前端技术之_CSS详解第六天--完结
前端技术之_CSS详解第六天--完结
一、复习第五天的知识
a标签的伪类4个:
a:link 没有被点击过的链接
a:visited 访问过的链接
a:hover 悬停
a:active 按下鼠标不松手
顺序就是“love hate”准则。
可以简写:
1 a{
3 }
4 a:hover{
6 }
background系列属性,CSS2.1层面
1 background-color 2 background-image 3 background-repeat 4 background-position 5 background-attachment
颜色表示法:red、rgb(255,0,0)、#ff0000、#f00
rgb和十六进制颜色是一样多的,是一一对应的。有换算关系。
background-image:url(images/1.jpg);
默认是平铺的。
background-repeat:no-repeat;
重复横向: repeat-x;
重复纵向: repeat-y;
不重复: no-repeat;
background-position:100px 200px;
背景图在盒子中右边移动100px,向下移动200px。
可以是负数,background-position:-100px -200px;
向左边100px,向上边200px。
英语单词来表示
background-position:right bottom; 右下角
background-position:center bottom; 下边居中
css精灵
css雪碧,要会用fireworks精确显示精灵图。
background-attachment
背景固定
1 background-attachment:fixed;
background属性大综合

1 background:url(images/1.jpg) no-repeat -100px -100px;
二、相对定位
定位有三种,分别是相对定位、绝对定位、固定定位。
相对定位:
1 position:relative;
固定定位:绝对定位:
1 position:absolute;
每一种定位,都暗藏玄机,所以我们分别讲解。
1 position:fixed;
2.1 认识相对定位
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xml:lang="en">
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html;charset=UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style type="text/css">
div{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
}
.box1{
background-color: yellowgreen;
}
.box2{
background-color: skyblue;
position: relative;
top: 100px;
left: 400px;
}
.box3{
background-color: orange;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1"></div>
<div class="box2"></div>
<div class="box3"></div>
</body>
</html>
相对定位,就是微调元素位置的。让元素相对自己原来的位置,进行位置调整。
也就是说,如果一个盒子想进行位置调整,那么就要使用相对定位
1 position:relative; → 必须先声明,自己要相对定位了, 2 left:100px; → 然后进行调整。 3 top:150px; → 然后进行调整。
2.2 不脱标,老家留坑,形影分离
相对定位不脱标,真实位置是在老家,只不过影子出去了,可以到处飘。
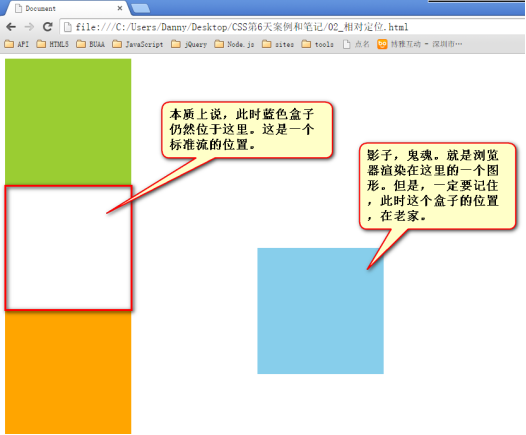
2.3 相对定位用途
相对定位有坑,所以一般不用于做“压盖”效果。页面中,效果极小。就两个作用:
1) 微调元素
2) 做绝对定位的参考,子绝父相(讲绝对定位的时候说)
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xml:lang="en">
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html;charset=UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style type="text/css">
.txt{
font-size: 30px;
}
.btn{
position: relative;
top: 4px;
left:;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>
<input type="text" class="txt"/>
<input type="button" class="btn" value="我是一个小按钮" />
</p>
</body>
</html>
2.4 相对定位的定位值
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xml:lang="en">
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html;charset=UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style type="text/css">
div{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: orange;
margin: 100px;
position: relative;
/*right: -300px;*/
bottom: 300px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div></div>
</body>
</html>
可以用left、right来描述盒子右、左的移动;
可以用top、bottom来描述盒子的下、上的移动。
↘:
1 position: relative; 2 top: 10px; 3 left: 40px;
↙:
1 position: relative; 2 right: 100px; → 往左边移动 3 top: 100px;
↖:
1 position: relative; 2 right: 100px; 3 bottom: 100px; → 移动方向是向上。
↗:
1 position: relative; 2 top: -200px; → 负数就是相反的方向,如果是正,就是下边,如果是负数就是上边 3 right: -200px;
↗:
1 position: relative; 2 right: -300px; 3 bottom: 300px;
完全等价于:
4 position: relative; 5 left: 300px; 1 bottom: 300px;
如图,有几种相对定位的移动方法?
方法1:
1 position:relative; 2 top:100px; 3 left:200px;
方法2:
1 position:relative; 2 bottom:-100px; 3 right:-200px;
方法3:
1 position:relative; 2 top:100px; 3 right:-200px;
方法4:
1 position:relative; 2 bottom:-100px; 3 left:200px;
三、绝对定位
绝对定位比相对定位更灵活。
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xml:lang="en">
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html;charset=UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style type="text/css">
*{
margin:;
padding:;
}
div{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
}
.box1{
background-color: yellowgreen;
}
.box2{
background-color: skyblue;
position: absolute;
top: 100px;
left: 140px;
}
.box3{
background-color: gold;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1"></div>
<div class="box2"></div>
<div class="box3"></div>
</body>
</html>

3.1 绝对定位脱标
绝对定位的盒子,是脱离标准文档流的。所以,所有的标准文档流的性质,绝对定位之后都不遵守了。
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xml:lang="en">
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html;charset=UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style type="text/css">
span{
position: absolute;
top: 100px;
left: 100px;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: pink;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<span></span>
</body>
</html>
绝对定位之后,标签就不区分所谓的行内元素、块级元素了,不需要display:block;就可以设置宽、高了:
1 span{
2 position: absolute;
3 top: 100px;
4 left: 100px;
5 width: 100px;
6 height: 100px;
8 }
3.2 参考点
绝对定位的参考点,如果用top描述,那么定位参考点就是页面的左上角,而不是浏览器的左上角:
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xml:lang="en">
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html;charset=UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style type="text/css">
div{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: blue;
position: absolute;
bottom: 100px;
left: 100px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div></div>
<img src="data:images/2.jpg" alt="" />
</body>
</html>
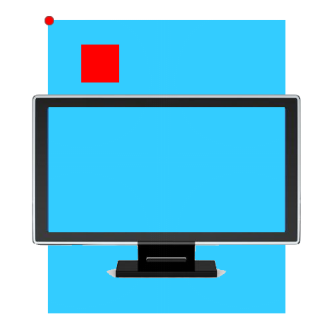
如果用bottom描述,那么就是浏览器首屏窗口尺寸,对应的页面的左下角:
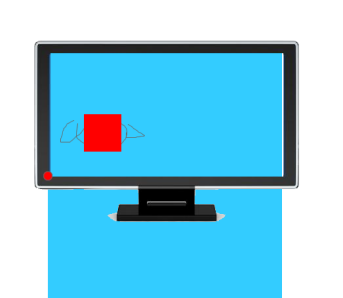
面试题:
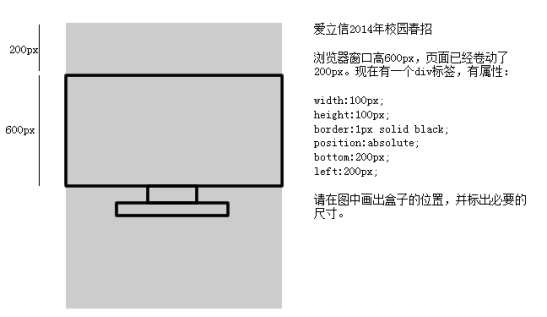
答案:
用bottom的定位的时候,参考的是浏览器首屏大小对应的页面左下角。
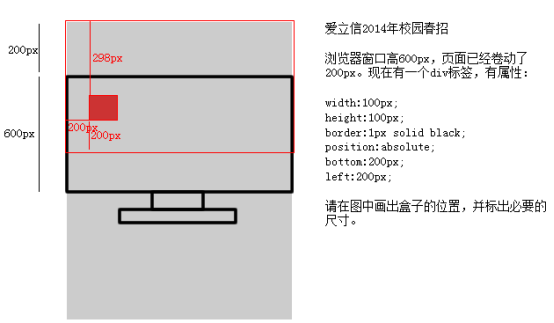
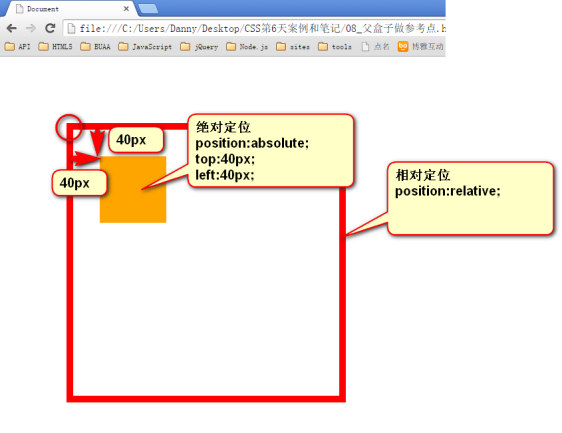
3.3 以盒子为参考点
一个绝对定位的元素,如果父辈元素中出现了也定位了的元素,那么将以父辈这个元素,为参考点。
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xml:lang="en">
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html;charset=UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style type="text/css">
*{
margin:;
padding:;
}
div{
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
border: 10px solid red;
margin: 100px;
position: relative;
}
p{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: orange;
position: absolute;
top: 40px;
left: 40px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<p></p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xml:lang="en">
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html;charset=UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style type="text/css">
*{
margin:;
padding:;
}
.box1{
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
padding: 100px;
border: 10px solid red;
margin: 100px;
position: relative;
}
.box2{
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
border: 50px solid blue;
}
p{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: orange;
position: absolute;
top: 40px;
left: 40px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1">
<div class="box2">
<p></p>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
● 要听最近的已经定位的祖先元素的,不一定是父亲,可能是爷爷:
1 <div class="box1"> → 相对定位 2 <div class="box2"> → 没有定位 3 <p></p> → 绝对定位,将以box1为参考,因为box2没有定位,box1就是最近的父辈元素 4 </div> 5 </div>
1 <div class="box1"> → 相对定位 2 <div class="box2"> → 相对定位 3 <p></p> → 绝对定位,将以box2为参考,因为box2是自己最近的父辈元素 4 </div> 1 </div>
● 不一定是相对定位,任何定位,都可以作为参考点
1 <div> → 绝对定位 2 <p></p> → 绝对定位,将以div作为参考点。因为父亲定位了。 3 </div>
子绝父绝、子绝父相、子绝父固,都是可以给儿子定位的。但是,工程上子绝、父绝,没有一个盒子在标准流里面了,所以页面就不稳固,没有任何实战用途。工程上,“子绝父相”有意义,父亲没有脱标,儿子脱标在父亲的范围里面移动。
1 <div class=”box1”> → 绝对定位 2 <div class=”box2”> → 相对定位 3 <div class=”box3”> → 没有定位 4 <p></p> → 绝对定位,以box2为参考定位。 5 </div> 6 </div> 7 </div>
● 绝对定位的儿子,无视参考的那个盒子的padding。
下图中,绿色部分是div的padding,蓝色部分是div的内容区域。那么此时,div相对定位,p绝对定位。
p将无视父亲的padding,在border内侧为参考点,进行定位:
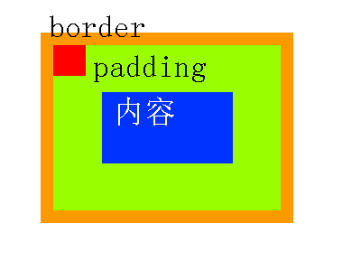
3.4 绝对定位的盒子居中
绝对定位之后,所有标准流的规则,都不适用了。所以margin:0 auto;失效。
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xml:lang="en">
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html;charset=UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style type="text/css">
div{
width: 400px;
height: 60px;
background-color: green;
position: absolute;
left: 50%;
margin-left: -200px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div></div>
</body>
</html>
|
|
1 width: 600px; 2 height: 60px; position: absolute; 3 left: 50%; 4 top: 0; 5 margin-left: -300px; → 宽度的一半
非常简单,当做公式记忆下来。就是left:50%; margin-left:负的宽度的一半。
四、固定定位
固定定位,就是相对浏览器窗口定位。页面如何滚动,这个盒子显示的位置不变。
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xml:lang="en">
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html;charset=UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style type="text/css">
p{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: orange;
position: fixed;
top: 100px;
left: 100px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p></p>
<img src="data:images/2.jpg" alt="" />
</body>
</html>
固定定位脱标!
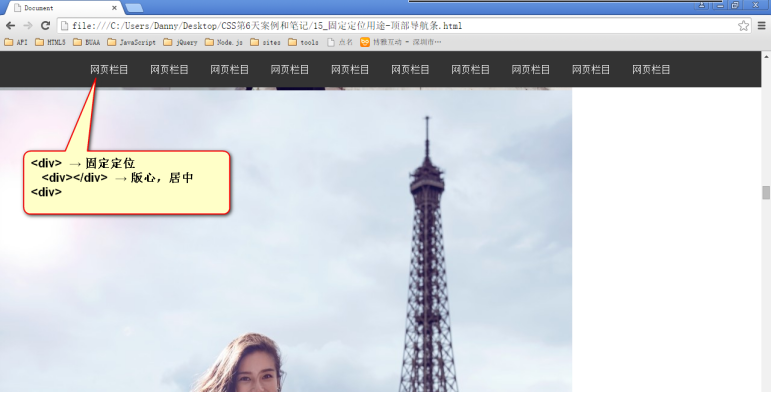
案例:
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xml:lang="en">
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html;charset=UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style type="text/css">
*{
margin:;
padding:;
}
body{
/*为什么要写这个?*/
/*不希望我们的页面被nav挡住*/
padding-top: 60px;
/*IE6不兼容固定定位,所以这个padding没有什么用,就去掉就行了*/
_padding-top:;
}
.nav{
position: fixed;
top:;
left:;
width: 100%;
height: 60px;
background-color: #333;
z-index:;
}
.inner_c{
width: 1000px;
height: 60px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
.inner_c ul{
list-style: none;
}
.inner_c ul li{
float: left;
width: 100px;
height: 60px;
text-align: center;
line-height: 60px;
}
.inner_c ul li a{
display: block;
width: 100px;
height: 60px;
color:white;
text-decoration: none;
}
.inner_c ul li a:hover{
background-color: gold;
}
p{
font-size: 30px;
}
.btn{
display: block;
width: 120px;
height: 30px;
background-color: orange;
position: relative;
top: 2px;
left: 1px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="nav">
<div class="inner_c">
<ul>
<li><a href="#">网页栏目</a></li>
<li><a href="#">网页栏目</a></li>
<li><a href="#">网页栏目</a></li>
<li><a href="#">网页栏目</a></li>
<li><a href="#">网页栏目</a></li>
<li><a href="#">网页栏目</a></li>
<li><a href="#">网页栏目</a></li>
<li><a href="#">网页栏目</a></li>
<li><a href="#">网页栏目</a></li>
<li><a href="#">网页栏目</a></li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
<img src="data:images/2.jpg" alt="" />
<p>
<a href="" class="btn">按钮</a>
</p>
<img src="data:images/2.jpg" alt="" />
<img src="data:images/2.jpg" alt="" />
<img src="data:images/2.jpg" alt="" />
<img src="data:images/2.jpg" alt="" />
<img src="data:images/2.jpg" alt="" />
<img src="data:images/2.jpg" alt="" />
<img src="data:images/2.jpg" alt="" />
<img src="data:images/2.jpg" alt="" />
<img src="data:images/2.jpg" alt="" />
<img src="data:images/2.jpg" alt="" />
</body>
</html>
IE6不兼容。
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xml:lang="en">
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html;charset=UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style type="text/css">
.backtop{
position: fixed;
bottom: 100px;
right: 30px;
width: 60px;
height: 60px;
background-color: gray;
text-align: center;
line-height:30px;
color:white;
text-decoration: none;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<a class="backtop">返回<br />顶部</a>
<img src="data:images/2.jpg" alt="" />
<img src="data:images/2.jpg" alt="" />
<img src="data:images/2.jpg" alt="" />
<img src="data:images/2.jpg" alt="" />
</body>
</html>
五、z-index
● z-index值表示谁压着谁。数值大的压盖住数值小的。
● 只有定位了的元素,才能有z-index值。也就是说,不管相对定位、绝对定位、固定定位,都可以使用z-index值。而浮动的东西不能用。
● z-index值没有单位,就是一个正整数。默认的z-index值是0。
● 如果大家都没有z-index值,或者z-index值一样,那么谁写在HTML后面,谁在上面能压住别人。定位了的元素,永远能够压住没有定位的元素。
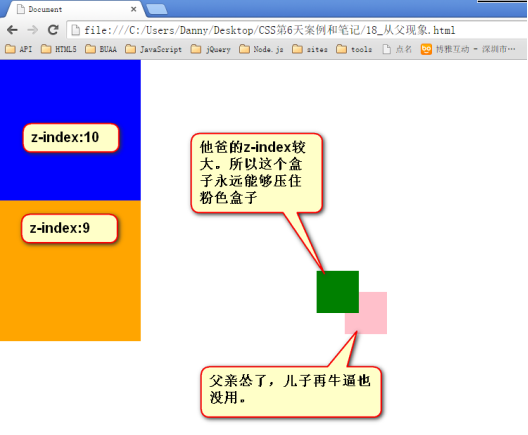
● 从父现象:父亲怂了,儿子再牛逼也没用。
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xml:lang="en">
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html;charset=UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style type="text/css">
*{
margin:;
padding:;
}
.box1{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background: yellowgreen;
position: absolute;
top: 100px;
left: 100px;
z-index:;
}
.box2{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background: skyblue;
position: absolute;
top: 180px;
left: 180px;
z-index:;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1">绿</div>
<div class="box2">蓝</div>
</body>
</html>
没有单位:
1 z-index: 988;
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xml:lang="en">
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html;charset=UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style type="text/css">
*{
margin:;
padding:;
}
.linzhiying{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: blue;
position: relative;
z-index:;
}
.tianliang{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: orange;
position: relative;
z-index:;
}
.kimi{
width: 60px;
height: 60px;
background-color: green;
position: absolute;
top: 300px;
left: 450px;
z-index:;
}
.cindy{
width: 60px;
height: 60px;
background-color: pink;
position: absolute;
top: 130px;
left: 490px;
z-index:;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="linzhiying">
<p class="kimi"></p>
</div>
<div class="tianliang">
<p class="cindy"></p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
前端技术之_CSS详解第六天--完结的更多相关文章
- 前端技术之_CSS详解第一天
前端技术之_CSS详解第一天 一html部分 略.... 二.列表 列表有3种 2.1 无序列表 无序列表,用来表示一个列表的语义,并且每个项目和每个项目之间,是不分先后的. ul就是英语unorde ...
- 前端技术之_CSS详解第二天
前端技术之_CSS详解第二天 1.css基础选择器 html负责结构,css负责样式,js负责行为. css写在head标签里面,容器style标签. 先写选择器,然后写大括号,大括号里面是样式. & ...
- 前端技术之_CSS详解第三天
前端技术之_CSS详解第三天 二.权重问题深入 2.1 同一个标签,携带了多个类名,有冲突: <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 ...
- 前端技术之_CSS详解第四天
前端技术之_CSS详解第四天 一.第三天的小总结 盒模型box model,什么是盒子? 所有的标签都是盒子.无论是div.span.a都是盒子.图片.表单元素一律看做文本. 盒模型有哪些组成: wi ...
- 前端技术之_CSS详解第五天
前端技术之_CSS详解第五天 一.行高和字号 1.1 行高 CSS中,所有的行,都有行高.盒模型的padding,绝对不是直接作用在文字上的,而是作用在“行”上的. <!DOCTYPE html ...
- Cisco路由技术基础知识详解
第一部分 请写出568A的线序(接触网络第一天就应该会的,只要你掐过,想都能想出来) .网卡MAC地址长度是( )个二进制位(16进制与2进制的换算关系,只是换种方式问,不用你拿笔去算) A.12 ...
- Spark技术内幕: Shuffle详解(一)
通过上面一系列文章,我们知道在集群启动时,在Standalone模式下,Worker会向Master注册,使得Master可以感知进而管理整个集群:Master通过借助ZK,可以简单的实现HA:而应用 ...
- 软件架构设计学习总结(3):QQ空间技术架构之详解
QQ空间作为腾讯海量互联网服务产品,经过近七年的发展,实现了从十万级到亿级同时在线的飞跃.在这个过程中,QQ空间团队遇到了哪些技术挑战?其站点前后台架构随着业务规模的变化又进行了怎样的演进与变迁?成长 ...
- AngularJS + CoffeeScript 前端开发环境配置详解
AngularJS 号称 '第一框架' ('The first framework') 确实是名不虚传.由其从jQuery中完全转入AngularJS后就有无法离开他的感觉了.虽然AngularJS的 ...
随机推荐
- 【Shader拓展】Illustrative Rendering in Team Fortress 2
写在前面 早在使用ramp texture控制diffuse光照一文就提到了这篇著名的论文.Valve公司发表的其他成果可见这里.这是Valve在2007年发表的一篇非常具有影响力的文章,我的导师也提 ...
- SpriteBuilder实现2D精灵光影明暗反射效果(一)
其实不用3D建模,用2D的图像就可以模拟3D场景中光照反射的效果. 这里我们不得不提到一个normalMap(法线图)的概念,请各位童鞋自己度娘吧,简单来说它可以使得2D表面生成一定细节程度的光照方向 ...
- 【shell脚本】ftp自动上传mysql备份文件
上一篇中 mysql每日备份shell脚本 给出了使用mysqldump备份到本地的脚本,接着下面是利用ftp把备份文件传输到远程服务器的脚本. 当然也可以用scp,rsync等等方案. #!/bin ...
- (六十九)使用block进行消息传递
在两个类之间进行消息传递,一般通过代理或者block进行,代理写起来较为麻烦,block较为简单,但是block需要特别注意内存泄漏问题,注意self和block之间要为弱引用,下面介绍使用block ...
- [C++学习历程]基础部分 C++中的类型和声明
前面搭起了C++的VS环境,可以在VS中编写C++代码了,也运行了最简单的一个程序Helloworld.那么我们该怎么才能写出功能强大的程序,怎样才能随心所欲的应用呢,那就需要重新回头来,从C++基础 ...
- 并发编程(一): POSIX 使用互斥量和条件变量实现生产者/消费者问题
boost的mutex,condition_variable非常好用.但是在Linux上,boost实际上做的是对pthread_mutex_t和pthread_cond_t的一系列的封装.因此通过对 ...
- Android图片加载库Fresco
在Android设备上面,快速高效的显示图片是极为重要的.过去的几年里,我们在如何高效的存储图像这方面遇到了很多问题.图片太大,但是手机的内存却很小.每一个像素的R.G.B和alpha通道总共要占用4 ...
- ssh连接原理介绍( 无密码连接登录的原理)
SSH(Secure Shell)一种在不安全网络上提供安全远程登录及其它安全网络服务的协议.由客户端和服务端的软件组成的,有两个不兼容的版本分别是:1.x和2.x.(SSH 2.x的客户程序是不能 ...
- 100个iOS开发面试题汇总
100个iOS开发面试题汇总 关于iOS开发面试,不管对于招聘和应聘来说,面试都是很重要的一个环节,特别对于开发者来说,面试中的技术问题环节不仅是企业对应聘者技能和积累的考察,也是一个开发者自我检验的 ...
- hadoop上C++开发两种方式的例子
百度在使用Hadoop过程中同样发现了Hadoop因为Java语言带来的低效问题,并对Hadoop进行扩展. 而在此之前,百度也尝试了 Hadoop PIPES 和 Hadoop Streamming ...

