sp-MVC-ideabaok
直接通过初始化器创建

或者通过创建maven工程在自己添加需要的东西
配置 dispatcher-servlet.xml
包括扫描加载包:
<context:component-scan base-package="com.quan"/>
包括试图解析器:
<!--指定视图解析器-->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<!-- 视图的路径 -->
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/jsp/"/>
<!-- 视图名称后缀 -->
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp"/>
</bean>
web.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"
version="4.0">
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet> <servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
controller
@Controller
@RequestMapping("hello")
public class controller {
@RequestMapping("hi")
public String hi(Model model){
model.addAttribute("msg","quanzhiqiang");
return "hi";
} }
将项目运行在tomcat中(前提是自己要下载tomcat)


@RequestMapping详解
用于映射url到控制器类或一个特定的处理程序方法。可用于类或方法上。用于类上,表示类中的所有响应请求的方法都是以该地址作为父路径
占位符:使用@PathVariable 注释方法参数的值绑定到一个URI模板变量
@RequestMapping("mapping/pp/{p1}/{p2}")
public String hipp(@PathVariable int p1,@PathVariable int p2, Model model){
model.addAttribute("msg",p1 + "==" + p2);
return "hi";
}
路径变量的好处:使路径变得更加简洁;获得参数更加方便,框架会自动进行类型转换。通过路径变量的类型可以约束访问参数,如果类型不一样,则访问不到action,

正则表达式:
@RequestMapping("mapping/repp/{p1:\\d{4}}-{p2:[A-Z]{4}}")
public String hippre(@PathVariable int p1,@PathVariable String p2, Model model){
model.addAttribute("msg",p1 + "==" + p2);
return "hi";
}

多个请求同一个方法
@RequestMapping(value = {"hi","/quan/hi","/zhi/hi","/qiang/hi"})
public String hii(Model model){
model.addAttribute("msg","quanzhiqiang");
return "hi";
}
/*
下面都是同一个结果
http://localhost:8080/untitled_war/hello/qiang/hi
http://localhost:8080/untitled_war/hello/zhi/hi
http://localhost:8080/untitled_war/hello/quan/hi
http://localhost:8080/untitled_war/hello/hi
*/
method属性指定谓词类型
用于约束请求的谓词类型,可以收窄请求范围。指定请求谓词的类型如GET, POST, HEAD, OPTIONS, PUT, PATCH, DELETE, TRACE
//method属性指定谓词类型
@RequestMapping(value = "hiii",method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String hiii(Model model){
model.addAttribute("msg","quanzhiqiang-post");
return "hi";
}


consumes属性指定请求的Content-Type
@RequestMapping 注解的 produces 和 consumes 这两个元素来缩小请求映射类型的范围,达到处理生产和消费对象的目的。
指定处理请求的提交内容类型(Content-Type),例如application/json, text/html,收窄请求范围,如果用户发送的请求内容类型不匹配则方法不会响应请求
// 请求内容类型必须为text/html,注意浏览器默认没有指定Content-type
@RequestMapping(value = "/action8",consumes="text/html")
public String action8(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("message", "请求的提交内容类型(Content-Type)是text/html");
return "foo/index";
}
produces属性指定响应的Content-Type,约束Accept类型
指定返回的内容类型,仅当request请求头中的(Accept)类型中包含该指定类型才返回,方法才处理客户端的请求否则会报406错误
produces = "text/plain" //客户端只接收纯文本
produces = {"text/plain", "application/*"} //客户端接收纯文本与application/*类型的内容
produces = "application/json; charset=UTF-8" //客户端接收json且编码为utf-8
params属性指定请求中必须有特定参数与值
映射请求的参数,收窄请求范围。可以限制客户端发送到服务器的请求参数为某些特定值或不为某些值
//请求的参数必须包含id=215与name不等于abc
@RequestMapping(value = "/action10",params={"id=215","name!=abc"})
public String action10(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("message", "请求的参数必须包含id=215与name不等于abc");
return "foo/index";
}
headers属性指定请求中必须有特定header值
映射请求头部,收窄请求范围。约束客户端发送的请求头部信息中必须包含某个特定的值或不包含某个值,作用范围明显大于前面讲过的几种
//header 必须有什么
@RequestMapping(value = "hiiii",headers = "Host=localhost:8088")
public String hiiii(Model model){
model.addAttribute("msg","quanzhiqiang-post");
return "hi";
}
RequesMapping快捷:
@GetMapping
@PostMapping
@PutMapping
@DeleteMapping
@PatchMapping
请求处理action
Spring MVC中每个控制器中可以定义多个请求处理方法,我们把这种请求处理方法简称为Action,每个请求处理方法可以有多个不同的参数,以及一个多种类型的返回结果。
方法的参数可以是任意基本数据类型,如果方法参数名与http中请求的参数名称相同时会进行自动映射,
//自动参数映射
@RequestMapping("/action0")
public String action0(Model model,int id,String name){
model.addAttribute("msg","name="+name+",id="+id);
return "action";
}
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Action</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>${msg}</h1>
</body>
</html>

自定义数据类型
自定义的数据类型,如一个自定义的POJO对象,Spring MVC会通过反射把请中的参数设置到对象中,转换类型
定义累
package classowner;
public class Acowner {
private String name;
private int id;
private int age;
public Acowner(String name, int id, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.id = id;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "acowner{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", id=" + id +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
//自定义数据类型-对象
@RequestMapping("/ownerac")
public String ownerac(Model model, Acowner acowner){
model.addAttribute("msg",acowner.toString());
return "action"; }

//自动参数映射数组数据类型
//自动参数映射数组数据类型
@RequestMapping("/array")
public String array(Model model,Integer[] num){
model.addAttribute("msg", Arrays.toString(num));
return "action";
}

@RequestParam参数绑定
然自动参数映射很方便,但有些细节是不能处理的,如参数是否为必须参数,名称没有办法指定,参数的默认值就没有有办法做到了。如果使用@RequestParam可以实现请求参数绑定,Spring MVC会自动查找请求中的参数转类型并将与参数进行绑定
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/hll")
public class AnnotateAction {
@RequestMapping("actionone")
public String actionone(Model model, @RequestParam(required = false,defaultValue = "99") int id){
model.addAttribute("msg",id);
return "action";
}
@RequestParam共有4个注解属性,required属性表示是否为必须,默认值为true,如果请求中没有指定的参数会报
异常;defaultValue用于设置参数的默认值,如果不指定值则使用默认值,只能是String类型的。name与value互
为别名关系用于指定参数名称

指定之后,不适用默认的

List与数组绑定基本数据类型
合@RequestParam可以轻松实现
数组
@RequestMapping("actiontwo")
public String actiontwo(Model model,@RequestParam("id") List<String> hll){
model.addAttribute("msg",hll.get(2)+"==="+hll.get(4));
return "action";
}

集合
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="hll/actiontwoform" method="post">
<p>
<label>爱好:</label>
<input type="checkbox" value="15" name="id" />阅读
<input type="checkbox" value="20" name="id" />上网
<input type="checkbox" value="73" name="id" />电游
</p>
<button>提交</button>
</form>
</body>
</html>
controller
@RequestMapping("actiontwoform")
public String actionform(Model model,@RequestParam("id") List<String> hll){
model.addAttribute("msg",hll);
return "action";
}
注意@RequestParam("id")是必须的,因为页面中的表单name的名称为id,所有服务器在收集数据时应该使用id页非ids,如果同名则可以省去。

结果

重定向:
在一个请求处理方法Action中如果返回结果为“index”字符则表示转发到视图index,有时候我们需要重定向,则可以在返回的结果前加上一个前缀“redirect:”,可以重定向到一个指定的页面也可以是另一个action
//重定向到的地方
@RequestMapping("ending")
public String ending(Model model,String msg){
model.addAttribute("msg",msg);
return "hi";
}
//重定向
@RequestMapping("starting")
public String starting(Model model){
model.addAttribute("msg","starting");
return "redirect:ending";
}
starting返回的结果为redirect:ending ,则表示重定向到ending这个请求的处理方法,所有重定向
都是以当前路径为起点,
注意:因为再starting中向model添加了msg的数据,所以回发起两次请求,为了保持action3中的数据Spring MVC自动将数据重写到了url中
hi
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>hihihihi</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>huolala</h1>
<h2>${msg}</h2>
</body>
</html>

实际网页的请求URL会变为下面这个

flash属性:传递更加复杂的数据类型
//利用flash属性
@RequestMapping("ending1")
public String ending1(Model model,Acowner acowner){
model.addAttribute("msg",acowner);
System.out.println(model.containsAttribute("msg"));
return "hi";
}
//重定向
@RequestMapping("starting1")
public String starting1(Model model, RedirectAttributes redirectAttributes){
Acowner acowner =new Acowner("aa",90,30);
//flash属性
redirectAttributes.addFlashAttribute("acowner",acowner);
return "redirect:ending1";
}


转发
str=”forward : 路径” 请求转发到一个页面中
str=”forward : controller的映射” 请求转发到一个controller方法中
数据存在可以直接使用。URL没有变化,
//转发:是不会改变请求的URL,而重定向会
@RequestMapping("ending2")
public String ending2(Model model,String msg){
model.addAttribute("msg",msg);
return "hi";
} @RequestMapping("starting2")
public String starting2(Model model){
model.addAttribute("msg","starting");
return "forward:ending";
}
请求URL:
http://localhost:8080/untitled_war/hll/starting2

@ModelAttribute模型特性
@ModelAttribute可以应用在方法参数上或方法上,他的作用主要是当注解在方法中时会将注解的参数对象添加到Model中;
当注解在请求处理方法Action上时会将该方法变成一个非请求处理的方法,但其它Action被调用时会首先调用该方法。
如果一个控制器类有多个请求处理方法,以及一个有@ModelAttribute注解的方法,则在调用其它Action时会先调用非请求处理的Action,
@ModelAttribute
public String starting4(){
String sententce = "staring first";
System.out.println(sententce);
return sententce;
}

Action的返回值类型,就是视图的类型
视图类型--图片:
@RequestMapping("imageaction")
public String imgaeAction(){
return "imageaction";
}

String
默认如果action返回String,此时的String为视图名称,会去视图解析器的设定的目录下查找,查找的规则是:URL= prefix前缀+视图名称 +suffix后缀组成
//String
@RequestMapping("stringaction")
@ResponseBody
public String stringaction(){
return "not <b>path</b>,but<h1>haha</h1>";
}
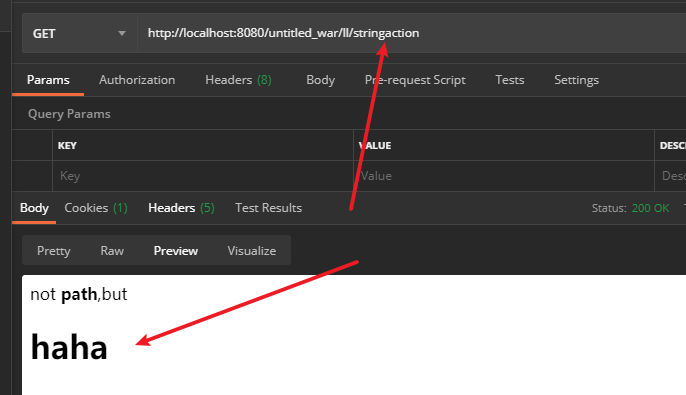
String作为内容输出
注解@ResponseBody ,将内容或对象作为 HTTP 响应正文返回,并调用适合HttpMessageConverter的Adapter转换对象,写入输出流。些时的String不再是路径而是内容,
返回值是void
11111
URL名默认作为视图名
//void,默认会以请求的Mapping的URL,最后加上前后缀
/*
property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/jsp/"/>
<!-- 视图名称后缀 -->
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp"/>
URL= prefix前缀+控制器路径+方法名称 +suffix后缀组成
就是[/WEB-INF/jsp/ll/voidaction.jsp]响应
// */
// @RequestMapping("voidaction")
// public void voidaction1(){
//
// }
// //等同于:
// @RequestMapping("voidaction")
// public String voidaction2(){
// return "ll/voidaction";
// }

222直接响应输出结果
当方法的返回值为void,但输出流中存在输出内容时,则不会去查找视图,而是将输入流中的内容直接响应到客户端,响应的内容类型是纯文本
返回值为Map
//返回值为Map
//与void的差不多 @RequestMapping("Mapperhll")
public Map<String,Integer> mapperHll(){
Map<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("aa",32);
map.put("bb",44);
return map;
}
返回值基本类型
/////////////////////
//返回基本类型
//需要加上注释ReponseBody 不然出现异常
@RequestMapping("fundamental")
@ResponseBody
public Integer fundamental(){
return 99;
}

返回值为Model类型
该接口Model定义在包org.springframework.ui下,model对象会用于页面渲染,视图路径使用方法名,与void类似。
当返值为自定义类型
自定义输出内容
//////////////////////////////
//自定义输出内容
//Excel
@RequestMapping("excel")
@ResponseBody
public String excel(HttpServletResponse response){
response.setHeader("Content-type","application/octet-stream");
response.setHeader("Content-Disposition","attachment;filename=quan.xls");
return "<table><tr><td>Hello</td><td>Excel</td></tr></table>";
}
//Maven项目下HttpServletRequest 或 HttpServletResponse需引用的依赖包:servlet-api.jar

sp-MVC-ideabaok的更多相关文章
- ASP.NET Core 中文文档 第四章 MVC(4.4)依赖注入和控制器
原文: Dependency Injection and Controllers 作者: Steve Smith 翻译: 刘浩杨 校对: 孟帅洋(书缘) ASP.NET Core MVC 控制器应通过 ...
- 6.在MVC中使用泛型仓储模式和依赖注入实现增删查改
原文链接:http://www.c-sharpcorner.com/UploadFile/3d39b4/crud-operations-using-the-generic-repository-pat ...
- .NET、C#和ASP.NET,ASP.NET MVC 四者之间的区别
经常,会有一些人搞不清楚.NET和c#和ASP.NET这三者之间的关系,她们都是什么呢?他们之间有什么关系呢?总结一下 首先:什么是.NET? .NET是微软公司下的一个开发平台,.NET核心就是.N ...
- 爱上MVC~图表的使用Chart
回到目录 图表在一个系统中是必须的,MVC架构把它当然是一个扩展集成了进来,通过简单的几句话就可以生成一个风格多样的图表,这给报表的开发带来了很大的方便,大叔的项目中也做了一个测试,把主要的代码贴出来 ...
- 4、ASP.NET MVC入门到精通——NHibernate构建一个ASP.NET MVC应用程序
下周就去办理离职手续了,之前没有使用过NHibernate,只知道NHibernate是一种ORM框架,但是听说新公司是使用NHibernate在做项目,所以,我就网上找资料学习一下NHibernat ...
- 8、ASP.NET MVC入门到精通——View(视图)
本系列目录:ASP.NET MVC4入门到精通系列目录汇总 View视图职责是向用户提供界面.负责根据提供的模型数据,生成准备提供给用户的格式界面. 支持多种视图引擎(Razor和ASPX视图引擎是官 ...
- 15、ASP.NET MVC入门到精通——MVC-路由
本系列目录:ASP.NET MVC4入门到精通系列目录汇总 Routing(路由) – URL url 作为广泛使用的Web用户接口,需要被重视 好的Url应该满足如下条件: URL应为获取某种资源提 ...
- Spring MVC配置
web配置 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><web-app xmlns:xsi="ht ...
- MVC中Action参数绑定的过程
一.题外话 上一篇:MVC中Action的执行过程 ControllerContext 封装有了与指定的 RouteBase 和 ControllerBase 实例匹配的 HTTP 请求的信息. 二. ...
- ASP.NET MVC系列:添加控制器
基于MVC的应用程序包含三个部分 Models(模型):对应用程序的数据进行处理 Views(视图):动态生成HTML,显示数据 Controllers(控制器):应用程序中处理用户交互的部分,处理浏 ...
随机推荐
- 内网流量操控---pingtunnel建立icmp隧道
一.pingtunnel工作原理 在上面的实验环境中,我们将分别在攻击机kali 2020和webserver上部署pingtunnel工具,在量太主机之间实现icmp隧道,再在kali2020上监听 ...
- 【C# .Net GC】GC初始化设置 和GcSetting
相关的类 GcSetting 类 GCLargeObjectHeapCompactionMode 枚举 GCLargeObjectHeapCompactionMode 枚举 属性的值 GCSettin ...
- 【C# Task】理解Task中的ConfigureAwait配置同步上下文
原文:https://devblogs.microsoft.com/dotnet/configureawait-faq/ 作者:Stephen 翻译:xiaoxiaotank 静下心来,你一定会有收获 ...
- 【基础概念】匹夫细说C#:不是“栈类型”的值类型,从生命周期聊存储位置
转载地址 https://www.cnblogs.com/murongxiaopifu/p/4419040.html 0x00 前言: 匹夫在日常和别人交流的时候,常常会发现一旦讨论涉及到" ...
- Ng ML笔记
目录 一.线性回归 1,假设函数.代价函数,梯度下降 2,特征处理 3,代价函数和学习速率 4,特征和多项式回归 5,正规方程 二.逻辑回归(Logistic Regression,LR) 1,假设函 ...
- weblogic集群自动批量化补丁升级
转至:http://blog.itpub.net/28833846/viewspace-2726722/ 一.前言介绍 Weblogic是一种基于J2EE架构的中间件,用于开发.集成.部署和管理大型分 ...
- Codeforces Round #769 (Div. 2)D,E
D.New Year Concert 传送门 题目大意: 一个长为 N ( 1 ≤ N ≤ 2 × 1 0 5 ) N(1\leq N\leq2\times 10^5) N(1≤N≤2×105)的序列 ...
- Docker入坑系列(二)
Docker入坑系列(二) 上一篇我们为Docker创造了一个良好的生活环境,这一篇我们就开始让Docker活起来. 安装Docker ok,原文地址在这里. 当然,我只是自己翻译了一下而已- -跟着 ...
- Leaflet:Marker、Popup类
Marker.Popup.Tooltip类都是继承自Layer类:Event与Layer Marker 1.用例 L.marker([41,123]).addTo(map); 2.实例化 L.mark ...
- selenium在爬虫中的使用
一. selenium概述 1.1 定义 Selenium是一个Web的自动化测试工具,最初是为网站自动化测试而开发的,Selenium 可以直接调用浏览器,它支持所有主流的浏览器(包括Phantom ...
