Andrew Ng机器学习 五:Regularized Linear Regression and Bias v.s. Variance
背景:实现一个线性回归模型,根据这个模型去预测一个水库的水位变化而流出的水量。
加载数据集ex5.data1后,数据集分为三部分:
1,训练集(training set)X与y;
2,交叉验证集(cross validation)Xval, yval;
3,测试集(test set): Xtest, ytest。
一:正则化线性回归(Regularized Linear Regression)
1,可视化训练集,如下图所示:
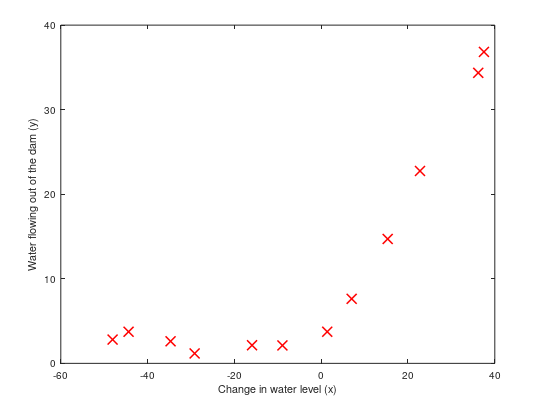
通过可视化数据,接下来我们使用线性回归去拟合这些数据集。
2,正则化线性回归代价函数:
$J(\theta)=\frac{1}{2m}(\sum_{i=1}^{m}(h_{\theta}(x^{(i)})-y^{(i)})^2)+\frac{\lambda }{2m}\sum_{j=1}^{n}\theta_{j}^{2}$,忽略偏差项$\theta_0$的正则化
3,正则化线性回归梯度:
$\frac{\partial J(\theta)}{\partial \theta_0}=\frac{1}{m}\sum_{i=1}^{m}[(h_\theta(x^{(i)})-y^{(i)})x^{(i)}_j]$ for $j=0$
$\frac{\partial J(\theta)}{\partial \theta_j}=(\frac{1}{m}\sum_{i=1}^{m}[(h_\theta(x^{(i)})-y^{(i)})x^{(i)}_j])+\frac{\lambda }{m}\theta_j $ for $j\geq 1$
function [J, grad] = linearRegCostFunction(X, y, theta, lambda)
%LINEARREGCOSTFUNCTION Compute cost and gradient for regularized linear
%regression with multiple variables
% [J, grad] = LINEARREGCOSTFUNCTION(X, y, theta, lambda) computes the
% cost of using theta as the parameter for linear regression to fit the
% data points in X and y. Returns the cost in J and the gradient in grad % Initialize some useful values
m = length(y); % number of training examples % You need to return the following variables correctly
J = ;
grad = zeros(size(theta)); % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Compute the cost and gradient of regularized linear
% regression for a particular choice of theta.
%
% You should set J to the cost and grad to the gradient.
% h=X*theta;
theta(,)=;
%线性回归代价函数
J=(sum(power((h-y),))+lambda*sum(power(theta,)))/(*m); %梯度下降
grad=((h-y)'*X).*(1/m)+(theta').*(lambda/m); % ========================================================================= grad = grad(:); end
linearRegCostFunction.m
4,拟合线性回归(Fitting linear regression):
在这我们不正则化,拟合如下图所示:
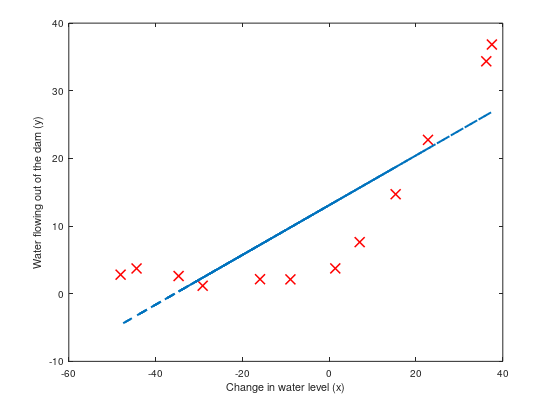
观察图可以拟合的直线为高偏差,因为数据集不是一条直线,而我们现在的数据集X只有一维,不足以拟合成一条曲线。
二:偏差与方差(Bias-variance)
1,学习曲线(Learning curves)
学习曲线将训练和交叉验证误差绘制为训练集大小的函数。
训练集误差(Training error): $J_{train}(\theta)=\frac{1}{2m}\sum_{i=1}^{m}(h_{\theta}(x^{(i)})-y^{(i)})^2$
在计算训练集误差时,在训练子集上进行计算(即$X(1:n,:)$和$y(1:n)$)(而不是整个训练集),
但是,对于交叉验证错误,在整个交叉验证集上对其进行计算。
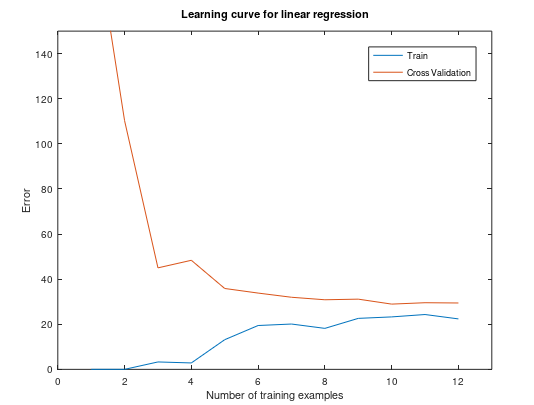
忽略正则化,我们可视化这个训练集的学习曲线,如下图所示:
function [error_train, error_val] = ...
learningCurve(X, y, Xval, yval, lambda)
%LEARNINGCURVE Generates the train and cross validation set errors needed
%to plot a learning curve
% [error_train, error_val] = ...
% LEARNINGCURVE(X, y, Xval, yval, lambda) returns the train and
% cross validation set errors for a learning curve. In particular,
% it returns two vectors of the same length - error_train and
% error_val. Then, error_train(i) contains the training error for
% i examples (and similarly for error_val(i)).
%
% In this function, you will compute the train and test errors for
% dataset sizes from up to m. In practice, when working with larger
% datasets, you might want to do this in larger intervals.
% % Number of training examples
m = size(X, ); % You need to return these values correctly
error_train = zeros(m, );
error_val = zeros(m, ); % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Fill in this function to return training errors in
% error_train and the cross validation errors in error_val.
% i.e., error_train(i) and
% error_val(i) should give you the errors
% obtained after training on i examples.
%
% Note: You should evaluate the training error on the first i training
% examples (i.e., X(:i, :) and y(:i)).
%
% For the cross-validation error, you should instead evaluate on
% the _entire_ cross validation set (Xval and yval).
%
% Note: If you are using your cost function (linearRegCostFunction)
% to compute the training and cross validation error, you should
% call the function with the lambda argument set to .
% Do note that you will still need to use lambda when running
% the training to obtain the theta parameters.
%
% Hint: You can loop over the examples with the following:
%
% for i = :m
% % Compute train/cross validation errors using training examples
% % X(:i, :) and y(:i), storing the result in
% % error_train(i) and error_val(i)
% ....
%
% end
% % ---------------------- Sample Solution ---------------------- for i=:m %给前i个样例拟合参数θ
theta = trainLinearReg(X(:i,:), y(:i,:), lambda);
%计算前i个样例的训练误差
[J, grad] = linearRegCostFunction(X(:i,:), y(:i,:), theta, );
error_train(i)=J;
%计算交叉验证集误差
[J, grad] = linearRegCostFunction(Xval, yval, theta, );
error_val(i)=J; end % ------------------------------------------------------------- % ========================================================================= end
learningCurve.m
观察此图,可以看到训练集数量增大时,误差还是很大,不会有太大改观,这是属于高偏差/欠拟合(High bias)问题--模型太过于简单,接下来我们将会增加更多的特征去拟合训练集。
2,多项式回归(Polynomial regression)
我们在上一步对于训练集的模型太过于简单,导致出现了欠拟合(高偏差)问题,接下来我们通过原有的特征增加更多新的特征,我们增加p维,每一维为原来特征的i次幂。
回归函数:$h_{\theta}(x)=\theta_0+\theta_1(waterLevel)+\theta_2(waterLevel)^{2}+...++\theta_p(waterLevel)^{p}$
$=h_{\theta}(x)=\theta_0+\theta_1(x_1)+\theta_2(x_2)^{2}+...++\theta_p(x_p)^{p}$
function [X_poly] = polyFeatures(X, p)
%POLYFEATURES Maps X (1D vector) into the p-th power
% [X_poly] = POLYFEATURES(X, p) takes a data matrix X (size m x ) and
% maps each example into its polynomial features where
% X_poly(i, :) = [X(i) X(i).^ X(i).^ ... X(i).^p];
% % You need to return the following variables correctly.
X_poly = zeros(numel(X), p); % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Given a vector X, return a matrix X_poly where the p-th
% column of X contains the values of X to the p-th power.
%
% ## for i=:p
## X_poly(:,i)=X .^ i;
## end for i=:p
X_poly(:,i)=X .^ i;
end % ========================================================================= end
polyFeatures.m
我们增加了新特征之后,要先进行特征缩放。然后我们使用新的训练集去拟合参数$\theta$(忽略正则化)。
此训练集模型的曲线:

将训练集和交叉验证集的代价函数误差与样本数绘制在同一张图表
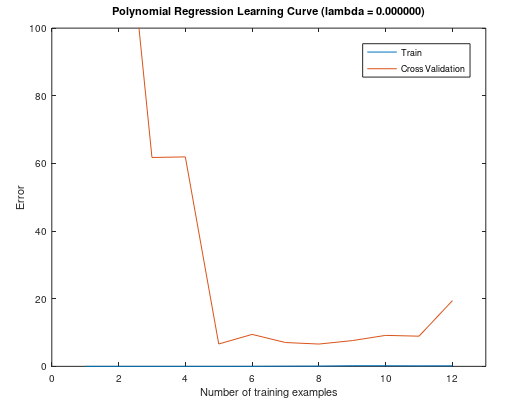
通过以上两图,我们可以看到,该模型完全适合于训练集,但对于交叉验证集,就不能很好的泛化了,此时出现了高方差/过拟合问题。那么接下来我们使用正则化来解决过拟合问题。
3,选择一个合适的正则化参数$\lambda$
我们尝试不同的$lambda$值来去选择一个较优的值,例如[0.001,0.003,0.01,0.03,0.1,0.3,1,3,10]
function [lambda_vec, error_train, error_val] = ...
validationCurve(X, y, Xval, yval)
%VALIDATIONCURVE Generate the train and validation errors needed to
%plot a validation curve that we can use to select lambda
% [lambda_vec, error_train, error_val] = ...
% VALIDATIONCURVE(X, y, Xval, yval) returns the train
% and validation errors (in error_train, error_val)
% for different values of lambda. You are given the training set (X,
% y) and validation set (Xval, yval).
% % Selected values of lambda (you should not change this)
lambda_vec = [ 0.001 0.003 0.01 0.03 0.1 0.3 ]'; % You need to return these variables correctly.
error_train = zeros(length(lambda_vec), );
error_val = zeros(length(lambda_vec), ); % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Fill in this function to return training errors in
% error_train and the validation errors in error_val. The
% vector lambda_vec contains the different lambda parameters
% to use for each calculation of the errors, i.e,
% error_train(i), and error_val(i) should give
% you the errors obtained after training with
% lambda = lambda_vec(i)
%
% Note: You can loop over lambda_vec with the following:
%
% for i = :length(lambda_vec)
% lambda = lambda_vec(i);
% % Compute train / val errors when training linear
% % regression with regularization parameter lambda
% % You should store the result in error_train(i)
% % and error_val(i)
% ....
%
% end
%
% for i=:length(lambda_vec)
lambda=lambda_vec(i);
[theta] = trainLinearReg(X, y, lambda)
error_train(i)=linearRegCostFunction(X, y, theta, ); %计算训练集的误差,忽略正则化的影响
error_val(i)=linearRegCostFunction(Xval, yval, theta, ); end % ========================================================================= end
validationCurve.m
可视化图如下所示:
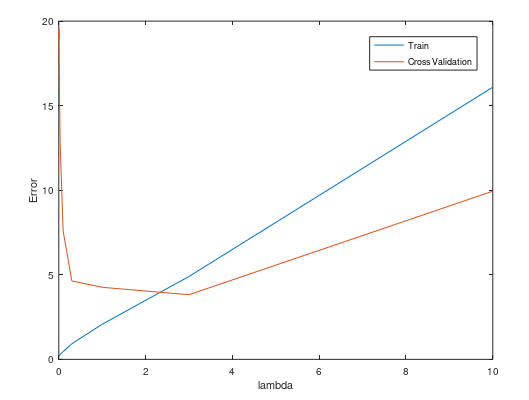
观察图,我们可以选择$lambda=3$。
总结:
1,获得更多的训练实例: 解决高偏差
2,尝试减少特征的数量:解决高方差
3,尝试获得更多的特征: 解决高偏差
4,尝试增加多项式的特征:解决高偏差
5,尝试减少正则化的程度$\lambda$:解决高偏差
6,尝试增加正则化的程度$\lambda$:解决高方差
Andrew Ng机器学习 五:Regularized Linear Regression and Bias v.s. Variance的更多相关文章
- 第五次编程作业-Regularized Linear Regression and Bias v.s. Variance
1.正规化的线性回归 (1)代价函数 (2)梯度 linearRegCostFunction.m function [J, grad] = linearRegCostFunction(X, y, th ...
- CheeseZH: Stanford University: Machine Learning Ex5:Regularized Linear Regression and Bias v.s. Variance
源码:https://github.com/cheesezhe/Coursera-Machine-Learning-Exercise/tree/master/ex5 Introduction: In ...
- Andrew Ng机器学习编程作业: Linear Regression
编程作业有两个文件 1.machine-learning-live-scripts(此为脚本文件方便作业) 2.machine-learning-ex1(此为作业文件) 将这两个文件解压拖入matla ...
- Andrew Ng机器学习 一: Linear Regression
一:单变量线性回归(Linear regression with one variable) 背景:在某城市开办饭馆,我们有这样的数据集ex1data1.txt,第一列代表某个城市的人口,第二列代表在 ...
- Andrew Ng机器学习编程作业:Logistic Regression
编程作业文件: machine-learning-ex2 1. Logistic Regression (逻辑回归) 有之前学生的数据,建立逻辑回归模型预测,根据两次考试结果预测一个学生是否有资格被大 ...
- Andrew Ng机器学习 二: Logistic Regression
一:逻辑回归(Logistic Regression) 背景:假设你是一所大学招生办的领导,你依据学生的成绩,给与他入学的资格.现在有这样一组以前的数据集ex2data1.txt,第一列表示第一次测验 ...
- Andrew Ng机器学习编程作业:Regularized Linear Regression and Bias/Variance
作业文件: machine-learning-ex5 1. 正则化线性回归 在本次练习的前半部分,我们将会正则化的线性回归模型来利用水库中水位的变化预测流出大坝的水量,后半部分我们对调试的学习算法进行 ...
- Andrew Ng机器学习课程笔记--汇总
笔记总结,各章节主要内容已总结在标题之中 Andrew Ng机器学习课程笔记–week1(机器学习简介&线性回归模型) Andrew Ng机器学习课程笔记--week2(多元线性回归& ...
- Andrew Ng机器学习课程笔记(五)之应用机器学习的建议
Andrew Ng机器学习课程笔记(五)之 应用机器学习的建议 版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,转载请指明转载地址 http://www.cnblogs.com/fydeblog/p/7368472.h ...
随机推荐
- C++之future和promise
future和promise的作用是在不同线程之间传递数据.使用指针也可以完成数据的传递,但是指针非常危险,因为互斥量不能阻止指针的访问:而且指针的方式传递的数据是固定的,如果更改数据类型,那么还需要 ...
- Metricbeat 轻量型指标采集器
一.介绍 用于从系统和服务收集指标.从 CPU 到内存,从 Redis 到 Nginx,Metricbeat 能够以一种轻量型的方式,输送各种系统和服务统计数据. 1.系统级监控,更简洁(轻量型指标采 ...
- 利用js来画图形(例如:条状图,圆饼图等)
背景:java开发的过程中,需要对数据进行可视化,这样方便客户理解此时的数据状态 语言:java,js,window7,echarts包文件 sample的例子下面的参照 https://www.ec ...
- 【mysql】开启远程连接
设置root用户可以远程连接 use mysql; update user set host = '%' where user = 'root'; FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
- Python脚本-自动下载安装
#coding=utf-8 import os import sys if os.getuid() == 0: pass else: print 'no' sys.exit(1) version = ...
- go 学习笔记(1)go command
常用命令 go command [arguments] 1) go build 跨平台编译: env GOOS=linux GOARCH=amd64 go build 2) go install : ...
- go语言学习笔记---读取文件io/ioutil 包
io/ioutil 包几个函数方法 名称 作用 备注 ReadAll 读取数据,返回读到的字节 slice 1 ReadDir 读取一个目录,返回目录入口数组 []os.FileInfo, 2 Re ...
- Unity项目 - MissionDemolition 愤怒的小鸟核心机制
目录 游戏原型 项目演示 绘图资源 代码实现 注意事项 技术探讨 参考来源 游戏原型 爆破任务 MissionDemolition 是一款核心机制类似于愤怒的小鸟的游戏,玩家将用弹弓发射炮弹,摧毁城堡 ...
- c#的一些书写技巧
从非创建线程访问线程资源 Invoke(new Action<int>((o)=> { textBox1.Text = (Convert.ToInt32(textBox1.Text ...
- Unity3d与iOS交互开发
一.Unity3d To iOS: 最近要做一个商品和人体模型T台秀相关的功能,要用到Unity3D,搜集了一些资料先保存下来. 1.创建一个C#文件 SdkToIOS.cs 这是调用iOS函数的 ...
