Volley(五)—— 自定义Request
详细解读Volley(四)—— 自定义Request
Volley中提供了几个Request,如果我们有特殊的需求,完全可以自定义Request的,自定义Request自然要继承Request,那么本篇就教大家来一步一步地定义一个自己的Request类。
一、继承Request
如果我们的request的对象不是string,也不是JsonObject,而是一个奇怪的对象呢?我这里建立了一个类,叫做:Kale,然后定义了一个CustomReqeust去继承Reqeust,得到如下的代码。


package com.kale.volleytest; import com.android.volley.NetworkResponse;
import com.android.volley.Request;
import com.android.volley.Response;
import com.android.volley.Response.ErrorListener;
import com.android.volley.Response.Listener; public class CustomReqeust extends Request<Kale>{ public CustomReqeust(int method, String url, ErrorListener listener) {
super(method, url, listener);
} @Override
protected Response<Kale> parseNetworkResponse(NetworkResponse response) {
// TODO 自动生成的方法存根
return null;
} @Override
protected void deliverResponse(Kale response) {
// TODO 自动生成的方法存根 } }


分析:
public CustomReqeust(int method, String url, ErrorListener listener)
构造函数中调用了父类的方法,初始化了当前对象。传入三个参数:①请求方式,即POST/GET,②请求的URL,③出错时的回调监听器
protected Response<Kale> parseNetworkResponse(NetworkResponse response)
解析网络响应的结果,从NetworkResponse的代码中我们就可以知道它里面有什么东西了。


/**
* Data and headers returned from {@link Network#performRequest(Request)}.
*/
public class NetworkResponse {
/**
* Creates a new network response.
* @param statusCode the HTTP status code
* @param data Response body
* @param headers Headers returned with this response, or null for none
* @param notModified True if the server returned a 304 and the data was already in cache
* @param networkTimeMs Round-trip network time to receive network response
*/
public NetworkResponse(int statusCode, byte[] data, Map<String, String> headers,
boolean notModified, long networkTimeMs)


响应码啊,请求头什么的,最最主要的就是这个比特数组的data,响应的结果就在里面。我们可以自由的进行处理了~
protected void deliverResponse(Kale response)
分发响应的结果,我们可以通过将这个response放到监听器里来获取响应结果。
二、分析StringRequest
我们现在已经对request的子类有了基本的认识,现在就来看看StringRequest的源码吧,别担心,很短!


package com.android.volley.toolbox;public class StringRequest extends Request<String> {
// 建立监听器来获得响应成功时返回的结果
private final Listener<String> mListener;
// 传入请求方法,url,成功时的监听器,失败时的监听器
public StringRequest(int method, String url, Listener<String> listener,
ErrorListener errorListener) {
super(method, url, errorListener);
// 初始化成功时的监听器
mListener = listener;
}
/**
* Creates a new GET request.
* 建立一个默认的GET请求,调用了上面的构造函数
*/
public StringRequest(String url, Listener<String> listener, ErrorListener errorListener) {
this(Method.GET, url, listener, errorListener);
}
@Override
protected void deliverResponse(String response) {
// 用监听器的方法来传递下响应的结果
mListener.onResponse(response);
}
@Override
protected Response<String> parseNetworkResponse(NetworkResponse response) {
String parsed;
try {
// 调用了new String(byte[] data, String charsetName) 这个构造函数来构建String对象,
// 将byte数组按照特定的编码方式转换为String对象
// 主要部分是data
parsed = new String(response.data, HttpHeaderParser.parseCharset(response.headers));
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
parsed = new String(response.data);
}
return Response.success(parsed, HttpHeaderParser.parseCacheHeaders(response));
}
}


分析完代码我们应该就能知道改如何自定义Request了,其实没啥高深的东西。
三、自定义XMLRequest
代码来自:http://blog.csdn.net/guolin_blog/article/details/17612763


public class XMLRequest extends Request<XmlPullParser> {
private final Listener<XmlPullParser> mListener;
public XMLRequest(int method, String url, Listener<XmlPullParser> listener,
ErrorListener errorListener) {
super(method, url, errorListener);
mListener = listener;
}
public XMLRequest(String url, Listener<XmlPullParser> listener, ErrorListener errorListener) {
this(Method.GET, url, listener, errorListener);
}
@Override
protected Response<XmlPullParser> parseNetworkResponse(NetworkResponse response) {
try {
String xmlString = new String(response.data,
HttpHeaderParser.parseCharset(response.headers));
XmlPullParserFactory factory = XmlPullParserFactory.newInstance();
XmlPullParser xmlPullParser = factory.newPullParser();
xmlPullParser.setInput(new StringReader(xmlString));
return Response.success(xmlPullParser, HttpHeaderParser.parseCacheHeaders(response));
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
return Response.error(new ParseError(e));
} catch (XmlPullParserException e) {
return Response.error(new ParseError(e));
}
}
@Override
protected void deliverResponse(XmlPullParser response) {
mListener.onResponse(response);
}
}


这里用到了XmlPull的知识,如果不是很了解,可以去这篇文章看看:http://www.cnblogs.com/tianzhijiexian/p/4020250.html
测试代码:


XMLRequest xmlRequest = new XMLRequest(
"http://flash.weather.com.cn/wmaps/xml/china.xml",
new Response.Listener<XmlPullParser>() {
@Override
public void onResponse(XmlPullParser response) {
try {
int eventType = response.getEventType();
while (eventType != XmlPullParser.END_DOCUMENT) {
switch (eventType) {
case XmlPullParser.START_TAG:
String nodeName = response.getName();
if ("city".equals(nodeName)) {
String pName = response.getAttributeValue(0);
Log.d("TAG", "pName is " + pName);
}
break;
}
eventType = response.next();
}
} catch (XmlPullParserException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, new Response.ErrorListener() {
@Override
public void onErrorResponse(VolleyError error) {
Log.e("TAG", error.getMessage(), error);
}
});
mQueue.add(xmlRequest);


结果:
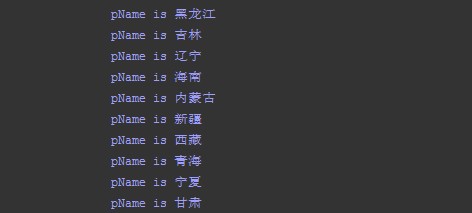
四、自定义GsonRequest
代码来自:http://blog.csdn.net/guolin_blog/article/details/17612763


public class GsonRequest<T> extends Request<T> {
private final Listener<T> mListener;
private Gson mGson;
private Class<T> mClass;
public GsonRequest(int method, String url, Class<T> clazz, Listener<T> listener,
ErrorListener errorListener) {
super(method, url, errorListener);
mGson = new Gson();
mClass = clazz;
mListener = listener;
}
public GsonRequest(String url, Class<T> clazz, Listener<T> listener,
ErrorListener errorListener) {
this(Method.GET, url, clazz, listener, errorListener);
}
@Override
protected Response<T> parseNetworkResponse(NetworkResponse response) {
try {
String jsonString = new String(response.data,
HttpHeaderParser.parseCharset(response.headers));
return Response.success(mGson.fromJson(jsonString, mClass),
HttpHeaderParser.parseCacheHeaders(response));
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
return Response.error(new ParseError(e));
}
}
@Override
protected void deliverResponse(T response) {
mListener.onResponse(response);
}
}


代码十分简单,先是将服务器响应的数据解析出来,然后通过调用Gson的fromJson方法将数据组装成对象。在deliverResponse方法中仍然是将最终的数据进行回调。
用法:
建立一个对象类,比如这里的weather、WeatherInfo类,然后初始化GsonRequest对象,最后把GsonRequest对象添加到队列中。
Weather:
public class Weather {
private WeatherInfo weatherinfo;
public WeatherInfo getWeatherinfo() {
return weatherinfo;
}
public void setWeatherinfo(WeatherInfo weatherinfo) {
this.weatherinfo = weatherinfo;
}
}
WeatherInfo:
public class WeatherInfo {
private String city;
private String temp;
private String time;
public String getCity() {
return city;
}
public void setCity(String city) {
this.city = city;
}
public String getTemp() {
return temp;
}
public void setTemp(String temp) {
this.temp = temp;
}
public String getTime() {
return time;
}
public void setTime(String time) {
this.time = time;
}
}
Java测试代码:


GsonRequest<Weather> gsonRequest = new GsonRequest<Weather>(
"http://www.weather.com.cn/data/sk/101010100.html", Weather.class,
new Response.Listener<Weather>() {
@Override
public void onResponse(Weather weather) {
WeatherInfo weatherInfo = weather.getWeatherinfo();
Log.d("TAG", "city is " + weatherInfo.getCity());
Log.d("TAG", "temp is " + weatherInfo.getTemp());
Log.d("TAG", "time is " + weatherInfo.getTime());
}
}, new Response.ErrorListener() {
@Override
public void onErrorResponse(VolleyError error) {
Log.e("TAG", error.getMessage(), error);
}
});
mQueue.add(gsonRequest);


五、重写getBody()方法来添加post参数
我们可以在JsonRequest类中发现如下代码:


/**
* Returns the raw POST or PUT body to be sent.
*
* @throws AuthFailureError in the event of auth failure
*/
@Override
public byte[] getBody() {
try {
return mRequestBody == null ? null : mRequestBody.getBytes(PROTOCOL_CHARSET);
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException uee) {
VolleyLog.wtf("Unsupported Encoding while trying to get the bytes of %s using %s",
mRequestBody, PROTOCOL_CHARSET);
return null;
}
}


不用看代码,直接看注释,说明这里执行post请求,所以我们可以在这里设置post参数。这里
return mRequestBody == null ? null : mRequestBody.getBytes(PROTOCOL_CHARSET);
返回的就是post参数了。
如果我们想要传递POST数据,可以参考上面的代码,重写Request的getBody()方法,放入自己的参数,举例如下:


/** http请求编码方式 */
private static final String PROTOCOL_CHARSET = "utf-8"; private String mUserName;




@Override
public byte[] getBody() {
try {
return mUserName == null ? null : mUserName.getBytes(PROTOCOL_CHARSET);
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException uee) {
VolleyLog.wtf("Unsupported Encoding while trying to get the bytes of %s using %s", mUserName, PROTOCOL_CHARSET);
return null;
}
}


完整代码(来自:http://blog.csdn.net/ttdevs/article/details/17586205):

public class CustomReqeust extends Request<String> {
/** http请求编码方式 */
private static final String PROTOCOL_CHARSET = "utf-8";
private Listener<String> mListener;
private String mUserName;
public CustomReqeust(String url, String userName, Listener<String> listener, ErrorListener errorListener) {
super(Method.POST, url, errorListener);
mUserName = userName;
mListener = listener;
}
@Override
protected Response<String> parseNetworkResponse(NetworkResponse response) {
String parsed;
try {
parsed = new String(response.data, HttpHeaderParser.parseCharset(response.headers));
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
parsed = new String(response.data);
}
return Response.success(parsed, HttpHeaderParser.parseCacheHeaders(response));
}
@Override
protected void deliverResponse(String response) {
mListener.onResponse(response);
}
@Override
public byte[] getBody() {
try {
return mUserName == null ? null : mUserName.getBytes(PROTOCOL_CHARSET);
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException uee) {
VolleyLog.wtf("Unsupported Encoding while trying to get the bytes of %s using %s", mUserName, PROTOCOL_CHARSET);
return null;
}
}
}

测试代码:


private void customRequest() {
CustomReqeust request = new CustomReqeust(URL, "CustomVolley", new Listener<String>() {
@Override
public void onResponse(String arg0) {
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), arg0, Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
Log.d("onResponse", arg0);
}
}, new ErrorListener() {
@Override
public void onErrorResponse(VolleyError arg0) {
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), arg0.toString(), Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
Log.d("onErrorResponse", arg0.toString());
}
});
mQueue.add(request);
}


抓包结果:
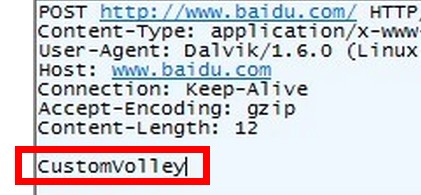
得到了传递的username = CustomVolley
Volley(五)—— 自定义Request的更多相关文章
- Android Volley 之自定义Request
转载标明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/lmj623565791/article/details/24589837 今天群里一哥们需要自定义Volley的Request的例子,于是产生 ...
- 详细解读Volley(四)—— 自定义Request
Volley中提供了几个Request,如果我们有特殊的需求,完全可以自定义Request的,自定义Request自然要继承Request,那么本篇就教大家来一步一步地定义一个自己的Request类. ...
- Volley自定义Request及使用单例封装RequestQueue
一.自定义Request Volley的所有的请求的超类型是Resuest,所有我们常用的请求都是这个类的子类,那么我们自定义View肯定也是基于这个类的. 案例: package com.zhy.v ...
- Volley 的使用以及自定义Request
Volley 的使用以及自定义Request 一.什么是 Volley 2013年Google I/O大会上推出了一个新的网络通信框架.Volley是Android平台上的网络通信库,能使网络通信更快 ...
- Android图表库MPAndroidChart(五)——自定义MarkerView实现选中高亮
Android图表库MPAndroidChart(五)--自定义MarkerView实现选中高亮 在学习本课程之前我建议先把我之前的博客看完,这样对整体的流程有一个大致的了解 Android图表库MP ...
- Android特效专辑(五)——自定义圆形头像和仿MIUI卸载动画—粒子爆炸
Android特效专辑(五)--自定义圆形头像和仿MIUI卸载动画-粒子爆炸 好的,各位亲爱的朋友,今天讲的特效还是比较炫的,首先,我们会讲一个自定义圆形的imageView,接着,我们会来实现粒子爆 ...
- 一、虚拟环境.二、路由配置主页与404.三、2.x路由分发.四、伪静态.五、request对象.六、FBV与CBV.七、文件上传.
一.虚拟环境 ''' 解决版本共存 1. 用pycharm选择File点击NewProject然后选择virtualenv创建一个纯净环境 2. 打开下载的目录将venv文件夹下的所有文件(纯净的环境 ...
- [Android] 开源框架 Volley 自定义 Request
今天在看Volley demo (https://github.com/smanikandan14/Volley-demo), 发现自定义GsonRequest那块代码不全, 在这里贴一个全的. pu ...
- Android网络开发之Volley--Volley自定义Request
1.自定义一个解析Json的Request,这里使用JackSon框架来解析Json.你也可以自定义一个解析XML的Request,或者使用FastSon来解析Json. 2.我们首先来看一下Stri ...
随机推荐
- 请用fontAwesome代替网页icon小图标
1. 引言 网页小图标到处可见,如果一个网页都是干巴巴的文字和图片,而没有小图标,会显得非常简陋.下面的小图标,你是不是会经常用到? 你可能说——“我们用的都是彩色的,不是黑白的”——别着急,下面会讲 ...
- [ html canvas 透明度 globalApha ] canvas绘图属性 透明度 globalApha 属性演示
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang='zh-cn'> <head> <title>Insert you title</title ...
- 配置SharePoint使用ADFS
1. 如果网站应用程序没有使用声明式验证 $wpp = Get-SPWebApplication <URL> $wpp.UseClaimsAuthentication = 1 $wpp.U ...
- STL--容器适配器(queue、priority_queue、stack)
适配器(Adaptor)是提供接口映射的模板类.适配器基于其他类来实现新的功能,成员函数可以被添加.隐藏,也可合并以得到新的功能. STL提供了三个容器适配器:queue.priority_queue ...
- 我为什么用 SQLite 和 FMDB 而不用 Core Data
凭良心讲,我不能告诉你不去使用Core Data.它不错,而且也在变好,并且它被很多其他Cocoa开发者所理解,当有新人加入你的组或者需要别人接手你的项目的时候,这点很重要.更重要的是,不值得花时间和 ...
- [VMware]设置VM虚拟机随系统自动启动
设置步骤: 1.找到VM的安装路径,右键vmware发送到桌面快捷方式 2.右键桌面快捷方式的属性,看到目标的属性框 3.找到需要自启动的虚拟机路径,如: D:\QC_VM\Clone of Wind ...
- swap分区
swap分区 一块的新加进来的硬盘,我们要怎么给它创建swap分区呢?要遵循下面四个步骤: (1)使用一个现有的分区,比如记为A (2)然后分区类型的16进制编码,即A的16进制编码. (3)格式化A ...
- 在Web api2 中传递复杂参数的一点心得
这两天在做的一个项目基于webapi2,期间遇到了复杂参数传递的问题.其中刚好看到园友的这篇文章,但是我测试收结果是失败的,还不知道是什么原因.最终经过思考后,找到了一种方法,和大家分享下. 在前端我 ...
- C# Socket和TCP连接的区别
网络通信七层参考模型介绍: 物理层: HUB,网线 链路层: MAC,ARP,交换机 网络层:IP,ICMP,IGMP,路由器 传输层: TCP,UDP 会话层: HTTP,SMTP,FTP,POP3 ...
- Web开发须知:URL编码与解码
通常如果一样东西需要编码,说明这样东西并不适合传输.原因多种多样,如Size过大,包含隐私数据,对于Url来说,之所以要进行编码,是因为Url中有些字符会引起歧义. 例如,Url参数字符串中使用key ...
