NodeJS路径的小问题
In this post we will explore the concept of refresh tokens as defined by OAuth2. We will learn why they came to be and how they compare to other types of tokens. We will also learn how to use them with a simple example. Read on!
Update: at the moment this article was written Auth0 had not gone through OpenID Connect certification. Some of the terms used in this article such as access token do not conform to this spec but do conform to the OAuth2 specification. OpenID Connect establishes a clear distinction between access tokens (used to access the API of the authorization server) and the id token(used for client authentication against a resource server).
Introduction
Modern authentication and/or authorization solutions have introduced the concept of tokens into their protocols. Tokens are specially crafted pieces of data that carry just enough information to either authorize the user to perform an action, or allow a client to get additional information about the authorization process (to then complete it). In other words, tokens are pieces of information that allow the authorization process to be performed. Whether this information is readable or parsable by the client (or any party other than the authorization server) is defined by the implementation. The important thing is: the client gets this information, and then uses it to get access to a resource. The JSON Web Token (JWT) spec defines a way in which common token information may be represented by an implementation.
A short JWT recap
JWT defines a way in which certain common information pertaining to the process of authentication/authorization may be represented. As the name implies, the data format is JSON. JWTs carry certain common fields such as subject, issuer, expiration time, etc. JWTs become really useful when combined with other specs such as JSON Web Signature (JWS) and JSON Web Encryption (JWE). Together these specs provide not only all the information usually needed for an authorization token, but also a means to validate the content of the token so that it cannot be tampered with (JWS) and a way to encrypt information so that it remains opaque to the client (JWE). The simplicity of the data format (and its other virtues) have helped JWTs become one of the most common types of tokens. If you are interested in learning how to implement JWTs in your web apps, check this excellent post by Ryan Chenkie.
Token types
For the purposes of this post, we will focus on the two most common types of tokens: access tokens and refresh tokens.
- Access tokens carry the necessary information to access a resource directly. In other words, when a client passes an access token to a server managing a resource, that server can use the information contained in the token to decide whether the client is authorized or not. Access tokens usually have an expiration date and are short-lived.
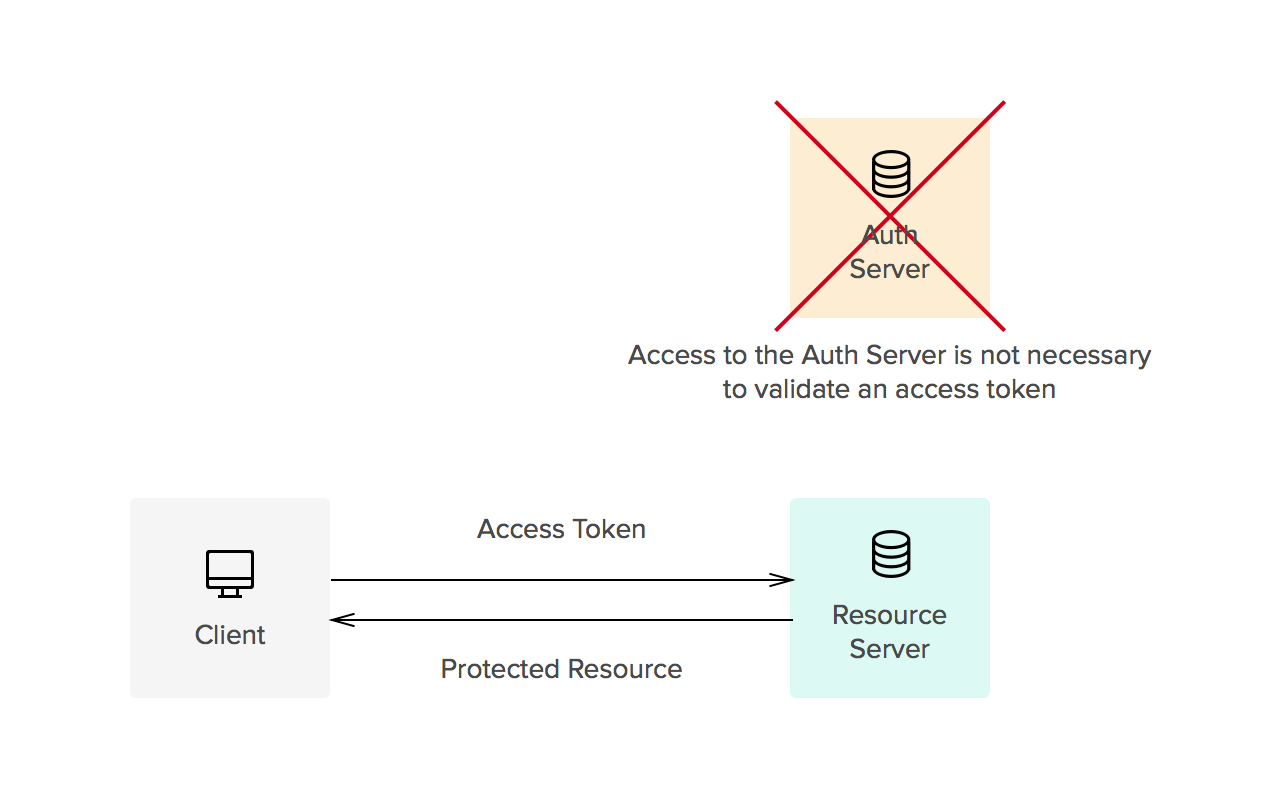
- Refresh tokens carry the information necessary to get a new access token. In other words, whenever an access token is required to access a specific resource, a client may use a refresh token to get a new access token issued by the authentication server. Common use cases include getting new access tokens after old ones have expired, or getting access to a new resource for the first time. Refresh tokens can also expire but are rather long-lived. Refresh tokens are usually subject to strict storage requirements to ensure they are not leaked. They can also be blacklisted by the authorization server.
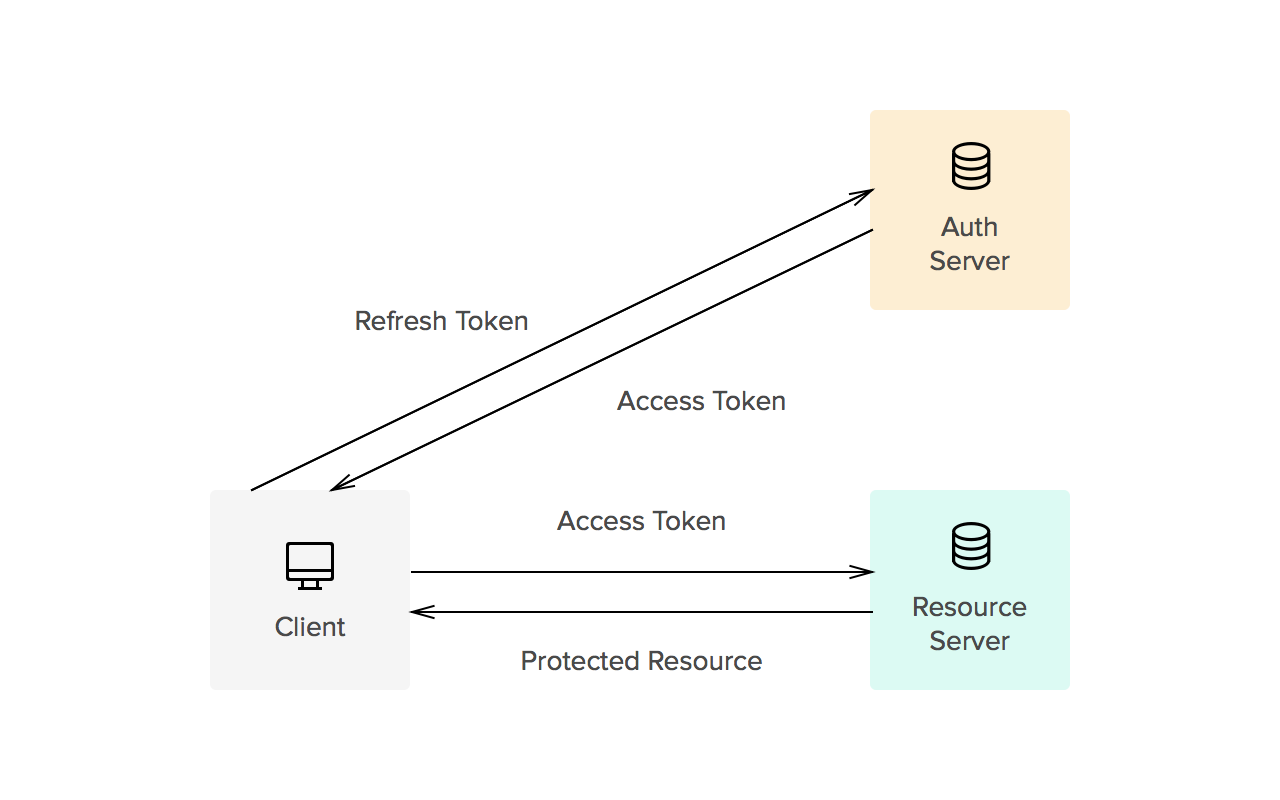
Whether tokens are opaque or not is usually defined by the implementation. Common implementations allow for direct authorization checks against an access token. That is, when an access token is passed to a server managing a resource, the server can read the information contained in the token and decide itself whether the user is authorized or not (no checks against an authorization server are needed). This is one of the reasons tokens must be signed (using JWS, for instance). On the other hand, refresh tokens usually require a check against the authorization server. This split way of handling authorization checks allows for three things:
- Improved access patterns against the authorization server (lower load, faster checks)
- Shorter windows of access for leaked access tokens (these expire quickly, reducing the chance of a leaked token allowing access to a protected resource)
- Sliding-sessions (see below)
Sliding-sessions
Sliding-sessions are sessions that expire after a period of inactivity. As you can imagine, this is easily implemented using access tokens and refresh tokens. When a user performs an action, a new access token is issued. If the user uses an expired access token, the session is considered inactive and a new access token is required. Whether this token can be obtained with a refresh token or a new authentication round is required is defined by the requirements of the development team.
Security considerations
Refresh tokens are long-lived. This means when a client gets a refresh token from a server, this token must be stored securely to keep it from being used by potential attackers. If a refresh token is leaked, it may be used to obtain new access tokens (and access protected resources) until it is either blacklisted or it expires (which may take a long time). Refresh tokens must be issued to a single authenticated client to prevent use of leaked tokens by other parties. Access tokens must be kept secret, but as you may imagine, security considerations are less strict due to their shorter life.
"Access tokens must be kept secret, security considerations are less strict due to their shorter life."
TWEET THIS
Example: a refresh-token issuing server
For the purposes of this example we will use a simple server based on node-oauth2-server that will issue access and refresh tokens. Access tokens will be required to access a protected resource. The client will be a simple CURL command. The code from this example is based on the examples from node-oauth2-server. We have modified the base examples to use JWT for access tokens.
Node-oauth2-server uses a predefined API for the model. You can find the docs here. The following code shows how to implement the model for JWT access tokens.
DISCLAIMER: Please note the code in the following example is not production ready.
model.generateToken = function(type, req, callback) {
//Use the default implementation for refresh tokens
console.log('generateToken: ' + type);
if(type === 'refreshToken') {
callback(null, null);
return;
}
//Use JWT for access tokens
var token = jwt.sign({
user: req.user.id
}, secretKey, {
expiresIn: model.accessTokenLifetime,
subject: req.client.clientId
});
callback(null, token);
}
model.getAccessToken = function (bearerToken, callback) {
console.log('in getAccessToken (bearerToken: ' + bearerToken + ')');
try {
var decoded = jwt.verify(bearerToken, secretKey, {
ignoreExpiration: true //handled by OAuth2 server implementation
});
callback(null, {
accessToken: bearerToken,
clientId: decoded.sub,
userId: decoded.user,
expires: new Date(decoded.exp * 1000)
});
} catch(e) {
callback(e);
}
};
model.saveAccessToken = function (token, clientId, expires, userId, callback) {
console.log('in saveAccessToken (token: ' + token +
', clientId: ' + clientId + ', userId: ' + userId.id +
', expires: ' + expires + ')');
//No need to store JWT tokens.
console.log(jwt.decode(token, secretKey));
callback(null);
};
The OAuth2 token endpoint (/oauth/token) handles issuing of all types of grants (password and refresh tokens). All other endpoints are protected by the OAuth2 middleware that checks for the access token.
// Handle token grant requests
app.all('/oauth/token', app.oauth.grant()); app.get('/secret', app.oauth.authorise(), function (req, res) {
// Will require a valid access_token
res.send('Secret area');
});
So, for instance, assuming there is a user 'test' with password 'test' and a client 'testclient' with a client secret 'secret', one could request a new access token/refresh token pair as follows:
$ curl -X POST -H 'Authorization: Basic dGVzdGNsaWVudDpzZWNyZXQ=' -d 'grant_type=password&username=test&password=test' localhost:3000/oauth/token
{
"token_type":"bearer",
"access_token":"eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJ1c2VyIjoiVlx1MDAxNcKbwoNUwoonbFPCu8KhwrYiLCJpYXQiOjE0NDQyNjI1NDMsImV4cCI6MTQ0NDI2MjU2M30.MldruS1PvZaRZIJR4legQaauQ3_DYKxxP2rFnD37Ip4",
"expires_in":20,
"refresh_token":"fdb8fdbecf1d03ce5e6125c067733c0d51de209c"
}
The authorization header contains the client id and secret encoded as BASE64 (testclient:secret).
To access a protected resource with that access token:
$ curl 'localhost:3000/secret?access_token=eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJ1c2VyIjoiVlx1MDAxNcKbwoNUwoonbFPCu8KhwrYiLCJpYXQiOjE0NDQyNjI1NDMsImV4cCI6MTQ0NDI2MjU2M30.MldruS1PvZaRZIJR4legQaauQ3_DYKxxP2rFnD37Ip4' Secret area
Access to the "secret area" will not cause a database lookup to validate the access token thanks to JWT.
Once the token has expired:
$ curl 'localhost:3000/secret?access_token=eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJ1c2VyIjoiVlx1MDAxNcKbwoNUwoonbFPCu8KhwrYiLCJpYXQiOjE0NDQyNjI2MTEsImV4cCI6MTQ0NDI2MjYzMX0.KkHI8KkF4nmi9z6rAQu9uffJjiJuNnsMg1DC3CnmEV0'
{
"code":401,
"error":"invalid_token",
"error_description":"The access token provided has expired."
}
Now we can use the refresh token to get a new access token by hitting the token endpoint like so:
curl -X POST -H 'Authorization: Basic dGVzdGNsaWVudDpzZWNyZXQ=' -d 'refresh_token=fdb8fdbecf1d03ce5e6125c067733c0d51de209c&grant_type=refresh_token' localhost:3000/oauth/token
{
"token_type":"bearer",
"access_token":"eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJ1c2VyIjoiVlx1MDAxNcKbwoNUwoonbFPCu8KhwrYiLCJpYXQiOjE0NDQyNjI4NjYsImV4cCI6MTQ0NDI2Mjg4Nn0.Dww7TC-d0teDAgsmKHw7bhF2THNichsE6rVJq9xu_2s",
"expires_in":20,
"refresh_token":"7fd15938c823cf58e78019bea2af142f9449696a"
}
DISCLAIMER: Please note the code in the previous example is not production ready.
See the full code here.
Aside: use refresh tokens in your Auth0 apps
At Auth0 we do the hard part of authentication for you. Refresh tokens are not an exception. Once you have setup your app with us, follow the docs here to learn how to get a refresh token.
Conclusion
Refresh tokens improve security and allow for reduced latency and better access patterns to authorization servers. Implementations can be simple using tools such as JWT + JWS. If you are interested in learning more about tokens (and cookies), check our article here.
You can also check the Refresh Tokens landing page for more information.
可以参考:http://www.haomou.net/2014/08/13/2014_web_token/ 对于使用json web token
NodeJS路径的小问题的更多相关文章
- inux关于readlink函数获取运行路径的小程序
inux关于readlink函数获取运行路径的小程序 相关函数: stat, lstat, symlink 表头文件: #include <unistd.h> 定义函数:int re ...
- nodeJs实现微信小程序的图片上传
今天我来介绍一下nodejs如何实现保存微信小程序传过来的图片及其返回 首先wx.uploadFile绝大部分时候是配合wx.chooseImage一起出现的,毕竟选择好了图片,再统一上传是实现用户图 ...
- 写给小前端er的nodejs,mongodb后端小攻略~ (windows系统~)
一.写在前面 迫于学校的压力,研二上准备回学校做实验发论文了,感觉真的没意思,这几天学着搞搞后端,踩了很多坑,整理一下这几天的坑以免以后再犯! 二.本文主要内容(由于是面向前端同学的,所以前端的内容就 ...
- nodejs和ionic小助手
nodejs已经安装完成的情况下,安装ionic小助手 win+r打开cmd. 命令: 1.node -v(查看版本信息) 2.npm -v(查看版本信息) 3.npm install -g cnpm ...
- js中获取项目路径的小插件
//立即执行的js (function() { //获取contextPath var contextPath = getContextPath(); //获取basePath var basePat ...
- 分享一个nodejs写的小论坛
引言:作为一个前端小菜鸟,最近迷上了node,于是乎空闲时间,为了练练手写了一个node的小社区,关于微信小程序的,欢迎大家批评指导. 项目架构部分 一.前端架构 作为一个写样式也得无聊的前端狮,我偷 ...
- linux关于readlink函数获取运行路径的小程序
http://blog.csdn.net/djzhao/article/details/8178375 相关函数: stat, lstat, symlink表头文件: #include <u ...
- nodejs 路径
在学习的时候遇到了 一些路劲方面的疑惑 便查询了一些 module.filename:开发期间,该行代码所在的文件.__filename:始终等于 module.filename.__dirname: ...
- nodejs路径处理方法和绝对路径
1. 路径处理方法 __dirname 表示当前文件所在的目录的绝对路径__filename 表示当前文件的绝对路径module.filename ==== __filename 等价process. ...
随机推荐
- c中static作用
1. static 变量 静态变量的类型 说明符是static. 静态变量当然是属于静态存储方式,但是属于静态存储方式的量不一定就是静态变量. 例如外部变量虽属于静态 存储方式,但不一定是静态变量 ...
- qt QSS文件伪状态
表 1. 伪状态列表伪状态 描述:checked button部件被选中:disabled 部件被禁用:enabled 部件被启用:focus 部件获得焦点:hover ...
- 2.1孙鑫C++
0.vc++6.0 工程---win32控制台程序 文件---c++ 1.建立结构体 #include <iostream.h> struct Point { int ...
- JavaScript设计模式与开发实践——JavaScript的多态
“多态”一词源于希腊文polymorphism,拆开来看是poly(复数)+ morph(形态)+ ism,从字面上我们可以理解为复数形态. 多态的实际含义是:同一操作作用于不同的对象上面,可以产生不 ...
- java 静态变量生命周期(类生命周期)
Static: 加载:java虚拟机在加载类的过程中为静态变量分配内存. 类变量:static变量在内存中只有一个,存放在方法区,属于类变量,被所有实例所共享 销毁:类被卸载时,静态变量被销毁,并释放 ...
- Java Day 12
包 编译格式 javac -d . **.java 包之间的访问 类找不到: 类名写错,包名.类名 包不存在:指定classpath 其他包的类无法访问:权限 public protected 包导入 ...
- Android -- 获取摄像头帧数据解码
由于Android下摄像头预览数据只能 ImageFormat.NV21 格式的,所以解码时要经过一翻周折. Camera mCamera = Camera.open(); Camera.Param ...
- Session invalidate
会清空所有已定义的session 而不是清空全部session的值也就是说 定义了一个名为 user 的session 调用invalidate()方法后使用Session.getValue(“use ...
- ORACLE 检查数据库表中是否存在不规范字 段的语句参考.sql
--查看是否有除number,char,date,varchar2,clob/blob之外的类型,比如:NVARCHAR2,TIMESTAMP(6),FLOATSELECT DISTINCT a.DA ...
- 这个好像、也许、或许、大概、应该、Maybe真的可以算是传说中的Spring.Net了吧
这个好像.也许.或许.大概.应该.Maybe真的可以算是传说中的Spring.Net了吧 ...

