面向对象的JavaScript-008-Function介绍
1.
// 函数
/* Declare the function 'myFunc' */
function myFunc(theObject) {
theObject.brand = "Toyota";
} /*
* Declare variable 'mycar';
* create and initialize a new Object;
* assign reference to it to 'mycar'
*/
var mycar = {
brand: "Honda",
model: "Accord",
year: 1998
}; /* Logs 'Honda' */
console.log(mycar.brand); /* Pass object reference to the function */
myFunc(mycar); /*
* Logs 'Toyota' as the value of the 'brand' property
* of the object, as changed to by the function.
*/
console.log(mycar.brand); //var y = function x() {};
//alert(x); // throws an error
//var foo = new Function("alert(anonymous);");
//foo(); //Uncaught ReferenceError: anonymous is not defined
foo(); // alerts FOO!
function foo() {
alert('FOO!');
}
var foo = (new Function("var bar = \'FOO!\';\nreturn(function() {\n\talert(bar);\n});"))();
foo(); // The segment "function() {\n\talert(bar);\n}" of the function body string is not re-parsed. var x = 0; // source element
if (x == 0) { // source element
x = 10; // not a source element
function boo() {} // not a source element
}
function foo() { // source element
var y = 20; // source element
function bar() {} // source element
while (y == 10) { // source element
function blah() {} // not a source element
y++; // not a source element
}
} // function declaration
function foo() {} // function expression
(function bar() {}) // function expression
x = function hello() {} if (x) {
// function expression
function world() {}
} // function declaration
function a() {
// function declaration
function b() {}
if (0) {
// function expression
function c() {}
}
} // This function returns a string padded with leading zeros
function padZeros(num, totalLen) {
var numStr = num.toString(); // Initialize return value as string
var numZeros = totalLen - numStr.length; // Calculate no. of zeros
for (var i = 1; i <= numZeros; i++) {
numStr = "0" + numStr;
}
return numStr;
}
var result;
result = padZeros(42,4); // returns "0042"
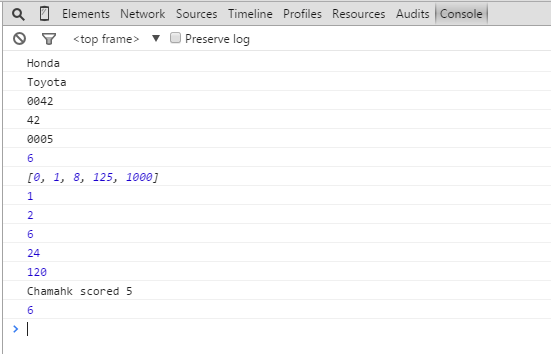
console.log(result);
result = padZeros(42,2); // returns "42"
console.log(result);
result = padZeros(5,4); // returns "0005"
console.log(result); // 菲波那其数
var factorial = function fac(n) { return n<2 ? 1 : n*fac(n-1) };
console.log(factorial(3)); function map(f,a) {
var result = [], // Create a new Array
i;
for (i = 0; i != a.length; i++)
result[i] = f(a[i]);
return result;
}
console.log(map(function(x) {return x * x * x}, [0, 1, 2, 5, 10])); // returns [0, 1, 8, 125, 1000]. // 阶乘
function factorial(n){
if ((n === 0) || (n === 1))
return 1;
else
return (n * factorial(n - 1));
}
var a, b, c, d, e;
a = factorial(1); // a gets the value 1
b = factorial(2); // b gets the value 2
c = factorial(3); // c gets the value 6
d = factorial(4); // d gets the value 24
e = factorial(5); // e gets the value 120
console.log(a);
console.log(b);
console.log(c);
console.log(d);
console.log(e); // Function scope
// The following variables are defined in the global scope
var num1 = 20,
num2 = 3,
name = "Chamahk"; // This function is defined in the global scope
function multiply() {
return num1 * num2;
} multiply(); // Returns 60 // A nested function example
function getScore () {
var num1 = 2,
num2 = 3; function add() {
return name + " scored " + (num1 + num2);
} return add();
} console.log(getScore()); // Returns "Chamahk scored 5" var x = 0;
while (x < 10) { // "x < 10" is the loop condition
// do stuff
x++;
} // can be converted into a recursive function and a call to that function:
function loop(x) {
if (x >= 10) // "x >= 10" is the exit condition (equivalent to "!(x < 10)")
return;
// do stuff
loop(x + 1); // the recursive call
}
loop(0); // However, some algorithms cannot be simple iterative loops. For example, getting all the nodes of a tree structure (e.g. the DOM) is more easily done using recursion:
function walkTree(node) {
if (node == null) //
return;
// do something with node
for (var i = 0; i < node.childNodes.length; i++) {
walkTree(node.childNodes[i]);
}
} // function foo(i) {
// if (i < 0)
// return;
// console.log('begin:' + i);
// foo(i - 1);
// console.log('end:' + i);
// }
//foo(3);
// Output: // begin:3
// begin:2
// begin:1
// begin:0
// end:0
// end:1
// end:2
// end:3 // Nested functions and closures
function addSquares(a,b) {
function square(x) {
return x * x;
}
return square(a) + square(b);
}
a = addSquares(2,3); // returns 13
b = addSquares(3,4); // returns 25
c = addSquares(4,5); // returns 41 // Since the inner function forms a closure, you can call the outer function and specify arguments for both the outer and inner function: function outside(x) {
function inside(y) {
return x + y;
}
return inside;
}
fn_inside = outside(3); // Think of it like: give me a function that adds 3 to whatever you give it
result = fn_inside(5); // returns 8 result1 = outside(3)(5); // returns 8 // Multiply-nested functions
function A(x) {
function B(y) {
function C(z) {
console.log(x + y + z);
}
C(3);
}
B(2);
}
A(1); // logs 6 (1 + 2 + 3) // Name conflicts
function outside() {
var x = 10;
function inside(x) {
return x;
}
return inside;
}
result = outside()(20); // returns 20 instead of 10 // Closures
var pet = function(name) { // The outer function defines a variable called "name"
var getName = function() {
return name; // The inner function has access to the "name" variable of the outer function
}
return getName; // Return the inner function, thereby exposing it to outer scopes
},
myPet = pet("Vivie"); myPet(); // Returns "Vivie" var createPet = function(name) {
var sex; return {
setName: function(newName) {
name = newName;
}, getName: function() {
return name;
}, getSex: function() {
return sex;
}, setSex: function(newSex) {
if(typeof newSex === "string" && (newSex.toLowerCase() === "male" || newSex.toLowerCase() === "female")) {
sex = newSex;
}
}
}
} var pet = createPet("Vivie");
pet.getName(); // Vivie pet.setName("Oliver");
pet.setSex("male");
pet.getSex(); // male
pet.getName(); // Oliver var getCode = (function(){
var secureCode = "0]Eal(eh&2"; // A code we do not want outsiders to be able to modify... return function () {
return secureCode;
};
})(); getCode(); // Returns the secureCode var createPet = function(name) { // Outer function defines a variable called "name"
return {
setName: function(name) { // Enclosed function also defines a variable called "name"
name = name; // ??? How do we access the "name" defined by the outer function ???
}
}
} // Using the arguments object
function myConcat(separator) {
var result = "", // initialize list
i;
// iterate through arguments
for (i = 1; i < arguments.length; i++) {
result += arguments[i] + separator;
}
return result;
} // returns "red, orange, blue, "
myConcat(", ", "red", "orange", "blue"); // returns "elephant; giraffe; lion; cheetah; "
myConcat("; ", "elephant", "giraffe", "lion", "cheetah"); // returns "sage. basil. oregano. pepper. parsley. "
myConcat(". ", "sage", "basil", "oregano", "pepper", "parsley"); // Default parameters
function multiply(a, b) {
b = typeof b !== 'undefined' ? b : 1; return a*b;
} multiply(5); // // function multiply2(a, b = 1) {
// return a*b;
// } // multiply2(5); // 5 // Rest parameters
// function multiply(multiplier, ...theArgs) {
// return theArgs.map(x => multiplier * x);
// } // var arr = multiply(2, 1, 2, 3);
// console.log(arr); // [2, 4, 6] // Arrow functions
var a = [
"Hydrogen",
"Helium",
"Lithium",
"Beryllium"
]; var a2 = a.map(function(s){ return s.length }); // var a3 = a.map( s => s.length ); // Lexical this function Person() {
// The Person() constructor defines `this` as itself.
this.age = 0; setInterval(function growUp() {
// In nonstrict mode, the growUp() function defines `this`
// as the global object, which is different from the `this`
// defined by the Person() constructor.
this.age++;
}, 1000);
} var p = new Person(); function Person() {
var self = this; // Some choose `that` instead of `self`.
// Choose one and be consistent.
self.age = 0; setInterval(function growUp() {
// The callback refers to the `self` variable of which
// the value is the expected object.
self.age++;
}, 1000);
} // function Person(){
// this.age = 0; // setInterval(() => {
// this.age++; // |this| properly refers to the person object
// }, 1000);
// } // var p = new Person();
面向对象的JavaScript-008-Function介绍的更多相关文章
- 摘抄--全面理解面向对象的 JavaScript
全面理解面向对象的 JavaScript JavaScript 函数式脚本语言特性以及其看似随意的编写风格,导致长期以来人们对这一门语言的误解,即认为 JavaScript 不是一门面向对象的语言,或 ...
- 深入全面理解面向对象的 JavaScript
深入全面理解面向对象的 JavaScript (原著: 曾 滢, 软件工程师, IBM,2013 年 4 月 17 日) JavaScript 函数式脚本语言特性以及其看似随意的编写风格,导致长期以来 ...
- 万字长文深度剖析面向对象的javascript
目录 简介 什么是对象 构造函数 构造函数的特点 new命令的原理 prototype对象 Object的prototype操作 Object.getPrototypeOf Object.setPro ...
- 前端开发:面向对象与javascript中的面向对象实现(二)构造函数与原型
前端开发:面向对象与javascript中的面向对象实现(二)构造函数与原型 前言(题外话): 有人说拖延症是一个绝症,哎呀治不好了.先不说这是一个每个人都多多少少会有的,也不管它究竟对生活有多么大的 ...
- 前端开发:面向对象与javascript中的面向对象实现(一)
前端开发:面向对象与javascript中的面向对象实现(一) 前言: 人生在世,这找不到对象是万万不行的.咱们生活中,找不到对象要挨骂,代码里也一样.朋友问我说:“嘿,在干嘛呢......”,我:“ ...
- 面向对象的 JavaScript
面向对象的javascript 一.创建对象 创建对象的几种方式: var obj = {}; var obj = new Object(); var obj = Object.create(fath ...
- JavaScript之Function函数深入总结
整理了JavaScript中函数Function的各种,感觉函数就是一大对象啊,各种知识点都能牵扯进来,不单单是 Function 这个本身原生的引用类型的各种用法,还包含执行环境,作用域,闭包,上下 ...
- JavaScript Date对象介绍
原文:JavaScript Date对象介绍 Date 日期和时间对象 1. 介绍 Date对象,是操作日期和时间的对象.Date对象对日期和时间的操作只能通过方法. 2. 构造函数 2.1 new ...
- javascript 之Function对象的apply(),call(),bind(),方法和arguments,caller,length属性
注:这篇文章原文:http://www.jb51.net/article/30883.htm 自己作为学习,重新写写. 一.写在前面的话 前端javascript编程还只是略懂皮毛,DOM知道一点,j ...
- 面向对象的JavaScript --- 动态类型语言
面向对象的JavaScript --- 动态类型语言 动态类型语言与面向接口编程 JavaScript 没有提供传统面向对象语言中的类式继承,而是通过原型委托的方式来实现对象与对象之间的继承. Jav ...
随机推荐
- BOM的编制与管理
Bill of Material BOM英文全称 Bill of Material,即“物料清单”,也称产品结构表.在制造业管理信息系统中,经常会提到BOM.物料清单是指产品所需零部件明细表及其结构. ...
- android之ffmpeg:设置cygwin
开发android ndk 的时候需要一个编译工具编译c程序,ndk需要linux下编译,所以win环境下提供Cygwin模拟linux编译C android-ndk 较低版本的这个工具的配置网上很多 ...
- 【BZOJ】1007: [HNOI2008]水平可见直线(凸包)
题目 传送门:QWQ 分析 在下面维护一个凸壳 好久没写博客了...... 代码 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; ; ,INF= ...
- 查看Unix/Linux的CPU个数和内存大小,系统位数(转载)
一.AIX 1.查看CPU数: (1) smtctl 从AIX5.3起,对于power5的机器,系统引入了SMT(Simultaneousmulti-threading)的功能,其允许两个处理线程在同 ...
- SQL Server 2008系统信息查询常用命令 查看表大小、记录数等
1.返回所有数据库信息(数据库名,创建日期,存储路径等). use master; GO select * from dbo.sysdatabases 2.返回当前数据库所有对象(可根据type字 ...
- 渗透辅助神器 - DZGEN
项目地址:https://github.com/joker25000/DZGEN git clone ┌─[root@sch01ar]─[/sch01ar] └──╼ #git clone https ...
- IE6中PNG图片背景无法透明显示的最佳解决方案
我想,对于像我这样的年轻的程序员来说,做网页开发时用chrome.firefox或者ie10什么的大约是被宠坏了.所以当最近做的项目不得不在恐龙化石般的ie6上运行时,ie6种种诡异的行径简直让我发指 ...
- 用C#操作IO端口1-用并口控制发光二极管
什么是端口? 端口包含了一系列信号线, 通过这个端口CPU可以同其他外部设备交换数据, 比如我们经常见到的Modem,打印机等. 通常情况下, 打开的信号是”1”, 关闭的信号是”0”. 并口在同一时 ...
- leetcode341
数据结构设计类题目,参考网上的代码: /** * // This is the interface that allows for creating nested lists. * // You sh ...
- Oracle11gr2_ADG管理之在备库上模拟failover的过程实战
技术建议和方案. 要求failover后不重建备库,并能够把failover的数据库重新切换回备库 主库为newtest,备库为snewtest 备库上已经开启了闪回 得到一个参考的SCN SQL&g ...
