二、Android应用的界面编程(二)布局管理器
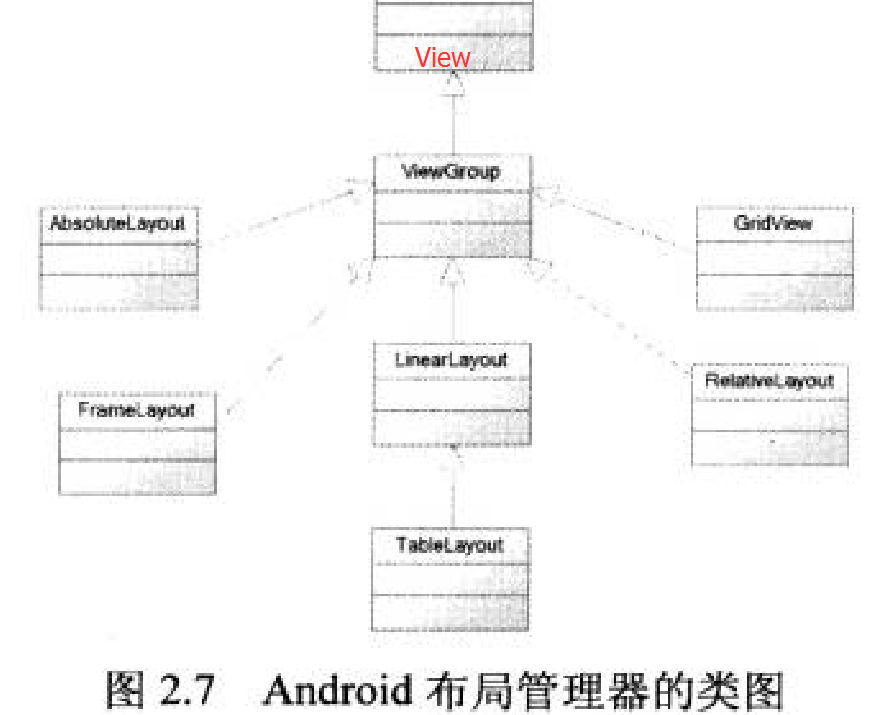
一、线性布局
所有布局都可以作为容器类使用,因此可以调用多个重载的addView()向布局管理器中添加组件。
实际上,我们完全可以用一个布局管理器嵌套到其他布局管理器中---因为布局管理器也继承了
View,也可以作为普通UI组件使用。
【LinearLayout的常用XML属性及相关方法】
android:baselineAligned setBaselineAligned(boolean)
该属性设置为false,将会阻止该布局管理器与它的子元素的基线对齐。
android:divider setDividerDrawable(Drawable)
设置垂直布局时两个按钮之间的分割条
android:gravity setGravity(int)
设置布局管理器内组件的对其方式,该属性支持top, buttom, left, right, center_vertical,
fill_vertical, center_horizontal, fill_horizontal, center, fill, clip_vertical,
clip_horizontal几个属性值,也可以同时指定多种对其方式的组合,中间用|隔开。
android:measureWithLargestChild setMeasureWithLargestChildEnabled(boolean)
当属性设置为true时,所有带权重的子元素都会具有最大子元素的最小尺寸。
android:orientation setOrientation(int)
设置布局管理器内组件的排列方式,可以设置为horizontal, vertical两个之一。
LinearLayout包含的所有子元素都受LinearLayout.LayoutParams控制。因此LinearLayout包含的
子元素可以额外指定以下属性。
android:layout_gravity 指定该子元素在LinearLayout中的对齐方式。
android:layout_weight 指定该子元素在LinearLayout中所占的权重。
二、表格布局
TableLayout,继承了LinearLayout。表格布局采用行、列的形式来管理UI组件。
在表格布局管理器中,可以为单元格设置如下三种行为方式。
# Shrinkable:如果某个列被设为Shrinkable,那么该列的所有单元格的宽度可以被收缩,以保证该表格能适应父容器的宽度。
# Stretchable:如果某个列被设为Stretchable,那么该列的所有单元格的宽度可以被拉伸,以保证组件能完全填满表格空余空间。
# Collapsed:如果某个列被设为Collapsed,那么该列的所有单元格会被隐藏。
除了完全可以支持LinearLayout所支持的全部XML属性外,还支持以下属性。
【TableLayout的常用XML属性及相关方法】
android:collapseColumns setColumnCollapsed(int, boolean)
设置需要被隐藏的列的列序号。多个列序号之间用逗号隔开。
android:shrinkColumns setShrinkAllColumns(boolean)
设置允许被收缩的列的列序号。多个列序号之间用逗号隔开。
android:stretchColumns setStretchAllColumns(boolean)
设置允许被拉伸的列的列序号。多个列序号之间用逗号隔开。
范例:丰富的表格布局
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" > <!-- 定义第一个表格布局,指定第2列允许收缩,第3列允许拉伸 -->
<TableLayout
android:id="@+id/TableLayout04"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:shrinkColumns="1"
android:stretchColumns="2" > <!-- 直接添加按钮,它自己会占一行 -->
<Button
android:id="@+id/ok1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="独自一行的按钮" /> <!-- 添加一个表格行 -->
<TableRow> <!-- 为该表格行添加3个按钮 -->
<Button
android:id="@+id/ok2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="普通按钮" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/ok3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="收缩的按钮" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/ok4"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="拉伸的按钮" />
</TableRow>
</TableLayout> <!-- 定义第二个表格布局 ,指定第二列隐藏 -->
<TableLayout
android:id="@+id/TableLayout02"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:collapseColumns="1" > <!-- 直接添加按钮,它自己会占一行 -->
<Button
android:id="@+id/ok5"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text=" 独自一行的按钮 " />
<!-- 定义一个表格行 -->
<TableRow> <!-- 为该表格行添加3个按钮 -->
<Button
android:id="@+id/ok6"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="普通按钮1" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/ok7"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="被隐藏的按钮" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/ok8"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="普通按钮 3" />
</TableRow>
</TableLayout> <!-- 定义第三个表格布局 ,指定第2、3两列可以被拉伸 -->
<TableLayout
android:id="@+id/TableLayout03"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:stretchColumns="1,2" > <!-- 直接添加按钮,它自己会占一行 -->
<Button
android:id="@+id/ok9"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="独自一行的按钮" />
<!-- 定义一个表格行 -->
<TableRow>
<!-- 为该表格行添加3个按钮 -->
<Button
android:id="@+id/ok10"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="普通按钮" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/ok11"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="拉伸的按钮" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/ok12"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="拉伸的按钮" />
</TableRow> <!-- 定义一个表格行 -->
<TableRow>
<!-- 为该表格行添加2个按钮 -->
<Button
android:id="@+id/ok13"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="普通按钮" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/ok14"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="拉伸的按钮" />
</TableRow>
</TableLayout> </LinearLayout>

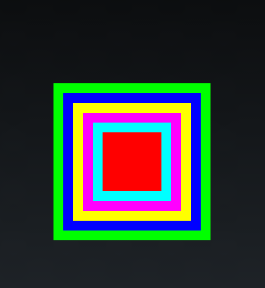
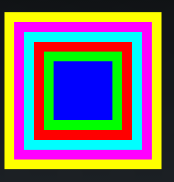
三、桢布局
FrameLayout。直接继承了ViewGroup组件。
桢布局容器为每个加入其中的组件创建一个空白的区域(称为一桢),每个子组件占据一桢,
这些桢都会根据gravity属性执行自动对齐。桢布局都是把组件一个个叠加在一起。
【FrameLayout的常用XML属性及相关方法】
android:foreground setForeground(Drawable)
设置该桢布局容器的前景图像
android:foregroundGravity setForegroundGravity(int)
定义绘制前景图像的gravity属性。
范例:霓虹灯效果
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<FrameLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent" > <!--
依次定义6个TextView,先定义的TextView位于底层
后定义的TextView位于上层
-->
<TextView
android:id="@+id/view01"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:background="#f00"
android:height="320px"
android:width="320px" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/view02"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:background="#0f0"
android:height="280px"
android:width="280px" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/view03"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:background="#00f"
android:height="240px"
android:width="240px" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/view04"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:background="#ff0"
android:height="200px"
android:width="200px" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/view05"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:background="#f0f"
android:height="160px"
android:width="160px" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/view06"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:background="#0ff"
android:height="120px"
android:width="120px" />
</FrameLayout>
import java.util.Timer;
import java.util.TimerTask;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.os.Message;
import android.widget.TextView; public class FrameLayoutTest extends Activity {
private int currentColor = 0;
// 定义一个颜色数组
final int[] colors = new int[] { R.color.color1, R.color.color2,
R.color.color3, R.color.color4, R.color.color5, R.color.color6 };
final int[] names = new int[] { R.id.view01, R.id.view02, R.id.view03,
R.id.view04, R.id.view05, R.id.view06 };
TextView[] views = new TextView[names.length];
Handler handler = new Handler() {
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
// 表明消息来自本程序所发送
if (msg.what == 0x123) {
for (int i = 0; i < names.length; i++) {
views[i].setBackgroundResource(colors[(i + currentColor)
% names.length]);
}
currentColor++;
}
super.handleMessage(msg);
}
}; @Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
for (int i = 0; i < names.length; i++) {
views[i] = (TextView) findViewById(names[i]);
} // 定义一个线程周期性的改变currentColor变量值
new Timer().schedule(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
// 发送一条空消息通知系统改变6个TextView组件的背景色
handler.sendEmptyMessage(0x123);
}
}, 0, 200);
}
}
四、相对布局 RelativeLayout
相对布局容器内子组件的位置总是相对兄弟组件,父容器来决定的。
【RelativeLayout的XML属性及相关方法说明】
android:gravity setGravity(int) 设置该布局容器内各子组件的对其方式。
android:ignoreGravity setIgnoreGravity(int) 设置哪个组件不受gravity属性的影响。
【RelativeLayout.LayoutParams里猪能设为boolean值的属性】
layout_alignParentBottom 当前控件低端与父控件的低端对齐(重合)
layout_alignParentLeft 当前控件左端与父控件的左端对齐(重合)
layout_alignParentRight 当前控件右端与父控件的右端对齐(重合)
layout_alignParentTop 当前控件上端与父控件的上端对齐(重合)
layout_centerHorizontal 当前控件位于父控件的横向中间位置(水平方向上的中间)
layout_centerInParent 当前控件位于父控件的纵横向中间位置(垂直方向上的中间)
layout_centerVertical 当前控件位于父控件的纵向中间位置(平面上的正中间)
【RelativeLayout.LayoutParams里只能设为其他UI组件ID的属性】
layout_above 使当前控件位于给出id控件的上方
layout_below 使当前控件位于给出id控件的下方
layout_toLeftOf 使当前控件位于给出id控件的左侧
layout_toRightOf 使当前控件位于给出id控件的右侧
layout_alignBottom 使当前控件与给出id控件的底部部重合(注意可用和给出id控件来对齐)
layout_alignLeft 使当前控件与给出id控件的左边重合
layout_alignRight 使当前控件与给出id控件的右边重合
layout_alignTop 使当前控件与给出id控件的顶部重合
layout_alignBaseline 使当前控件的BaseLine与给出id控件t的BaseLine重合,这个主要用于
Label或者其他包含文本的widgets。
五、绝对布局 AbsoluteLayout
layout_x:指定该子组件的X坐标。
layout_y:指定该子组件的Y坐标。
六、Android4.0新增的网格布局
GridLayout的作用类似于HTML中的table标签。它把整个容器划分成rows X columns个网格。
每个网格可以放置一个组件。除此之外,也可以设置一个组件横跨多少列。一个组件纵跨多少行。
GridLayout提供了setRowCount(int)和setColumnCount(int)来控制该网格的行数量和列数量。
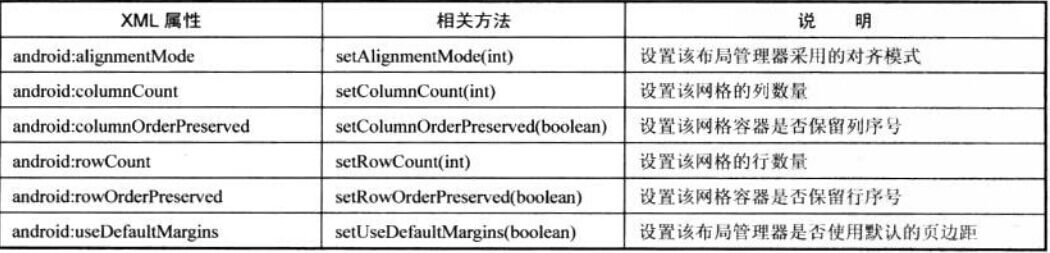
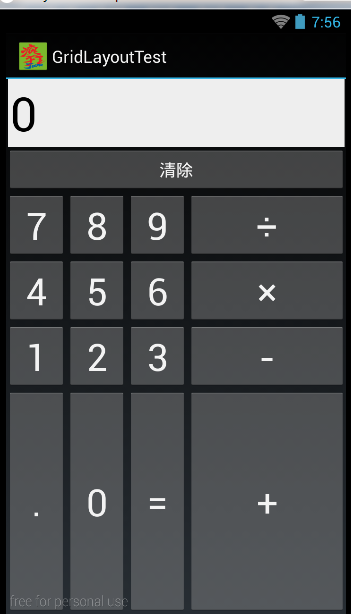
范例:计算器界面
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<GridLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/root"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:columnCount="4"
android:rowCount="6" > <!--
定义一个横跨4列的文本框,
并设置该文本框的前景色、背景色等属性
--> <TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_columnSpan="4"
android:layout_gravity="right"
android:layout_marginLeft="4px"
android:layout_marginRight="4px"
android:background="#eee"
android:padding="5px"
android:text="0"
android:textColor="#000"
android:textSize="50sp" />
<!-- 定义一个横跨4列的按钮 --> <Button
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_columnSpan="4"
android:text="清除" /> </GridLayout>
public class GridLayoutTest extends Activity {
GridLayout gridLayout;
// 定义16个按钮的文本
String[] chars = new String[] { "7", "8", "9", "÷", "4", "5", "6", "×",
"1", "2", "3", "-", ".", "0", "=", "+" };
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
gridLayout = (GridLayout) findViewById(R.id.root);
for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; i++) {
Button bn = new Button(this);
bn.setText(chars[i]);
// 设置该按钮的字体大小
bn.setTextSize(40);
// 指定该组件所在的行
GridLayout.Spec rowSpec = GridLayout.spec(i / 4 + 2);
// 指定该组件所在列
GridLayout.Spec columnSpec = GridLayout.spec(i % 4);
GridLayout.LayoutParams params = new GridLayout.LayoutParams(
rowSpec, columnSpec);
// 指定该组件占满父容器
params.setGravity(Gravity.FILL);
gridLayout.addView(bn, params);
}
}
}

二、Android应用的界面编程(二)布局管理器的更多相关文章
- 【详细】Android入门到放弃篇-YES OR NO-》各种UI组件,布局管理器,单元Activity
问:达叔,你放弃了吗? 答:不,放弃是不可能的,丢了Android,你会心疼吗?如果别人把你丢掉,你是痛苦呢?还是痛苦呢?~ 引导语 有人说,爱上一个人是痛苦的,有人说,喜欢一个人是幸福的. 人与人之 ...
- 一步一步学android之布局管理器——LinearLayout
线性布局是最基本的一种布局,在基本控件篇幅中用到的都是LinearLayout,线性布局有两种方式,前面也有用到,一种是垂直的(vertical),一种是水平的(horizontal).我们同样来看下 ...
- 物联网大赛 - Android学习笔记(二)Andriod 应用界面编程
学习目标: Android的程序界面和View组件 View组件和ViewGroup组件 常见的布局管理器 文本框组件TextView和EditView 按钮组件Button 和ImageButton ...
- 二、Android应用的界面编程(一)界面编程与视图(View)组件
Android应用的绝大部分UI组件都放在android.widget包及其子包.android.view包及其子包中,Android应用的所有UI组件都继承了View类.它代表一个空白的矩形区域.V ...
- android中常用的布局管理器(二)
接上篇博客 (3)LinearLayout 线性布局管理器 线性布局管理器是将放入其中的组件按照垂直或水平方向来布局,每一行或每一列只能放一个组件,并且不会换行,当组件排列到窗体的边缘后,后面 ...
- android应用的界面编程----View与ViewGroup的概念
1 UI OverView Android中所有的UI元素都是通过View与ViewGroup来构建的,View是指屏幕中一块可与用户进行交互的空白,类似于java界面编程中的JPanel.为了界面布 ...
- [置顶] Android布局管理器 - 详细解析布局实现
布局管理器都是以ViewGroup为基类派生出来的; 使用布局管理器可以适配不同手机屏幕的分辨率,尺寸大小; 布局管理器之间的继承关系 : 在上面的UML图中可以看出, 绝对布局 帧布局 网格布局 相 ...
- 【Android 应用开发】AndroidUI设计之 布局管理器 - 详细解析布局实现
写完博客的总结 : 以前没有弄清楚的概念清晰化 父容器与本容器属性 : android_layout...属性是本容器的属性, 定义在这个布局管理器的LayoutParams内部类中, 每个布局管理器 ...
- android的布局管理器
理论上通过setContentView(view)能够把一个view设置到activity中,但当你有很多个view控件的时候,就需要用android的布局管理器来管理view控件了. android ...
随机推荐
- Netty4 initAndRegister 解析
我们从框架的应用层面来分析,NioEventLoopGroup在netty中的使用. 这是我们需要配置的地方. 紧接着我们进入netty的运行中.ServerBootstrap.bind(PORT); ...
- hdu1698 Just a Hook (线段树区间更新 懒惰标记)
Just a Hook Time Limit: 4000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others) Tota ...
- Django——如何使用Template以及如何向template传递变量
如何使用模板系统 在Python代码中使用Django模板的最基本方式如下: 可以用原始的模板代码字符串创建一个 Template 对象, Django同样支持用指定模板文件路径的方式来创建 Temp ...
- cocos2d-x OpenGL ES 坐标系总结
很多教程都说cocos2d-x OpenGL ES世界坐标系原点在左下角,但至于为什么在左下角却从来没有人提过,这导致大部分人觉得这是OpenGL ES的规定,事实上这是错的.OpenGL ES的坐标 ...
- 帮朋友转发招聘信息 南京知名互联网公司招聘java、测试、前端,具体私聊
一.java开发 1.5年及以上J2EE方向开发经验 2.精通spring等开源框架 3.熟悉html.javascript.css.jsp/freemarker.jquery的使用 4.熟悉使用my ...
- Android模拟器Genymotion安装apk
一.下载apk 选择你需要安装的apk进行下载,下载完以后放在与adb.exe同一目录下: 看我的 二.安装apk遇到的问题 开启Genymotion模拟器,然后cmd到你的platform-tool ...
- curl Error : maximum redirects followed , 这种问题的一种原因 .
在stack overflow 上查找到有些网站上需要返回一些cookie的,所以当我们curl当相应的网站时,必须要将返回的cookie保存起来. $cookie = tempnam (" ...
- jquery ajax 脑图
- Linux Chrome Tab 标题 乱码
1. 刚装完ubuntu 14.04 英文版, 又装了google chrome 浏览器. 2. 打开chrome浏览器,发现tab也没的标题是乱码: 3. 而系统自带的firefox却没有这个问题, ...
- Atitit atiMail atiDns新特性 v2 q39
Atitit atiMail atiDns新特性 v2 q39 V1 实现了基础的功能 V2 重构..使用自然语言的方式 c.According_to_the_domain_name(&quo ...
