JDBC的结果集
以下内容引用自http://wiki.jikexueyuan.com/project/jdbc/result-sets.html:
SQL语句从数据库查询中获取数据,并将数据返回到结果集中。SELECT语句是一种标准的方法,它从一个数据库中选择行记录,并显示在一个结果集中。java.sql.ResultSet接口表示一个数据库查询的结果集。
一个ResultSet对象控制一个光标指向当前行的结果集。术语“结果集”是指包含在ResultSet对象中的行和列的数据。
ResultSet接口的方法可细分为三类:
- 导航方法(Navigational):用于移动光标。
- 获取方法(Get):用于查看当前行被光标所指向的列中的数据。
- 更新方法(Update):用于更新当前行的列中的数据。这些更新也会更新数据库中的数据。
光标的移动基于ResultSet的属性。用相应的语句生成ResultSet对象时,同时生成ResultSet的属性。
JDBC提供了连接方法通过下列创建语句来生成所需的ResultSet对象:
- createStatement(int RSType, int RSConcurrency);
- prepareStatement(String SQL, int RSType, int RSConcurrency);
- prepareCall(String sql, int RSType, int RSConcurrency);
第一个参数表示ResultSet对象的类型,第二个参数是两个ResultSet常量之一,该常量用于判断该结果集是只读的还是可修改的。
一、ResultSet的类型
可能的RSType如下所示。如果不指定ResultSet类型,将自动获得的值是TYPE_FORWARD_ONLY。
| 类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| ResultSet.TYPE_FORWARD_ONLY | 光标只能在结果集中向前移动。 |
| ResultSet.TYPE_SCROLL_INSENSITIVE | 光标可以向前和向后移动。当结果集创建后,其他人对数据库的操作不会影响结果集的数据。 |
| ResultSet.TYPE_SCROLL_SENSITIVE. | 光标可以向前和向后移动。当结果集创建后,其他人对数据库的操作会影响结果集的数据。 |
二、ResultSet的并发性
RSConcurrency的值如下所示,如果不指定并发类型,将自动获得的值是CONCUR_READ_ONLY。
| 并发性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| ResultSet.CONCUR_READ_ONLY | 创建一个只读结果集,这是默认的值。 |
| ResultSet.CONCUR_UPDATABLE | 创建一个可修改的结果集。 |
到目前为止示例可以如下所示,可以写成初始化一个Statement对象来创建一个只能前进,而且只读的ResultSet对象:
try {
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement(ResultSet.TYPE_FORWARD_ONLY, ResultSet.CONCUR_READ_ONLY);
}
catch(Exception ex) {
....
}
finally {
....
}
三、导航结果集
在ResultSet接口中包括如下几种方法涉及移动光标:
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| public void beforeFirst() throws SQLException |
将光标移动到第一行之前。 |
| public void afterLast() throws SQLException |
将光标移动到最后一行之后。 |
| public boolean first() throws SQLException |
将光标移动到第一行。 |
| public void last() throws SQLException |
将光标移动到最后一行。 |
| public boolean absolute(int row) throws SQLException |
将光标移动到指定的第row行。 |
| public boolean relative(int row) throws SQLException |
将光标移动到当前指向的位置往前或往后第row行的位置。 |
| public boolean previous() throws SQLException |
将光标移动到上一行,如果超过结果集的范围则返回false。 |
| public boolean next() throws SQLException |
将光标移动到下一行,如果是结果集的最后一行则返回false。 |
| public int getRow() throws SQLException |
返回当前光标指向的行数的值。 |
| public void moveToInsertRow() throws SQLException |
将光标移动到结果集中指定的行,可以在数据库中插入新的一行。当前光标位置将被记住。 |
| public void moveToCurrentRow() throws SQLException |
如果光标处于插入行,则将光标返回到当前行,其他情况下,这个方法不执行任何操作。 |
示例:
//STEP 1. Import required packages
import java.sql.*; public class JDBCExample {
// JDBC driver name and database URL
static final String JDBC_DRIVER = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
static final String DB_URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost/Test?serverTimezone=UTC"; // Database credentials
static final String USER = "root";
static final String PASS = "root"; public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
try {
// STEP 2: Register JDBC driver
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); // STEP 3: Open a connection
System.out.println("Connecting to database...");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(DB_URL, USER, PASS); // STEP 4: Execute a query to create statment with
// required arguments for RS example.
System.out.println("Creating statement...");
stmt = conn.createStatement(ResultSet.TYPE_SCROLL_INSENSITIVE, ResultSet.CONCUR_READ_ONLY);
String sql;
sql = "SELECT id, first, last, age FROM Employees";
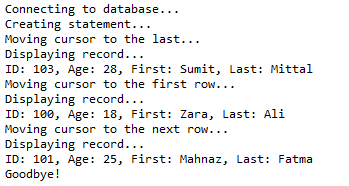
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql); // Move cursor to the last row.
System.out.println("Moving cursor to the last...");
rs.last(); // STEP 5: Extract data from result set
System.out.println("Displaying record...");
// Retrieve by column name
int id = rs.getInt("id");
int age = rs.getInt("age");
String first = rs.getString("first");
String last = rs.getString("last"); // Display values
System.out.print("ID: " + id);
System.out.print(", Age: " + age);
System.out.print(", First: " + first);
System.out.println(", Last: " + last); // Move cursor to the first row.
System.out.println("Moving cursor to the first row...");
rs.first(); // STEP 6: Extract data from result set
System.out.println("Displaying record...");
// Retrieve by column name
id = rs.getInt("id");
age = rs.getInt("age");
first = rs.getString("first");
last = rs.getString("last"); // Display values
System.out.print("ID: " + id);
System.out.print(", Age: " + age);
System.out.print(", First: " + first);
System.out.println(", Last: " + last);
// Move cursor to the first row. System.out.println("Moving cursor to the next row...");
rs.next(); // STEP 7: Extract data from result set
System.out.println("Displaying record...");
id = rs.getInt("id");
age = rs.getInt("age");
first = rs.getString("first");
last = rs.getString("last"); // Display values
System.out.print("ID: " + id);
System.out.print(", Age: " + age);
System.out.print(", First: " + first);
System.out.println(", Last: " + last); // STEP 8: Clean-up environment
rs.close();
stmt.close();
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException se) {
// Handle errors for JDBC
se.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception e) {
// Handle errors for Class.forName
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// finally block used to close resources
try {
if (stmt != null)
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException se2) {
} // nothing we can do
try {
if (conn != null)
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException se) {
se.printStackTrace();
} // end finally try
} // end try
System.out.println("Goodbye!");
}// end main
}// end JDBCExample
这将产生如下所示结果:
四、查看结果集
ResultSet接口中含有几十种从当前行获取数据的方法。
每个可能的数据类型都有一个get方法,并且每个get方法有两个版本:
- 一个需要列名。
- 一个需要列的索引。
例如,如果想查看的列包含一个int类型,需要在ResultSet中调用getInt()方法:
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| public int getInt(String columnName) throws SQLException |
返回当前行中名为columnName的列的int值。 |
| public int getInt(int columnIndex) throws SQLException |
返回当前行中指定列的索引的int值。列索引从1开始,意味着行中的第一列是1 ,第二列是2 ,以此类推。 |
同样的,在ResultSet接口中还有获取八个Java原始类型的get方法,以及常见的类型,比如java.lang.String,java.lang.Object和java.net.URL。
也有用于获取SQL数据类型java.sql.Date,java.sql.Time,java.sql.Timestamp,java.sql.Clob,java.sql.Blob中的方法。查看官方Java文档可以了解使用这些SQL数据类型的更多的信息。
示例:
//STEP 1. Import required packages
import java.sql.*; public class JDBCExample2 {
// JDBC driver name and database URL
static final String JDBC_DRIVER = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
static final String DB_URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost/Test?serverTimezone=UTC"; // Database credentials
static final String USER = "root";
static final String PASS = "root"; public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
try {
// STEP 2: Register JDBC driver
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); // STEP 3: Open a connection
System.out.println("Connecting to database...");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(DB_URL, USER, PASS); // STEP 4: Execute a query to create statment with
// required arguments for RS example.
System.out.println("Creating statement...");
stmt = conn.createStatement(ResultSet.TYPE_SCROLL_INSENSITIVE, ResultSet.CONCUR_READ_ONLY);
String sql;
sql = "SELECT id, first, last, age FROM Employees";
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql); // Move cursor to the last row.
System.out.println("Moving cursor to the last...");
rs.last(); // STEP 5: Extract data from result set
System.out.println("Displaying record...");
// Retrieve by column name
int id = rs.getInt("id");
int age = rs.getInt("age");
String first = rs.getString("first");
String last = rs.getString("last"); // Display values
System.out.print("ID: " + id);
System.out.print(", Age: " + age);
System.out.print(", First: " + first);
System.out.println(", Last: " + last); // Move cursor to the first row.
System.out.println("Moving cursor to the first row...");
rs.first(); // STEP 6: Extract data from result set
System.out.println("Displaying record...");
// Retrieve by column name
id = rs.getInt("id");
age = rs.getInt("age");
first = rs.getString("first");
last = rs.getString("last"); // Display values
System.out.print("ID: " + id);
System.out.print(", Age: " + age);
System.out.print(", First: " + first);
System.out.println(", Last: " + last);
// Move cursor to the first row. System.out.println("Moving cursor to the next row...");
rs.next(); // STEP 7: Extract data from result set
System.out.println("Displaying record...");
id = rs.getInt(1);//The first column index
age = rs.getInt("age");
first = rs.getString("first");
last = rs.getString("last"); // Display values
System.out.print("ID: " + id);
System.out.print(", Age: " + age);
System.out.print(", First: " + first);
System.out.println(", Last: " + last); // STEP 8: Clean-up environment
rs.close();
stmt.close();
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException se) {
// Handle errors for JDBC
se.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception e) {
// Handle errors for Class.forName
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// finally block used to close resources
try {
if (stmt != null)
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException se2) {
} // nothing we can do
try {
if (conn != null)
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException se) {
se.printStackTrace();
} // end finally try
} // end try
System.out.println("Goodbye!");
}// end main
}// end JDBCExample
这将产生如下所示结果:

五、更新的结果集
ResultSet接口包含了一系列的更新方法,该方法用于更新结果集中的数据。
用get方法可以有两个更新方法来更新任一数据类型:
- 一个需要列名。
- 一个需要列的索引。
例如,要更新一个结果集的当前行的String列,可以使用任一如下所示的updateString()方法:
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| public void updateString(int columnIndex, String s) throws SQLException |
将指定列的字符串的值改为s。 |
| public void updateString(String columnName, String s) throws SQLException |
类似于前面的方法,不同之处在于指定的列是用名字来指定的,而不是它的索引。 |
八个原始数据类型都有其更新方法,比如String,Object,URL,和在java.sql包中的SQL数据类型。
更新结果集中的行将改变当前行的列中的ResultSet对象,而不是基础数据库中的数据。要更新数据库中一行的数据,需要调用以下的任一方法:
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| public void updateRow() |
通过更新数据库中相对应的行来更新当前行。 |
| public void deleteRow() |
从数据库中删除当前行。 |
| public void refreshRow() |
在结果集中刷新数据,以反映数据库中最新的数据变化。 |
| public void cancelRowUpdates() |
取消对当前行的任何修改。 |
| public void insertRow() |
在数据库中插入一行。本方法只有在光标指向插入行的时候才能被调用。 |
示例:
//STEP 1. Import required packages
import java.sql.*; public class JDBCExample3 {
// JDBC driver name and database URL
static final String JDBC_DRIVER = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
static final String DB_URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost/Test?serverTimezone=UTC"; // Database credentials
static final String USER = "root";
static final String PASS = "root"; public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
try {
// STEP 2: Register JDBC driver
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); // STEP 3: Open a connection
System.out.println("Connecting to database...");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(DB_URL, USER, PASS); // STEP 4: Execute a query to create statment with
// required arguments for RS example.
System.out.println("Creating statement...");
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement(ResultSet.TYPE_SCROLL_INSENSITIVE, ResultSet.CONCUR_UPDATABLE);
// STEP 5: Execute a query
String sql = "SELECT id, first, last, age FROM Employees";
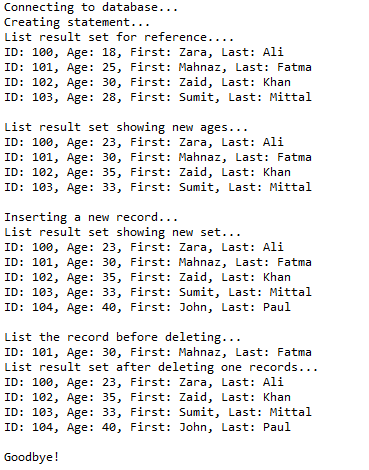
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql); System.out.println("List result set for reference....");
printRs(rs); // STEP 6: Loop through result set and add 5 in age
// Move to BFR postion so while-loop works properly
rs.beforeFirst();
// STEP 7: Extract data from result set
while (rs.next()) {
// Retrieve by column name
int newAge = rs.getInt("age") + 5;
rs.updateDouble("age", newAge);
rs.updateRow();
}
System.out.println("List result set showing new ages...");
printRs(rs);
// Insert a record into the table.
// Move to insert row and add column data with updateXXX()
System.out.println("Inserting a new record...");
rs.moveToInsertRow();
rs.updateInt("id", 104);
rs.updateString("first", "John");
rs.updateString("last", "Paul");
rs.updateInt("age", 40);
// Commit row
rs.insertRow(); System.out.println("List result set showing new set...");
printRs(rs); // Delete second record from the table.
// Set position to second record first
rs.absolute(2);
System.out.println("List the record before deleting...");
// Retrieve by column name
int id = rs.getInt("id");
int age = rs.getInt("age");
String first = rs.getString("first");
String last = rs.getString("last"); // Display values
System.out.print("ID: " + id);
System.out.print(", Age: " + age);
System.out.print(", First: " + first);
System.out.println(", Last: " + last); // Delete row
rs.deleteRow();
System.out.println("List result set after deleting one records...");
printRs(rs); // STEP 8: Clean-up environment
rs.close();
stmt.close();
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException se) {
// Handle errors for JDBC
se.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception e) {
// Handle errors for Class.forName
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// finally block used to close resources
try {
if (conn != null)
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException se) {
se.printStackTrace();
} // end finally try
} // end try
System.out.println("Goodbye!");
}// end main public static void printRs(ResultSet rs) throws SQLException {
// Ensure we start with first row
rs.beforeFirst();
while (rs.next()) {
// Retrieve by column name
int id = rs.getInt("id");
int age = rs.getInt("age");
String first = rs.getString("first");
String last = rs.getString("last"); // Display values
System.out.print("ID: " + id);
System.out.print(", Age: " + age);
System.out.print(", First: " + first);
System.out.println(", Last: " + last);
}
System.out.println();
}// end printRs()
}// end JDBCExample
这将产生如下所示结果:
测试工程:https://github.com/easonjim/5_java_example/tree/master/jdbcbasics/test2
JDBC的结果集的更多相关文章
- com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerException: 结果集没有当前行
參考博客com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerException: 结果集没有当前行 java获取结果集,if(rs!=null).和while(rs.next( ...
- 将JDBC ResultSet结果集变成List
private List<Map<String, Object>> list = new ArrayList<Map<String,Object>>() ...
- 将JDBC ResultSet结果集转成List
private List<Map<String, Object>> list = new ArrayList<Map<String,Object>>() ...
- JavaEE JDBC RowSet行集
RowSet行集 @author ixenos 应用背景 1.基于结果集的缺点:在与用户的整个交互过程中,必须始终与数据库保持连接 后果:当用户长时间离开时,数据库连接长时间被占用,而这属于稀缺资源: ...
- JDBC——ResultSet结果集对象
ResultSet结果集对象,封装结果.它是怎么做到封装结果的呢? 游标,类似指针索引最初指在“列名”上,要取到数据就需要让游标向下移动移动后就指向了第一行数据,然后通过一些方法把第一行的每一列都取出 ...
- Jdbc连接Oracle12C集群环境
jdbc.url=jdbc:Oracle:thin:@(DESCRIPTION =(ADDRESS_LIST =(ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = 192.31.0. ...
- 连接sqlServer数据库&jpa调用存储过程Java获取存储过程返回的多个结果集JAVA调用sqlserver存储过程的实现(返回多个结果集的实现)jdbc多结果集(getMoreResults)
存储过程: BEGIN select * from teacher; SELECT * FROM student; END public Object GetMyBOProjectProductLis ...
- 完整的jdbc查询结果集编码
public static ArrayList<HashMap<String,Object>> query(Connection conn,String sql, Object ...
- [JDBC]查询结果集把字段名和字段值一起竖向输出
代码: package com.hy.fieldandvalue; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DriverManager; import ...
随机推荐
- iOS-控件响应用户控制事件之事件处理
事件处理 响应者对象 在iOS中不是任何对象都能处理事件,只有继承了UIResponder的对象才能接收并处理事件.我们称之为“响应者对象” UIApplication.UIViewControlle ...
- [Windows Server 2012] MySQL移机方法
★ 欢迎来到[护卫神·V课堂],网站地址:http://v.huweishen.com ★ 护卫神·V课堂 是护卫神旗下专业提供服务器教学视频的网站,每周更新视频. ★ 本节我们将带领大家:MySQL ...
- shellinabox的安装使用
一.简介 Shell In A Box(发音是shellinabox)是一款基于Web的终端模仿器,由Markus Gutschke开辟而成.它有内置的Web办事器,在指定的端口上作为一个基于Web的 ...
- 查看MySQL默认字符集
MySQL默认字符集相信大家都有所了解,下面就为您介绍一下查看MySQL默认字符集的命令,希望对您学习MySQL默认字符集能有些帮助. MySQL的字符集支持(Character Set Suppor ...
- JS Object 属性判断
in 方法 var shapeInfo = {name:“lium”}; if (“name” in shapeInfo) {...}
- 梦想CAD控件,用于浏览和编辑DWG文件,在脱离AUTOCAD的情况下独立运行,相当于简易CAD
(百度百科连接) 梦想绘图控件5.2 是国内最强,最专业的CAD开发组件(控件),不需要AutoCAD就能独立运行.控件使用VC 2010开发,最早从2007年第一个版本完成,经过多年的累积已经非常 ...
- AngularJS小练习20170508
首先可能需要安装npm,并且配置环境. 1.打开Dos(命令提示符).按Windows徽标键+R组合键,输入cmd然后按回车键进入Dos. 2.安装Yeoman.在Dos下输入npm install ...
- 03CSS内容背景
CSS内容背景 设置背景颜色——background-color 插入背景图片——background-image 设置背景图片位置——background-position 设置重复背景图片—— ...
- 16.04 下 ufw 防火墙的的开启、禁用、开放端口、关闭端口
16.04 下的 ufw 防火墙相关操作使用ufw命令.通过ufw --help可以查看所有相关命令. 打开防火墙 sudo ufw enable 重启防火墙 sudo ufw reload 打开指定 ...
- vue 全局组件的注册
第一步 在main.js里面 引入需要注册的组件例如: //引入组件 import header from './components/header.vue' import footer from ...
