GSM:嗅探语音流量
GSM: Sniffing voice traffic
I wrap up the GSM series with a walkthrough on how to decrypt voice traffic. Voice is the way most people interact on a telecommunications network and therefore a major componenent of GSM traffic. I’ve explained a lot of the background on GSM communication in the previous posts so I’ll get right to it.
We will capture the traffic using the HackRF one and the call will take place between two Safaricom lines. The capture will take place on the downlink - that is the receiving end of the call. I’ll use a Blackberry as the receiving device so that I can easily get the TMSI and Kc.
Capturing the traffic
I’ll speed through a lot of these steps as they are similar to the sniffing SMS traffic scenario. I’ll use the Absolute Radio Frequency Channel Number ARFCN in specifying the radio channel. GSM uses ARFCNs to represent the various frequencies the BTS and mobile device communicate on. I’ll use the ARFCN instead of the frequency in the commands I’ll run for variety as I’ve been using frequency in the previous posts. We begin by getting the ARFCN, TMSI and Kc from the Blackberry. On a Blackberry these are readily available from the engineering screen menu. The ARFCN is gotten by navigating to the Cell Identity submenu, the TMSI from the Mobile Identity submenu and finally the Kc from the SIM Browser submenu.
The values I get are:
ARFCN: 17 TMSI: 8D4812F8 Kc: 239E4C213612C000
I use the airprobe_rtlsdr_capture module of gr-gsm to capture the voice traffic. I begin the capture by running the following command:
airprobe_rtlsdr_capture.py -a 17 -s 1000000 -g 40 -c voice_capture.cfile -T 150
-a is the ARFCN, -s the sample rate in Hz, -g the gain, -c the output file and -T the duration of our capture in seconds.
I then make a call while the capture is in progress.
Decoding BCCH
As explained in the previous post, in idle mode the phone has to listen on the BCCH to detect traffic to be sent to it. Our aim here is to identify what SDCCH (Standalone Dedicated Control Channel) is used for our call setup.
We first start wireshark, monitor the loopback interface and then run the following command:
airprobe_decode.py -c voice_capture.cfile -s 1000000 -a 17 -m BCCH -t 0
voice_capture.cfile is the file with the voice traffic we captured. We then search for traffic specific to our TMSI by searching for it in wireshark packet details. we look for the paging request and inspect the Immediate Assignment that follows:
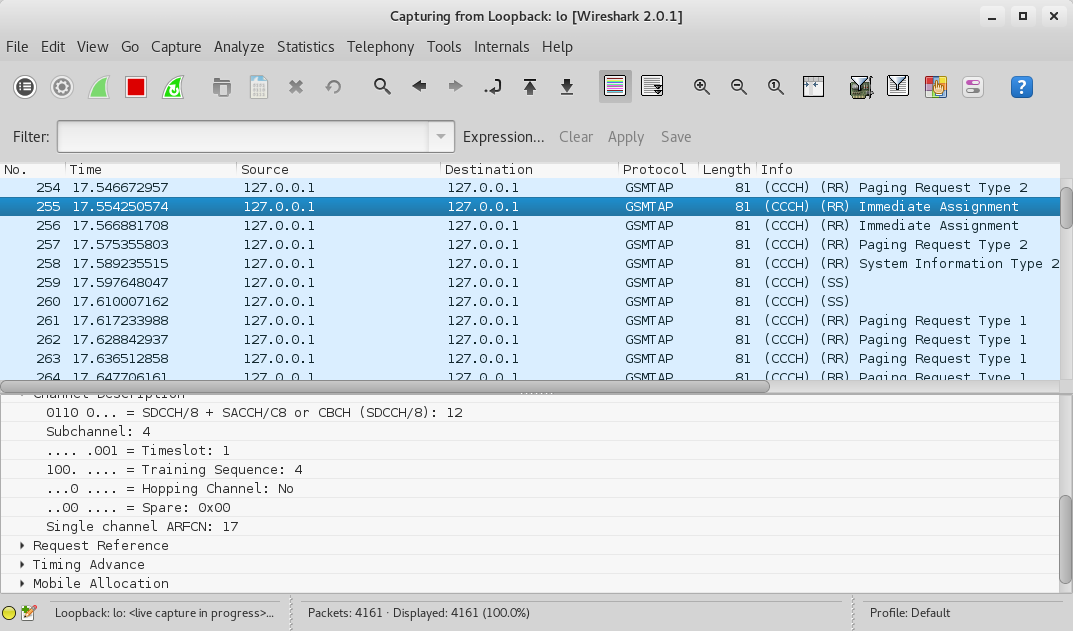
Note that it’s SDCCH/8, Timeslot 1.
Decoding SDCCH
We now need to identify the ciphering mode the BTS tells the phone to use. We restart wireshark on the loopback interface and then run the following command specifying SDCCH8 and Timeslot 1:
airprobe_decode.py -c voice_capture.cfile -s 1000000 -a 17 -m SDCCH8 -t 1
We look for a Paging Response followed by a Ciphering Mode Command.
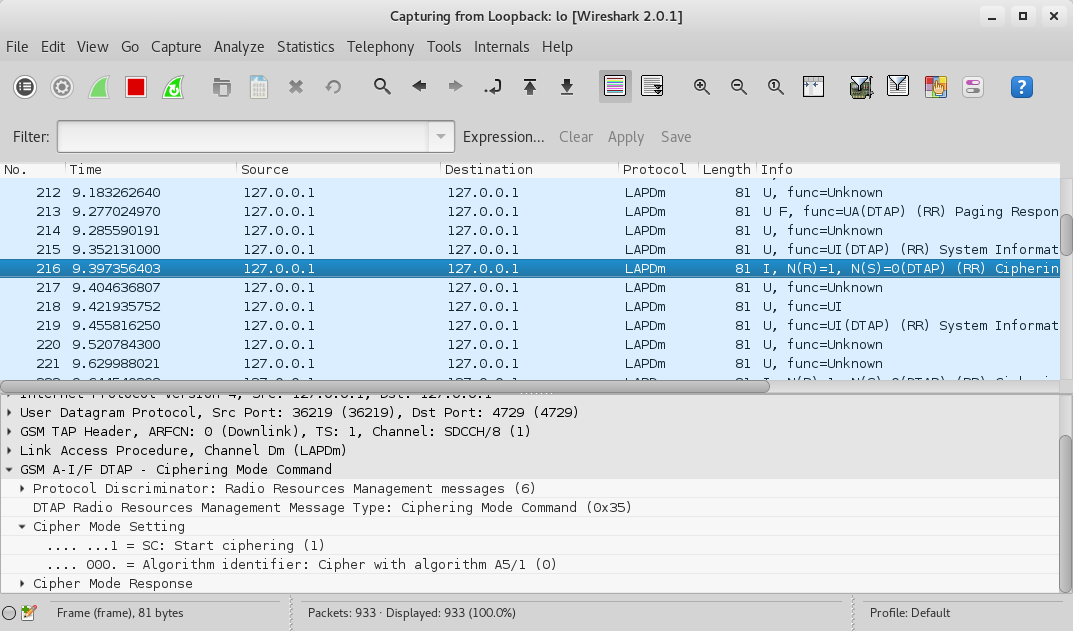
We see that the algorithm in use is A5/1.
Decoding TCH
TCH is the Traffic Channel in GSM and is used to carry voice traffic and data. It could either be full rate TCH/F or half rate TCH/H. You can read up more on it here.
We now restart wireshark on the loopback interface and run the following command:
airprobe_decode.py -c voice_capture.cfile -s 1000000 -a 17 -m SDCCH8 -t 1 -e 1 -k 0x23,0x9E,0x4C,0x21,0x36,0x12,0xC0,0x00
-e 1 specifies the algorithm A5/1, -k 0x23,0x9E,0x4C,0x21,0x36,0x12,0xC0,0x00 specifies the Kc.
On wireshark we first look for the Call Control Setup traffic and we can actually see the calling party number as below.
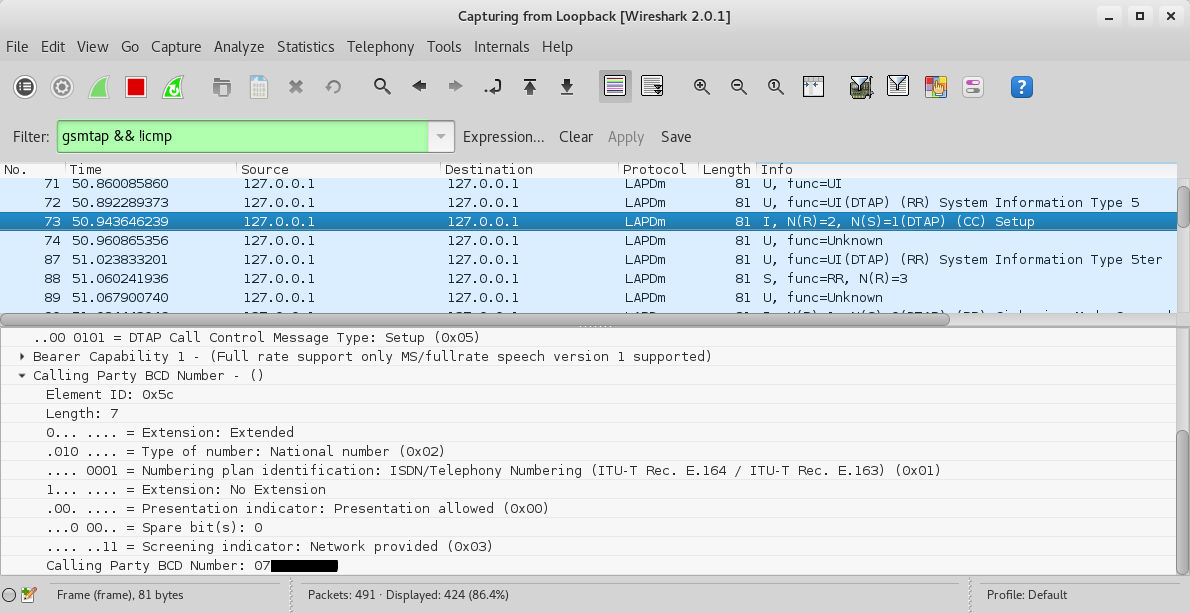
A bit down the capture we should see an Assignment command. We see that the voice call is assigned to Timeslot 7 and the Traffic Channel is full rate (TCH/F).

Decoding the voice traffic
We can now finally decode the voice traffic by running the following command:
airprobe_decode.py -c voice_capture.cfile -s 1000000 -a 17 -m TCHF -t 7 -e 1 -k 0x23,0x9E,0x4C,0x21,0x36,0x12,0xC0,0x00 -d FR -o speech.au.gsm
-m TCHF specifies the traffic channel, -t 7 the TCH/F timeslot, -d FR specifies the voice codec of the channel as full rate, and speech.au.gsm specifies the output file.
speech.au.gsm contains the voice traffic. We convert it to an audio file using toast as follows:
toast -d speech.au.gsm
We will get a file called speech.au which we can play back and listen to the captured voice call :).
Alternative method
Alternatively one could use the mainstream airprobe modules instead of gr-gsm with the same results. The original modules had issues with the HackRF and later GNU Radio versions. I however did some patching and you can clone the patched version from my Github here.
The equivalent commands for the whole process starting from decoding BCCH to decoding voice are:
./go.sh voice_capture.cfile 64 0B
./go.sh voice_capture.cfile 64 1S 239E4C213612C00001
./go.sh voice_capture.cfile 64 7T 239E4C213612C00001
toast -d speech.au.gsm
That concludes the GSM radio series for now. Till next time, happy hacking!
原文链接:https://www.ckn.io/blog/2016/01/25/gsm-sniffing-voice-traffic/
GSM:嗅探语音流量的更多相关文章
- BUUCTF-被嗅探的流量
被嗅探的流量 提示告知是文件传输的流量,那进去过滤http流量包即可,找到一个upload目录的,并且是post方式即可,追踪http流即可发现flag
- 一种基于SDR实现的被动GSM嗅探
软件定义无线电(SDR)是一种无线电通信系统,简单来说,就是通过数字信号处理技术在通用可编程数字信号处理硬件平台上,利用软件定义来实现无线电台的各单元功能,从而对无线电信号进行调制.解调.测量.SDR ...
- GSM嗅探
GSM初探 大家应该都听说过HTTP协议,又听说WEB服务,每一个服务的背后都有一个协议在工作着.所谓的没有规矩不成方圆,说的就是这个道理,每一个细小的部分,都已经规定好,只要按照协议执行,就不会出现 ...
- Tor真的匿名和安全吗?——如果是http数据,则在出口节点容易被嗅探明文流量,这就是根本问题
Tor真的匿名和安全吗? from:http://baham.github.io/04_03_torzhen-de-ni-ming-he-an-quan-ma-%3F.html 很多人相信Tor是完全 ...
- linux 下如何抓取HTTP流量包(httpry)
基于某些原因你需要嗅探HTTP Web流量(即HTTP请求和响应).例如,你可能会测试Web服务器的性能,或者x奥uy调试Web应用程序或RESTful服务 ,又或者试图解决PAC(代理自动配置)问题 ...
- metasploit framework(七):密码嗅探
run 当嗅探到流量中的用户密码信息时打印出来,目前只支持FTP,http get , pop3 还可以对抓包文件,进行密码提取,设置需要提取的文件路径 run就能提取里面的用户密码信息 查看和停掉某 ...
- 虚拟局域网(VLAN)__语音VLAN
1.语音VLAN特性使得访问端口能够携带来自IP电话的IP语音流量.当交换机连接到Cisco IP电话时,IP电话就用第3层IP优先级(precedence)和第2层服务级别(class of ser ...
- 3G 2G GPRS 1G的概念
3G, 第三代移动通信技术(3rd-generation,3G),是指支持高速数据传输的蜂窝移动通讯技术.3G服务 能够同时传送声音及数据信息,速率一般在几百kbps以上.3G标准:它们分别是WCDM ...
- GPRS优点介绍及GPRS上网相关知识(转)
源:http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-20745340-id-1878732.html 单片机微控制器以其体积小.功耗低.使用方便等特点,广泛应用于各种工业.民用的嵌入式系统 ...
随机推荐
- HTML5地理定位API在chrome中不能正常使用
navigator.geolocation.getCurrentPosition在chrome中不能正常使用. 经测试发现,FQ后就能正常使用,估计是因为chrome 对这个API的实现使用了goog ...
- vue项目中使用插件将字符串装化为格式化的json数据(可伸缩)
插件地址:https://www.npmjs.com/package/vue-json-viewer 第一步:安装vue-json-viewer插件 $ npm install vue-json-vi ...
- redis 持久化文章分析的很到位
https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1611955931705092609&wfr=spider&for=pc
- Git - 生成 ssh key for Mac
终端: cd ~/ .ssh 生成 SSH KEY ssh-keygen -t rsa -C 你的油箱 前往以下目录找到生成好的 SSH KEY /Users/wzz/.ssh/id_rsa.pub
- for 循环常见内置参数
系统相关的信息模块: import sys sys.argv 是一个 list,包含所有的命令行参数. sys.stdout sys.stdin sys.stderr 分别表示标准输入输出,错误输出的 ...
- 初学python之感悟
python的强大有目共睹,现将初学python,觉得其中比较重要的知识罗列如下: 类似于数组的东西:列表.元组.集合.字符串以及字典,这几个东西充分体现了python的强大和逆天. 列表: x=[1 ...
- System.out.print()执行顺序
今天使用递归调用计算的时候发现一个很奇怪的问题 代码: public class practice20 { public static double nStep(double N) { if (N&l ...
- http协议与https协议的前世今生
一.Http与Https的区别: HTTP 的URL 以http:// 开头,而HTTPS 的URL 以https:// 开头 HTTP 是不安全的,而 HTTPS 是安全的 HTTP 标准端口是80 ...
- Vue学习Day003
事件修饰符 在事件处理程序中调用 event.preventDefault() 或 event.stopPropagation() 是非常常见的需求.尽管我们可以在方法中轻松实现这点,但更好的方式是: ...
- pandas 常用技巧总结
切片: loc:df.loc[num]:选择df 某一行 seriesdf.loc[[num1,num2]]: 选择df 某几行df.loc[[True,False,True, ,True]]: ...
