PWM DAC vs. Standalone
Posted by AnalogAdvocate on April 09, 2010
Design, General
In today’s highly competitive electronics environment, designers are constantly looking for ways to reduce overall system costs. One of the most commonly asked questions that analog specialists at digital microcontroller (MCU) companies hear from customers is, is the almost cost-free Pulse-Width-Modulation (PWM) Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC) good enough for my application, or do I need a higher-performance, standalone DAC instead?”
The generation of an analog voltage using a digital Pulse-Width-Modulated signal is known as a PWM DAC. As most designers’ PCB boards have a microcontroller with a built-in PWM-output feature onboard, a simple digital-to-analog data conversion can be easily realized by adding a few passive components at the MCU’s PWM-output pin. This is an alternative to using a standalone DAC. In the MCU application environment, system designers can have DAC functionality nearly free of charge. PWM DACs are widely used in very low-cost applications, where accuracy is not a primary concern. Standalone DACs, however, are used for applications requiring higher accuracy.
Although the PWM DAC can be realized with the simple addition of a few passive components, implementing a PWM DAC for system applications is not a simple task. There are many limitations associated with this. Understanding the complexities of using the PWM DAC and its effects can save significant development time and effort. This article presents a technique for converting a PWM pulse to an analog voltage using a simple, RC low-pass filter. This entry also reviews the PWM DAC’s limitations and its key design constraints on resolution, frequency, ripple, settling time and current consumption are discussed, which are very important design parameters that are largely affected by the R and C values, as well as the PWM duty cycle and frequency.
Standalone DACs
Figure 1 shows an example of a standalone DAC. Its analog output voltage is given by:
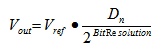
Where Dn is the digital code. For example, with a 12-bit DAC, the user can get Vout = 2.5V with Vref = 5V and Dn = 1000-0000-0000. Typical standalone DAC devices provide good linearity and a short settling time, which is the time required to update each output voltage.

Figure 1 Configuration of Standalone DAC
How PWM DACs Work
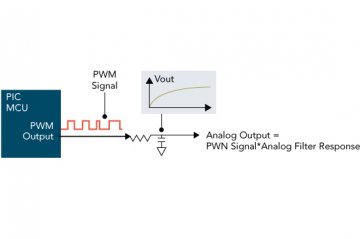
Figure 2 shows a basic configuration of the PWM DAC. The MCU outputs a PWM signal to an RC low pass-filter. The PWM pulse train’s digital value becomes an analog voltage, when it passes through the RC filter. At a given period of time, the analog output is proportional to the PWM pulse’s high durations.

Figure 2 Block Diagram of a PWM DAC
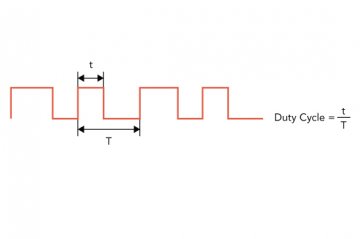
A PWM signal is defined as a digital signal with a fixed frequency, but a varying duty cycle. Figure 3 illustrates a PWM signal. The PWM period (T) is the time interval required to complete one full PWM cycle. The duty cycle is the ratio of the high duration (t) to the total period (T).
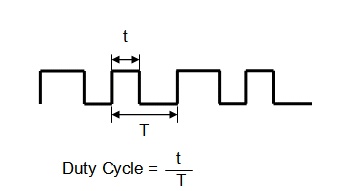
Figure 3 PWM Signal
The PWM signal and RC-filter circuit parameters affect the analog output’s resolution, amplitude, settling time and ripple. The PWM DAC’s limitations are clearly demonstrated by analyzing the interaction of the PWM parameters and the RC filter. A better understanding of the relationship between these parameters enables designers to optimize the PWM to best suit their application’s requirements, while minimizing design time.
PWM DAC Bit Resolution
The PWM counter length (L) and the smallest duty-cycle change in the PWM counter (C) determine the PWM DAC’s bit resolution. The following equation expresses the maximum bit resolution of the PWM DAC:

For example, if the system generates an analog output voltage from a PWM DAC with a counter of 4096 (L) and a minimum count step of one (C), the PWM DAC’s bit resolution is 12-bits.
When the PWM resolution is determined, it is possible to calculate the Least Significant Bit (LSB) size. The LSB size is dependant upon the PWM resolution and the PWM’s output-high level voltage (VOH), and can be calculated using the following equation.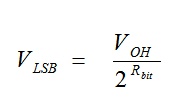
For example, a 12-bit PWM DAC with a VOH of 5V has an LSB size of 1.2mV.
RC Filter Design Considerations for PWM DAC
One key design consideration when determining the PWM’s resolution is output-voltage ripple. Ripple occurs due to overshoot and undershoot as the PWM charges and discharges the RC circuit. One way to approximate the charge characteristics is to modify the equations to charge and discharge an RC-filter circuit. As the effects of this are cumulative, the following equations can be used as approximations.
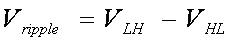 (4)
(4) (5)
(5)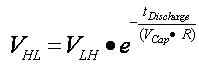 (6)
(6)
VLH is the voltage increase for a specific PWM period, and VHL is the voltage decrease for a specific PWM period. The values of VLH and VHL are dependant upon not only the RC filter values, but also upon the PWM frequency and duty cycle. The PWM frequency and duty cycle determine the time available for the PWM to charge (tcharge) and discharge (tdischarge) the capacitor. Vripple is the difference between VLH and VHL for the same PWM period.
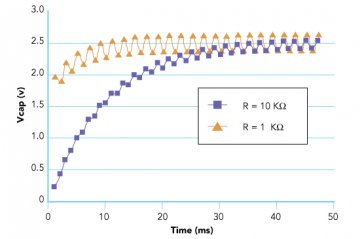
Figure 4 illustrates the magnitude of the voltage ripple across the output capacitor vs. time. The vertical axis displays the magnitude of the ripple voltage, while the horizontal axis provides the corresponding time. The plot shows how the ripple voltage settles at approximately 125 mV in a time interval of approximately 40 ms for R = 10K ohms, and 250 mV at 20 ms for R = 1 K ohm. In the previous example, an LSB size of less than 1.2mV for a 12-bit system was needed. This ripple is greater than 100 LSB for 12-bit DAC with a 5V reference, meaning that the resulting PWM DAC solution has an effective resolution of less than 6 bits due to the ripples.
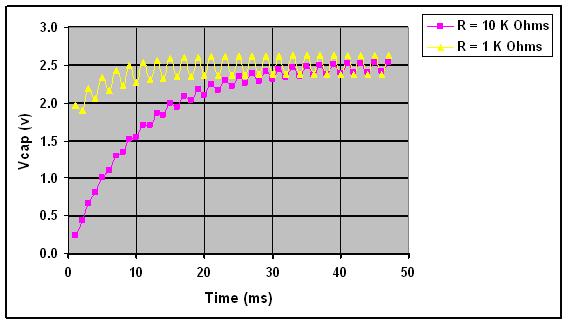
Figure 4: Voltage Ripple Comparison for VOH = 5V, C = 1μF, PWM frequency = 1 kHz, Duty Cycle = 50%
The ripple can be reduced by increasing the capacitor and the resistor values or increasing the PWM frequency. All of these will decrease the ripple’s magnitude.
As shown in Figure 4, the ripple decreases as the resistance value increases. However, nothing comes without a price-the settling time doubles as the ripple decreases by 50 %.
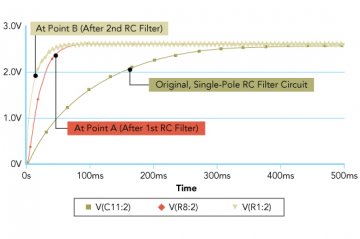
For applications that require faster settling time (increased bandwidth) and higher resolution, one could add a second RC filter. The obvious tradeoffs include the cost of additional components and the increased board space occupied. Figure 5 shows a model for a two-pole RC low-pass filter. Figure 6 shows the analog output voltage of this model.
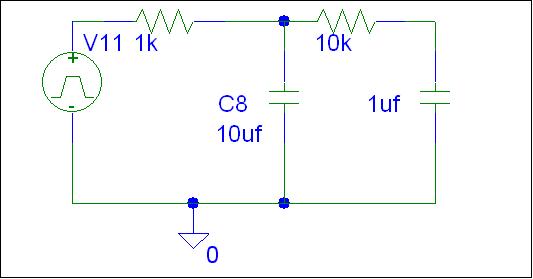
Figure 5: PSPICE Model for Two-Pole RC Low-Pass Filter
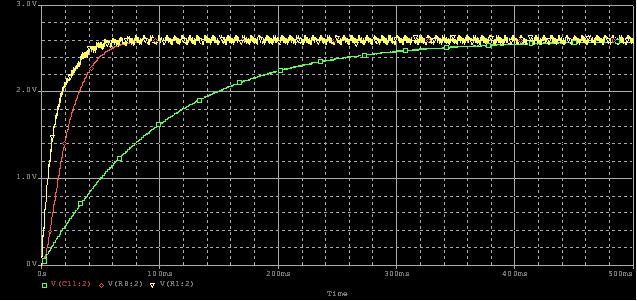
Figure 6: Analog Voltage Output vs. Settling Time of the Two Pole RC Low-Pass Filtere
There are a couple of things to keep in mind when designing the filter. First, make sure that the pole of the RC is set at a much greater frequency than that of the signal being generated. Secondly, if you are designing a two-pole filter, make sure that R2 > R1.
The 3dB corner frequency of the RC filter is given by:
 (7)
(7)
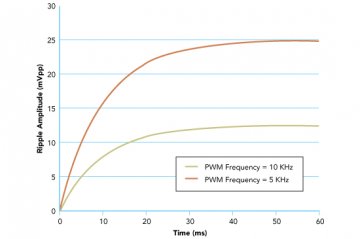
There are a couple of additional things to consider. Increasing the PWM frequency will also decrease the ripple, but the tradeoff is increased settling time. Figure 7 shows the cases for 10 kHz and 5 kHz

Figure 7: Voltage Ripple at the PWM DAC when PWM Frequency Changes. Where VOH = 5V, C = 1μF, R = 10 kΩ, Duty Cycle = 50 %, PWM Frequency = 10 kHz and 5 kHz
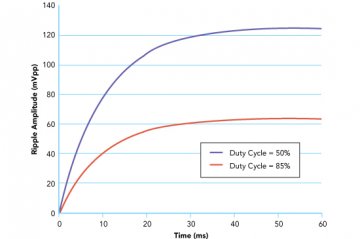
The worst-case ripple occurs at a 50% duty cycle. The ripple will decrease as the duty cycle moves closer to 0% or 100%. Figure 8 shows the peak-to-peak magnitude of ripples on the PWM DAC output. The ripple decreases almost two times as the duty cycle changes from 50 % to 85 %.
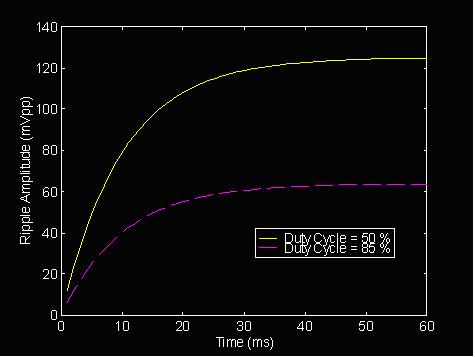
Figure 8: Voltage Ripple at the PWM DAC when PWM Duty Cycle Changes. VOH = 5V, C = 10 μF, R = 1 kΩ, PWM Frequency = 1 kHz, Duty Cycle = 50 % (Solid Curve) and 85 % (Dotted Curve)
PWM DACs and Power Consumption
Many electronic products today are portable or handheld devices. These devices are battery powered, and many have strict constraints with regard to power consumption. Therefore, it is a good idea to minimize the PWM DAC’s power consumption. The current consumed in the PWM solution is simple to approximate, using the following equation:
 (8)
(8)
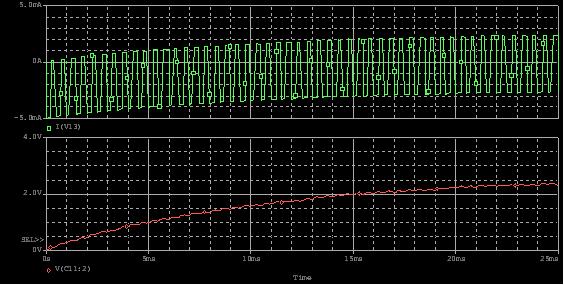
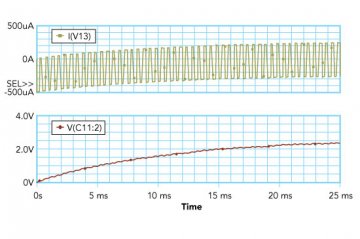
Figure 9: Current and Voltage Plots of PWM DAC with R =1000 Ω, C = 10μF, Duty Cycle = 50 %, VOH = 5V
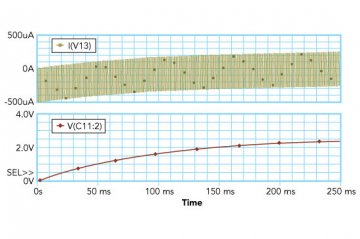
Figure 9 shows the current and voltage plots. As sown in the plot, the PWM DAC with a lower resistor draws a significant amount of current (in the range of a few mA). This high level of current consumption is unacceptable for many battery-powered applications. Current can be decreased by increasing the resistor value.
In Figure 10, the resistor value has been increased by a factor of ten, which has likewise decreased the current consumption by a factor of ten.

Figure 10: Current and Voltage Plots of PWM DAC with R =10,000 Ω, C = 10μF, Duty Cycle = 50 %, VOH = 5V
As the resistor limits the current available to charge/discharge the capacitor, decreasing the amount of current available (increasing resistance) to the circuit will increase the settling time.
Another factor to consider is the filter’s pole. As the resistor value increases, the 3 dB frequency decreases by the same magnitude. This can be compensated for by reducing the capacitor value by the same magnitude, which offsets the increased settling time and maintains the original pole of the filter. Figure 11 demonstrates this. Note that, as the capacitor value reduces, the circuit becomes more susceptible to loading. This is another important design consideration.
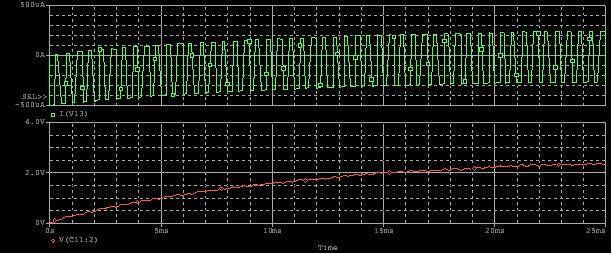
Figure 11: Current and Voltage Plots of PWM DAC with R =10,000 Ω, C = 1μF, Duty Cycle = 50 %, VOH = 5Vircuit

PWM DAC vs. Standalone的更多相关文章
- 【STM32】PWM DAC基本原理(实验:PWM实现DAC)
虽然STM32F103ZET6具有内部DAC,但是也仅仅只有两条DAC通道,并且STM32还有其他的很多型号是没有DAC的.通常情况下,采用专用的D/A芯片来实现,但是这样就会带来成本的增加. 不过S ...
- PWM DAC Low Pass Filtering
[TI博客大赛][原创]LM3S811之基于PWM的DAC http://bbs.ednchina.com/BLOG_ARTICLE_3005301.HTM http://www.fpga4fun.c ...
- How determine the RC time constant in PWM DAC low-pass filter?
how determine the RC time constant in PWM digital to analog low-pass filter? I 'm looking for the be ...
- MCU PWM DAC OP Voltage Output
- Make a DAC with a microcontroller's PWM timer
http://www.edn.com/design/analog/4337128/Make-a-DAC-with-a-microcontroller-s-PWM-timer Many embedded ...
- how to generate an analog output from a in-built pwm of Atmega 32AVR microcontrloller?
how to generate an analog output from a in-built pwm of Atmega 32AVR microcontrloller? you need a re ...
- PEM DAC note
开发指南V1.0库函数版本,PWM DAC实验 350页 STM32 的定时器最快的计数频率是72Mhz,8 为分辨率的时候,PWM 频率为72M/256=281.25Khz.如果是1阶RC滤波,则要 ...
- 说说M451例程之PWM
/**************************************************************************//** * @file main.c * @ve ...
- DIY FSK RFID Reader
This page describes the construction of an RFID reader using only an Arduino (Nano 3.0 was tested, b ...
随机推荐
- asterisk各种报错
1.控制台打印出: Got SIP response "Temporarily Unavailable" back from 210.13.87.110:5060 造成原因:在 ...
- php内存管理机制与垃圾回收机制
PHP内存管理机制 1 var_dump(memory_get_usage()); //获取内存 2 $a = "laruence"; //定义一个变量 3 var_dump(me ...
- php 的swoole 和websocket 连接wss
1. 下载证书 $serv = new swoole_server('0.0.0.0', 9501, SWOOLE_PROCESS, SWOOLE_SOCK_TCP | SWOOLE_SSL); $s ...
- redis持久化的两种方式
redis是一个内存型数据库.当redis服务器重启时,数据会丢失.我们可以将redis内存中的数据持久化保存到硬盘的文件中. redis持久化有两种机制.RDB与AOF.默认方式是RDB. 1.RD ...
- 一步一步学习IdentityServer4 (5) .NETCore2.0 Swagger
首先添加nuget: Swashbuckle.AspNetCore services.AddSwaggerGen(c => { c.SwaggerDoc("v1", new ...
- hdu 5112 (2014北京现场赛 A题)
给出某个时刻对应的速度 求出相邻时刻的平均速度 输出最大值 Sample Input23 // n2 2 //t v1 13 430 31 52 0 Sample OutputCase #1: 2.0 ...
- 【LOJ】#2067. 「SDOI2016」硬币游戏
题解 c一样的就是一个独立的游戏 我们对于2和3的指数 sg[i][j] 表示\(c \cdot 2^i \cdot 3^j\)的棋子,只有这个硬币是反面,翻转的硬币是正面的sg值 枚举sg函数所有可 ...
- bzoj [SDOI2009]学校食堂Dining
感觉这个状压dp比较难想.. dp[ i ][ s ][ k ] 表示前i - 1个都排好了, 从i开始的7个的取没取的状态为s, 且最后一个相对i的位置为k的最少花费. 状态转移方程 if(s &a ...
- nginx、php-fpm、swoole HTTP/TCP压测对比
本次测试是在win7下docker环境中进行压测,共创建一个nginx容器.一个php-fpm容器和一个swoole容器,客户端请求nginx服务器,nginx接收用户访问请求并转发给php-fpm, ...
- eschop购物实现立即购买和加入购物车
后台=>平台=>商店设置=>购物流程 是否一步购物设置为否 2:修改代码 .js/common.js function addToCartShowDivResponse(result ...
