Caffe FCN:可视化featureMaps和Weights(C++)、获取FCN结果
为何不使用C++版本FCN获取最后的分割掩模,何必要使用python呢!因此需要获取网络最后层的featureMaps,featureMaps的结果直接对应了segmentation的最终结果,可以直接用于掩模分析。
caffe源码给出了提取中间层featureMap的源代码,位置在tools/extract_features.cpp。
参考文章链接: caffe模型可视化featureMaps和Weights(C++) ,文章有大量修改,如有不适,请移步原文。
1. 可视化最后一层featureMap的代码段(稍作修改):
int Classifier::visualize_featuremap( const cv::Mat& img, string layer_name, std::vector<cv::Mat> &Maps )
{
Maps.resize(0);
Blob<float>* input_layer = net_->input_blobs()[0];
input_layer->Reshape(1, num_channels_, input_geometry_.height, input_geometry_.width); net_->Reshape(); std::vector<cv::Mat> input_channels;
WrapInputLayer(&input_channels); Preprocess(img, &input_channels); net_->Forward(); std::cout << "网络中的Blobs名称为:\n";
vector<shared_ptr<Blob<float> > > blobs = net_->blobs();
vector<string> blob_names = net_->blob_names();
std::cout << blobs.size() << " " << blob_names.size() << std::endl;
for (int i = 0; i < blobs.size(); i++){
std::cout << blob_names[i] << " " << blobs[i]->shape_string() << std::endl;
}
std::cout << std::endl; assert(net_->has_blob(layer_name));
shared_ptr<Blob<float> > conv1Blob = net_->blob_by_name(layer_name);
std::cout << "测试图片的特征响应图的形状信息为:" << conv1Blob->shape_string() << std::endl; float maxValue = -10000000, minValue = 10000000;
const float* tmpValue = conv1Blob->cpu_data();
for (int i = 0; i < conv1Blob->count(); i++){
maxValue = std::max(maxValue, tmpValue[i]);
minValue = std::min(minValue, tmpValue[i]);
} int width = conv1Blob->shape(3); //响应图的高度
int height = conv1Blob->shape(2); //响应图的宽度
int channel = conv1Blob->shape(1); //通道数
int num = conv1Blob->shape(0); //个数
int imgHeight = (int)(1 + sqrt(channel))*height;
int imgWidth = (int)(1 + sqrt(channel))*width;
cv::Mat img(imgHeight, imgWidth, CV_8UC1, cv::Scalar(0)); int kk = 0;
for (int x = 0; x < imgHeight; x += height){
for (int y = 0; y < imgWidth; y += width){
if (kk >= channel)
continue;
cv::Mat roi(height, width, CV_8UC1);
//cv::Mat roi = img(cv::Rect(y, x, width, height));
for (int i = 0; i < height; i++){
for (int j = 0; j < width; j++){
float value = conv1Blob->data_at(0, kk, i, j);//速度稍慢,应该有快速复制方法
//roi.at<uchar>(i, j) = (value - minValue) / (maxValue - minValue) * 255;
value = (value - minValue) / (maxValue - minValue);
roi.at<uchar>(i, j) = 255* floor(value / 0.5) ;
}
}
Maps.push_back(roi);
kk++;
}
} return Maps.size();
}
2. 获取FCN的最终输出
vector<Blob<float>* > outBlob = net_->Forward();//得到的结果仍为151个//输出结果为151个模板
int channel = outBlob[0]->shape(1);
int hi = outBlob[0]->shape(2);
int wi = outBlob[0]->shape(3);
int area = wi*hi;
vector<shared_ptr<Blob<float> > > blobs = net_->blobs();
vector<string> blob_names = net_->blob_names();
获取最大标记
int Classifier::GetMaxMask( const cv::Mat& img, int layerIdx, double thres,cv::Mat &maskMax )
{
vector<boost::shared_ptr<Blob<float> > > blobs = net_->blobs();
vector<string> blob_names = net_->blob_names(); int num_features = net_->output_blobs()[0]->shape(1);
int channel = net_->output_blobs()[0]->shape(1);
int hi = net_->output_blobs()[0]->shape(2);
int wi = net_->output_blobs()[0]->shape(3);
int area = wi*hi;
std::vector<int> image_indices(num_features, 0); int i = layerIdx;
const boost::shared_ptr<Blob<float> > feature_blob
= net_->blob_by_name(blob_names[i]);
int batch_size = feature_blob->num();
int dim_features = feature_blob->count() / batch_size; float maxValue = -10000000, minValue = 10000000;
const float* tmpValue = feature_blob->cpu_data();
for (int i = 0; i < feature_blob->count(); i++){
maxValue = std::max(maxValue, tmpValue[i]);
minValue = std::min(minValue, tmpValue[i]);
} std::vector<int> areal(channel);
for (int i = 0; i < channel;++i){
areal[i] = i*area;
}
const float* feature_blob_data;
const float minv = 10000000;
const float maxv = -10000000;
int classI = 0;
for ( int n = 0; n < batch_size; ++n){
feature_blob_data =
feature_blob->cpu_data() + feature_blob->offset(n);
int img_index = 0;
for (int h = 0; h < hi; ++h)
{
uchar* ptr = (unsigned char*)(maskMax.data + h * maskMax.step);
int idxH = h*wi;
img_index = idxH;
for ( int w = 0; w < wi; ++w)
{
float valueG = maxv;
for ( int c = 0; c < channel; ++c){
int datum_index = areal[c] + img_index;// area*c;
float value = static_cast<float>(feature_blob_data[datum_index]);
if ( valueG < value ){
valueG = value;
classI = c;
}
}
*ptr = (uchar)classI;
++ptr;
++img_index;
}
}
}
return 1;
}
获取所有标记
//获取特定的元,使用点数限制
int Classifier::getAllSeg(cv::Mat &im_inp, cv::Mat &maskMax,
std::vector<cv::Mat > &segs,std::vector<std::pair<int,float> > &labels,
const int nPointMin)
{
std::vector<int> numsc(m_nClass);
int h = maskMax.rows;
int w = maskMax.cols; for (int i = 0; i < maskMax.rows; ++i)
{
uchar *ptrm = maskMax.ptr<uchar>(i);
for (int j = 0; j < maskMax.cols; ++j)
{
int c = *ptrm;
numsc[c]++;
++ptrm;
}
} //添加限制,获取分割图
std::map<int, int> maps;
int k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < numsc.size();++i){
if (numsc[i]>nPointMin){
auto idx =make_pair(i,1.0f);
labels.push_back(idx);
auto idxm = make_pair(i, k);
maps.insert(idxm);
++k;
}
} //获取图像
for (int i = 0; i < labels.size(); ++i){
cv::Mat seg(h, w, CV_8UC3);
segs.push_back(seg);
} std::vector<uchar *> ptres(labels.size());
for (int idx = 0; idx < labels.size(); ++idx){
ptres[idx] = (uchar *)segs[idx].data;
} for ( int i = 0; i < maskMax.rows; ++i )
{
uchar *ptr = im_inp.ptr<uchar>(i);
uchar *ptrm = maskMax.ptr<uchar>(i);
for (int n = 0; n < labels.size(); ++n)
ptres[n] = (uchar *)segs[n].ptr<uchar>(i); for ( int j = 0; j < maskMax.cols; ++j )
{
int c = *ptrm;
int pos;// = maps[c];
auto l_it = maps.find(c);
if ( l_it == maps.end() )
pos = -1;
else
pos = l_it->second; if ( pos>-1) *(ptres[pos]) = *ptr;
++ptr;
for (int n = 0; n < labels.size();++n) ++ptres[n];
if (pos>-1) *(ptres[pos]) = *ptr;
++ptr;
for (int n = 0; n < labels.size(); ++n) ++ptres[n];
if (pos>-1) *(ptres[pos]) = *ptr;
++ptr;
for (int n = 0; n < labels.size(); ++n) ++ptres[n];
++ptrm;
}
}
int nseg = segs.size();
return nseg;
}
3.此外,可视化权值的代码段,直接摘抄
cv::Mat visualize_weights(string prototxt, string caffemodel, int weights_layer_num)
{ ::google::InitGoogleLogging("0");
#ifdef CPU_ONLY
Caffe::set_mode(Caffe::CPU);
#else
Caffe::set_mode(Caffe::GPU);
#endif Net<float> net(prototxt, TEST);
net.CopyTrainedLayersFrom(caffemodel);
vector<shared_ptr<Blob<float> > > params = net.params();
std::cout << "各层参数的维度信息为:\n";
for (int i = 0; i<params.size(); ++i)
std::cout << params[i]->shape_string() << std::endl; int width = params[weights_layer_num]->shape(3); //宽度
int height = params[weights_layer_num]->shape(2); //高度
int channel = params[weights_layer_num]->shape(1); //通道数
int num = params[weights_layer_num]->shape(0); //个数 int imgHeight = (int)(1 + sqrt(num))*height;
int imgWidth = (int)(1 + sqrt(num))*width;
Mat img(imgHeight, imgWidth, CV_8UC3, Scalar(0, 0, 0)); float maxValue = -1000, minValue = 10000;
const float* tmpValue = params[weights_layer_num]->cpu_data();
for (int i = 0; i<params[weights_layer_num]->count(); i++){
maxValue = std::max(maxValue, tmpValue[i]);
minValue = std::min(minValue, tmpValue[i]);
} int kk = 0;
for (int y = 0; y<imgHeight; y += height){
for (int x = 0; x<imgWidth; x += width){
if (kk >= num)
continue;
Mat roi = img(Rect(x, y, width, height));
for (int i = 0; i<height; i++){
for (int j = 0; j<width; j++){
for (int k = 0; k<channel; k++){
float value = params[weights_layer_num]->data_at(kk, k, i, j); roi.at<Vec3b>(i, j)[k] = (value - minValue) / (maxValue - minValue) * 255; }
}
}
++kk;
}
} return img;
}
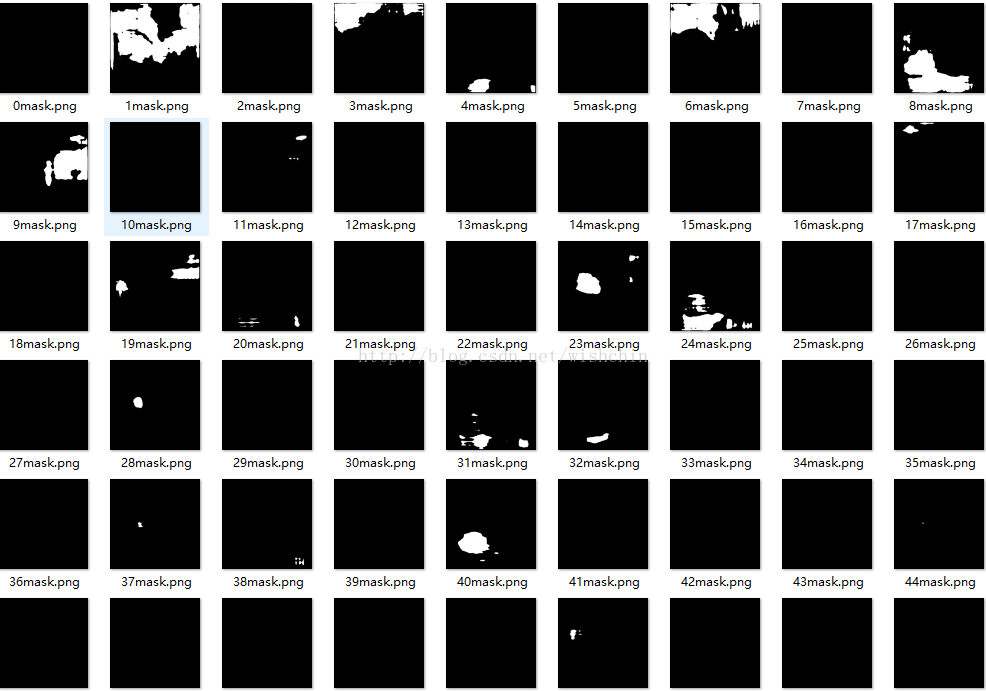
3.FeatureMap获取结果
原图:
分割结果显示:
参考:经典论文Fully Convolutional Networks for semantic Segmentation
作者又翻译了一遍
总结:
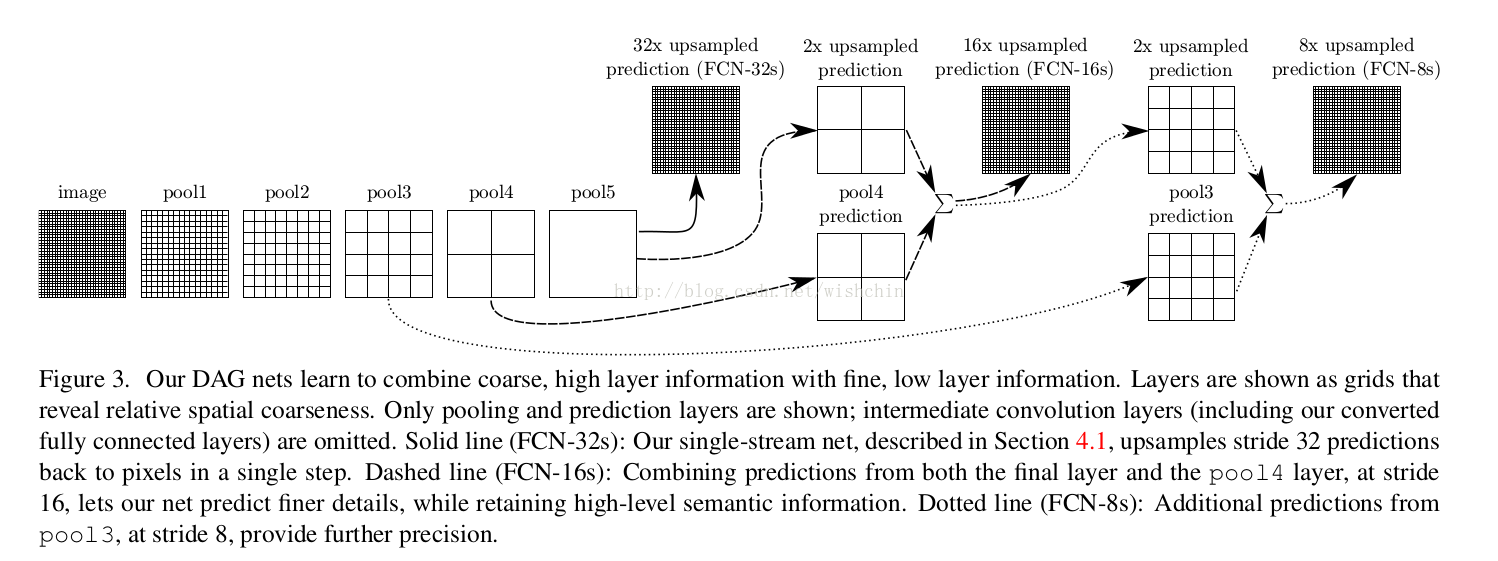
pooling层的多层分布,最终用于预测每个点的类别信息,pooling层的粒度与最终分割的精度产生关联。
Caffe FCN:可视化featureMaps和Weights(C++)、获取FCN结果的更多相关文章
- 神经网络:caffe特征可视化的代码例子
caffe特征可视化的代码例子 不少读者看了我前面两篇文章 总结一下用caffe跑图片数据的研究流程 deep learning实践经验总结2--准确率再次提升,到达0.8.再来总结一下 之后.想知道 ...
- caffe net 可视化工具,,层特征可视化
1.只用网络在线结构绘制可视化网络模型 http://ethereon.github.io/netscope/#/editor 将对应的网络输入到里面,然后按shift+enter即可查看对应的网络结 ...
- caffe model 可视化
1. 打开网址 http://ethereon.github.io/netscope/#/editor 2.将自己的train_test.prototxt里的复制粘贴到左边 3.然后同时shift+e ...
- caffe net 可视化工具
http://ethereon.github.io/netscope/#/editor 将对应的网络输入到里面,然后按shift+enter即可查看对应的网络结构
- caffe网络结构可视化在线工具
http://ethereon.github.io/netscope/#/editor shift+enter
- Caffe使用step by step:r-cnn目标检测代码
深度学习算法火起来之后,基于深度学习各种模型都如雨后春笋一般在各个领域广泛应用. 由于想把深度学习算法应用在在视频目标检测方向,得到一个较好的结果.由于视频数据的复杂性,因此使用深度学习算法在视频中的 ...
- Caffe入门随笔
Caffe入门随笔 分享一下自己入门机器学习的一些资料:(1)课程,最推荐Coursera上的Andrew NG的Machine Learning,最好注册课程,然后跟下来.其次是华盛顿大学的Ma ...
- Tensorflow可视化MNIST手写数字训练
简述] 我们在学习编程语言时,往往第一个程序就是打印“Hello World”,那么对于人工智能学习系统平台来说,他的“Hello World”小程序就是MNIST手写数字训练了.MNIST是一个手写 ...
- 【caffe Net】使用举例和代码中文注释
首先是Net使用的小例子: #include <vector> #include <iostream> #include <caffe/net.hpp> using ...
随机推荐
- JavaMelody开源系统性能监控
https://blog.csdn.net/itopme/article/details/8618067
- T5090 众数 codevs
http://codevs.cn/problem/5090/ 时间限制: 1 s 空间限制: 1000 KB 题目等级 : 青铜 Bronze 题目描述 Description 由文件给出N个1到 ...
- 【Android】自己定义圆形ImageView(圆形头像 可指定大小)
近期在仿手Q的UI,这里面常常要用到的就是圆形头像,看到 在android中画圆形图片的几种办法 这篇文章,了解了制作这样的头像的原理.只是里面提供的方法另一个不足的地方就是不能依据实际需求改变图片的 ...
- nodejs 安装express
在命令行中执行 "npm install -g express"等待下载并且自动完成安装.测试express完成安装的一个方法就是查看其版本号,执行命令 “express -V”正 ...
- Android百度地图SDK 导航初始化和地图初始化引起的冲突
如题,相同是百度地图SDK开发过程中遇到的一个问题.交代下背景: 开发了一款内嵌百度地图的应用,因此里面差点儿相同将眼下百度地图SDK开放的主要功能都用到了,定位,地图显示,覆盖物标示.POI搜索,行 ...
- 推荐美丽的flash网页MP3音乐播放器
文章来源:PHP开发学习门户 地址:http://www.phpthinking.com/archives/491 在网页制作中.假设想在网页中插入mp3音乐来增添网页的互动感,提升用户体验度,这个时 ...
- 安装 openCV 2.4.10
近期试验了一下 ubuntu 12.06 (x86) 安装.openCV 安装脚本 最好的文章是 https://help.ubuntu.com/community/OpenCV. 它提供一个脚本( ...
- Android高仿UC浏览器和360手机卫士消息常驻栏(通知栏)
之前网上看了下自己定义消息栏,通知栏,了解到了Notification这个控件.发现UC浏览器等都是这样的类型,今天写个demo实现下.如图: 当中每一个button都有不同的功能.代码例如以下: p ...
- javaBean注意事项
1.重写tostring方法 2.属性第一位小写
- [luogu_U15116]珈百璃堕落的开始
https://www.zybuluo.com/ysner/note/1239458 题面 给定\(n\)个二元组\((x,y)\),问有多少种方案,使得选出其中几个后,\(\sum x=\sum y ...