[Unity算法]A星寻路(一):基础版本
参考链接:
https://www.cnblogs.com/yangyxd/articles/5447889.html
一.原理
1.将场景简化,分割为一个个正方形格子,这些格子称之为节点(node),从一个节点到另一个节点的距离称之为代价(cost)。一个节点与水平/垂直方向的相邻节点的代价是1,与对角节点的代价是1.4。这里引用公式f = g + h,f表示该节点的总代价,g表示该节点与上一路径节点的代价,h表示该节点与目标节点的代价。
2.需要两个列表,开启列表(openList)和关闭列表(closeList)。开启列表用来记录需要考虑的节点,关闭列表用来记录不会再考虑的节点。
3.在开启列表中添加起始节点。
4.在开启列表中找到总代价最低的节点,然后从开启列表中移除该节点,从关闭列表中添加该节点,把与该节点相邻的可通行的节点添加到开启列表,并且更新这些节点的代价。
5.循环第四步,如果当前节点等于目标节点,则退出循环。
二.实现
FindWayNode.cs
using UnityEngine;
public class FindWayNode {
public bool isObstacle;//是否是障碍物
public Vector3 scenePos;//场景位置
public int x, y;//坐标
public int gCost;//与起始点的距离
public int hCost;//与目标点的距离
public int fCost {
get { return gCost + hCost; }
}//总距离
public FindWayNode parentNode;//父节点
public FindWayNode(bool isObstacle, Vector3 scenePos, int x, int y)
{
this.isObstacle = isObstacle;
this.scenePos = scenePos;
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
FindWayGrid.cs
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine; public class FindWayGrid { public int width;//格子水平方向个数
public int height;//格子垂直方向个数
public float nodeLength;//格子长度 private FindWayNode[,] findWayNodes;//格子数组
private float halfNodeLength;//格子长度的一半
private Vector3 startPos;//场景坐标起点 public FindWayGrid(int width, int height, float nodeLength = 1f)
{
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
this.nodeLength = nodeLength; findWayNodes = new FindWayNode[width, height];
halfNodeLength = nodeLength / ;
startPos = new Vector3(-width / * nodeLength + halfNodeLength, , -height / * nodeLength + halfNodeLength); for (int x = ; x < width; x++)
{
for (int y = ; y < height; y++)
{
Vector3 pos = CoordinateToScenePos(x, y);
findWayNodes[x, y] = new FindWayNode(false, pos, x, y);
}
}
} //坐标转场景坐标
public Vector3 CoordinateToScenePos(int x, int y)
{
Vector3 pos = new Vector3(startPos.x + x * nodeLength, startPos.y, startPos.z + y * nodeLength);
return pos;
} //根据场景坐标获取节点
public FindWayNode GetNode(Vector3 pos)
{
int x = (int)(Mathf.RoundToInt(pos.x - startPos.x) / nodeLength);
int y = (int)(Mathf.RoundToInt(pos.z - startPos.z) / nodeLength);
x = Mathf.Clamp(x, , width - );
y = Mathf.Clamp(y, , height - );
return GetNode(x, y);
} //根据坐标获取节点
public FindWayNode GetNode(int x, int y)
{
return findWayNodes[x, y];
} //获取相邻节点列表
public List<FindWayNode> GetNearbyNodeList(FindWayNode node)
{
List<FindWayNode> list = new List<FindWayNode>();
for (int i = -; i <= ; i++)
{
for (int j = -; j <= ; j++)
{
if (i == && j == )
{
continue;
}
int x = node.x + i;
int y = node.y + j;
if (x >= && x < width && y >= && y < height)
{
list.Add(findWayNodes[x, y]);
}
}
}
return list;
} //获取两个节点之间的距离
int GetDistance(FindWayNode nodeA, FindWayNode nodeB)
{
int countX = Mathf.Abs(nodeA.x - nodeB.x);
int countY = Mathf.Abs(nodeA.y - nodeB.y);
if (countX > countY)
{
return * countY + * (countX - countY);
}
else
{
return * countX + * (countY - countX);
}
} //找出起点到终点的最短路径
public List<FindWayNode> FindWay(Vector3 startPos, Vector3 endPos)
{
FindWayNode startNode = GetNode(startPos);
FindWayNode endNode = GetNode(endPos); List<FindWayNode> openList = new List<FindWayNode>();
List<FindWayNode> closeList = new List<FindWayNode>();
openList.Add(startNode); while (openList.Count > )
{
FindWayNode nowNode = openList[]; //选择花费最低的
for (int i = ; i < openList.Count; i++)
{
if (openList[i].fCost <= nowNode.fCost &&
openList[i].hCost < nowNode.hCost)
{
nowNode = openList[i];
}
} openList.Remove(nowNode);
closeList.Add(nowNode); //找到目标节点
if (nowNode == endNode)
{
return GeneratePath(startNode, endNode);
} List<FindWayNode> nearbyNodeList = GetNearbyNodeList(nowNode);
for (int i = ; i < nearbyNodeList.Count; i++)
{
FindWayNode node = nearbyNodeList[i];
//如果是墙或者已经在关闭列表中
if (node.isObstacle || closeList.Contains(node))
{
continue;
}
//计算当前相邻节点与开始节点的距离
int gCost = nowNode.gCost + GetDistance(nowNode, node);
//如果距离更小,或者原来不在打开列表
if (gCost < node.gCost || !openList.Contains(node))
{
//更新与开始节点的距离
node.gCost = gCost;
//更新与结束节点的距离
node.hCost = GetDistance(node, endNode);
//更新父节点为当前选定的节点
node.parentNode = nowNode;
//加入到打开列表
if (!openList.Contains(node))
{
openList.Add(node);
}
}
}
} return null;
} //生成路径
public List<FindWayNode> GeneratePath(FindWayNode startNode, FindWayNode endNode)
{
List<FindWayNode> nodeList = new List<FindWayNode>();
if (endNode != null)
{
FindWayNode tempNode = endNode;
while (tempNode != startNode)
{
nodeList.Add(tempNode);
tempNode = tempNode.parentNode;
}
nodeList.Reverse();//反转路径
}
return nodeList;
}
}
TestFindWay.cs
using UnityEngine;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic; public class TestFindWay : MonoBehaviour { public Transform startTra;//起点tra
public Transform endTra;//终点tra
public Transform floorTra;//地板tra public GameObject obstacleGridPrefab;//障碍物格子
public GameObject pathGridPrefab;//路径格子
public LayerMask obstacleLayer;//障碍物所在的层 private FindWayGrid findWayGrid; private GameObject obstacleRootGo;//障碍物格子的父go
private GameObject pathRootGo;//路径格子的父go
private List<GameObject> pathGridGoList;//路径格子go列表 void Start ()
{
MeshFilter meshFilter = floorTra.GetComponent<MeshFilter>();
int width = Mathf.CeilToInt(meshFilter.mesh.bounds.size.x) * (int)floorTra.localScale.x;
int height = Mathf.CeilToInt(meshFilter.mesh.bounds.size.z) * (int)floorTra.localScale.z; findWayGrid = new FindWayGrid(width, height); obstacleRootGo = new GameObject("ObstacleRoot");
pathRootGo = new GameObject("PathRoot");
pathGridGoList = new List<GameObject>(); ShowObstacle();
} void Update ()
{
List<FindWayNode> nodeList = findWayGrid.FindWay(startTra.position, endTra.position);
if (nodeList != null)
{
ShowPath(nodeList);
}
} //展示路径
public void ShowPath(List<FindWayNode> list)
{
for (int i = ; i < list.Count; i++)
{
if (i < pathGridGoList.Count)
{
pathGridGoList[i].transform.position = list[i].scenePos;
pathGridGoList[i].SetActive(true);
}
else
{
GameObject go = Instantiate(pathGridPrefab);
go.transform.SetParent(pathRootGo.transform);
go.transform.position = list[i].scenePos;
pathGridGoList.Add(go);
}
} for (int i = list.Count; i < pathGridGoList.Count; i++)
{
pathGridGoList[i].SetActive(false);
}
} //展示障碍物
public void ShowObstacle()
{
int width = findWayGrid.width;
int height = findWayGrid.height;
float halfNodeLength = findWayGrid.nodeLength / ; for (int x = ; x < width; x++)
{
for (int y = ; y < height; y++)
{
FindWayNode node = findWayGrid.GetNode(x, y);
bool isObstacle = Physics.CheckSphere(node.scenePos, halfNodeLength, obstacleLayer);
if (isObstacle)
{
GameObject go = GameObject.Instantiate(obstacleGridPrefab, node.scenePos, Quaternion.identity) as GameObject;
go.transform.SetParent(obstacleRootGo.transform);
}
node.isObstacle = isObstacle;
}
}
}
}
三.使用
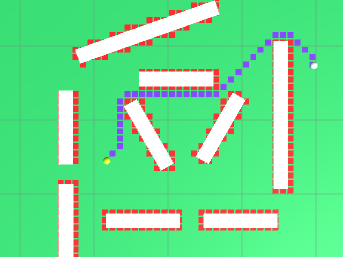
把TestFindWay.cs挂上,然后对public变量进行拖拽赋值即可。效果如下:
[Unity算法]A星寻路(一):基础版本的更多相关文章
- 基于Unity的A星寻路算法(绝对简单完整版本)
前言 在上一篇文章,介绍了网格地图的实现方式,基于该文章,我们来实现一个A星寻路的算法,最终实现的效果为: 项目源码已上传Github:AStarNavigate 在阅读本篇文章,如果你对于里面提到的 ...
- A星寻路算法入门(Unity实现)
最近简单学习了一下A星寻路算法,来记录一下.还是个萌新,如果写的不好,请谅解.Unity版本:2018.3.2f1 A星寻路算法是什么 游戏开发中往往有这样的需求,让玩家控制的角色自动寻路到目标地点, ...
- A星寻路算法介绍
你是否在做一款游戏的时候想创造一些怪兽或者游戏主角,让它们移动到特定的位置,避开墙壁和障碍物呢? 如果是的话,请看这篇教程,我们会展示如何使用A星寻路算法来实现它! 在网上已经有很多篇关于A星寻路算法 ...
- 用简单直白的方式讲解A星寻路算法原理
很多游戏特别是rts,rpg类游戏,都需要用到寻路.寻路算法有深度优先搜索(DFS),广度优先搜索(BFS),A星算法等,而A星算法是一种具备启发性策略的算法,效率是几种算法中最高的,因此也成为游戏中 ...
- A星寻路算法
A星寻路算法 1.准备一个close关闭列表(存放已被检索的点),一个open开启列表(存放未被检索的点),一个当前点的对象cur 2.将cur设成开始点 3.从cur起,将cur点放入close表中 ...
- cocos2d-x学习日志(13) --A星寻路算法demo
你是否在做一款游戏的时候想创造一些怪兽或者游戏主角,让它们移动到特定的位置,避开墙壁和障碍物呢?如果是的话,请看这篇教程,我们会展示如何使用A星寻路算法来实现它! A星算法简介: A*搜寻算法俗称A星 ...
- 无递归 A星寻路算法
整理硬盘的时候,发现我早些年写的A星寻路算法.特放上来,待有缘人拿去,无递归噢,性能那是杠杠的. 码上伺候 public class Node { public int X { get; set; } ...
- A星寻路算法(A* Search Algorithm)
你是否在做一款游戏的时候想创造一些怪兽或者游戏主角,让它们移动到特定的位置,避开墙壁和障碍物呢? 如果是的话,请看这篇教程,我们会展示如何使用A星寻路算法来实现它! 在网上已经有很多篇关于A星寻路算法 ...
- A星寻路算法-Mind&Hand(C++)
//注1:Mind & Hand,MIT校训,这里指的理解与实现(动脑也动手) //注2:博文分为两部分:(1)理解部分,为参考其他优秀博文的摘要梳理:(2)代码部分,是C++代码实现的,源码 ...
随机推荐
- ubuntu-docker入门到放弃(五)docker网络管理
查看docker宿主机的网卡信息我们会发现,有一个docker0的网卡,这个网卡就是用于跟docker容器进行通讯的,这个网段跟我们docker容器的网段是一样的: #ifconfig docker容 ...
- 开IE时 暴卡
待打开IE后,在“工具”-“管理加载项”中禁用所有加载项.
- Azure PowerShell (13) 批量设置Azure ARM Network Security Group (NSG)
<Windows Azure Platform 系列文章目录> 刚刚在帮助一个合作伙伴研究需求,他们的虚拟机全面的网络安全组(Network Security Group, NSG)会经常 ...
- Tomcat默认工具manager管理页面访问配置
Tomcat的默认工具manager配置,在很多的生产环境中由于基本用不到.或者是不太需要使用Tomcat默认的manager管理页面时一般都会把Tomcat的默认webapp下的内容给删除了,但是如 ...
- LaTex与数学公式
w(t) \longrightarrow \bigg[\frac{\sqrt{2\sigma ^2\beta}}{s+\beta}\bigg] \longrightarrow \bigg[\frac ...
- PREV-9_蓝桥杯_大臣的旅费
问题描述 很久以前,T王国空前繁荣.为了更好地管理国家,王国修建了大量的快速路,用于连接首都和王国内的各大城市. 为节省经费,T国的大臣们经过思考,制定了一套优秀的修建方案,使得任何一个大城市都能从首 ...
- Ubuntu 14.10 下SSH配置
安装Hadoop时候需要设置SSH ,故将此过程记录下来 推荐安装 OpenSSH , Hadoop 需要通过 SSH 来启动 Slave 列表中各台主机的守护进程,因此 SSH 是必需安装的.虽 ...
- JDK类集框架实验(ArrayList,LinkedList,TreeSet,HashSet,TreeMap,HashMap)
ArrayList import java.util.ArrayList; public class C8_3 { public static void main(String[] args) ...
- JSON: 介绍、应用
ylbtech-JSON: 介绍.应用 JSONP(JSON with Padding)是 JSON 的一种“使用模式”,可以让网页从别的域名(网站)那获取资料,即跨域读取数据. 为什么我们从不同的 ...
- [转][Centos]一、了解关机
来自:https://blog.csdn.net/ronmy/article/details/79117390 Linux centos关机与重启命令详解与实战 Linux centos重启命令: 1 ...
