笨办法学Python(十五)
习题 15: 读取文件
你已经学过了 raw_input 和 argv,这些是你开始学习读取文件的必备基础。你可能需要多多实验才能明白它的工作原理,所以你要细心做练习,并且仔细检查结果。处理文件需要非常仔细,如果不仔细的话,你可能会吧有用的文件弄坏或者清空。导致前功尽弃。
这节练习涉及到写两个文件。一个正常的 ex15.py 文件,另外一个是 ex15_sample.txt,第二个文件并不是脚本,而是供你的脚本读取的文本文件。以下是后者的内容:
This is stuff I typed into a file.
It is really cool stuff.
Lots and lots of fun to have in here.
我们要做的是把该文件用我们的脚本“打开(open)”,然后打印出来。然而把文件名ex15_sample.txt 写死(hardcode)在代码中不是一个好主意,这些信息应该是用户输入的才对。如果我们碰到其他文件要处理,写死的文件名就会给你带来麻烦了。我们的解决方案是使用 argv 和 raw_input 来从用户获取信息,从而知道哪些文件该被处理。
from sys import argv script, filename = argv txt = open(filename) print "Here's your file %r:" % filename
print txt.read() print "Type the filename again:"
file_again = raw_input("> ") txt_again = open(file_again) print txt_again.read()
这个脚本中有一些新奇的玩意,我们来快速地过一遍:
代码的 1-3 行使用 argv 来获取文件名,这个你应该已经熟悉了。接下来第 5 行我们看到 open 这个新命令。现在请在命令行运行 pydocopen 来读读它的说明。你可以看到它和你自己的脚本、或者 raw_input 命令类似,它会接受一个参数,并且返回一个值,你可以将这个值赋予一个变量。这就是你打开文件的过程。
第 7 行我们打印了一小行,但在第 8 行我们看到了新奇的东西。我们在 txt 上调用了一个函数。你从 open 获得的东西是一个 file (文件),文件本身也支持一些命令。它接受命令的方式是使用句点 . (英文称作 dot 或者 period),紧跟着你的命令,然后是类似 open 和 raw_input 一样的参数。不同点是:当你说 txt.read 时,你的意思其实是:“嘿 txt!执行你的 read 命令,无需任何参数!”
脚本剩下的部分基本差不多,不过我就把剩下的分析作为加分习题留给你自己了。
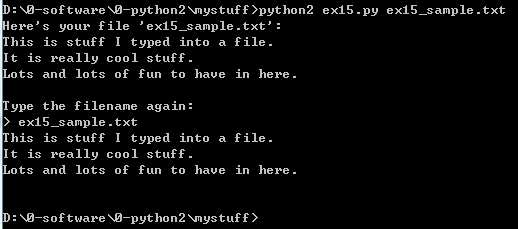
你应该看到的结果
我的脚本叫 “ex15_sample.txt”,以下是执行结果:
加分习题
这节的难度跨越有点大,所以你要尽量做好这节加分习题,然后再继续后面的章节。
1. 在每一行的上面用注解说明这一行的用途。
2. 如果你不确定答案,就问别人,或者上网搜索。大部分时候,只要搜索 “python” 加上你要搜的东西就能得到你要的答案。比如搜索一下“python open”。
3. 我使用了“命令”这个词,不过实际上它们的名字是“函数(function)”和“方法(method)。上网搜索一下这两者的意义和区别。看不明白也没关系,迷失在别的程序员的知识海洋里是很正常的一件事情。
4. 删掉 10-15 行使用到 raw_input 的部分,再运行一遍脚本。
5. 只是用 raw_input 写这个脚本,想想那种得到文件名称的方法更好,以及为什么。
6. 运行 pydoc file 向下滚动直到看见 read() 命令(函数/方法)。看到很多别的命令了吧,你可以找几条试试看。不需要看那些包含 __ (两个下划线)的命令,这些只是垃圾而已。
7. 再次运行 python 在命令行下使用 open 打开一个文件,这种 open 和 read 的方法也值得你一学。
8. 让你的脚本针对 txt and txt_again 变量执行一下 close() ,处理完文件后你需要将其关闭,这是很重要的一点。
习题练习
1.
from sys import argv #导入参数变量模组 script, filename = argv #设两个参数 script 和 filename txt = open(filename) #用 open 函数接收文件名参数,并返回一个值,此处把返回值赋予了 txt 变量 print "Here's your file %r:" % filename #打印
print txt.read() #打印读取的文本内容 print "Type the filename again:" #打印
file_again = raw_input("> ") #把输入值赋予 file_again 变量 txt_again = open(file_again) #用 open 命令返回文件对象操作值,此处把返回值赋予了 txt_again print txt_again.read() #打印读取的文本内容
2.
open 函数的使用:http://www.jb51.net/article/80302.htm
官方文档描述:
open(name[, mode[, buffering]])
Open a file, returning an object of the file type described in section File Objects. If the file cannot be opened, IOError is raised. When opening a file, it’s preferable to use open() instead of invoking the file constructor directly. The first two arguments are the same as for stdio‘s fopen(): name is the file name to be opened, and mode is a string indicating how the file is to be opened. The most commonly-used values of mode are 'r' for reading, 'w' for writing (truncating the file if it already exists), and 'a' for appending (which on some Unix systems means that all writes append to the end of the file regardless of the current seek position). If mode is omitted, it defaults to 'r'. The default is to use text mode, which may convert '\n' characters to a platform-specific representation on writing and back on reading. Thus, when opening a binary file, you should append 'b' to the mode value to open the file in binary mode, which will improve portability. (Appending 'b' is useful even on systems that don’t treat binary and text files differently, where it serves as documentation.) See below for more possible values of mode. The optional buffering argument specifies the file’s desired buffer size: 0 means unbuffered, 1 means line buffered, any other positive value means use a buffer of (approximately) that size (in bytes). A negative buffering means to use the system default, which is usually line buffered for tty devices and fully buffered for other files. If omitted, the system default is used. [2] Modes 'r+', 'w+' and 'a+' open the file for updating (reading and writing); note that 'w+' truncates the file. Append 'b' to the mode to open the file in binary mode, on systems that differentiate between binary and text files; on systems that don’t have this distinction, adding the 'b' has no effect. In addition to the standard fopen() values mode may be 'U' or 'rU'. Python is usually built with universal newlines support; supplying 'U' opens the file as a text file, but lines may be terminated by any of the following: the Unix end-of-line convention '\n', the Macintosh convention '\r', or the Windows convention '\r\n'. All of these external representations are seen as '\n' by the Python program. If Python is built without universal newlines support a mode with 'U' is the same as normal text mode. Note that file objects so opened also have an attribute called newlines which has a value of None (if no newlines have yet been seen), '\n', '\r', '\r\n', or a tuple containing all the newline types seen. Python enforces that the mode, after stripping 'U', begins with 'r', 'w' or 'a'. Python provides many file handling modules including fileinput, os, os.path, tempfile, and shutil. Changed in version 2.5: Restriction on first letter of mode string introduced.
7.
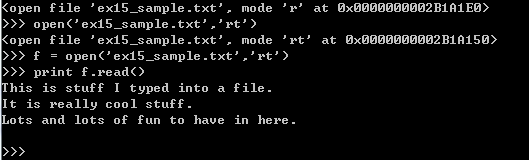
可以看出 open 函数的返回值是十六进制表示的正整数
笨办法学Python(十五)的更多相关文章
- 笨办法学Python(五)
习题 5: 更多的变量和打印 我们现在要键入更多的变量并且把它们打印出来.这次我们将使用一个叫“格式化字符串(format string)”的东西. 每一次你使用 " 把一些文本引用起来,你 ...
- 笨办法学 Python (Learn Python The Hard Way)
最近在看:笨办法学 Python (Learn Python The Hard Way) Contents: 译者前言 前言:笨办法更简单 习题 0: 准备工作 习题 1: 第一个程序 习题 2: 注 ...
- 笨办法学 Python (第三版)(转载)
笨办法学 Python (第三版) 原文地址:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_72b8298001019xg8.html 摘自https://learn-python ...
- 笨办法学Python - 习题1: A Good First Program
在windows上安装完Python环境后,开始按照<笨办法学Python>书上介绍的章节进行练习. 习题 1: 第一个程序 第一天主要是介绍了Python中输出函数print的使用方法, ...
- 笨办法学python 13题:pycharm 运行
笨办法学python 13题 代码: # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- from sys import argv # argv--argument variable 参数变量 scrip ...
- 笨办法学python - 专业程序员的养成完整版PDF免费下载_百度云盘
笨办法学python - 专业程序员的养成完整版PDF免费下载_百度云盘 提取码:xaln 怎样阅读本书 由于本书结构独特,你必须在学习时遵守几条规则 录入所有代码,禁止复制粘贴 一字不差地录入代码 ...
- 笨办法学Python 3|百度网盘免费下载|新手基础入门书籍
点击下方即可百度网盘免费提取 百度网盘免费下载:笨办法学Python 3 提取码:to27 内容简介: 本书是一本Python入门书,适合对计算机了解不多,没有学过编程,但对编程感兴趣的读者学习使用. ...
- 《笨办法学 Python(第四版)》高清PDF|百度网盘免费下载|Python编程
<笨办法学 Python(第四版)>高清PDF|百度网盘免费下载|Python编程 提取码:jcl8 笨办法学 Python是Zed Shaw 编写的一本Python入门书籍.适合对计算机 ...
- 笨办法学python 第四版 中文pdf高清版|网盘下载内附提取码
笨办法学 Python是Zed Shaw 编写的一本Python入门书籍.适合对计算机了解不多,没有学过编程,但对编程感兴趣的朋友学习使用.这本书以习题的方式引导读者一步一步学习编 程,从简单的打印一 ...
- 《笨办法学Python 3》python入门书籍推荐|附下载方式
<笨办法学Python 3>python入门书籍免费下载 内容简介 本书是一本Python入门书,适合对计算机了解不多,没有学过编程,但对编程感兴趣的读者学习使用.这本书以习题的方式引导读 ...
随机推荐
- DJ 算法的队列优先优化
DJ算法就是求单源最短路的算法,但是时间复杂度不太理想,所以在此献上用最小堆来优化的算法. 如果不懂优先队列可以先去看STL分类关于优先队列的介绍: ///POJ 2387为例 #include< ...
- Python 错误总结
1.以一种访问权限不允许的方式做了一个访问套接字的尝试. 解决方法:这个问题缘由是有端口被占用
- Linux忘记roo密码的解决办法
Linux忘记root密码有三种解决办法: 下面详细介绍第一种: 重启系统后出现GRUB界面在引导装载程序菜单上,用上下方向键选择你忘记密码的那个系统键入“e” 来进入编辑模式. 接下来你可以看到 ...
- Jenkins安全配置详解
一.进入安全配置界面 首页后点击进入系统管理(Manage Jenkins) ——下拉下方看到安全配置(Configure Global Security) ——进入安全配置界面 二,详解安全配置的选 ...
- vue 子组件调用父组件的函数
子组件调用父组件的函数,使用$emit(eventName,[...args]),触发当前实例上的事件.附加参数都会传给监听器回调. 子组件 <template> <div> ...
- php数组·的方法1-数组的操作
//range() 创建一个含指定范围的数组 可设置间隔 var_dump(range(1, 9, 2)); echo '<br>'; //array_combine() 合并两个数组创建 ...
- DRF接入Oauth2.0认证[微博登录]报错21322重定向地址不匹配
DRF接入Oauth2.0认证[微博登录]报错21322重定向地址不匹配 主题自带了微博登陆接口,很简单的去新浪微博开放平台创建了网页应用,然后把APP ID和 AppSecret填好后,以为大功告成 ...
- XAMPP 更换其它路径
打开安装路径: xampp\apache\conf\httpd.conf DocumentRoot “C:/xampp/htdocs” <Directory “C:/xampp/htdocs”& ...
- C# 通过 Hessian服务调用java
1.下载Hessiancsharp.dll 2.新建一个c#窗体程序,然后在添加一个类库 3.添加一个接口类,接口中的方法名和参数与java中的服务方法名和参数保持一致 public partial ...
- leetcode 175 Combine Two Tables join用法
https://leetcode.com/problemset/database/ ACM退役,刚好要学sql,一定要刷题才行,leetcode吧. 这一题,说了两个表,一个左一个右吧,左边的pers ...
