迁移学习(PAT)《Pairwise Adversarial Training for Unsupervised Class-imbalanced Domain Adaptation》
论文信息
论文标题:Pairwise Adversarial Training for Unsupervised Class-imbalanced Domain Adaptation
论文作者:Weili Shi, Ronghang Zhu, Sheng Li
论文来源:KDD 2022
论文地址:download
论文代码:download
视屏讲解:click
1 摘要
提出问题:类不平衡问题;
解决方法:
- 提出了一种新颖的成对对抗训练方法,该方法从源域和目标域的成对样本中生成对抗样本,并进一步利用这些样本来增强训练数据;
- 提出了一种新的优化算法来解决成对对抗训练问题;
2 问题定义
In class-imbalanced domain adaptation, both the source and target domains suffer from label distribution shift. We are given a source domain $\mathcal{D}_{s}=\left\{\left(x_{i}^{s}, y_{i}^{s}\right)\right\}_{i=1}^{N_{s}}$ with $N^{s}$ labelled samples and a target domain $\mathcal{D}_{t}=\left\{x_{i}^{t}\right\}_{i=1}^{N_{t}}$ with $N^{t}$ unlabelled samples. Each domain contains $K$ classes, and the class label is denoted as $y^{S} \in\{1,2, \ldots, K\}$ . Let $p$ and $q$ denote the probability distributions of the source and target domains, respectively. We assume that both the covariate shift (i.e., $p(x) \neq q(x)$ ) and label distribution shift (i.e., $p(y) \neq q(y)$ and $p(x \mid y) \neq q(x \mid y)$) exist in two domains. The model typically consists of a feature extractor $g: \mathcal{X} \rightarrow \mathcal{Z}$ and a classifier $f: \mathcal{Z} \rightarrow \boldsymbol{y}$ . The predicted label $\hat{y}=f(g(x))$ and empirical risk is defined as $\epsilon=\operatorname{Pr}_{x \sim \mathcal{D}}(\hat{y} \neq y)$ , where $y$ is ground-truth label. The source error and target error are denoted as $\epsilon_{S}$ and $\epsilon_{T}$ , respectively. Our goal is to train a model that can reduce gap between source and target domains and minimize $\epsilon_{S}$ and $\epsilon_{T}$ under label distribution shift.
3 方法
3.1 标签偏移
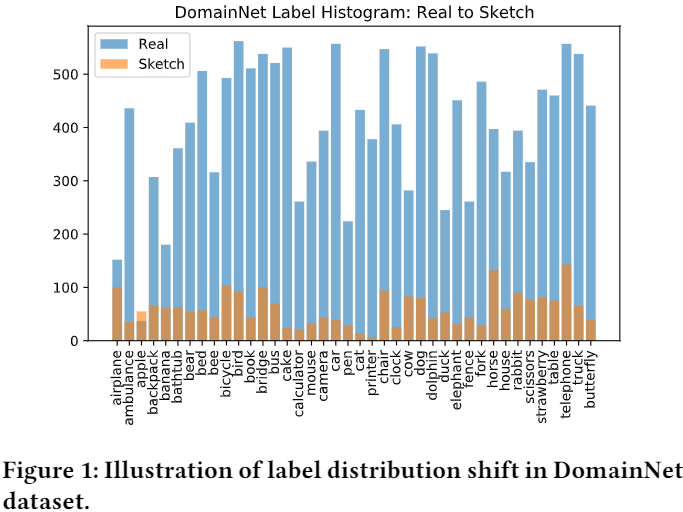
Note:简单增加两个域的数据来解决标签偏移是微不足道的,因为还要考虑域偏移的影响,本文通过生成对抗样本来缓解源域和目标域中的不平衡问题;
3.2 整体框架
整体框架:
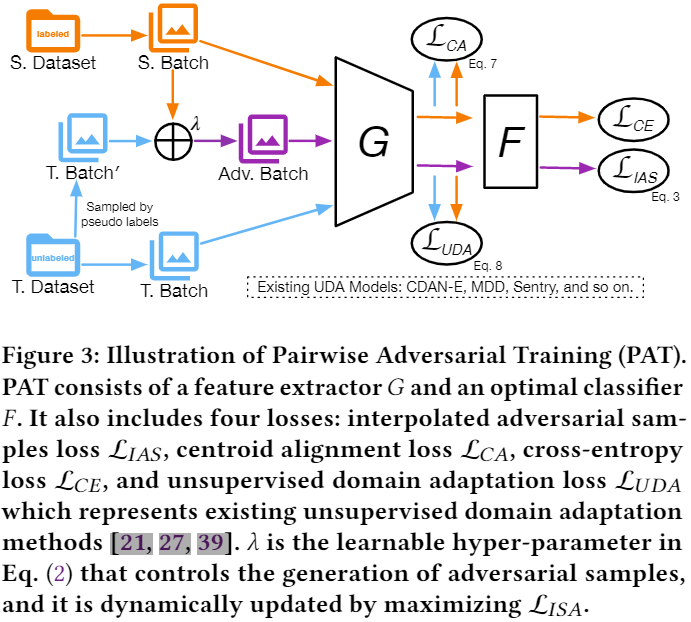
使用对抗训练增强模型鲁棒性,对抗损失如下:
$\begin{array}{l}\mathcal{L}_{c e}\left(x+\delta^{*}, y ; \theta\right) \\where \quad \delta^{*}:=\arg \max \mathcal{L}_{c e}(x+\delta, y ; \theta) , \|\delta\|_{p} \leq \epsilon \end{array} \quad\quad\quad(1)$
传统对抗训练在 CDA 中不适用的原因:
- 大多仅从原始样本的邻域生成对抗样本,没有考虑源域和目标域之间的域差距;
- 无法处理类不平衡问题;
基于上述两个原因,本文提出从源和目标域使用动态线性差值动态生成对抗样本来缓解类不平衡问题,以及 通过显式对齐源域和目标域的条件特征分布来减少域差异,如 Figure 3 所示:
3.3 内插对抗样本生成
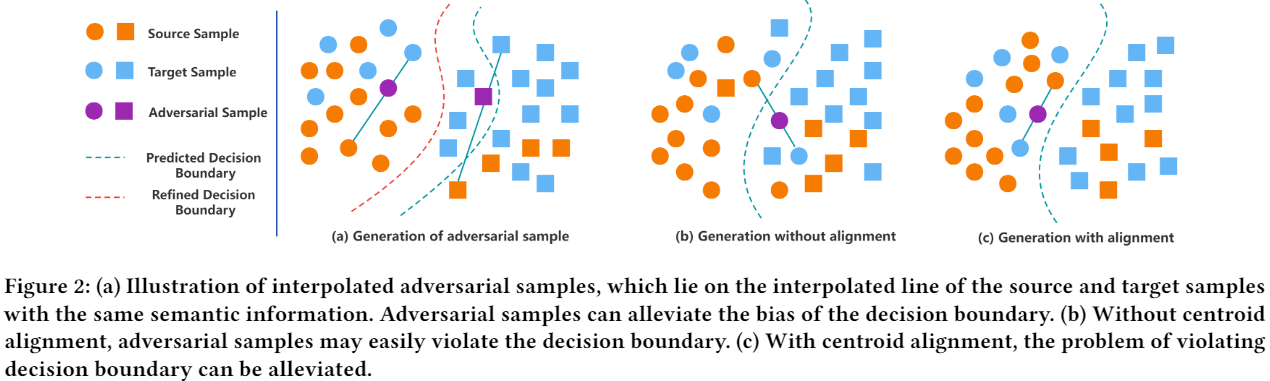
如 Figure2(a) 所示,对来自同一类的成对源和目标样本进行线性插值来生成对抗样本,插值对抗样本 (IAS) 应与其对应的源样本和目标样本具有相同的语义。通过动态利用内插对抗样本明确解决了源域中的数据不平衡问题,提高了无偏模型的泛化能力,并且可以隐式地解决目标域中的数据不平衡问题。
对于第 $k$ 类,插值的对抗样本可以定义为:
$X_{k}^{a d v}=\left\{x_{i}^{a d v} \mid x_{i}^{a d v}=x_{i}^{s}+\lambda\left(x_{i}^{t}-x_{i}^{s}\right), \lambda \in[0,1)^{C}, y_{i}^{s}=\hat{y}_{i}^{t}=k\right\} \quad\quad\quad(2)$
其中:
$\hat{y}_{i}^{t}$ 是通过分类器生成的伪标签;
尽管采用伪标签来生成对抗样本,但 PAT 对潜在的错误累积问题具有鲁棒性,原因:
- 错误分类的目标样本通常存在于决策边界,尽管目标样本的伪标签实际上并不正确,但由于新样本可能更接近源样本,因此生成的对抗样本很有可能仍然与相应的源样本保持相同的语义信息;
- 生成的对抗样本是动态产生的,随着模型逐渐收敛,不良对抗样本的不利影响可能减小;
Note:本文中并非所有类都有相同的机会生成对抗样本,采用概率阈值 $P_{k}$ 来控制来自第 $k$ 类的一对源样本和目标样本的对抗样本的生成。
插值对抗样本的生成可以通过解决以下优化问题来实现:
$\begin{array}{l}\mathcal{L}_{I A S}:=\mathcal{L}_{C E}\left(\hat{x}^{a d v}, y ; \theta\right) \\\text { where } \quad \hat{x}^{a d v}=\underset{x^{a d v} \in \mathcal{X}^{a d v}}{\arg \max } \mathcal{L}_{C E}^{\prime}\left(x^{a d v}, y ; \theta\right)\end{array} \quad\quad\quad(3) $
外部最小化使用标准交叉熵损失 $\mathcal{L}_{C E}$,即:
$\mathcal{L}_{C E}\left(\hat{x}^{a d v}, y ; \theta\right)=-\log \left(\sigma_{y}\left(f\left(g\left(\hat{x}^{a d v}\right)\right)\right)\right) \quad\quad\quad(4)$
内部最大化使用交叉熵的修改版,可以缓解熵损失最大化时梯度爆炸或消失的问题,它写成:
$\mathcal{L}_{C E}^{\prime}\left(x^{a d v}, y ; \theta\right)=\log \left(1-\sigma_{y}\left(f\left(g\left(x^{a d v}\right)\right)\right)\right. \quad\quad\quad(5)$
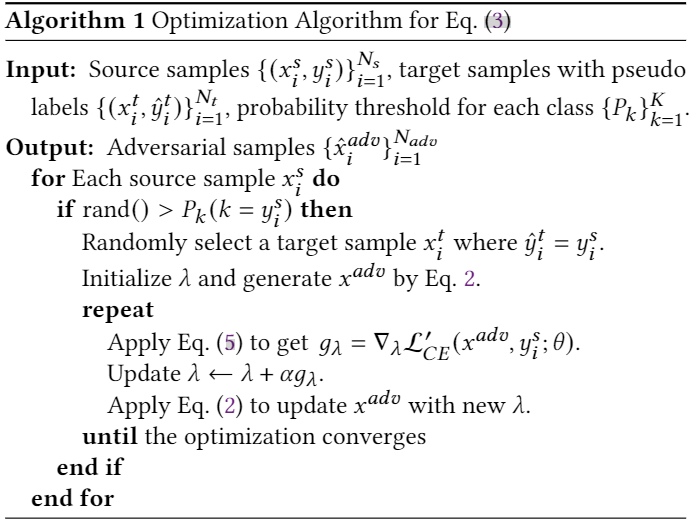
本文生成对抗样本的方法如 Algorithm 1:
IAS 代码:


def get_perturb_point(self,input_source,labels_source):
self.model.train(False)
src_point = []
tgt_point = []
point_label = [] for src_index,label in enumerate(labels_source):
if torch.rand(1) > self.thresh_prob_class[label.cpu().item()]:
cond_one = self.target_label == label
cond_two = self.target_prob > self.thresh_prob_pesudo
cond = torch.bitwise_and(cond_one, cond_two)
cond_index = torch.nonzero(cond,as_tuple=True)[0]
if cond_index.size(0) > 0:
src_sample = input_source[src_index]
tgt_index = cond_index[torch.randint(cond_index.size(0),(1,))]
_,tgt_sample,_ = self.target_dataset[tgt_index]
src_point.append(src_sample)
tgt_point.append(tgt_sample)
point_label.append(label) if len(point_label) <= 1:
return None src_point = torch.stack(src_point)
tgt_point = torch.stack(tgt_point)
point_label = torch.as_tensor(point_label).long() src_point = src_point.to(self.device)
tgt_point = tgt_point.to(self.device)
point_label = point_label.to(self.device) perturb_num = src_point.size(0)
cof = torch.rand(perturb_num,3,1,1,device=self.device)
cof.requires_grad_(True) optim = SGD([cof],lr=0.001,momentum=0.9)
loop = self.max_loop
for i in range(loop):
optim.zero_grad()
perturbed_point = src_point + cof * (tgt_point - src_point)
_,perturbed_output,_,_ = self.model(perturbed_point) perturbed_output_softmax = 1 - F.softmax(perturbed_output, dim=1)
perturbed_output_logsoftmax = torch.log(perturbed_output_softmax.clamp(min=self.epsilon))
loss = F.nll_loss(perturbed_output_logsoftmax, point_label,reduction='none')
final_loss = torch.sum(loss)
final_loss.backward() optim.step()
cof.data.clamp_(0,1)
self.model.zero_grad() cof = cof.detach()
perturbed_point = src_point + cof * (tgt_point - src_point)
self.model.train(True)
return (perturbed_point,point_label)
IAS Code
3.4 类不平衡语义质心对齐
本文中并非所有类都有相同的机会生成对抗样本,采用概率阈值 $P_{k}$ 来控制来自第 $k$ 类的一对源样本和目标样本的对抗样本的生成。
${\large P_{k}=\frac{n_{k}}{n_{\max }+\tau}} \quad\quad\quad(6)$
其中:
$n_{k}$ 是第 $k$ 类的样本数;
$n_{\max }= \max _{k}\left\{n_{k}\right\}_{k=1}^{K}$;
此外,使用移动平均质心对齐[38],显式匹配两个域的质心来对齐源域和目标域的条件特征分布。
如 Figure 2b 所示,如果没有质心对齐,则可能会从一对样本中生成对抗性样本,其中一个样本与其他类未对齐,从而使对抗性样本的嵌入超出决策边界。 通过 Figure 2c 所示的质心对齐,可以消除这种越界对抗样本的出现。 移动平均质心对齐的损失函数定义为:
$\mathcal{L}_{C A}=\sum_{k=1}^{K} \operatorname{dist}\left(C_{k}^{S}, C_{k}^{t}\right) \quad\quad\quad(7)$
其中,$C_{k}^{s}$ 和 $C_{k}^{t}$ 分别表示源域和目标域中第 $k$ 类的质心。
3.5 用于类不平衡域自适应的 PAT
训练目标:
$\mathcal{L}=\mathcal{L}_{U D A}+\mathcal{L}_{C E}+\alpha \mathcal{L}_{I A S}+\beta \mathcal{L}_{C A} \quad\quad\quad(8)$
其中:
- interpolated adversarial samples loss $\mathcal{L}_{I A S}$ which aims to dynamically generate adversarial samples to alleviate imbalance issue
- centroid alignment loss $\mathcal{L}_{C A}$ is designed to align the conditional feature distributions of source and target
- standard cross-entropy loss $\mathcal{L}_{C E}$
- unsupervised domain adaptation loss $\mathcal{L}_{U D A}$ which is adopted from existing UDA methods
4 实验
略
5 总结
略
迁移学习(PAT)《Pairwise Adversarial Training for Unsupervised Class-imbalanced Domain Adaptation》的更多相关文章
- 迁移学习(IIMT)——《Improve Unsupervised Domain Adaptation with Mixup Training》
论文信息 论文标题:Improve Unsupervised Domain Adaptation with Mixup Training论文作者:Shen Yan, Huan Song, Nanxia ...
- 迁移学习(DIFEX)《Domain-invariant Feature Exploration for Domain Generalization》
论文信息 论文标题:Domain-invariant Feature Exploration for Domain Generalization论文作者:Wang Lu, Jindong Wang, ...
- 迁移学习(Transformer),面试看这些就够了!(附代码)
1. 什么是迁移学习 迁移学习(Transformer Learning)是一种机器学习方法,就是把为任务 A 开发的模型作为初始点,重新使用在为任务 B 开发模型的过程中.迁移学习是通过从已学习的相 ...
- 迁移学习(DANN)《Domain-Adversarial Training of Neural Networks》
论文信息 论文标题:Domain-Adversarial Training of Neural Networks论文作者:Yaroslav Ganin, Evgeniya Ustinova, Hana ...
- 迁移学习(JDDA) 《Joint domain alignment and discriminative feature learning for unsupervised deep domain adaptation》
论文信息 论文标题:Joint domain alignment and discriminative feature learning for unsupervised deep domain ad ...
- 迁移学习(ADDA)《Adversarial Discriminative Domain Adaptation》
论文信息 论文标题:Adversarial Discriminative Domain Adaptation论文作者:Eric Tzeng, Judy Hoffman, Kate Saenko, Tr ...
- 中文NER的那些事儿2. 多任务,对抗迁移学习详解&代码实现
第一章我们简单了解了NER任务和基线模型Bert-Bilstm-CRF基线模型详解&代码实现,这一章按解决问题的方法来划分,我们聊聊多任务学习,和对抗迁移学习是如何优化实体识别中边界模糊,垂直 ...
- 【深度学习系列】迁移学习Transfer Learning
在前面的文章中,我们通常是拿到一个任务,譬如图像分类.识别等,搜集好数据后就开始直接用模型进行训练,但是现实情况中,由于设备的局限性.时间的紧迫性等导致我们无法从头开始训练,迭代一两百万次来收敛模型, ...
- Adversarial Training
原于2018年1月在实验室组会上做的分享,今天分享给大家,希望对大家科研有所帮助. 今天给大家分享一下对抗训练(Adversarial Training,AT). 为何要选择这个主题呢? 我们从上图的 ...
- 【迁移学习】2010-A Survey on Transfer Learning
资源:http://www.cse.ust.hk/TL/ 简介: 一个例子: 关于照片的情感分析. 源:比如你之前已经搜集了大量N种类型物品的图片进行了大量的人工标记(label),耗费了巨大的人力物 ...
随机推荐
- ddddd
项目二阶段总结 账户微服务 短信发送 1.压测发现问题 首先对短信smscomponent的send方法在test单元测试类中测试,不是真的发短信测试,可以建立请求开始和结束的时间戳来确定请求的耗时. ...
- Crypto入门 (六)幂数加密(云影密码)
前言: 这次题目说的是幂数加密,但是它本身 幂数加密: 题目:8842101220480224404014224202480122 分析一波,只有8.4.2.1.0五种数字,然后先根据提示百度一下幂数 ...
- 【javascript】关于charCodeAt()方法
在做算法题目leetcode 2283时,看见某些答案会使用charCodeAt(),因为自己没用过,所以作此纪录 描述在 JavaScript 中,charCodeAt() 是一种字符串方法,用于检 ...
- mysql-开启日志记录功能
开启日志记录功能 -- 开启功能 SET GLOBAL general_log = ON; -- 保存到文件 SET GLOBAL log_output = 'file'; 查看日志内容 -- 查看日 ...
- Unity打包ARCore项目失败,但是其他安卓项目成功
https://blog.csdn.net/lxbhahaha/article/details/111269980
- mybatis-plus自动填充踩坑
学习使用mybatis-plus的自动填充功能,对create_time和update_time做一个自动填充,期间碰到了一些问题,记录一下问题和相关代码 在实体类字段上增加注解@TableField ...
- 116、商城业务---分布式事务---seata的AT模式存在的问题&&最终一致性库存解锁逻辑
seata的AT模式不适合高并发的项目,因为它需要加锁来保证回滚.因此我们的订单服务方法中就尽量不能使用@GlobalTransactional来管理分布式事务. 因此在订单服务中,我们使用下面这种方 ...
- excel编辑受限的密码保护破解
录制一个宏并且执行: Public Sub 工作表保护密码() Const DBLSPACE As String = vbNewLine & vbNewLine Const AUTHORS A ...
- adb 全局
win10: 我的电脑-右键属性--系统保护--高级--环境变量--选择path--编辑--点击新建 在新建条目下输入 C:\Users\GL\platform-tool--重新打开cmd 测试adb ...
- 【新版】使用 go-cqhttp 扫码登录,一键接入 ChatGPT 机器人到 QQ 群
目录 项目效果 安装 go-cqhttp 虚拟文件 启动 ChatGPT 项目效果 由于 ChatGPT 目前只能在漂亮国使用,所以想要在国内使用 ChatGPT 必然险阻重重 不仅时时刻刻要跟企鹅公 ...
