[C++ Primer Plus] 第8章、函数探幽(一)程序清单——内联、引用、格式化输入输出、模板、decltype
程序清单8.1(inline内联函数)
#include<iostream>
using namespace std; inline double square(double x) {//inline表示内联函数
return x*x;
} void main()
{
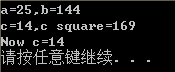
double a, b, c = 13.0;
a = square(5.0);
b = square(4.5+7.5);
cout << "a=" << a << ",b=" << b << endl;
cout << "c=" << c << ",c square=" << square(c++) << endl;
cout << "Now c=" <<c<< endl;
system("pause");
}

程序清单8.2+8.3(引用变量)
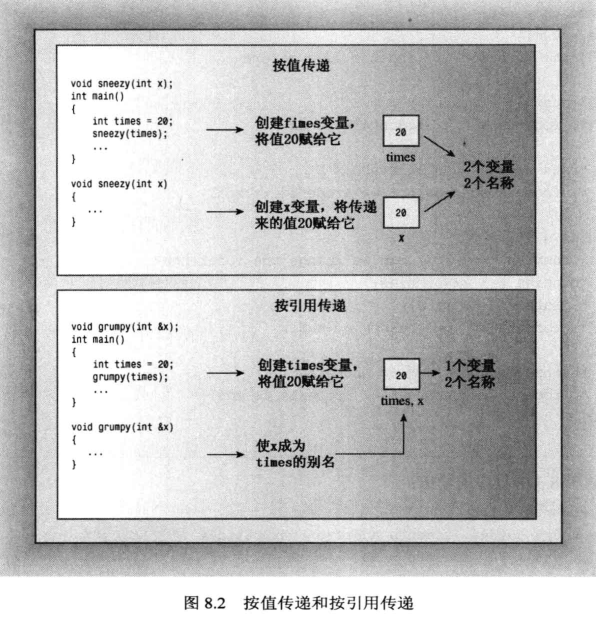
引用变量的主要用途是作为函数的形参:引用变量做参数,函数将使用原始数据。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std; void main()
{
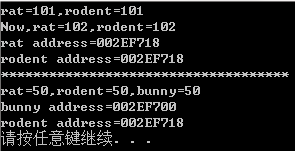
int rat = ;
int &rodent = rat;//将rodent的类型声明为int&,即指向int变量的引用
cout << "rat=" <<rat<< ",rodent=" <<rodent<< endl;
rodent++;
cout << "Now,rat=" << rat << ",rodent=" << rodent << endl;
cout << "rat address=" << &rat << endl;
cout << "rodent address=" <<&rodent<< endl; cout << "************************************" << endl;
int bunny = ;
rodent = bunny;
cout << "rat=" << rat << ",rodent=" << rodent<<",bunny="<<bunny << endl;
cout << "bunny address=" << &bunny << endl;
cout << "rodent address=" << &rodent << endl; system("pause");
}
临时变量、引用参数和const
如果实参与引用参数不匹配,仅当参数为const引用时,C++将生成临时变量。


程序清单8.6
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std; struct free_throw
{
string name;
int made;
int attempt;
float percent;
};
void display(const free_throw &ft) {
cout << "Name=" << ft.name << endl;
cout << "Made=" << ft.made << "\t\t";
cout << "Attempt=" << ft.attempt<< "\t";
cout << "Percent=" << ft.percent<<endl;
}
void set(free_throw &ft) {
if (ft.attempt != )
ft.percent = 100.0f*float(ft.made) / float(ft.attempt);
else
ft.percent = ;
}
free_throw & accumulate(free_throw &target,const free_throw &source) {
target.attempt += source.attempt;
target.made += source.made;
set(target);
return target;
} void main()
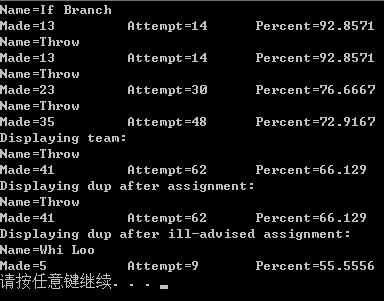
{
free_throw one = { "If Branch",, };
free_throw two = { "Andor Knott",, };
free_throw three = { "Min Max",, };
free_throw four = { "Whi Loo",, };
free_throw five = { "Long Long",, };
free_throw team = { "Throw",,};
free_throw dup; set(one);
display(one);
accumulate(team, one);
display(team);
display(accumulate(team,two));
accumulate(accumulate(team, three), four);
display(team);
dup = accumulate(team, five);//返回的team赋给dup
cout << "Displaying team:" << endl;
display(team);//team经过48行代码,已经发生了变化
cout << "Displaying dup after assignment:" << endl;
display(dup);
set(four);
accumulate(dup, five) = four;//four赋给dup
cout << "Displaying dup after ill-advised assignment:" << endl;
display(dup); system("pause");
}
程序清单8.7
string:标准库允许把字符串字面值和字符字面值转换为 string 对象,当把 string 对象和字符字面值以及字符串字面值混在一条语句中使用时,必须确保加法运算符( + )的两侧运算对象至少有一个是 string:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std; string version1(const string &s1, const string &s2) {
string tmp;
tmp = s2 + s1 + s2;
return tmp;//返回main函数时,tmp不复存在,但tmp的内容被复制到临时存储单元
}
string & version2(string &s1, const string &s2) {//有副作用,改变了s1的内容
s1 = s2 + s1 + s2;
return s1;
}
string & version3(string &s1, const string &s2) {//坏设计
string tmp;
tmp = s2 + s1 + s2;
return tmp;//返回main函数时,tmp内存已被释放,程序不能引用已经释放的内存
} void main()
{
string input, copy, result;
cout << "Enter a string:";
getline(cin, input);//用于字符串的输入
copy = input;//C++中,string可以直接赋值
cout << "Your string as entered:" << input << endl;
result = version1(input, "***");
cout << "Your string enhanced:" << result << endl;
cout << "Your original string:" << input << endl; result = version2(input, "###");
cout << "Your string enhanced:" << result << endl;
cout << "Your original string:" << input << endl; cout << "Resetting original string." << endl;
input = copy;
result = version3(input, "@@@");//version3返回地址值时报错,因为该地址已释放
cout << "Your string enhanced:" << result << endl;
cout << "Your original string:" << input << endl; system("pause");
}

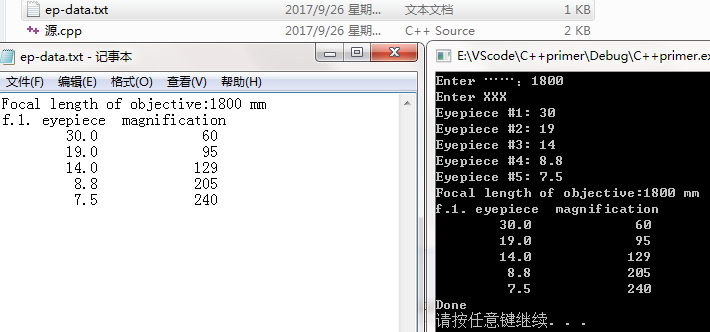
程序清单8.8(格式化输入输出)
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <cstdlib>
using namespace std;
const int LIMIT = ; void file_it(ostream &os,double fo,const double fe[],int n) {//参数os可以指向ostream对象(如cout),也可以指向ofstream对象(如fout)
ios_base::fmtflags initial;//ios_base::fmtflags是存储这种信息所需的数据类型名称
initial = os.setf(ios_base::fixed);//setf(ios_base::fixed)使用定点表示法 表示对象
os.precision();//指定显示多少位小数(假定处于定点模式下)
os << "Focal length of objective:" << fo << " mm"<<endl;
os.setf(ios::showpoint);//使用小数点 表示对象,即使小数部分为0
os.precision();
os.width();//设置下一次输出操作使用的字段宽度,只在显示下一个值时有效
os << "f.1. eyepiece";
os.width();
os << "magnification" << endl;
for (int i = ; i < n; i++)
{
os.width();
os << fe[i];
os.width();
os << int(fo / fe[i] + 0.5) << endl;
}
os.setf(initial);//返回调用它之前有效的所有格式化设置,即将对象回到传递给file_it()之前的状态
//当程序将cout传递给file_it()时,cout的设置将被修改,然后被恢复;fout同样如此
}
void main()
{
ofstream fout;
const char *fn = "ep-data.txt";
fout.open(fn);
if (!fout.is_open()) {
cout << "Can't open "<< fn <<".Bye."<< endl;
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
double objective;
cout << "Enter ……:";
cin >> objective;
double eps[LIMIT];
cout << "Enter XXX" << endl;
for (int i = ; i < LIMIT; i++)
{
cout << "Eyepiece #" << i + << ": ";
cin >> eps[i];
}
file_it(fout, objective, eps, LIMIT);//将数据写入文件ep-data.txt
file_it(cout, objective, eps, LIMIT);//将同样的信息以相同的格式显示到屏幕上
cout << "Done" << endl;
system("pause");
}
以下是一些常见的控制函数的:
dec 置基数为10 相当于"%d"
hex 置基数为16 相当于"%X"
oct 置基数为8 相当于"%o"
setfill(c) 设填充字符为c
setprecision(n) 设显示小数精度为n位
setw(n) 设域宽为n个字符
setioflags(ios::fixed) 固定的浮点显示
setioflags(ios::scientific) 指数表示
setiosflags(ios::left) 左对齐
setiosflags(ios::right) 右对齐
setiosflags(ios::skipws 忽略前导空白
setiosflags(ios::uppercase) 16进制数大写输出
setiosflags(ios::lowercase) 16进制小写输出
setiosflags(ios::showpoint) 强制显示小数点
setiosflags(ios::showpos) 强制显示符号
程序清单8.9(默认参数)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std; const int Size = ;
char *left(const char *str, int n = );//默认n为1 void main()
{
char sample[Size];
cout << "Enter a string:\n";
cin.get(sample, Size);
char *p = left(sample, );//调用此方法后要记得delete
cout << p << endl;
delete[] p; p = left(sample);
cout << p << endl;
delete[] p;
system("pause");
} char *left(const char *str, int n) {//内部使用了new未delete,所以在main函数调用此方法后一定要记得delete
if (n < )
n = ;
char *p = new char[n + ];//new和delete成对出现
int i;
for (i = ; i < n&&str[i]; i++)
p[i] = str[i];
while (i <= n)
p[i++] = '\0';
return p;
}
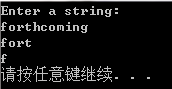
程序清单8.10(函数重载)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std; char *left(const char *str, int n) {//内部使用了new未delete,所以在main函数调用此方法后一定要记得delete
if (n < )
n = ;
char *p = new char[n + ];//new和delete成对出现
int i;
for (i = ; i < n&&str[i]; i++)
p[i] = str[i];
while (i <= n)
p[i++] = '\0';
return p;
}
unsigned long left(unsigned long num, unsigned ct) {
if (ct == || num == )
return ;
unsigned digit = ;
unsigned long n = num;
while (n /= )
digit++;
if (digit > ct) {
ct = digit - ct;
while (ct--)
num /= ;
return num;
}
else
return num;
}
void main()
{
char *trip = "Hawaii!!";
unsigned long n = ;
int i;
char * temp;
for (i = ; i < ; i++)
{
cout << left(n, i) << endl;
temp = left(trip, i);
cout << temp << endl;
delete[] temp;
}
system("pause");
}
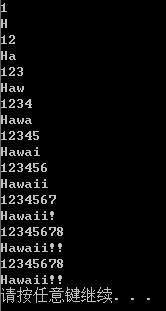
程序清单8.11+12(函数模板,模板重载)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std; template <typename T> //函数模板
void swap2(T &a, T &b) { //引用 不能用swap函数名,用户自己定义的swap()函数与STL库定义的函数重载冲突
T temp;
temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
template <typename T>
void swap2(T a[], T b[],int n) {
T temp;
for (int i = ; i < n; i++)
{
temp = a[i];
a[i] = b[i];
b[i] = temp;
}
} const int Size = ;
template <class Te>//模板的另一种表示方式
void show(Te a[]) {
for (int i = ; i < Size; i++)
{
cout << a[i] << "\t";
}
cout << endl;
} void main()
{
int i = , j = ;
cout << "i=" << i << ",j=" << j << endl;
swap2(i, j);
cout << "Now,i=" << i << ",j=" << j << endl; double x[Size] = { ,,,, };
double y[] = {,,,,};
show(x);
show(y);
swap2(x, y ,Size);
cout << "Now" << endl;
show(x);
show(y); system("pause");
}
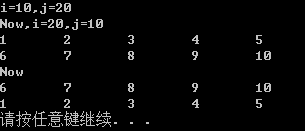
程序清单8.13(模板显示具体化)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std; //模板:交换a、b值
template <typename T>
void Swap(T &a, T &b) {
T temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
} struct job {
char name[];
double salary;
int floor;
};
//显示具体化:交换结构体内部成员值
template <> void Swap<job>(job &j1, job &j2) {//引用
double t1;
int t2;
t1 = j1.salary;
j1.salary = j2.salary;
j2.salary = t1; t2 = j1.floor;
j1.floor = j2.floor;
j2.floor = t2;
} void show(job &j) {//引用
cout << j.name << ":$"<<j.salary<<" on floor "<<j.floor<<endl;
} void main()
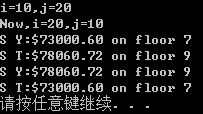
{
cout.precision();//指定显示多少位小数(假定处于定点模式下):看有没有set ios::fixed,如果没有的话, 是代表2位有效数字, 不是3位小数
cout.setf(ios::fixed,ios::floatfield);//ios::fixed设置为定点输出格式,floatfield设置输出时按浮点格式,小数点后有6位数字
int i = , j = ;
cout << "i=" << i << ",j=" << j << endl;
Swap(i, j);
cout << "Now,i=" << i << ",j=" << j << endl; job sue = { "S Y",73000.60, };
job sid = { "S T",78060.72, };
show(sue);
show(sid);
Swap(sue, sid);
show(sue);
show(sid);
system("pause");
}
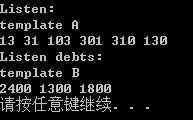
程序清单8.14
#include <iostream>
using namespace std; template <typename T>
void show(T arr[],int n) {
cout << "template A" << endl;
for (int i = ; i < n; i++)
cout << arr[i] << ' ';
cout << endl;
}
template <typename T>
void show(T * arr[], int n) {//指针数组:[]比*优先级高
cout << "template B" << endl;
for (int i = ; i < n; i++)
cout << *arr[i] << ' ';
cout << endl;
} struct debt {
char name[];
double amount;
}; void main()
{
int thing[] = { ,,,,, };
struct debt mr_E[] = {
{ "I W",2400.0 },
{ "U F",1300.0 },
{ "I S",1800.0 }
};
double *pd[];
for (int i = ; i < ; i++)
pd[i] = &mr_E[i].amount;
cout << "Listen:" << endl;
show(thing, );
cout << "Listen debts:" << endl;
show(pd, ); system("pause");
}
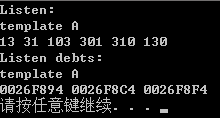
如果去掉 template B ,打印出来的将是地址
程序清单8.15
#include <iostream>
using namespace std; //返回小值
template <typename T>
T lesser(T a,T b) {
return a < b ? a : b;
}
//先取绝对值,再返回绝对值中的小值
int lesser(int a, int b) {
a = a < ? -a : a;
b = b < ? -b : b;
return a < b ? a : b;
} void main()
{
int m = , n = -;
double x = 15.5, y = 25.9;
cout << lesser(m, n) << endl;//调用函数
cout << lesser(x, y) << endl;//调用模板函数
cout << lesser<>(m, n) << endl;//<>表示调用模板函数
cout << lesser<int>(x,y)<<endl;//<int>表示 显示实例化,强转xy值 system("pause");
}

关键字decltype

[C++ Primer Plus] 第8章、函数探幽(一)程序清单——内联、引用、格式化输入输出、模板、decltype的更多相关文章
- C++ primer plus读书笔记——第8章 函数探幽
第8章 函数探幽 1. 对于内联函数,编译器将使用相应的函数代码替换函数调用,程序无需跳到一个位置执行代码,再调回来.因此,内联函数的运行速度比常规函数稍快,但代价是需要占用更多内存. 2. 要使用内 ...
- 《C++ Primer Plus》第8章 函数探幽 学习笔记
C++ 扩展了 C 语言的函数功能.通过将 inline 关键字用于函数定义,并在首次调用该函数前提供其函数定义,可以使得 C++ 编译器将该函数视为内联函数.也就是说,编译器不是让程序跳到独立的代码 ...
- C++ Primer 5th 第6章 函数
正如第一章所说:C++的函数是一个能够完成一个功能的模块或者说是一段命名了的代码块. 如下图所示,函数可以重载,是一段实现某些功能命名了的代码. 一个完整的函数的构成有四部分: 1.返回类型 2.函数 ...
- 不可或缺 Windows Native (16) - C++: 函数重载, 缺省参数, 内联函数, 函数模板
[源码下载] 不可或缺 Windows Native (16) - C++: 函数重载, 缺省参数, 内联函数, 函数模板 作者:webabcd 介绍不可或缺 Windows Native 之 C++ ...
- 《C++ Primer Plus 6th》读书笔记 - 第8章 函数探幽
1. 摘录 默认参数指的是当函数调用中省略了实参时自动使用的一个值. 默认参数并非编程方面的重大突破,而只是提供了一种便捷的方式.使用默认参数,可以减少要定义的析构函数.方法以及方法重载的数量. 试图 ...
- C Primer Plus 第9章 函数 编程练习
复习题: 8. int choice(int a,int b,int c){ int max; max = a; if (b > max) max = b; if (c > max) ma ...
- 第四章 函数之lambda 表达式和内置函数
4.5 lambda 表达式 用于表示简单的函数. # 三元运算,为了解决简单的if else的情况,如:if 1 == 1: a = 123else: a = 456# 相当于a = 1 ...
- 【C++】《C++ Primer 》第六章
第六章 函数 一.函数基础 函数定义:包括返回类型.函数名字和0个或者多个形参(parameter)组成的列表和函数体. 调用运算符:调用运算符的形式是一对圆括号 (),作用于一个表达式,该表达式是函 ...
- C++—函数探幽
一.内联函数 1.内联函数的机制 内联函数是C++为提高程序运行速度而做的一项改进. 函数调用机制:常规函数调用使程序使程序跳到被掉函数的地址,并在函数结束时返回. 内联函数的机制:内联函数的代码与其 ...
随机推荐
- C#获取项目程序及运行路径的方
1.asp.net webform用“Request.PhysicalApplicationPath获取站点所在虚拟目录的物理路径,最后包含“\”: 2.c# winform用 A:“Applic ...
- Python 学习笔记7 条件语句 If
Python中条件语句if 是通过一条或者多条的执行语句的结果,来判断是否执行其包含的代码块. 通常会配合else.elif一起使用,达到根据条件进行多个代码块的执行操作. 简单的if score = ...
- 新人上手:如何做好一个App的推广?
App推广是现在所有公司都绕不开的槛,而一般App推广又分为线上线下两个方面,其中,App线上推广是互联网时代运营人员接触最多的一种推广方式.一款App应用推广的最终目的是为了吸引目标用户,为推销的产 ...
- python中关于汉诺塔问题和使用turtle库实现其搬运过程
一.汉诺塔问题 汉诺塔(又称河内塔)问题是源于印度一个古老传说的益智玩具.大梵天创造世界的时候做了三根金刚石柱子,在一根柱子上从下往上按照大小顺序摞着64片黄金圆盘.大梵天命令婆罗门把圆盘从下面开始按 ...
- Servlet(自己实现的Servlet)细节
Java中无状态的对象就是指某种没用任何属性的仅仅由方法组成的对象. *无状态:无状态方法的好处之一,就是在各种环境下,都可以安全调用.衡量一个方法 是否有状态的,就看它是否改动了其他东西. *有状态 ...
- js手机浏览器浏览WebApp弹出的键盘遮盖住文本框的解决办法
if(window.navigator.userAgent.indexOf('Android') > -1 || window.navigator.userAgent.indexOf('Adr' ...
- Lists.newArrayList的一个小坑
把一个用户ID转换成List存储,最开始我使用的方法是: // 用户ID Integer userId = 120; // id 转 List List<integer> userIds ...
- try catch的使用场景
- 解决centos7.x图形化界面卡死(鼠标能动,但不能点击)问题
有时会由于某些原因(CPU过热?Mem占用过高?)导致centos7.x图形界面卡死,下面是解决办法,此方法不会关闭你打开的terminal. 1. 首先top命令查看gnome-shell的PID ...
- win openssl 生成证书
第1步:生成私钥 有密码:openssl genrsa -des3 -out private.key 1024无密码:openssl genrsa -out private.key 1024 说明:生 ...
