载到配置文件,并将文件包装成一个Resource对象.这篇文章我们将要探讨的就是,如何从这个Resouce对象中加载到我们的容器?加载到容器后又 ...
- 【原】AFNetworking源码阅读(一)
[原]AFNetworking源码阅读(一) 本文转载请注明出处 —— polobymulberry-博客园 1. 前言 AFNetworking版本:3.0.4 由于我平常并没有经常使用AFNetw ...
随机推荐
- android中ScrollView嵌套ListView或GridView显示位置问题
Android中ScrollView中嵌套ListView或GridView时在开始进入界面时总是显示中间位置,开头的位置显示不出来.这种情况下只需要在ScrollView的父控件中添加以下两行代码即 ...
- [基础篇] 01_MySQL的安装与配置
- vue项目跳转到外部链接
vue项目中遇到一个打印的功能.思考之后决定点击按钮,跳转到一个HTML页面(后台写的),利用window.print()方法调用浏览器的打印的功能. 所以,现在的问题是,怎样跳转到外部链接.开发vu ...
- python基础之Day24
1.补充内置函数 2.反射 什么是? 通过字符串操作类或者对象的属性 hasattri(a,"b") 判断能否访问到a.b setattri(a,"b",c) ...
- 使用struts2框架后的拦截器
过滤特殊字符的过滤器 struts2会在web.xml中配置如下的过滤器: <filter> <filter-name>struts</filter-name> & ...
- django .all .values .value_list 数据库获取数据
.all 获取所有的对象 .values 获取所有的字典 .value_list 获取所有的元组
- java8 学习记录
一. lambda表达式 参考 https://www.cnblogs.com/franson-2016/p/5593080.html package com.mytest.java8; impor ...
- Moving or disabling the package cache for Visual Studio 2017
Moving or disabling the package cache for Visual Studio 2017 | Setup & Install by Heath Stewart ...
- Idea如果添加Maven模块
1.要创建一个和heaton-app同级的Maven模块,如果所示 2.点击下一步,添加ArtifactId,其中 groupId : 定义了项目属于哪个组,举个例子,如果你的公司是myc ...
- Linq语言,由红色部分可直接代替绿色(List,dictionary)
/// <summary> /// 获取最近5分钟缓存的车量 /// </summary> /// <param name="carNo">&l ...
