linux磁盘管理系列一:磁盘配额管理
磁盘管理系列
linux磁盘管理系列一:磁盘配额管理 http://www.cnblogs.com/zhaojiedi1992/p/zhaojiedi_linux_040_quota.html
linux磁盘管理系列二:软RAID的实现 http://www.cnblogs.com/zhaojiedi1992/p/zhaojiedi_linux_041_raid.html
linux磁盘管理系列三:LVM的使用 http://www.cnblogs.com/zhaojiedi1992/p/zhaojiedi_linux_042_lvm.html
1 前言
在linux系统中,由于是多用户、多任务的环境,如果有少数几个用户大量使用磁盘空间,导致其他用户的正常使用,因此需要对各个用户的磁盘空间进行管理和限定。
2 quota的用途
限制某一个用户的最大磁盘配额
3 quota的使用限制
- 仅能针对整个文件系统
- 内核必须支持
- 只对一般用户生效
- 这里提供一个样例,针对样例对quota的配置管理做个描述
4 案例讲解
4.1案例描述
- 创建5个用户user1,user2,user3,user4,user5,密码和用户名相同,初始组为usergrp组。
- 5个用户都可以取得300M的磁盘使用空间,文件数量不限。超过250M,给于提示。
- usergrp这个组内成员最大使用空间1GB。
- 如果有用户超过soft限制,给14天的宽限时间。
4.2 准备磁盘
[root@mail ~]# fdisk -l #查看磁盘情况 Disk /dev/sda: 42.9 GB, bytes, sectors
Units = sectors of * = bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): bytes / bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): bytes / bytes
Disk label type: dos
Disk identifier: 0x000bd275 Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sda1 * Linux
/dev/sda2 8e Linux LVM Disk /dev/sdb: 10.7 GB, bytes, sectors
Units = sectors of * = bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): bytes / bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): bytes / bytes Disk /dev/mapper/cl-root: 39.7 GB, bytes, sectors
Units = sectors of * = bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): bytes / bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): bytes / bytes Disk /dev/mapper/cl-swap: MB, bytes, sectors
Units = sectors of * = bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): bytes / bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): bytes / bytes [root@mail ~]# fdisk /dev/sdb #对sdb这个盘进行分区,这里就分一个区
Welcome to fdisk (util-linux 2.23.). Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them.
Be careful before using the write command. Device does not contain a recognized partition table
Building a new DOS disklabel with disk identifier 0xbcd17d69. Command (m for help): n
Partition type:
p primary ( primary, extended, free)
e extended
Select (default p): p
Partition number (-, default ):
First sector (-, default ):
Using default value
Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (-, default ):
Using default value
Partition of type Linux and of size GiB is set Command (m for help): p Disk /dev/sdb: 10.7 GB, bytes, sectors
Units = sectors of * = bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): bytes / bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): bytes / bytes
Disk label type: dos
Disk identifier: 0xbcd17d69 Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 Linux Command (m for help): w
The partition table has been altered! Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
Syncing disks.
[root@mail ~]# mkfs.ext4 /dev/sdb1
mke2fs 1.42. (-Dec-)
Filesystem label=
OS type: Linux
Block size= (log=)
Fragment size= (log=)
Stride= blocks, Stripe width= blocks
inodes, blocks
blocks (5.00%) reserved for the super user
First data block=
Maximum filesystem blocks=
block groups
blocks per group, fragments per group
inodes per group
Superblock backups stored on blocks:
, , , , , , , Allocating group tables: done
Writing inode tables: done
Creating journal ( blocks): done
Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done [root@mail ~]# mkdir /mnt/home #创建一个目录
[root@mail ~]# mount /dev/sdb1 /mnt/home #测试挂载下
4.4.创建用户
[root@mail ~]# vim adduserbat.sh #创建一个添加用户的脚本
[root@mail ~]# cat adduserbat.sh #确认下脚本
#!/bin/bash groupadd usergrp
for user in user1 user2 user3 user4 user5
do
useradd -g usergrp -b /mnt/home $user
echo $user |passwd --stdin $user
done
[root@mail ~]# sh adduserbat.sh #运行脚本去创建用户
useradd: warning: the home directory already exists.
Not copying any file from skel directory into it.
Creating mailbox file: File exists
Changing password for user user1.
passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
useradd: warning: the home directory already exists.
Not copying any file from skel directory into it.
Creating mailbox file: File exists
Changing password for user user2.
passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
useradd: warning: the home directory already exists.
Not copying any file from skel directory into it.
Creating mailbox file: File exists
Changing password for user user3.
passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
useradd: warning: the home directory already exists.
Not copying any file from skel directory into it.
Creating mailbox file: File exists
Changing password for user user4.
passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
useradd: warning: the home directory already exists.
Not copying any file from skel directory into it.
Creating mailbox file: File exists
Changing password for user user5.
passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
[root@mail ~]# finger user1 #查看用户信息,确保家目录在/dev/sdb1的挂载目录上。
Login: user1 Name:
Directory: /mnt/home/user1 Shell: /bin/bash
Never logged in.
No mail.
No Plan.
[root@mail ~]# id user1 #查看用户信息
uid=(user1) gid=(usergrp) groups=(usergrp)
4.5.检查操作系统支持
前面提到了quota仅仅针对整个文件系统来进行规划的。需要确认我们为各个用户提供存储的位置是独立的文件系统。
[root@mail ~]# df -h /mnt/home #查看我们的挂载点是否是独立文件系统
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/sdb1 .8G 37M .2G % /mnt/home
[root@mail ~]# mount |grep /mnt/home #查看我们的文件系统
/dev/sdb1 on /mnt/home type ext4 (rw,relatime,data=ordered)
4.6.让文件系统支持quota设置
[root@mail ~]# mount -o remount,usrquota,grpquota /mnt/home #重新挂载/mnt/home 支持usrquota,grpquota
[root@mail ~]# mount |grep /mnt/home #确认下
/dev/sdb1 on /mnt/home type ext4 (rw,relatime,quota,usrquota,grpquota,data=ordered)
[root@mail ~]# tail -n /etc/mtab >> /etc/fstab #追加到/etc/fstab中去,确保开机启用quota
[root@mail ~]# cat /etc/fstab #确保fstab文件正确性 #
# /etc/fstab
# Created by anaconda on Fri Feb ::
#
# Accessible filesystems, by reference, are maintained under '/dev/disk'
# See man pages fstab(), findfs(), mount() and/or blkid() for more info
#
/dev/mapper/cl-root / xfs defaults
UUID=dd4c6743-bdf5--a43b-814cbe75c618 /boot xfs defaults
/dev/mapper/cl-swap swap swap defaults
/dev/sr0 /mnt/cdrom iso9660 ro,relatime,uid=,gid=,iocharset=utf8,mode=,dmode=
/dev/sdb1 /mnt/home ext4 rw,relatime,quota,usrquota,grpquota,data=ordered
4.7.扫描文件系统并新建quota的配置文件
[root@mail ~]# quotacheck -avug
quotacheck: Your kernel probably supports journaled quota but you are not using it. Consider switching to journaled quota to avoid running quotacheck after an unclean shutdown.
quotacheck: Scanning /dev/sdb1 [/mnt/home] done
quotacheck: Cannot stat old user quota file /mnt/home/aquota.user: No such file or directory. Usage will not be subtracted.
quotacheck: Cannot stat old group quota file /mnt/home/aquota.group: No such file or directory. Usage will not be subtracted.
quotacheck: Cannot stat old user quota file /mnt/home/aquota.user: No such file or directory. Usage will not be subtracted.
quotacheck: Cannot stat old group quota file /mnt/home/aquota.group: No such file or directory. Usage will not be subtracted.
quotacheck: Checked directories and files
quotacheck: Old file not found.
quotacheck: Old file not found.
主要参数
- -a: 扫描所有在/etc/mtab内含有quota参数的文件系统
- -u: 针对用户扫描文件与目录的使用情况,会新建一个aquota.user文件
- -g: 针对用户组扫描文件与目录的使用情况,会新增一个aquota.group文件
- -v: 显示扫描过程的信息
4.8 启用quota
[root@mail ~]# quotaon -avug #启用quota
/dev/sdb1 [/mnt/home]: group quotas turned on
/dev/sdb1 [/mnt/home]: user quotas turned on
这个命令(quotaon) 几乎只需要在第一次启动quota时才需要进行,因为下次等你重新启动时,系统的/etc/rc.d/rc.sysinit这个初始化脚本就会自动执行这个命令。
如果想关闭可以使用quotaoff -avug
4.9.编辑账户的的限值
[root@mail ~]# edquota -u user1
会打开一个vi编辑器,修改我们的设置如下图。

- 软限制: 这个值超过了基本上没事,还是可以创建文件继续使用文件,但是在指定grace天过后就不能在创建文件了。
- 硬限值: 这个值不能超过。
执行如下命令将user1的设置应用到其他用户上
[root@mail ~]# edquota -p user1 -u user2 #-p 指定参考用户,这句话的意思就是将user1的quota信息赋值给user2
[root@mail ~]# edquota -p user1 -u user3
[root@mail ~]# edquota -p user1 -u user4
[root@mail ~]# edquota -p user1 -u user5
4.10.编辑组的设置
[root@mail ~]# edquota -g usergrp
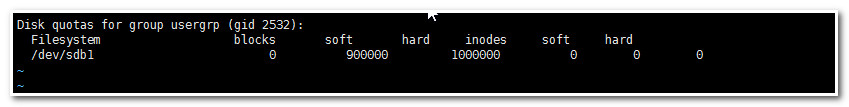
4.11.修改宽限时间
[root@mail ~]# edquota -t
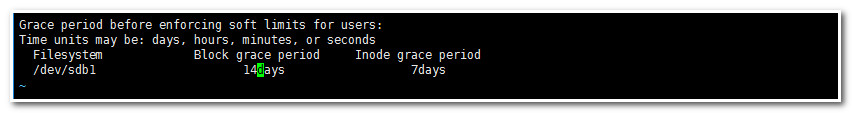
4.12.对用户和组合quota限制查看
[root@mail ~]# quota -uvs user1 #查看user1的限制信息
Disk quotas for user user1 (uid ):
Filesystem space quota limit grace files quota limit grace
/dev/sdb1 28K 245M 293M
[root@mail ~]# quota -gvs usergrp
Disk quotas for group usergrp (gid ): #查看usergrp的限制信息
Filesystem space quota limit grace files quota limit grace
/dev/sdb1 0K 879M 977M
参数说明
- -u: 指定用户
- -g: 指定用户组
- -s: 以1024为倍数来指定单位,显示M之类的单位
- -v: 显示用户在文件系统的quota值
4.13对文件系统quota限制查看
[root@mail ~]# repquota -as
*** Report for user quotas on device /dev/sdb1 #这里看到是针对/dev/sdb1的文件系统的
Block grace time: 14days; Inode grace time: 7days
Space limits File limits
User used soft hard grace used soft hard grace
----------------------------------------------------------------------
root -- 20K 0K 0K
zhao -- 52K 0K 0K
user1 -- 28K 245M 293M
user2 -- 28K 245M 293M
user3 -- 28K 245M 293M
user4 -- 28K 245M 293M
user5 -- 28K 245M 293M
4.14.quota测试
[user1@mail ~]$ dd if=/dev/zero of=bigfile bs=1M count=270 #先创建一个270M的文件看看
sdb1: warning, user block quota exceeded. #这里提示警告了。 也就是我们超过了软限制的值250了。
+ records in
+ records out
bytes ( MB) copied, 0.715086 s, MB/s
[user1@mail ~]$ dd if=/dev/zero of=bigfile2 bs=1M count=40 #这里我们创建一个40M的文件
sdb1: write failed, user block limit reached. #提示错误了。超出限制了。
dd: error writing ‘bigfile2’: Disk quota exceeded
+ records in
+ records out
bytes ( MB) copied, 0.1165 s, MB/s
[user1@mail ~]$ du -sk #查看两个文件占用情况
.
4.12脚本设置quota信息
上面我们对用户和组的设置,它会启动一个vi编辑器,修改保存才生效。需要交互。如果我们想使用script方式快速设置,那就需要使用setquota命令了。
命令使用 setquota [ -u | -g ] 用户名或者组名 块大小软限制 块大小硬限制 文件数量软限制 文件数量大小硬限制 文件系统
[root@mail ~]# quota -usv user1 #查看user1的quota信息
Disk quotas for user user1 (uid ):
Filesystem space quota limit grace files quota limit grace
/dev/sdb1 293M* 245M 293M 13days
[root@mail ~]# setquota -u user1 /dev/sdb1 #使用setquota修改
[root@mail ~]# quota -usv user1 #再次查看quota信息
Disk quotas for user user1 (uid ):
Filesystem space quota limit grace files quota limit grace
/dev/sdb1 293M 391M 489M
linux磁盘管理系列一:磁盘配额管理的更多相关文章
- ASP.NET MVC+EF框架+EasyUI实现权限管理系列(10)- VSS源代码管理
原文:ASP.NET MVC+EF框架+EasyUI实现权限管理系列(10)- VSS源代码管理 ASP.NET MVC+EF框架+EasyUI实现权限管系列 (开篇) (1):框架搭建 ( ...
- iOS 非ARC基本内存管理系列 2-多对象内存管理(3) 利用@property来自动管理内存
iOS 基本内存管理-多对象内存管理(2)中可以看到涉及到对象的引用都要手动管理内存:每个对象都需要写如下代码 // 1.对要传入的"新车"对象car和目前Person类对象所拥有 ...
- iOS 非ARC基本内存管理系列 2-多对象内存管理(2)
/* 多对象内存管理: 以人拥有车为例涉及到@property底层set方法管理内存的实现 注意:人在换车的时候要进行当前传入的车和人所拥有的车进行判断 */ /******************* ...
- iOS 非ARC基本内存管理系列 2-多对象内存管理(1)
单个对象的内存管理非常简单无非就是alloc对应release,retain对应release.但是如果涉及到很多对象,而且对象与对象有联系的时候该怎么去管理对象的内存呢. 比如同样一本书有好3个人购 ...
- Linux磁盘管理系列 — 磁盘配额管理
一.磁盘管理的概念 Linux系统是多用户任务操作系统,在使用系统时,会出现多用户共同使用一个磁盘的情况,如果其中少数几个用户占用了大量的磁盘空间,势必压缩其他用户的磁盘的空间和使用权限.因此,系统管 ...
- linux磁盘管理系列-软RAID的实现
1 什么是RAID RAID全称是独立磁盘冗余阵列(Redundant Array of Independent Disks),基本思想是把多个磁盘组合起来,组合一个磁盘阵列组,使得性能大幅提高. R ...
- linux磁盘管理系列-LVM的使用
LVM是什么 LVM是Linux操作系统的逻辑卷管理器. 现在有两个Linux版本的LVM,分别是 LVM1,LVM2.LVM1是一种已经被认为稳定了几年的成熟产品,LVM2 是最新最好的LVM版本. ...
- linux磁盘管理系列三:LVM的使用
磁盘管理系列 linux磁盘管理系列一:磁盘配额管理 http://www.cnblogs.com/zhaojiedi1992/p/zhaojiedi_linux_040_quota.html l ...
- linux磁盘管理系列二:软RAID的实现
磁盘管理系列 linux磁盘管理系列一:磁盘配额管理 http://www.cnblogs.com/zhaojiedi1992/p/zhaojiedi_linux_040_quota.html l ...
随机推荐
- CentOS修改yum源
在安装完CentOS后一般需要修改yum源,才能够在安装更新rpm包时获得比较理想的速度.国内比较快的有163源.sohu源.这里以163源为例子. 1. cd /etc/yum.repos.d 2. ...
- 平时作业五 Java
使用I/O流和文件对象实现目录备份功能.用户指定源目录.目标目录以及备份文件类型(如果是任意文件使用通配符*号),通过此程序可将源目录及其所有子目录下的指定类型文件保存到目标目录. package c ...
- NOIP2006普及组 Jam的计数法
普及组重要的模拟题.附上题目链接 https://www.luogu.org/problem/show?pid=1061 (写水题题解算是巩固提醒自己细心吧qwq) 样例输入: bdfij 样例输出: ...
- textarea--去掉空格的办法
我在初次用到textarea多行文本框时,遇到的问题是:默认出现了两行空格,如图: 代码是(错误的写法): 最后才发现,原来是: textarea标签是需要写在同一行,不能换行,正确的写法:
- VS2017 生成事件去除未修改项目
1.右键“解决方案”→“配置管理器” 2.列“生成”,反勾选无需编译的项目 3.点击“确定”,重新编译即可跳过未勾选的项目.
- 转 c#性能优化秘密
原文:http://www.dotnetperls.com/optimization Generally, using the simplest features of the language pr ...
- asp.net core 下载文件,上传excel文件
下载文件: 代码: 后端代码: public IActionResult DownloadFile() { var FilePath = @"./files/deparment.xlsx&q ...
- ArcGIS Runtime For Android 100.3天地图不加载问题
ArcGIS Runtime 100.3 不加载天地图问题 参考这篇帖子:https://community.esri.com/thread/220496-1003-webtiledlayer-can ...
- [.net 面向对象程序设计深入](31)实战设计模式——使用Ioc模式(控制反转或依赖注入)实现松散耦合设计(1)
[.net 面向对象程序设计深入](31)实战设计模式——使用IoC模式(控制反转或依赖注入)实现松散耦合设计(1) 1,关于IOC模式 先看一些名词含义: IOC: Inversion of con ...
- solr与Elasticsearch对比
搜索引擎:Solr与Elasticsearch比较分析 Elasticsearch是一个实时的分布式搜索和分析引擎.它可以帮助你用前所未有的速度去处理大规模数据. 它可以用于全文搜索,结构化搜索以及分 ...
