ural 2016 Magic and Science
2016. Magic and Science
Memory limit: 64 MB
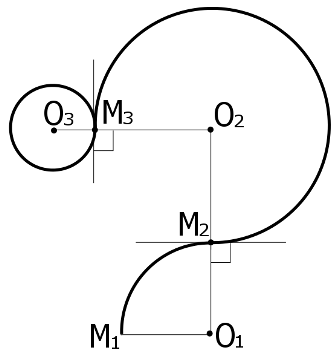
- At this moment the magion has to be at the point of the circle omega1 which is the nearest to O2. Let’s denote it M2.
- The magion has to be at the point M2 for the first time, i. e. a new bundle will appear before the magion makes the full circle along omega1.
Input
Output
Sample
| input | output |
|---|---|
1 |
35.3929206868 |
Notes
from point (0,0,0) to point (4,0,2): an arc with measure equal to arcsin(0.8) of the circle with the radius 5;
from point (4,0,2) to point (20,16,2): a quarter of the circle with the radius 16;
from point (20,16,2) to point (20,16,2): a full circle with the radius 1.
Problem Source: NEERC 2014, Eastern subregional contest
All submissions (421) All accepted submissions (38) Solutions rating (14)
ural 2016 Magic and Science的更多相关文章
- (转)Is attacking machine learning easier than defending it?
转自:http://www.cleverhans.io/security/privacy/ml/2017/02/15/why-attacking-machine-learning-is-easier- ...
- 防CSRF攻击:一场由重复提交的问题引发的前端后端测试口水战
重复提交,这是一直以来都会存在的问题,当在网站某个接口调用缓慢的时候就会有可能引起表单重复提交的问题,不论form提交,还是ajax提交都会有这样的问题,最近在某社交app上看到这么一幕,这个团队没有 ...
- 【转载】【翻译】Breaking things is easy///机器学习中安全与隐私问题(对抗性攻击)
原文:Breaking things is easy 译文:机器学习中安全与隐私问题(对抗性攻击) 我是通过Infaraway的那篇博文才发现cleverhans-blog的博客的,这是一个很有意思的 ...
- SpringBoot入门系列(七)Spring Boot整合Redis缓存
前面介绍了Spring Boot 中的整合Mybatis并实现增删改查,.不清楚的朋友可以看看之前的文章:https://www.cnblogs.com/zhangweizhong/category/ ...
- 2016中国大学生程序设计竞赛 - 网络选拔赛 C. Magic boy Bi Luo with his excited tree
Magic boy Bi Luo with his excited tree Problem Description Bi Luo is a magic boy, he also has a migi ...
- URAL - 1920 Titan Ruins: the Infinite Power of Magic(乱搞)
搞死人的题目,,, 就是在n*n的方格中找路径长度为L的回路. 开始的思路值适合n为偶数的情况,而忽视了奇数的case,所以wa了一次. 然后找奇数case的策略,代码从70多行变成了100多,然后改 ...
- URAL 1920 Titan Ruins: the Infinite Power of Magic
大意: 有一张N*N的网格,你每次可以走一步,每格只能走一次,有没有一种方法让走了L步后回到一个距原点1步远的格子? 没有输出Unsuitable device,否则输出Overwhelming p ...
- URAL 1727. Znaika's Magic Numbers(数学 vector)
主题链接:http://acm.timus.ru/problem.aspx?space=1&num=1727 1727. Znaika's Magic Numbers Time limit: ...
- Ural 2003: Simple Magic(数论&思维)
Do you think that magic is simple? That some hand-waving and muttering incomprehensible blubber is e ...
随机推荐
- python并发之IO模型(二)
blocking IO (阻塞IO) 在linux中,默认情况下所有的socket都是blocking,一个典型的读操作流程大概是这样: 当用户进程调用了recvfrom这个系统调用,kernel就开 ...
- EM算法(expectation maximization)
EM算法简述 EM算法是一种迭代算法,主要用于含有隐变量的概率模型参数的极大似然估计,或极大后验概率估计.EM算法的每次迭代由两步完成: E步,求期望 M步,求极大. EM算法的引入 如果概率模型的变 ...
- Java基础—抽象类和接口
1.抽象类 在Java语言中使用abstrac关键字来定义抽象类和抽象方法,抽象方法没有定义,方法名后面直接跟一个分号,而不是花括号. public abstract class Employee { ...
- ABAP权限检查,TCode与权限对象进行关联
一.确认权限对象,和关联字段: Tcode:SU21 维护权限对象例如"M_MSEG_WMB",它关联字段为'WERKS'M_MSEG_WMB 物料凭证:工厂 二.在ABAP代码中 ...
- TLS and SSL
SSL:(Secure Socket Layer,安全套接字层),位于可靠的面向连接的网络层协议和应用层协议之间的一种协议层.SSL通过互相认证.使用数字签名确保完整性.使用加密确保私密性,以实现客户 ...
- 2.4 使用ARDUINO控制MC20进行GPS数据的获取和解析
需要准备的硬件 MC20开发板 1个 https://item.taobao.com/item.htm?id=562661881042 GSM/GPRS天线 1根 https://item.taoba ...
- django事物回滚
往数据库写入数据时,不经意间就会写入不完整的数据,我们称之为脏数据.事务管理(transaction)可以防止这种情况发生.事务管理一旦检测到写入异常,会执行回滚操作,即要么写入完整的数据,要么不写入 ...
- C语言预处理命令的使用
cppreference.com -> 预处理命令 -> 详细说明 预处理命令 #,## # 和 ## 操作符是和#define宏使用的. 使用# 使在#后的首个参数返回为一个带引号的字符 ...
- Hibernate一对多、多对一关联
一对多.多对一关联:在多方加外键 示例:Group(一方)和User(多方),一个Group可以有多个User,每个User只能属于一个Group 多对一单向关联 在User(多方)中建Group ...
- I.MX6Q(TQIMX6Q/TQE9)学习笔记——U-Boot移植
其实Freescale的BSP移植文档已经将u-boot的移植步骤讲述的非常详细了,但为了以后方便查阅,还是按照自己的理解记录在这里. 获取源码 根据前一篇文章搭建好LTIB环境后就可以非常方便的导出 ...