浅谈Android系统开发中LOG的使用【转】
本文转载自:http://blog.csdn.net/luoshengyang/article/details/6581828
在程序开发过程中,LOG是广泛使用的用来记录程序执行过程的机制,它既可以用于程序调试,也可以用于产品运营中的事件记录。在Android系统中,提供了简单、便利的LOG机制,开发人员可以方便地使用。在这一篇文章中,我们简单介绍在Android内核空间和用户空间中LOG的使用和查看方法。
一. 内核开发时LOG的使用。Android内核是基于Linux Kerne 2.36的,因此,Linux Kernel的LOG机制同样适合于Android内核,它就是有名的printk,与C语言的printf齐名。与printf类似,printk提供格式化输入功能,同时,它也具有所有LOG机制的特点--提供日志级别过虑功能。printk提供了8种日志级别(<linux/kernel.h>):
#define KERN_EMERG "<0>" /* system is unusable */
#define KERN_ALERT "<1>" /* action must be taken immediately */
#define KERN_CRIT "<2>" /* critical conditions */
#deinfe KERN_ERR "<3>" /* error conditions */
#deinfe KERN_WARNING "<4>" /* warning conditions */
#deinfe KERN_NOTICE "<5>" /* normal but significant condition */
#deinfe KERN_INFO "<6>" /* informational */
#deinfe KERN_DEBUG "<7>" /* debug-level messages */
printk的使用方法:
printk(KERN_ALERT"This is the log printed by printk in linux kernel space.");
KERN_ALERT表示日志级别,后面紧跟着要格式化字符串。
在Android系统中,printk输出的日志信息保存在/proc/kmsg中,要查看/proc/kmsg的内容,参照在Ubuntu上下载、编译和安装Android最新内核源代码(Linux Kernel)一文,在后台中运行模拟器:
USER-NAME@MACHINE-NAME:~/Android$ emulator &
启动adb shell工具:
USER-NAME@MACHINE-NAME:~/Android$ adb shell
查看/proc/kmsg文件:
root@android:/ # cat /proc/kmsg
二. 用户空间程序开发时LOG的使用。Android系统在用户空间中提供了轻量级的logger日志系统,它是在内核中实现的一种设备驱动,与用户空间的logcat工具配合使用能够方便地跟踪调试程序。在Android系统中,分别为C/C++ 和Java语言提供两种不同的logger访问接口。C/C++日志接口一般是在编写硬件抽象层模块或者编写JNI方法时使用,而Java接口一般是在应用层编写APP时使用。
Android系统中的C/C++日志接口是通过宏来使用的。在system/core/include/android/log.h定义了日志的级别:
/*
* Android log priority values, in ascending priority order.
*/
typedef enum android_LogPriority {
ANDROID_LOG_UNKNOWN = ,
ANDROID_LOG_DEFAULT, /* only for SetMinPriority() */
ANDROID_LOG_VERBOSE,
ANDROID_LOG_DEBUG,
ANDROID_LOG_INFO,
ANDROID_LOG_WARN,
ANDROID_LOG_ERROR,
ANDROID_LOG_FATAL,
ANDROID_LOG_SILENT, /* only for SetMinPriority(); must be last */
} android_LogPriority;
在system/core/include/cutils/log.h中,定义了对应的宏,如对应于ANDROID_LOG_VERBOSE的宏LOGV
/*
* This is the local tag used for the following simplified
* logging macros. You can change this preprocessor definition
* before using the other macros to change the tag.
*/
#ifndef LOG_TAG
#define LOG_TAG NULL
#endif /*
* Simplified macro to send a verbose log message using the current LOG_TAG.
*/
#ifndef LOGV
#if LOG_NDEBUG
#define LOGV(...) ((void)0)
#else
#define LOGV(...) ((void)LOG(LOG_VERBOSE, LOG_TAG, __VA_ARGS__))
#endif
#endif /*
* Basic log message macro.
*
* Example:
* LOG(LOG_WARN, NULL, "Failed with error %d", errno);
*
* The second argument may be NULL or "" to indicate the "global" tag.
*/
#ifndef LOG
#define LOG(priority, tag, ...) \
LOG_PRI(ANDROID_##priority, tag, __VA_ARGS__)
#endif /*
* Log macro that allows you to specify a number for priority.
*/
#ifndef LOG_PRI
#define LOG_PRI(priority, tag, ...) \
android_printLog(priority, tag, __VA_ARGS__)
#endif /*
* ================================================================
*
* The stuff in the rest of this file should not be used directly.
*/
#define android_printLog(prio, tag, fmt...) \
__android_log_print(prio, tag, fmt)
因此,如果要使用C/C++日志接口,只要定义自己的LOG_TAG宏和包含头文件system/core/include/cutils/log.h就可以了:
#define LOG_TAG "MY LOG TAG"
#include <cutils/log.h>
就可以了,例如使用LOGV:
LOGV("This is the log printed by LOGV in android user space.");
再来看Android系统中的Java日志接口。Android系统在Frameworks层中定义了Log接口(frameworks/base/core/java/android/util/Log.java):
................................................
public final class Log {
................................................
/**
* Priority constant for the println method; use Log.v.
*/
public static final int VERBOSE = ;
/**
* Priority constant for the println method; use Log.d.
*/
public static final int DEBUG = ;
/**
* Priority constant for the println method; use Log.i.
*/
public static final int INFO = ;
/**
* Priority constant for the println method; use Log.w.
*/
public static final int WARN = ;
/**
* Priority constant for the println method; use Log.e.
*/
public static final int ERROR = ;
/**
* Priority constant for the println method.
*/
public static final int ASSERT = ;
.....................................................
public static int v(String tag, String msg) {
return println_native(LOG_ID_MAIN, VERBOSE, tag, msg);
}
public static int v(String tag, String msg, Throwable tr) {
return println_native(LOG_ID_MAIN, VERBOSE, tag, msg + '\n' + getStackTraceString(tr));
}
public static int d(String tag, String msg) {
return println_native(LOG_ID_MAIN, DEBUG, tag, msg);
}
public static int d(String tag, String msg, Throwable tr) {
return println_native(LOG_ID_MAIN, DEBUG, tag, msg + '\n' + getStackTraceString(tr));
}
public static int i(String tag, String msg) {
return println_native(LOG_ID_MAIN, INFO, tag, msg);
}
public static int i(String tag, String msg, Throwable tr) {
return println_native(LOG_ID_MAIN, INFO, tag, msg + '\n' + getStackTraceString(tr));
}
public static int w(String tag, String msg) {
return println_native(LOG_ID_MAIN, WARN, tag, msg);
}
public static int w(String tag, String msg, Throwable tr) {
return println_native(LOG_ID_MAIN, WARN, tag, msg + '\n' + getStackTraceString(tr));
}
public static int w(String tag, Throwable tr) {
return println_native(LOG_ID_MAIN, WARN, tag, getStackTraceString(tr));
}
public static int e(String tag, String msg) {
return println_native(LOG_ID_MAIN, ERROR, tag, msg);
}
public static int e(String tag, String msg, Throwable tr) {
return println_native(LOG_ID_MAIN, ERROR, tag, msg + '\n' + getStackTraceString(tr));
}
..................................................................
/**@hide */ public static native int println_native(int bufID,
int priority, String tag, String msg);
}
因此,如果要使用Java日志接口,只要在类中定义的LOG_TAG常量和引用android.util.Log就可以了:
private static final String LOG_TAG = "MY_LOG_TAG";
Log.i(LOG_TAG, "This is the log printed by Log.i in android user space.");
要查看这些LOG的输出,可以配合logcat工具。如果是在Eclipse环境下运行模拟器,并且安装了Android插件,那么,很简单,直接在Eclipse就可以查看了:
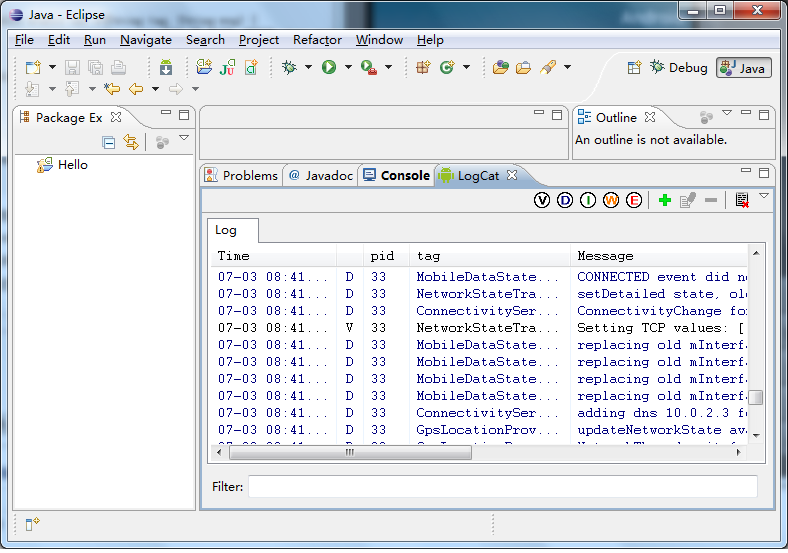
如果是在自己编译的Android源代码工程中使用,则在后台中运行模拟器:
USER-NAME@MACHINE-NAME:~/Android$ emulator &
启动adb shell工具:
USER-NAME@MACHINE-NAME:~/Android$ adb shell
使用logcat命令查看日志:
root@android:/ # logcat
这样就可以看到输出的日志了。
浅谈Android系统开发中LOG的使用【转】的更多相关文章
- 浅谈Android系统开发中LOG的使用
文章转载至CSDN社区罗升阳的安卓之旅,原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/luoshengyang/article/details/6581828 在程序开发过程中,LOG是广泛使用 ...
- 浅谈Android系统进程间通信(IPC)机制Binder中的Server和Client获得Service Manager接口之路
文章转载至CSDN社区罗升阳的安卓之旅,原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/luoshengyang/article/details/6627260 在前面一篇文章浅谈Service ...
- 浅谈Android样式开发之布局优化
引言 今天我们来谈一下Android中布局优化常用的一些手段.官方给出了3种优化方案,分别是</include>.</viewstub>.</merge>标签,下面 ...
- 浅谈Android系统移植、Linux设备驱动
一.Android系统架构 第一层:Linux内核 包括驱动程序,管理内存.进程.电源等资源的程序 第二层:C/C++代码库 包括Linux的.so文件以及嵌入到APK程序中的NDK代码 第三层:An ...
- 浅谈Android系统的图标设计规范
http://homepage.yesky.com/89/11620089.shtml 目前移动平台的竞争日益激烈,友好的用户界面可以帮助提高用户体验满意度,图标Icon是用户界面中一个重要的组成部分 ...
- 浅谈Android移动开发程序员的职业发展之路
现在几乎每个it公司都在开发移动产品,我最早知道Android还是在09年成都某学院上大学的时候,从新闻上知道有这么一家公司,创始人安迪·鲁宾很有名,但安卓到底是做什么的,我并没有关注. 到2010年 ...
- 【Unity游戏开发】浅谈Unity游戏开发中的单元测试
一.单元测试的定义与作用 单元测试定义:单元测试在传统软件开发中是非常重要的工具,它是指对软件中的最小可测试单元进行检查和验证,一般情况下就是对代码中的一个函数去进行验证,检查它的正确性.一个单元测试 ...
- 浅谈在Java开发中的枚举的作用和用法
枚举(enum),是指一个经过排序的.被打包成一个单一实体的项列表.一个枚举的实例可以使用枚举项列表中任意单一项的值.枚举在各个语言当中都有着广泛的应用,通常用来表示诸如颜色.方式.类别.状态等等数目 ...
- 安卓开发_浅谈Android动画(四)
Property动画 概念:属性动画,即通过改变对象属性的动画. 特点:属性动画真正改变了一个UI控件,包括其事件触发焦点的位置 一.重要的动画类及属性值: 1. ValueAnimator 基本属 ...
随机推荐
- Delphi Math里的基本函数,以及浮点数比较函数
Delphi里的好东西太多,多到让人觉得烦.这种感觉就是当年打游戏<英雄无敌3>,改了钱以后,有钱了每天都要造建筑,明明是好事,可是让人觉得烦. 先记录下来,以后再回来加强对Math单元的 ...
- nginx根据目录反向代理到后端服务器
nginx根据目录反向代理到后端不同的服务器 server { listen 80; server_name demo.domain.com; #通过访 ...
- linux epoll机制对TCP 客户端和服务端的监听C代码通用框架实现
1 TCP简介 tcp是一种基于流的应用层协议,其“可靠的数据传输”实现的原理就是,“拥塞控制”的滑动窗口机制,该机制包含的算法主要有“慢启动”,“拥塞避免”,“快速重传”. 2 TCP socket ...
- CAN协议学习(一)协议介绍
一.简介 CAN 是 Controller Area Network 的缩写(以下称为 CAN),是 ISO 国际标准化的串行通信协议. 在当前的汽车产业中,出于对安全性.舒适性.方便性.低公害.低成 ...
- iOS SDWebImage Error Domain=NSURLErrorDomain Code=-1202 “此服务器的证书无效
sdwebImage 加载网络图片的时候,如果使用的https证书未经过认证,或者证书有问题,会出现Error Domain=NSURLErrorDomain Code=-1202 "此服务 ...
- C#趣味程序---理財高手
问题:如果银行存款分五种 利率:0.63% 一年 月 利率:0.66% 二年 月 利率:0.69% 三年 月 利率:0.75% 五年 月 利率:0.84% 八年 月 如今 ...
- Windows找出占用端口的进程
第一步:找出监听指定端口的进程号: C:\> netstat -ao | findstr 443 TCP 0.0.0.0:443 Sean-NotePC:0 ...
- java 中 集合类相关问题
1,Java中Collection和Collections的差别 java.util.Collection 是一个集合接口.它提供了对集合对象进行基本操作的通用接口方法. Collection接口在J ...
- 解决xcode5升级后,Undefined symbols for architecture arm64:问题
The issue is that the cocoapods have not been built for arm64 architecture yet thus they cannot be l ...
- Python 基本数据类型和序列类型
python 3.6.4 中,有9种数据类型: int, float, bool, complex, list, tuple, string, set, dict (1).int 整型,不可变 (2) ...
