HDU 1533 Going home
Going Home
Time Limit: 10000/5000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 2829 Accepted Submission(s): 1423
a grid map there are n little men and n houses. In each unit time,
every little man can move one unit step, either horizontally, or
vertically, to an adjacent point. For each little man, you need to pay a
$1 travel fee for every step he moves, until he enters a house. The
task is complicated with the restriction that each house can accommodate
only one little man.
Your task is to compute the minimum amount
of money you need to pay in order to send these n little men into those
n different houses. The input is a map of the scenario, a '.' means an
empty space, an 'H' represents a house on that point, and am 'm'
indicates there is a little man on that point. 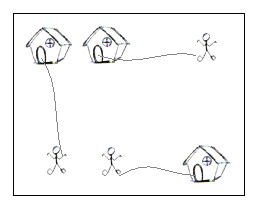
You
can think of each point on the grid map as a quite large square, so it
can hold n little men at the same time; also, it is okay if a little man
steps on a grid with a house without entering that house.
are one or more test cases in the input. Each case starts with a line
giving two integers N and M, where N is the number of rows of the map,
and M is the number of columns. The rest of the input will be N lines
describing the map. You may assume both N and M are between 2 and 100,
inclusive. There will be the same number of 'H's and 'm's on the map;
and there will be at most 100 houses. Input will terminate with 0 0 for N
and M.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <stdlib.h> #define N 110
#define INF 99999999 int n, m;
char map[N][N]; //存储原始字符地图的
int ma[N][N]; //类似边表的可匹配存储
int lx[N], ly[N];
int vtx[N], vty[N];
int match[N];
int slack[N];
int cnt; int max(int a, int b)
{
return a>b?a:b;
}
int min(int a, int b)
{
return a>b?b:a;
} int hungary(int dd) //匈牙利算法
{
int i;
vtx[dd]=1;
for(i=0; i<cnt; i++)
{
if(vty[i])
continue;
else
{
if(lx[dd]+ly[i] == ma[dd][i] )
{
vty[i]=1; if(match[i]==-1 || hungary(match[i]) )
{
match[i] = dd;
return 1;
}
}
else
slack[i] = min( slack[i], lx[dd] + ly[i]-ma[dd][i] );
}
}
return 0;
} void km_match() //最大权匹配
{
int i, j;
int temp;
memset(lx, 0, sizeof(lx));
memset(ly, 0, sizeof(ly));
for(i=0; i<cnt; i++)
{
for(j=0; j<cnt; j++)
{
lx[i]=max(lx[i], ma[i][j] );
} //表示当前的i号人,去某一个房子的最大距离
}
for(i=0; i<cnt; i++)
{
for(j=0; j<cnt; j++)
{
slack[j]=INF; //初始无穷大
}
while(1)
{
memset(vtx, 0, sizeof(vtx));
memset(vty, 0, sizeof(vty));
if(hungary(i)) //匈牙利算法
break;
else
{
temp=INF;
for(j=0; j<cnt; j++)
{
if(!vty[j])
{
temp=min(temp, slack[j] );
}
}
for( j=0; j<cnt; j++ )
{
if( vtx[j] )
lx[j] -= temp;
if( vty[j] )
ly[j] += temp;
else
slack[j] -= temp;
}
}
}
}
} int main()
{
int i, j, k, ll;
int ci, cj;
int sum;
while(scanf("%d %d", &n, &m) && n!=0 && m!=0 )
{
memset(match, -1, sizeof(match ));//match数组初始 -1,记录父节点
cnt=0;
for(i=0; i<n; i++ )
{
scanf("%*c"); //每行先取一个回车换行
for(j=0; j<m; j++)
{
scanf("%c", & map[i][j] );
if(map[i][j] == 'm' ) //如果是个人
{
cnt++; //记录 人数, 建图时需要
}
}
}
//四层循环 前两层遍历map寻找m 内两层循环找h
ci=0;
cj=0;
for(i=0; i<n; i++)
{
for(j=0; j<m; j++)
{
if(map[i][j]=='m') //找到一个人
{
//找到人之后遍历map找 H
for(k=0; k<n; k++)
{
for(ll=0; ll<m; ll++)
{
if(map[k][ll]=='H')
{
ma[ci][cj++] = 100-(abs(k-i)+abs(ll-j));
//大数减边
}
}
}
ci++; //换到下一行存储
cj=0; //cj指针回到0位置
}
}
}
km_match(); //最大权匹配
sum=0;
for(i=0; i<cnt; i++)
{
sum+=ma[match[i]][i] ;
}
printf("%d\n", 100*cnt-sum );
}
return 0;
}
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<climits>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#define N 110
using namespace std; char maps[N][N]; //存储原始字符地图的 int map[N][N]; //类似边表的可匹配存储 int lx[N], ly[N];
int slack[N];
int match[N];
bool visitx[N], visity[N];
int n; bool Hungary( int u ) //匹配
{
int i ;
visitx[u] = true;
for( i=0; i < n; ++i)
{
if(visity[i]==true )
continue;
else
{
if(lx[u] + ly[i] == map[u][i] )
{
visity[i] = true;
if(match[i] == -1 || Hungary(match[i]) )
{
match[i] = u;
return true;
}
}
else
slack[i] = min(slack[i], lx[u] + ly[i]-map[u][i] );
}
}
return false;
} void KM_perfect_match() //匈牙利算法
{
int temp;
memset(lx, 0, sizeof(lx)); // 清零??
memset(ly, 0, sizeof(ly)); // 清零?? for(int i=0; i<n; ++i)
for(int j=0; j<n; ++j)
lx[i] = max( lx[i], map[i][j] ); //表示当前的i号人,去某一个房子的最大距离 for(int i=0; i<n; ++i)
{
/*
我们给每个Y顶点一个“松弛量”函数slack,每次开始找增广路时初始化为无穷大。
在寻找增广路的过程中,检查边(i,j)时,如果它不在相等子图中,则让slack[j]变成
原值与A[i]+B[j]-w[i,j]的较小值。
这样,在修改顶标时,取所有不在交错树中的Y顶点的slack值中的最小值作为d值即可。
但还要注意一点:修改顶标后,要把所有的不在交错树中的Y顶点的slack值都减去d。
*/
for(int j=0; j<n; ++j)
slack[j] = INT_MAX;
while(1)
{
memset(visitx, false, sizeof(visitx)); //清零
memset(visity, false, sizeof(visity)); //清零
if( Hungary(i) )
break;
else
{
temp = INT_MAX;
for(int j=0; j<n; ++j )
{
if(!visity[j])
{
temp = min(temp, slack[j]);
}
}
for(int j=0; j<n; ++j )
{
if( visitx[j] )
lx[j] -= temp;
if( visity[j] )
ly[j] += temp;
else
slack[j] -= temp;
}
}
}
}
} int main()
{
int row, col, ans, numi, numj;
while(scanf("%d %d", &row, &col) && (row + col) ) //行 列
{
n = ans = numi = numj = 0;
memset(match, -1, sizeof(match)); //match数组初始 -1
for(int i=0; i<row; ++i)
{
scanf("%*c");//取回车
for(int j=0; j<col; ++j)
{
scanf("%c", &maps[i][j]);
if(maps[i][j] == 'm')
n++; //记录 人数
}
}
//果然是四层循环啊,和预想的一样 for(int i=0; i<row; ++i) //建图
{
for(int j=0; j<col; ++j)
{ //如果当前的是: 人
if(maps[i][j] == 'm')
{ //暴力一遍整个map,
for(int k=0; k<row; ++k )
{
for(int l = 0; l < col; ++l)
{
if(maps[k][l] == 'H') // 如果当前找到了一所房子
{ //建图时的特殊处理(类似入栈, 不过这次入得是二维数组
map[numi][numj++] = 100 - (abs(k - i) + abs(l - j)); //大数减边
} //等同于给每个人开了一个一位数组
}
}
numi++ ; //当找到下一个人的时候, 二维数组挪到下一行
numj = 0 ; //位置指针归零
}
}
} KM_perfect_match(); //调用匈牙利算法 for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i )
{
ans = ans + map[match[i]][i];
}
printf("%d\n", 100 * n - ans) ;
}
return 0;
} ///////////////
HDU 1533 Going home的更多相关文章
- 【HDU 1533】 Going Home (KM)
Going Home Problem Description On a grid map there are n little men and n houses. In each unit time, ...
- POJ 2195 Going Home / HDU 1533(最小费用最大流模板)
题目大意: 有一个最大是100 * 100 的网格图,上面有 s 个 房子和人,人每移动一个格子花费1的代价,求最小代价让所有的人都进入一个房子.每个房子只能进入一个人. 算法讨论: 注意是KM 和 ...
- HDU 1533 Going Home(KM完美匹配)
HDU 1533 Going Home 题目链接 题意:就是一个H要相应一个m,使得总曼哈顿距离最小 思路:KM完美匹配,因为是要最小.所以边权建负数来处理就可以 代码: #include <c ...
- HDU 1533 最小费用最大流(模板)
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1533 这道题直接用了模板 题意:要构建一个二分图,家对应人,连线的权值就是最短距离,求最小费用 要注意void ...
- hdu 1533 Going Home 最小费用最大流
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1533 On a grid map there are n little men and n house ...
- Going Home HDU - 1533 费用流
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1533 给一个网格图,每两个点之间的匹配花费为其曼哈顿距离,问给每个的"$m$"匹配到一个&q ...
- HDU 1533
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1533 人和房子数量相同,每个人进房子,费用是人到房子的曼哈顿距离,求最小费用 可用最小费用最大流求解,建立虚拟的 ...
- 【hdu 1533】Going Home
[链接]http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1533 [题意] 一个N*M地图上有相同数量的字符H和字符m,m代表一个 人,H代表一个房子.人到房子的花 ...
- HDU 1533:Going Home(KM算法求二分图最小权匹配)
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1533 Going Home Problem Description On a grid map there ...
- HDU 1533 & KM模板
题意 求二分图最小完备匹配. SOL 建个图那么方便的事情是吧...然后边权都是正的(好像根边权也没什么关系),既然要求最小那么把边权取个相反数跑个KM就好了.. CODE: /*========== ...
随机推荐
- 转 【MQTT】在Windows下搭建MQTT服务器
MQTT简介 MQ 遥测传输 (MQTT) 是轻量级基于代理的发布/订阅的消息传输协议,设计思想是开放.简单.轻量.易于实现.这些特点使它适用于受限环境.该协议的特点有: 使用发布/订阅消息模式,提供 ...
- 安卓SAX解析XML文件
XML文件经常使用的解析方式有DOM解析,SAX解析. 一.Sax SAX(simpleAPIforXML)是一种XML解析的替代方法. 相比于DOM.SAX是一种速度更快,更有效的方法. 它逐行扫描 ...
- 小技巧之Selenium如何切换到弹出的Tab页中
今天群里讨论了一个问题,如何将selenium的操作焦点切换到浏览器中新弹出来的Tab页中,正好对应到了昨天的那篇文章“小技巧之在浏览器中打开新的页签”.今天就带大家来解决这个问题: 先封装一个Tab ...
- Mac Python建立简单的本地服务器
由于Mac自带Python 所以省去我们去下载了 打开终端 执行python stm-macmini:~ apple$ pythonPython 2.7.10 (default, Jul 14 20 ...
- Laravel开发:多用户登录验证(1)
之前实现了一次,后来代码忘记放哪了,所以有跳了一次坑. 先贴上Laravel自带的验证代码: 路由:routes/web.php // Authentication Routes... $this-& ...
- Excel中批量把数字类型转换为文本类型
客户给的excel文件中的内容全部是数值类型,这些我们要当成文本存入到数据库,所以需要把所有的数值转换为文本,但是直接通过修改单元格属性来修改的话会变成科学技数法,还有一种方法是在数值得前面加个英文的 ...
- CAFFE学习笔记(三)在VS2013下生成需要的exe文件
如我们所知,CAFFE_ROOT下有一个文件夹叫tools,里面中有许多cpp文件,它们各自有其不同的功能.但是很显然,当我们要完成某样工作时,我们是不能直接用cpp文件的,只能用exe文件.如何利用 ...
- AOP原理及其实现
AOP 是 Aspect-Oriented programming 的缩写,中文翻译为面向切面编程,它是OOP(Object-Oriented Programing,面向对象编程)的补充和完善. ...
- MoQ(基于.net3.5,c#3.0的mock框架)简单介绍(转)
https://www.cnblogs.com/nuaalfm/archive/2009/11/25/1610755.html
- C#彻底解决Oledb连接Excel数据类型不统一的问题
在使用Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0连接Excel,进行读取数据,相对使用传统的COM来读取数据,效率是很高的.但相对传统COM操作Excel来说,及存在数据类型转换的问题.因为使用O ...
