Learn Python the Hard Way,ex37-2
本练习为复习python的符号和关键字
数据类型有:True False None Strings numbers floats lists dict tuple set
"""
Data Types
True False None Strings numbers floats lists dict tuple set
"""
dicts = {'1':'apple', '2':"pear", 3:"bear", 4:5, 'aa':6.1, 'bb':1.1, 5.1:"cc", 6.1:"beach"}
lists = ['1', '2', 'a', 'afds', 3, 463]
tuples = ('1', '2', 'a', 'afds', 3, 463)
sets = {'1', '2', 'a', 'afds', 3, 463}
string = "strings"
boo1, boo2 = True, False
num1, num2, num3, num4 = 9, 0.5, complex(1, 0), complex(0, 5)
bit1, bit2 = 0x11, 0x12 # number: real(int float) complex
print(type(boo1))
print(type(None))
print(type(string))
print(type(num1))
print(type(num2))
print(type(num3))
print(type(lists))
print(type(dicts))
print(type(tuples))
print(type(sets))
输出结果:
<class 'bool'>
<class 'NoneType'>
<class 'str'>
<class 'int'>
<class 'float'>
<class 'complex'>
<class 'list'>
<class 'dict'>
<class 'tuple'>
<class 'set'>
String Escape Sequences:\\ \' \'' \a \b \f \n \r \t \v
Operators:+ - * ** / // % < > <= >= == != <> () [] {} @ , : . = ; += -= *= /= //= %= **+
其中:() [] {} @ , : . ;现不知怎么使用
string = "strings"
num1, num2, num3, num4 = 9, 0.5, complex(1, 0), complex(0, 5)
bit1, bit2 = 0x11, 0x12 #operators
print("1*%5d" % (num1 + num2)) # addition
print("2*%3.1f, %3.1F" % ((num1 - num2), (num1 - num2))) # subtraction
print("3*", num3 * num4) # multiplication
print("4*", num3 / num4) # division
print("5*%e, %E" % ((num1 % num2), (num1 % num2))) # remainder
print("6*", num1 // num2) # x//y "divmod(x,y)[0] * y + x % y"
print("7*", num1 ** num2) # pow
print("8*", num1 < num2) # less-than
print("9*", num1 <= num2) # less-than-equal
print("1", num1 > num2) # greater-than
print("2", num1 >= num2) # greater-than-equal
print("3", num1 != num2) # un-equal
#print("4", num1 <> num2) # un-equal
print("5", num1 == num2) # equal
print("6-%g, %G" % ((num1 and num2), (num1 and num2))) # and
print("7", num1 or num2) # or
print("8", not num2) # not
print("9, 10-%d, 8-o%o, 16-0x%x" % ((bit1 & bit2), (bit1 & bit2), (bit1 & bit2))) # and
print("ar-%r, u-%-7u, X-%X" % ((bit1 | bit2), (bit1 | bit2), (bit1 | bit2))) # or
print("b%%", bit1 ^ bit2) # not
print("c", bit2>>1) # shift right
print("d", bit2<<1) # shift left
print("*%s" % string)
print("*%c" % string[0]) #binary operation
num1 += num2
print("e", num1)
num1 -= num2
print("f", num1)
num1 *= num2
print("g", num1)
num1 /= num2
print("h", num1)
num1 //= num2
print("i", num1)
num1 **= num2
print("j", num1)
bit1 >>= 1
print("k", bit1)
bit1 <<= 1
print("l", bit1)
bit1 &= bit2
print("m", bit1)
bit1 |= bit2
print("n", bit1)
bit1 ^= bit2
print("o", bit1)
输出结果
1* 9
2*8.5, 8.5
3* 5j
4* -0.2j
5*0.000000e+00, 0.000000E+00
6* 18.0
7* 3.0
8* False
9* False
1 True
2 True
3 True
5 False
6-0.5, 0.5
7 9
8 False
9, 10-16, 8-o20, 16-0x10
ar-19, u-19 , X-13
b%% 3
c 9
d 36
*strings
*s
e 9.5
f 9.0
g 4.5
h 9.0
i 18.0
j 4.242640687119285
k 8
l 16
m 16
n 18
o 0
String Formats:%d %i %o %u %x %X %e %E %f %F %g %G %c %r %s %%
string = "strings"
#String Escape Sequence
print("p-" + string + '\\' + string)
print("q-" + string + '\'' + string)
print("r-" + string + '\"' + string)
print("s-" + string + '\a' + string)
print("t-" + string + '\b' + string)
print("u-" + string + '\f' + string)
print("v-" + string + '\n' + string)
print("w-" + string + '\r' + string)
print("x-" + string + '\t' + string)
print("y-" + string + '\v' + string)
输出结果:
p-strings\strings
q-strings'strings
r-strings"strings
s-stringsstrings
t-stringstrings
u-stringsstrings
v-strings
strings
stringsgs
x-strings strings
y-stringsstrings
tuple:元组 tuple(iterable=(), /)
If no argument is given, the constructor returns an empty tuple.
| If iterable is specified the tuple is initialized from iterable's items.
| If the argument is a tuple, the return value is the same object.
tuples = ('1', '2', 3, 4, 'aa', 'bb', 5.1, 6.1,'1')
#output
print(tuples)
print(tuples[0:3])
for i in range(len(tuples)):
print(tuples[i])
#functions
print(tuples.count('1')) #Return number of occurrences of value.
print(tuples.index(3)) #Return first index of value.
输出结果:
('1', '2', 3, 4, 'aa', 'bb', 5.1, 6.1, '1')
('1', '2', 3)
1
2
3
4
aa
bb
5.1
6.1
1
2
2
list列表
If no argument is given, the constructor creates a new empty list.
| The argument must be an iterable if specified.
lists = ['1', '3', 5, 3]
#select
print(lists)
print(lists[0:3])
print(lists.index(3)) # Return first index of value.
['1', '3', 5, 3]
['1', '3', 5]
3
#+(append\copy\insert\extend)
lists.append('3') #+ Append object to the end of the list.
print(lists)
lists1 = lists.copy() #++ Return a shallow copy of the list.
print(lists1)
lists.insert(0, 'aas') #+ Insert object before index.
print(lists)
lists.extend('te') #+* Extend list by appending elements from the iterable.
print(lists)
['1', '3', 5, 3, '3']
['1', '3', 5, 3, '3']
['aas', '1', '3', 5, 3, '3']
['aas', '1', '3', 5, 3, '3', 't', 'e']
#-(remove\pop\clear)
lists.remove('aas') #- Remove first occurrence of value.
print(lists)
lists.pop(-3) #- Remove and return item at index (default last).
print(lists)
lists.clear() #- Remove all items from list.
print(lists)
['1', '3', 5, 3, '3', 't', 'e']
['1', '3', 5, 3, 't', 'e']
[]
lists.extend('temp')
#sort
lists.reverse()
print(lists) # Reverse *IN PLACE*.
lists.sort()
print(lists) #Sort the list in ascending order and return None
['p', 'm', 'e', 't']
['e', 'm', 'p', 't']
#others
print(lists.count('e'))
1
set(集合): Build an unordered collection of unique elements.
sets = {'4', 3, 2, 'aa', 'bb'}
sets1 = {'7', '4', 3, 2, 'cc', 'dd'}
# select
print(sets)
{'aa', 2, 3, '4', 'bb'}
# new(copy\difference)
sets2 = sets.copy() #+ Return a shallow copy of a set.
print(sets2)
sets3 = sets1.difference(sets) # Return the difference of two or more sets as a new set.
print(sets3)
set4 = sets1.intersection(sets) # Return the intersection of two sets as a new set.
print(set4)
set5 = sets1.union(sets) # Return the union of sets as a new set.
print(set5)
set5 = sets1.symmetric_difference(sets) # Return the symmetric difference of two sets as a new set.
print(set5)
{'aa', 2, 3, '4', 'bb'}
{'cc', 'dd', '7'}
{'4', 2, 3}
{2, 3, 'dd', '7', 'aa', '4', 'bb', 'cc'}\
{'bb', 'cc', 'dd', 'aa', '7'}
# +(add)
sets.add('ee') #+ Add an element to a set.
print(sets)
{'aa', 2, 3, '4', 'bb', 'ee'}
# update(difference_update)
sets3.difference_update(sets) # Remove all elements of another set from this set.
print(sets3)
# update(difference_update)
sets3.intersection_update(sets) # Update a set with the intersection of itself and another.
print(sets3)
sets3.symmetric_difference_update(sets) # Update a set with the symmetric difference of itself and another.
print(sets3)
{'7', 'dd', 'cc'}
set()
{2, 3, '4', 'ee', 'bb', 'aa'}
# -(discard\clear)
sets2.remove('aa') #- Remove an element from a set if it is a member. ERROEKEY
print(sets2)
sets2.discard('aa') #- Remove an element from a set if it is a member.
print(sets2)
sets2.clear() #- Remove all elements from this set.
print(sets2)
{2, 3, '4', 'bb'}
set()
# other
print(sets1.isdisjoint(sets)) # Return True if two sets have a null intersection.
print(sets1.isdisjoint(sets)) # Report whether another set contains this set.
print(sets1.issuperset(sets)) # Report whether this set contains another set.
False
False
False
dict 字典
dicts = {1:'a', 2:'ss', 'apple':'A', 'bear':'D'}
dicts1 = {4:'d', 2:'r', 'beach':3, 'bear':'D'}
# new(fromkeys\copy)
dicts2 = dicts.fromkeys(dicts, 'default') # Create a new dictionary with keys from iterable and values set to value.
print(dicts2)
dict3 = dicts.copy() # D.copy() -> a shallow copy of D
print(dict3)
{1: 'default', 2: 'default', 'apple': 'default', 'bear': 'default'}
{1: 'a', 2: 'ss', 'apple': 'A', 'bear': 'D'}
# select(copy\get\items\keys\values)
print(dicts.get(1)) # Return the value for key if key is in the dictionary, else default.
print(dicts.items()) # D.items() -> a set-like object providing a view on D's items
print(dicts.keys()) # D.keys() -> a set-like object providing a view on D's keys
print(dicts.values()) # D.values() -> an object providing a view on D's values
a
dict_items([(1, 'a'), (2, 'ss'), ('apple', 'A'), ('bear', 'D')])
dict_keys([1, 2, 'apple', 'bear'])
dict_values(['a', 'ss', 'A', 'D'])
# +(setdefault)
print(dicts.setdefault(3, 'bb')) # Return the value for key if key is in the dictionary, else default.
print(dicts) # Insert key with a value of default if key is not in the dictionary.
bb
{1: 'a', 2: 'ss', 'apple': 'A', 'bear': 'D', 3: 'bb'}
# update(update)
print("\ncomparecomparecomparecomparecompare")
dicts.update(dicts1) # D.update([E, ]**F) -> None. Update D from dict/iterable E and F.
print(dicts)
{1: 'a', 2: 'r', 'apple': 'A', 'bear': 'D', 3: 'bb', 4: 'd', 'beach': 3}
# -(pop\clear)
dicts.pop('apple') # D.pop(k[,d]) -> v, remove specified key and return the corresponding value.
print(dicts)
for i in dict3.popitem(): # Remove and return a (key, value) pair as a 2-tuple.
print(i)
print(dict3)
dicts.clear() # D.clear() -> None. Remove all items from D.
print(dicts)
{1: 'a', 2: 'r', 'bear': 'D', 3: 'bb', 4: 'd', 'beach': 3}
bear
D
{1: 'a', 2: 'ss', 'apple': 'A'}
{}
tuple+list+set+dict的汇总
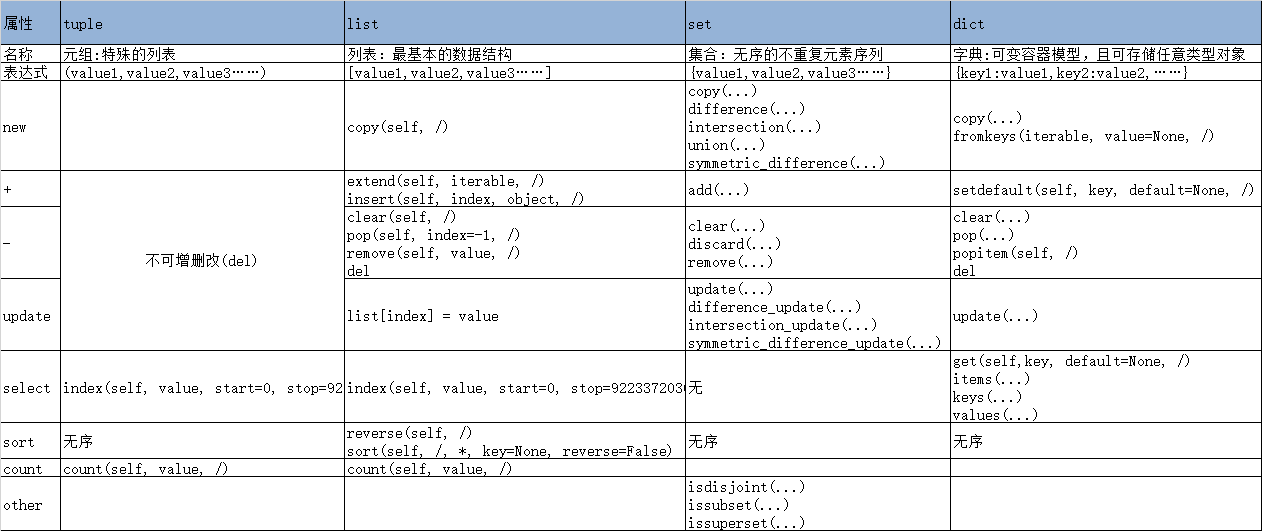
string: 字符串
string = "this IS a string \t example." # select
print(string)
print(string[0])
print(string[0:3])
print(string.find('t')) # Return the lowest index in S where substring sub is found,
print(string.rfind('t')) # Return the highest index in S where substring sub is found ERROR
print(string.index('t')) # Return True if all characters in S are alphanumeric and there is at least one character in S, False otherwise.
print(string.rindex('t')) # Like S.rfind() but raise ValueError when the substring is not found.
this IS a string example.
t
thi
0
11
0
11 # new
string3 = string.center(30, 'i')
print(string3.capitalize()) # Return a capitalized version of the string.
print(string3.expandtabs(4)) # Return a copy where all tab characters are expanded using spaces.
print(string3.join(string1)) # Return a string which is the concatenation of the strings in the iterable. The separator between elements is S.
print(string3.lower()) # Return a copy of the string S converted to lowercase.
print(string3.upper()) # Return a copy of the string S converted to uppercase.
print(string3.swapcase()) # Return a copy of the string S with uppercase characters converted to lowercase and vice versa.
print(string3.title()) # Return a titlecased version of S, i.e. words start with uppercase characters, all remaining cased characters have lowercase.
Ithis is a string example.ii
ithis IS a string example.ii
aithis IS a string example.iibithis IS a string example.iic
ithis is a string example.ii
ITHIS IS A STRING EXAMPLE.II
ITHIS is A STRING EXAMPLE.II
Ithis Is A String Example.Ii # split
string3 = "this is a \n string \t example."
print("****", string3.partition(' ')) # (head, sep, tail) Search for the separator sep in S, and return the part before it,the separator itself, and the part after it. If the separator is not found, return S and two empty strings.
print(string3.rpartition(' ')) # (head, sep, tail) Search for the separator sep in S, starting at the end of S, and return the part before it, the separator itself, and the part after it. If the separator is not found, return two empty strings and S.
print(string3.split(' ')) # Return a list of the words in the string S, using sep as the delimiter string.
print(string3.rsplit(' ')) # Return a copy of the string S with trailing whitespace removed.
print(string3.splitlines(False)) # \n分割 Return a list of the lines in S, breaking at line boundaries.
print(string3.replace(' ','*')) # Return a copy of string S with all occurrences of substring old replaced by new. If the optional argument count is given, only the first count occurrences are replaced.
**** ('this', ' ', 'is a \n string \t example.')
('this is a \n string \t', ' ', 'example.')
['this', 'is', 'a', '\n', 'string', '\t', 'example.']
['this', 'is', 'a', '\n', 'string', '\t', 'example.']
['this is a ', ' string \t example.']
this*is*a*
*string* *example. # other
print(string.count(' ')) # S.count(sub[, start[, end]]) -> int
#print(string.swapcase()) # Return a copy of the string S with uppercase characters converted to lowercase and vice versa.
trantab = str.maketrans('abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz','ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ')
print(string.translate(trantab)) # 第二个参数加不进去?? Return a copy of the string S, where all characters occurring in the optional argument deletechars are removed, and the remaining characters have been mapped through the given translation table, which must be a string of length 256 or None.
5
THIS IS A STRING EXAMPLE. # just
string4 = string.center(30, '*')
print(string.center(40, '*')) # Return a centered string of length width.
print(string4.zfill(40)) # 右对齐+0 Pad a numeric string S with zeros on the left, to fill a field of the specified width. The string S is never truncated.
print(string4.ljust(40)) # 左对齐 Return S left-justified in a string of length width. Padding is done using the specified fill character (default is a space).
print(string4.rjust(40)) # 右对齐 Return S right-justified in a string of length width.
print(string4.strip('*')) # 左右删除 Return a copy of the string S with leading and trailing whitespace removed.
print(string4.rstrip('*')) # 右删除 Return a copy of the string S with leading and trailing whitespace removed.
print(string4.lstrip('*')) # 左删除 Return a copy of the string S with leading whitespace removed
******this IS a string example.*******
0000000000*this IS a string example.**
*this IS a string example.**
*this IS a string example.**
this IS a string example.
*this IS a string example.
this IS a string example.** # judge
print(string.endswith('789')) # S.endswith(suffix[, start[, end]]) -> bool
print(string.startswith('a')) # Return True if S starts with the specified prefix, False otherwise.
print(string2.isalnum()) # Return True if all characters in S are alphanumeric and there is at least one character in S, False otherwise.
print(string1.isalpha()) # Return True if all characters in S are alphabetic and there is at least one character in S, False otherwise.
print(string2.isdigit()) # Return True if all characters in S are digits and there is at least one character in S, False otherwise.
print(string1.islower()) # Return True if all cased characters in S are lowercase and there is at least one cased character in S, False otherwise.
print(string1.isupper()) # Return True if all cased characters in S are uppercase and there is at least one cased character in S, False otherwise.
print(string1.isspace()) # Return True if all characters in S are whitespace and there is at least one character in S, False otherwise.
print(string1.istitle()) # Return True if S is a titlecased string
False
False
True
True
True
True
False
False
False # format
print("string is :%s"%string)
# print(f"string is :{string}") # python3
print(string.format('s')) # 这个不太会用 Return a formatted version of S, using substitutions from args and kwargs. The substitutions are identified by braces ('{' and '}').
"""
标准编码格式:将文字/数字/其他对应编成信息/数据等信息
各国家:
ASCII(American Standard Code Information Interchange) 128个代码 0~9 a~z A~Z +-*/\% ,.':;=><?@(){}&!~
ANSI 0x80~oxFFFF:GB2312(中文) GBK(Chinese Internal Code Specification) GB18030(信息交换用汉字编码字符集) JIS(window-日文)
UNICODE:各种语言中使用到的所有字符 UTF-8(Universal Character Set/Unicode Transformation Format)
"""
string_utf_8 = string.encode('utf-8') # Encode the string using the codec registered for encoding.
string_gbk = string.encode('gbk')
print(string_utf_8)
print(string_gbk)
print(string_utf_8.decode('utf-8')) # S.decode([encoding[,errors]]) -> object
print(string_gbk.decode('gbk'))
string is :this IS a string example.
this IS a string example.
b'this IS a string \t example.'
b'this IS a string \t example.'
this IS a string example.
this IS a string example.
Learn Python the Hard Way,ex37-2的更多相关文章
- Learn Python the Hard Way,ex37-1
本练习为复习python的符号和关键字 关键字有: #and or False True print(1==0 and 2==0, 1==0 or 2==0) print(False) print(T ...
- [IT学习]Learn Python the Hard Way (Using Python 3)笨办法学Python3版本
黑客余弦先生在知道创宇的知道创宇研发技能表v3.1中提到了入门Python的一本好书<Learn Python the Hard Way(英文版链接)>.其中的代码全部是2.7版本. 如果 ...
- 笨办法学 Python (Learn Python The Hard Way)
最近在看:笨办法学 Python (Learn Python The Hard Way) Contents: 译者前言 前言:笨办法更简单 习题 0: 准备工作 习题 1: 第一个程序 习题 2: 注 ...
- 《Learn python the hard way》Exercise 48: Advanced User Input
这几天有点时间,想学点Python基础,今天看到了<learn python the hard way>的 Ex48,这篇文章主要记录一些工具的安装,以及scan 函数的实现. 首先与Ex ...
- 学 Python (Learn Python The Hard Way)
学 Python (Learn Python The Hard Way) Contents: 译者前言 前言:笨办法更简单 习题 0: 准备工作 习题 1: 第一个程序 习题 2: 注释和井号 习题 ...
- 算是休息了这么长时间吧!准备学习下python文本处理了,哪位大大有好书推荐的说下!
算是休息了这么长时间吧!准备学习下python文本处理了,哪位大大有好书推荐的说下!
- python安装完毕后,提示找不到ssl模块的解决步骤
转载自 醇酒醉影 python安装完毕后,提示找不到ssl模块: [root@localhost ~]# python2.7.5 Python 2.7.5 (default, Jun 3 2013, ...
- linux下,Python 多版本共存,及Pip,Easy_install 安装扩展包
Python2与Python3共存 安装Python3后,建立ln,使用Python(Python2),Python3 来区分两个版本 使用sudo apt-get install python3-s ...
- python学习03——设计,与input有关
笨办法学python第36节,我写的代码如下: from sys import exit def rule(): print "Congratulations! You made the r ...
随机推荐
- CentOS7系统时间和硬件时间不同步问题
CentOS7系统中有两个时间:系统时间 和 硬件时间 我们常用命令 date 会输出系统时间,用 date 命令修改的也是系统时间 硬件时间是写入到 BIOS 中的时间,用 hwclock -r 命 ...
- spring再学习之基本概念
二.spring之IOC与DI 注入的方式: set方法注入: 构造方法注入: 字段注入: 注入类型: 值类型注入:8中基本类型 引用类型注入: BeanFaactory是原始接口:功能比较单一. A ...
- 2018ACM上海大都会赛 F Color it【基础的扫描线】
题目:戳这里 题意:有n*m个点全为白色,q个圆,将q个圆内所有的点都染成黑色,问最后剩下多少白色的点. 解题思路:每一行当做一个扫描线,扫描所有的圆,记录每一行在圆中的点即可,O(n*q). 附ac ...
- 牛客网-n的约数【dfs】
题目描述:戳这里 解题思路:这题思路好想,n最多也就是20个不同的素数相乘,把所有可能的素数找到,然后枚举素数个数就行了. n = p1^q1 + p2^q2 + p3 ^q3 + ... + pi ...
- vue 二级子路由跳转不了 bug
vue 二级子路由跳转不了 bug @click.prevent 阻止原生事件的冒泡 <li class="tools-hover-box-list-item" v-for= ...
- LeetCode 题解 593. Valid Square (Medium)
LeetCode 题解 593. Valid Square (Medium) 判断给定的四个点,是否可以组成一个正方形 https://leetcode.com/problems/valid-squa ...
- VSCode & SQL
VSCode & SQL MySQL MySQL https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=formulahendry.vscod ...
- base 64 bug & encodeURIComponent
base64 bug & encodeURIComponent window.btoa("jëh²H¶�%28"); // "autoskiptoclMjiu&q ...
- anatomy app
anatomy app https://appolicious.com/the-best-iphone-apps-for-anatomy-students/ ios anatomy app Compl ...
- TypeScript 如何编写类库声明文件 .d.ts
TypeScript 如何编写类库声明文件 .d.ts how to write a d.ts file declaration-files/ https://www.typescriptlang.o ...
