logger(一)slf4j简介及其实现原理
一、slf4j简介
slf4j(Simple logging facade for Java)是对所有日志框架制定的一种规范、标准、接口,并不是一个框架的具体的实现,因为接口并不能独立使用,需要和具体的日志框架实现配合使用
slf4j是门面模式的典型应用,外部与一个子系统的通信必须通过一个统一的外观对象进行,使得子系统更易于使用。用一张图来表示门面模式的结构为
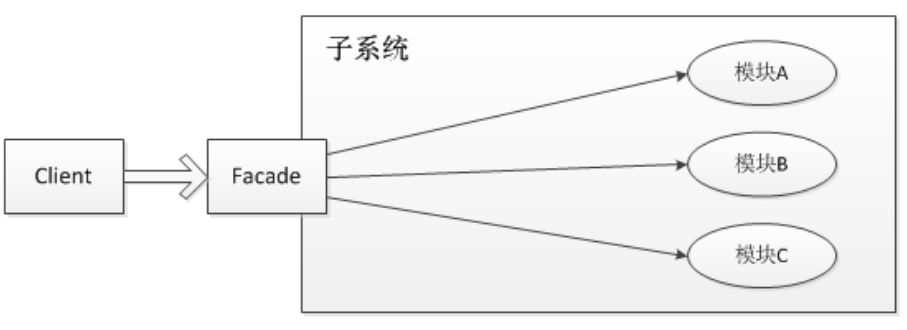
日志实现(log4j、logback、log4j2)
- log4j是apache实现的一个开源日志组件
- logback同样是由log4j的作者设计完成的,拥有更好的特性,用来取代log4j的一个日志框架,是slf4j的原生实现
- log4j2是log4j 1.x和logback的改进版,据说采用了一些新技术(无锁异步、等等),使得日志的吞吐量、性能比log4j 1.x提高10倍,并解决了一些死锁的bug,而且配置更加简单灵活。
为什么要使用slf4j
- SLF4J提供了统一的记录日志的接口,对不同日志系统的具体实现进行了抽象化,只要按照其提供的方法记录即可,最终日志的格式、记录级别、输出方式等通过绑定具体的日志系统来实现。在项目中使用了SLF4J记录日志,并且绑定了log4j,则日志会以log4j的风格输出;后期需要改为以logback的风格输出日志,只需要将jar包log4j替换成logback即可,不用修改项目中的代码。
- SLF4J支持
{}作为占位符,等价于C语言中的%s,而不必再进行字符串的拼接,效率有显著的提升
maven jar包
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId>
<version>1.7.21</version>
</dependency>
如下图所示,slf4j不能单独使用,比如要使用logback实现,需要导入logback的jar包
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId>
<version>1.7.21</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-core</artifactId>
<version>1.1.7</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId>
<version>1.1.7</version>
</dependency>
比如要使用log4j或者 jdk自带的logging,需要使用桥接包如slf4j-jdk14.jar包
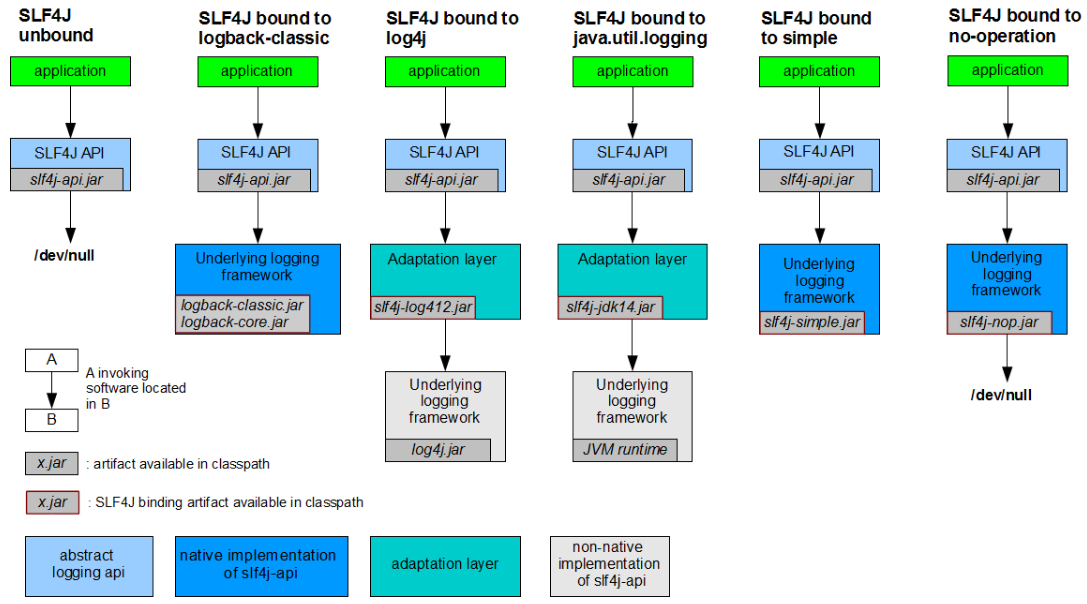
二、实现原理
slf4j只是一个日志标准,并不是日志系统的具体实现。slf4j只提做两件事情:Logger类用来打日志,LoggerFactory类用来获取Logger;
- 提供日志接口 (Logger.class)
- 提供获取具体日志对象的方法 (LoggerFactory.class)
Logger.class
public interface Logger {
/**
* Case insensitive String constant used to retrieve the name of the root logger.
*
* @since 1.3
*/
final public String ROOT_LOGGER_NAME = "ROOT";
/**
* Return the name of this <code>Logger</code> instance.
* @return name of this logger instance
*/
public String getName();
/**
* Is the logger instance enabled for the TRACE level?
*
* @return True if this Logger is enabled for the TRACE level,
* false otherwise.
* @since 1.4
*/
public boolean isTraceEnabled();
/**
* Log a message at the TRACE level.
*
* @param msg the message string to be logged
* @since 1.4
*/
public void trace(String msg);
/**
* Log a message at the TRACE level according to the specified format
* and argument.
* <p/>
* <p>This form avoids superfluous object creation when the logger
* is disabled for the TRACE level. </p>
*
* @param format the format string
* @param arg the argument
* @since 1.4
*/
public void trace(String format, Object arg);
/**
* Log a message at the TRACE level according to the specified format
* and arguments.
* <p/>
* <p>This form avoids superfluous object creation when the logger
* is disabled for the TRACE level. </p>
*
* @param format the format string
* @param arg1 the first argument
* @param arg2 the second argument
* @since 1.4
*/
public void trace(String format, Object arg1, Object arg2);
/**
* Log a message at the TRACE level according to the specified format
* and arguments.
* <p/>
* <p>This form avoids superfluous string concatenation when the logger
* is disabled for the TRACE level. However, this variant incurs the hidden
* (and relatively small) cost of creating an <code>Object[]</code> before invoking the method,
* even if this logger is disabled for TRACE. The variants taking {@link #trace(String, Object) one} and
* {@link #trace(String, Object, Object) two} arguments exist solely in order to avoid this hidden cost.</p>
*
* @param format the format string
* @param arguments a list of 3 or more arguments
* @since 1.4
*/
public void trace(String format, Object... arguments);
/**
* Log an exception (throwable) at the TRACE level with an
* accompanying message.
*
* @param msg the message accompanying the exception
* @param t the exception (throwable) to log
* @since 1.4
*/
public void trace(String msg, Throwable t);
/**
* Similar to {@link #isTraceEnabled()} method except that the
* marker data is also taken into account.
*
* @param marker The marker data to take into consideration
* @return True if this Logger is enabled for the TRACE level,
* false otherwise.
*
* @since 1.4
*/
public boolean isTraceEnabled(Marker marker);
/**
* Log a message with the specific Marker at the TRACE level.
*
* @param marker the marker data specific to this log statement
* @param msg the message string to be logged
* @since 1.4
*/
public void trace(Marker marker, String msg);
/**
* This method is similar to {@link #trace(String, Object)} method except that the
* marker data is also taken into consideration.
*
* @param marker the marker data specific to this log statement
* @param format the format string
* @param arg the argument
* @since 1.4
*/
public void trace(Marker marker, String format, Object arg);
/**
* This method is similar to {@link #trace(String, Object, Object)}
* method except that the marker data is also taken into
* consideration.
*
* @param marker the marker data specific to this log statement
* @param format the format string
* @param arg1 the first argument
* @param arg2 the second argument
* @since 1.4
*/
public void trace(Marker marker, String format, Object arg1, Object arg2);
/**
* This method is similar to {@link #trace(String, Object...)}
* method except that the marker data is also taken into
* consideration.
*
* @param marker the marker data specific to this log statement
* @param format the format string
* @param argArray an array of arguments
* @since 1.4
*/
public void trace(Marker marker, String format, Object... argArray);
/**
* This method is similar to {@link #trace(String, Throwable)} method except that the
* marker data is also taken into consideration.
*
* @param marker the marker data specific to this log statement
* @param msg the message accompanying the exception
* @param t the exception (throwable) to log
* @since 1.4
*/
public void trace(Marker marker, String msg, Throwable t);
/**
* Is the logger instance enabled for the DEBUG level?
*
* @return True if this Logger is enabled for the DEBUG level,
* false otherwise.
*/
public boolean isDebugEnabled();
/**
* Log a message at the DEBUG level.
*
* @param msg the message string to be logged
*/
public void debug(String msg);
/**
* Log a message at the DEBUG level according to the specified format
* and argument.
* <p/>
* <p>This form avoids superfluous object creation when the logger
* is disabled for the DEBUG level. </p>
*
* @param format the format string
* @param arg the argument
*/
public void debug(String format, Object arg);
/**
* Log a message at the DEBUG level according to the specified format
* and arguments.
* <p/>
* <p>This form avoids superfluous object creation when the logger
* is disabled for the DEBUG level. </p>
*
* @param format the format string
* @param arg1 the first argument
* @param arg2 the second argument
*/
public void debug(String format, Object arg1, Object arg2);
/**
* Log a message at the DEBUG level according to the specified format
* and arguments.
* <p/>
* <p>This form avoids superfluous string concatenation when the logger
* is disabled for the DEBUG level. However, this variant incurs the hidden
* (and relatively small) cost of creating an <code>Object[]</code> before invoking the method,
* even if this logger is disabled for DEBUG. The variants taking
* {@link #debug(String, Object) one} and {@link #debug(String, Object, Object) two}
* arguments exist solely in order to avoid this hidden cost.</p>
*
* @param format the format string
* @param arguments a list of 3 or more arguments
*/
public void debug(String format, Object... arguments);
/**
* Log an exception (throwable) at the DEBUG level with an
* accompanying message.
*
* @param msg the message accompanying the exception
* @param t the exception (throwable) to log
*/
public void debug(String msg, Throwable t);
/**
* Similar to {@link #isDebugEnabled()} method except that the
* marker data is also taken into account.
*
* @param marker The marker data to take into consideration
* @return True if this Logger is enabled for the DEBUG level,
* false otherwise.
*/
public boolean isDebugEnabled(Marker marker);
/**
* Log a message with the specific Marker at the DEBUG level.
*
* @param marker the marker data specific to this log statement
* @param msg the message string to be logged
*/
public void debug(Marker marker, String msg);
/**
* This method is similar to {@link #debug(String, Object)} method except that the
* marker data is also taken into consideration.
*
* @param marker the marker data specific to this log statement
* @param format the format string
* @param arg the argument
*/
public void debug(Marker marker, String format, Object arg);
/**
* This method is similar to {@link #debug(String, Object, Object)}
* method except that the marker data is also taken into
* consideration.
*
* @param marker the marker data specific to this log statement
* @param format the format string
* @param arg1 the first argument
* @param arg2 the second argument
*/
public void debug(Marker marker, String format, Object arg1, Object arg2);
/**
* This method is similar to {@link #debug(String, Object...)}
* method except that the marker data is also taken into
* consideration.
*
* @param marker the marker data specific to this log statement
* @param format the format string
* @param arguments a list of 3 or more arguments
*/
public void debug(Marker marker, String format, Object... arguments);
/**
* This method is similar to {@link #debug(String, Throwable)} method except that the
* marker data is also taken into consideration.
*
* @param marker the marker data specific to this log statement
* @param msg the message accompanying the exception
* @param t the exception (throwable) to log
*/
public void debug(Marker marker, String msg, Throwable t);
/**
* Is the logger instance enabled for the INFO level?
*
* @return True if this Logger is enabled for the INFO level,
* false otherwise.
*/
public boolean isInfoEnabled();
/**
* Log a message at the INFO level.
*
* @param msg the message string to be logged
*/
public void info(String msg);
/**
* Log a message at the INFO level according to the specified format
* and argument.
* <p/>
* <p>This form avoids superfluous object creation when the logger
* is disabled for the INFO level. </p>
*
* @param format the format string
* @param arg the argument
*/
public void info(String format, Object arg);
/**
* Log a message at the INFO level according to the specified format
* and arguments.
* <p/>
* <p>This form avoids superfluous object creation when the logger
* is disabled for the INFO level. </p>
*
* @param format the format string
* @param arg1 the first argument
* @param arg2 the second argument
*/
public void info(String format, Object arg1, Object arg2);
/**
* Log a message at the INFO level according to the specified format
* and arguments.
* <p/>
* <p>This form avoids superfluous string concatenation when the logger
* is disabled for the INFO level. However, this variant incurs the hidden
* (and relatively small) cost of creating an <code>Object[]</code> before invoking the method,
* even if this logger is disabled for INFO. The variants taking
* {@link #info(String, Object) one} and {@link #info(String, Object, Object) two}
* arguments exist solely in order to avoid this hidden cost.</p>
*
* @param format the format string
* @param arguments a list of 3 or more arguments
*/
public void info(String format, Object... arguments);
/**
* Log an exception (throwable) at the INFO level with an
* accompanying message.
*
* @param msg the message accompanying the exception
* @param t the exception (throwable) to log
*/
public void info(String msg, Throwable t);
/**
* Similar to {@link #isInfoEnabled()} method except that the marker
* data is also taken into consideration.
*
* @param marker The marker data to take into consideration
* @return true if this logger is warn enabled, false otherwise
*/
public boolean isInfoEnabled(Marker marker);
/**
* Log a message with the specific Marker at the INFO level.
*
* @param marker The marker specific to this log statement
* @param msg the message string to be logged
*/
public void info(Marker marker, String msg);
/**
* This method is similar to {@link #info(String, Object)} method except that the
* marker data is also taken into consideration.
*
* @param marker the marker data specific to this log statement
* @param format the format string
* @param arg the argument
*/
public void info(Marker marker, String format, Object arg);
/**
* This method is similar to {@link #info(String, Object, Object)}
* method except that the marker data is also taken into
* consideration.
*
* @param marker the marker data specific to this log statement
* @param format the format string
* @param arg1 the first argument
* @param arg2 the second argument
*/
public void info(Marker marker, String format, Object arg1, Object arg2);
/**
* This method is similar to {@link #info(String, Object...)}
* method except that the marker data is also taken into
* consideration.
*
* @param marker the marker data specific to this log statement
* @param format the format string
* @param arguments a list of 3 or more arguments
*/
public void info(Marker marker, String format, Object... arguments);
/**
* This method is similar to {@link #info(String, Throwable)} method
* except that the marker data is also taken into consideration.
*
* @param marker the marker data for this log statement
* @param msg the message accompanying the exception
* @param t the exception (throwable) to log
*/
public void info(Marker marker, String msg, Throwable t);
/**
* Is the logger instance enabled for the WARN level?
*
* @return True if this Logger is enabled for the WARN level,
* false otherwise.
*/
public boolean isWarnEnabled();
/**
* Log a message at the WARN level.
*
* @param msg the message string to be logged
*/
public void warn(String msg);
/**
* Log a message at the WARN level according to the specified format
* and argument.
* <p/>
* <p>This form avoids superfluous object creation when the logger
* is disabled for the WARN level. </p>
*
* @param format the format string
* @param arg the argument
*/
public void warn(String format, Object arg);
/**
* Log a message at the WARN level according to the specified format
* and arguments.
* <p/>
* <p>This form avoids superfluous string concatenation when the logger
* is disabled for the WARN level. However, this variant incurs the hidden
* (and relatively small) cost of creating an <code>Object[]</code> before invoking the method,
* even if this logger is disabled for WARN. The variants taking
* {@link #warn(String, Object) one} and {@link #warn(String, Object, Object) two}
* arguments exist solely in order to avoid this hidden cost.</p>
*
* @param format the format string
* @param arguments a list of 3 or more arguments
*/
public void warn(String format, Object... arguments);
/**
* Log a message at the WARN level according to the specified format
* and arguments.
* <p/>
* <p>This form avoids superfluous object creation when the logger
* is disabled for the WARN level. </p>
*
* @param format the format string
* @param arg1 the first argument
* @param arg2 the second argument
*/
public void warn(String format, Object arg1, Object arg2);
/**
* Log an exception (throwable) at the WARN level with an
* accompanying message.
*
* @param msg the message accompanying the exception
* @param t the exception (throwable) to log
*/
public void warn(String msg, Throwable t);
/**
* Similar to {@link #isWarnEnabled()} method except that the marker
* data is also taken into consideration.
*
* @param marker The marker data to take into consideration
* @return True if this Logger is enabled for the WARN level,
* false otherwise.
*/
public boolean isWarnEnabled(Marker marker);
/**
* Log a message with the specific Marker at the WARN level.
*
* @param marker The marker specific to this log statement
* @param msg the message string to be logged
*/
public void warn(Marker marker, String msg);
/**
* This method is similar to {@link #warn(String, Object)} method except that the
* marker data is also taken into consideration.
*
* @param marker the marker data specific to this log statement
* @param format the format string
* @param arg the argument
*/
public void warn(Marker marker, String format, Object arg);
/**
* This method is similar to {@link #warn(String, Object, Object)}
* method except that the marker data is also taken into
* consideration.
*
* @param marker the marker data specific to this log statement
* @param format the format string
* @param arg1 the first argument
* @param arg2 the second argument
*/
public void warn(Marker marker, String format, Object arg1, Object arg2);
/**
* This method is similar to {@link #warn(String, Object...)}
* method except that the marker data is also taken into
* consideration.
*
* @param marker the marker data specific to this log statement
* @param format the format string
* @param arguments a list of 3 or more arguments
*/
public void warn(Marker marker, String format, Object... arguments);
/**
* This method is similar to {@link #warn(String, Throwable)} method
* except that the marker data is also taken into consideration.
*
* @param marker the marker data for this log statement
* @param msg the message accompanying the exception
* @param t the exception (throwable) to log
*/
public void warn(Marker marker, String msg, Throwable t);
/**
* Is the logger instance enabled for the ERROR level?
*
* @return True if this Logger is enabled for the ERROR level,
* false otherwise.
*/
public boolean isErrorEnabled();
/**
* Log a message at the ERROR level.
*
* @param msg the message string to be logged
*/
public void error(String msg);
/**
* Log a message at the ERROR level according to the specified format
* and argument.
* <p/>
* <p>This form avoids superfluous object creation when the logger
* is disabled for the ERROR level. </p>
*
* @param format the format string
* @param arg the argument
*/
public void error(String format, Object arg);
/**
* Log a message at the ERROR level according to the specified format
* and arguments.
* <p/>
* <p>This form avoids superfluous object creation when the logger
* is disabled for the ERROR level. </p>
*
* @param format the format string
* @param arg1 the first argument
* @param arg2 the second argument
*/
public void error(String format, Object arg1, Object arg2);
/**
* Log a message at the ERROR level according to the specified format
* and arguments.
* <p/>
* <p>This form avoids superfluous string concatenation when the logger
* is disabled for the ERROR level. However, this variant incurs the hidden
* (and relatively small) cost of creating an <code>Object[]</code> before invoking the method,
* even if this logger is disabled for ERROR. The variants taking
* {@link #error(String, Object) one} and {@link #error(String, Object, Object) two}
* arguments exist solely in order to avoid this hidden cost.</p>
*
* @param format the format string
* @param arguments a list of 3 or more arguments
*/
public void error(String format, Object... arguments);
/**
* Log an exception (throwable) at the ERROR level with an
* accompanying message.
*
* @param msg the message accompanying the exception
* @param t the exception (throwable) to log
*/
public void error(String msg, Throwable t);
/**
* Similar to {@link #isErrorEnabled()} method except that the
* marker data is also taken into consideration.
*
* @param marker The marker data to take into consideration
* @return True if this Logger is enabled for the ERROR level,
* false otherwise.
*/
public boolean isErrorEnabled(Marker marker);
/**
* Log a message with the specific Marker at the ERROR level.
*
* @param marker The marker specific to this log statement
* @param msg the message string to be logged
*/
public void error(Marker marker, String msg);
/**
* This method is similar to {@link #error(String, Object)} method except that the
* marker data is also taken into consideration.
*
* @param marker the marker data specific to this log statement
* @param format the format string
* @param arg the argument
*/
public void error(Marker marker, String format, Object arg);
/**
* This method is similar to {@link #error(String, Object, Object)}
* method except that the marker data is also taken into
* consideration.
*
* @param marker the marker data specific to this log statement
* @param format the format string
* @param arg1 the first argument
* @param arg2 the second argument
*/
public void error(Marker marker, String format, Object arg1, Object arg2);
/**
* This method is similar to {@link #error(String, Object...)}
* method except that the marker data is also taken into
* consideration.
*
* @param marker the marker data specific to this log statement
* @param format the format string
* @param arguments a list of 3 or more arguments
*/
public void error(Marker marker, String format, Object... arguments);
/**
* This method is similar to {@link #error(String, Throwable)}
* method except that the marker data is also taken into
* consideration.
*
* @param marker the marker data specific to this log statement
* @param msg the message accompanying the exception
* @param t the exception (throwable) to log
*/
public void error(Marker marker, String msg, Throwable t);
}
LoggerFactory.class
public final class LoggerFactory {
static final String CODES_PREFIX = "http://www.slf4j.org/codes.html";
static final String NO_STATICLOGGERBINDER_URL = CODES_PREFIX + "#StaticLoggerBinder";
static final String MULTIPLE_BINDINGS_URL = CODES_PREFIX + "#multiple_bindings";
static final String NULL_LF_URL = CODES_PREFIX + "#null_LF";
static final String VERSION_MISMATCH = CODES_PREFIX + "#version_mismatch";
static final String SUBSTITUTE_LOGGER_URL = CODES_PREFIX + "#substituteLogger";
static final String LOGGER_NAME_MISMATCH_URL = CODES_PREFIX + "#loggerNameMismatch";
static final String REPLAY_URL = CODES_PREFIX + "#replay";
static final String UNSUCCESSFUL_INIT_URL = CODES_PREFIX + "#unsuccessfulInit";
static final String UNSUCCESSFUL_INIT_MSG = "org.slf4j.LoggerFactory in failed state. Original exception was thrown EARLIER. See also " + UNSUCCESSFUL_INIT_URL;
static final int UNINITIALIZED = 0;
static final int ONGOING_INITIALIZATION = 1;
static final int FAILED_INITIALIZATION = 2;
static final int SUCCESSFUL_INITIALIZATION = 3;
static final int NOP_FALLBACK_INITIALIZATION = 4;
static volatile int INITIALIZATION_STATE = UNINITIALIZED;
static final SubstituteLoggerFactory SUBST_FACTORY = new SubstituteLoggerFactory();
static final NOPLoggerFactory NOP_FALLBACK_FACTORY = new NOPLoggerFactory();
// Support for detecting mismatched logger names.
static final String DETECT_LOGGER_NAME_MISMATCH_PROPERTY = "slf4j.detectLoggerNameMismatch";
static final String JAVA_VENDOR_PROPERTY = "java.vendor.url";
static boolean DETECT_LOGGER_NAME_MISMATCH = Util.safeGetBooleanSystemProperty(DETECT_LOGGER_NAME_MISMATCH_PROPERTY);
/**
* It is LoggerFactory's responsibility to track version changes and manage
* the compatibility list.
* <p/>
* <p/>
* It is assumed that all versions in the 1.6 are mutually compatible.
*/
static private final String[] API_COMPATIBILITY_LIST = new String[] { "1.6", "1.7" };
// private constructor prevents instantiation
private LoggerFactory() {
}
/**
* Force LoggerFactory to consider itself uninitialized.
* <p/>
* <p/>
* This method is intended to be called by classes (in the same package) for
* testing purposes. This method is internal. It can be modified, renamed or
* removed at any time without notice.
* <p/>
* <p/>
* You are strongly discouraged from calling this method in production code.
*/
static void reset() {
INITIALIZATION_STATE = UNINITIALIZED;
}
private final static void performInitialization() {
bind();
if (INITIALIZATION_STATE == SUCCESSFUL_INITIALIZATION) {
versionSanityCheck();
}
}
private static boolean messageContainsOrgSlf4jImplStaticLoggerBinder(String msg) {
if (msg == null)
return false;
if (msg.contains("org/slf4j/impl/StaticLoggerBinder"))
return true;
if (msg.contains("org.slf4j.impl.StaticLoggerBinder"))
return true;
return false;
}
private final static void bind() {
try {
Set<URL> staticLoggerBinderPathSet = null;
// skip check under android, see also
// http://jira.qos.ch/browse/SLF4J-328
if (!isAndroid()) {
staticLoggerBinderPathSet = findPossibleStaticLoggerBinderPathSet();
reportMultipleBindingAmbiguity(staticLoggerBinderPathSet);
}
// the next line does the binding
StaticLoggerBinder.getSingleton();
INITIALIZATION_STATE = SUCCESSFUL_INITIALIZATION;
reportActualBinding(staticLoggerBinderPathSet);
fixSubstituteLoggers();
replayEvents();
// release all resources in SUBST_FACTORY
SUBST_FACTORY.clear();
} catch (NoClassDefFoundError ncde) {
String msg = ncde.getMessage();
if (messageContainsOrgSlf4jImplStaticLoggerBinder(msg)) {
INITIALIZATION_STATE = NOP_FALLBACK_INITIALIZATION;
Util.report("Failed to load class \"org.slf4j.impl.StaticLoggerBinder\".");
Util.report("Defaulting to no-operation (NOP) logger implementation");
Util.report("See " + NO_STATICLOGGERBINDER_URL + " for further details.");
} else {
failedBinding(ncde);
throw ncde;
}
} catch (java.lang.NoSuchMethodError nsme) {
String msg = nsme.getMessage();
if (msg != null && msg.contains("org.slf4j.impl.StaticLoggerBinder.getSingleton()")) {
INITIALIZATION_STATE = FAILED_INITIALIZATION;
Util.report("slf4j-api 1.6.x (or later) is incompatible with this binding.");
Util.report("Your binding is version 1.5.5 or earlier.");
Util.report("Upgrade your binding to version 1.6.x.");
}
throw nsme;
} catch (Exception e) {
failedBinding(e);
throw new IllegalStateException("Unexpected initialization failure", e);
}
}
private static void fixSubstituteLoggers() {
synchronized (SUBST_FACTORY) {
SUBST_FACTORY.postInitialization();
for (SubstituteLogger substLogger : SUBST_FACTORY.getLoggers()) {
Logger logger = getLogger(substLogger.getName());
substLogger.setDelegate(logger);
}
}
}
static void failedBinding(Throwable t) {
INITIALIZATION_STATE = FAILED_INITIALIZATION;
Util.report("Failed to instantiate SLF4J LoggerFactory", t);
}
private static void replayEvents() {
final LinkedBlockingQueue<SubstituteLoggingEvent> queue = SUBST_FACTORY.getEventQueue();
final int queueSize = queue.size();
int count = 0;
final int maxDrain = 128;
List<SubstituteLoggingEvent> eventList = new ArrayList<SubstituteLoggingEvent>(maxDrain);
while (true) {
int numDrained = queue.drainTo(eventList, maxDrain);
if (numDrained == 0)
break;
for (SubstituteLoggingEvent event : eventList) {
replaySingleEvent(event);
if (count++ == 0)
emitReplayOrSubstituionWarning(event, queueSize);
}
eventList.clear();
}
}
private static void emitReplayOrSubstituionWarning(SubstituteLoggingEvent event, int queueSize) {
if (event.getLogger().isDelegateEventAware()) {
emitReplayWarning(queueSize);
} else if (event.getLogger().isDelegateNOP()) {
// nothing to do
} else {
emitSubstitutionWarning();
}
}
private static void replaySingleEvent(SubstituteLoggingEvent event) {
if (event == null)
return;
SubstituteLogger substLogger = event.getLogger();
String loggerName = substLogger.getName();
if (substLogger.isDelegateNull()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Delegate logger cannot be null at this state.");
}
if (substLogger.isDelegateNOP()) {
// nothing to do
} else if (substLogger.isDelegateEventAware()) {
substLogger.log(event);
} else {
Util.report(loggerName);
}
}
private static void emitSubstitutionWarning() {
Util.report("The following set of substitute loggers may have been accessed");
Util.report("during the initialization phase. Logging calls during this");
Util.report("phase were not honored. However, subsequent logging calls to these");
Util.report("loggers will work as normally expected.");
Util.report("See also " + SUBSTITUTE_LOGGER_URL);
}
private static void emitReplayWarning(int eventCount) {
Util.report("A number (" + eventCount + ") of logging calls during the initialization phase have been intercepted and are");
Util.report("now being replayed. These are subject to the filtering rules of the underlying logging system.");
Util.report("See also " + REPLAY_URL);
}
private final static void versionSanityCheck() {
try {
String requested = StaticLoggerBinder.REQUESTED_API_VERSION;
boolean match = false;
for (String aAPI_COMPATIBILITY_LIST : API_COMPATIBILITY_LIST) {
if (requested.startsWith(aAPI_COMPATIBILITY_LIST)) {
match = true;
}
}
if (!match) {
Util.report("The requested version " + requested + " by your slf4j binding is not compatible with "
+ Arrays.asList(API_COMPATIBILITY_LIST).toString());
Util.report("See " + VERSION_MISMATCH + " for further details.");
}
} catch (java.lang.NoSuchFieldError nsfe) {
// given our large user base and SLF4J's commitment to backward
// compatibility, we cannot cry here. Only for implementations
// which willingly declare a REQUESTED_API_VERSION field do we
// emit compatibility warnings.
} catch (Throwable e) {
// we should never reach here
Util.report("Unexpected problem occured during version sanity check", e);
}
}
// We need to use the name of the StaticLoggerBinder class, but we can't
// reference
// the class itself.
private static String STATIC_LOGGER_BINDER_PATH = "org/slf4j/impl/StaticLoggerBinder.class";
static Set<URL> findPossibleStaticLoggerBinderPathSet() {
// use Set instead of list in order to deal with bug #138
// LinkedHashSet appropriate here because it preserves insertion order
// during iteration
Set<URL> staticLoggerBinderPathSet = new LinkedHashSet<URL>();
try {
ClassLoader loggerFactoryClassLoader = LoggerFactory.class.getClassLoader();
Enumeration<URL> paths;
if (loggerFactoryClassLoader == null) {
paths = ClassLoader.getSystemResources(STATIC_LOGGER_BINDER_PATH);
} else {
paths = loggerFactoryClassLoader.getResources(STATIC_LOGGER_BINDER_PATH);
}
while (paths.hasMoreElements()) {
URL path = paths.nextElement();
staticLoggerBinderPathSet.add(path);
}
} catch (IOException ioe) {
Util.report("Error getting resources from path", ioe);
}
return staticLoggerBinderPathSet;
}
private static boolean isAmbiguousStaticLoggerBinderPathSet(Set<URL> binderPathSet) {
return binderPathSet.size() > 1;
}
/**
* Prints a warning message on the console if multiple bindings were found
* on the class path. No reporting is done otherwise.
*
*/
private static void reportMultipleBindingAmbiguity(Set<URL> binderPathSet) {
if (isAmbiguousStaticLoggerBinderPathSet(binderPathSet)) {
Util.report("Class path contains multiple SLF4J bindings.");
for (URL path : binderPathSet) {
Util.report("Found binding in [" + path + "]");
}
Util.report("See " + MULTIPLE_BINDINGS_URL + " for an explanation.");
}
}
private static boolean isAndroid() {
String vendor = Util.safeGetSystemProperty(JAVA_VENDOR_PROPERTY);
if (vendor == null)
return false;
return vendor.toLowerCase().contains("android");
}
private static void reportActualBinding(Set<URL> binderPathSet) {
// binderPathSet can be null under Android
if (binderPathSet != null && isAmbiguousStaticLoggerBinderPathSet(binderPathSet)) {
Util.report("Actual binding is of type [" + StaticLoggerBinder.getSingleton().getLoggerFactoryClassStr() + "]");
}
}
/**
* Return a logger named according to the name parameter using the
* statically bound {@link ILoggerFactory} instance.
*
* @param name
* The name of the logger.
* @return logger
*/
public static Logger getLogger(String name) {
ILoggerFactory iLoggerFactory = getILoggerFactory();
return iLoggerFactory.getLogger(name);
}
/**
* Return a logger named corresponding to the class passed as parameter,
* using the statically bound {@link ILoggerFactory} instance.
*
* <p>
* In case the the <code>clazz</code> parameter differs from the name of the
* caller as computed internally by SLF4J, a logger name mismatch warning
* will be printed but only if the
* <code>slf4j.detectLoggerNameMismatch</code> system property is set to
* true. By default, this property is not set and no warnings will be
* printed even in case of a logger name mismatch.
*
* @param clazz
* the returned logger will be named after clazz
* @return logger
*
*
* @see <a
* href="http://www.slf4j.org/codes.html#loggerNameMismatch">Detected
* logger name mismatch</a>
*/
public static Logger getLogger(Class<?> clazz) {
Logger logger = getLogger(clazz.getName());
if (DETECT_LOGGER_NAME_MISMATCH) {
Class<?> autoComputedCallingClass = Util.getCallingClass();
if (autoComputedCallingClass != null && nonMatchingClasses(clazz, autoComputedCallingClass)) {
Util.report(String.format("Detected logger name mismatch. Given name: \"%s\"; computed name: \"%s\".", logger.getName(),
autoComputedCallingClass.getName()));
Util.report("See " + LOGGER_NAME_MISMATCH_URL + " for an explanation");
}
}
return logger;
}
private static boolean nonMatchingClasses(Class<?> clazz, Class<?> autoComputedCallingClass) {
return !autoComputedCallingClass.isAssignableFrom(clazz);
}
/**
* Return the {@link ILoggerFactory} instance in use.
* <p/>
* <p/>
* ILoggerFactory instance is bound with this class at compile time.
*
* @return the ILoggerFactory instance in use
*/
public static ILoggerFactory getILoggerFactory() {
if (INITIALIZATION_STATE == UNINITIALIZED) {
synchronized (LoggerFactory.class) {
if (INITIALIZATION_STATE == UNINITIALIZED) {
INITIALIZATION_STATE = ONGOING_INITIALIZATION;
performInitialization();
}
}
}
switch (INITIALIZATION_STATE) {
case SUCCESSFUL_INITIALIZATION:
return StaticLoggerBinder.getSingleton().getLoggerFactory();
case NOP_FALLBACK_INITIALIZATION:
return NOP_FALLBACK_FACTORY;
case FAILED_INITIALIZATION:
throw new IllegalStateException(UNSUCCESSFUL_INIT_MSG);
case ONGOING_INITIALIZATION:
// support re-entrant behavior.
// See also http://jira.qos.ch/browse/SLF4J-97
return SUBST_FACTORY;
}
throw new IllegalStateException("Unreachable code");
}
}
这里看下获取getLogger函数的源码,我们发现LoggerFactory.getLogger()首先获取一个ILoggerFactory接口,然后使用该接口获取具体的Logger。获取ILoggerFactory的时候用到了一个StaticLoggerBinder类,仔细研究我们会发现StaticLoggerBinder这个类并不是slf4j-api这个包中的类,而是实现日志框架里的类,所有的实现框架都需要定义该类,提供具体的Logger实现。
接下来具体分析日志实现框架 logback和log4j2。
logger(一)slf4j简介及其实现原理的更多相关文章
- logger(三)log4j2简介及其实现原理
一.log4j2简介 log4j2是log4j 1.x和logback的改进版,据说采用了一些新技术(无锁异步.等等),使得日志的吞吐量.性能比log4j 1.x提高10倍,并解决了一些死锁的bug, ...
- logger(二)logback简介及其实现原理
一.logback简介 logback是log4j创始人写的,性能比log4j要好,目前主要分为3个模块 logback-core:核心代码模块 logback-classic:log4j的一个改良版 ...
- Lucene底层原理和优化经验分享(1)-Lucene简介和索引原理
Lucene底层原理和优化经验分享(1)-Lucene简介和索引原理 2017年01月04日 08:52:12 阅读数:18366 基于Lucene检索引擎我们开发了自己的全文检索系统,承担起后台PB ...
- slf4j介绍以及实现原理窥探
一.概述 slf4j(全称是Simple Loging Facade For Java)是一个为Java程序提供日志输出的统一接口,并不是一个具体的日志实现方案,就好像我们经常使用的JDBC一样,只是 ...
- slf4j简介
SLF4J不是日志框架而是一个简单日志门面,它的目的是允许最终用户在部署时使用期望的日志框架. The Simple Logging Facade for Java (SLF4J) serves as ...
- Java日志框架:slf4j作用及其实现原理
简单回顾门面模式 slf4j是门面模式的典型应用,因此在讲slf4j前,我们先简单回顾一下门面模式, 门面模式,其核心为外部与一个子系统的通信必须通过一个统一的外观对象进行,使得子系统更易于使用.用一 ...
- Neo4j图数据库简介和底层原理
现实中很多数据都是用图来表达的,比如社交网络中人与人的关系.地图数据.或是基因信息等等.RDBMS并不适合表达这类数据,而且由于海量数据的存在,让其显得捉襟见肘.NoSQL数据库的兴起,很好地解决了海 ...
- 1.JSP 简介及工作原理
1.JSP 简介 JSP(Java Server Pages)是由Sun Microsystems公司倡导.许多公司参与一起建立的一种动态网页技术标准.JSP技术有点类似ASP技术,它是在传统的网页H ...
- LoadRunner系统架构简介与运行原理
1.LoadRunner系统架构简介 LoadRunner是通过创建虚拟用户来代替真实实际用户来操作客户端软件比如Internet Explorer,来向IIS.Apache等Web服务器发送HTTP ...
随机推荐
- 逆向工程文件example完美结合使用PageHelper分页插件及分页不成功原因
原生的mybatis需要手写sql语句,项目数据库表多了之后,可以让你写sql语句写到手软,于是mybatis官方提供了mybatis-generator:mybatis逆向工程代码生成工具,用于简化 ...
- 莫烦TensorFlow_11 MNIST优化使用CNN
import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data #number 1 to 10 d ...
- 重新学习SpringMVC——高级
30. SpringMVC_RESTRUL_CRUD_显示所有员工信息31. SpringMVC_RESTRUL_CRUD_添加操作&表单标签32. SpringMVC_RESTRUL_CRU ...
- Nginx的负载均衡配置(七)
原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/knowledgesea/p/5199046.html 首先给大家说下upstream这个配置的,这个配置是写一组被代理的服务器地址,然后配置 ...
- VIJOS-P1423 最佳路线
VIJOS-P1423 最佳路线 JDOJ 1507 https://neooj.com/oldoj/problem.php?id=1507 Description 年久失修的赛道令国际汽联十分不满. ...
- cnpm包管理
C:\Users\Administrator>npm config set registry http://registry.npm.taobao.org vue 安装 npm install ...
- 10.24考试题解qwq
考点难度都很合适的一套题目,大概在day1到day2之前 T1 猴猴最喜欢在树上玩耍,一天猴猴又跳上了一棵树,这棵树有N个苹果,每个苹果有一个编号,分别为0~N-1,它们之间由N-1个树枝相连,猴猴可 ...
- Codechef August Challenge 2019 Division 2
Preface 老年菜鸡终于开始打CC了,由于他太弱了所以只能打Div2 因为台风的原因challenge并没有写,所以水了个Rank7 A Football SB模拟题不解释 #include< ...
- MySQL学习记录(导入Excel表到数据库,并筛选条件输出)
附上:重置mysql账号密码方法 ubuntu系统下mysql重置密码和修改密码操作 - skh2015java的博客 - CSDN博客(改完重启,登录mysql要root/sudo权限) Cento ...
- 仅逗oier们一笑(不定期更新中)(update.2019年12月8日)
CCF的正确解释: //部分来自:朝阳的二愣子的CSDN博客.ydclyq 的博客 .拱垲的博客.Randolph's Blog. 编译下列程序,会有意想不到的惊喜哦(注意打开声音): #includ ...
