斐波那契堆(一)之 图文解析 和 C语言的实现
概要
本章介绍斐波那契堆。和以往一样,本文会先对斐波那契堆的理论知识进行简单介绍,然后给出C语言的实现。后续再分别给出C++和Java版本的实现;实现的语言虽不同,但是原理如出一辙,选择其中之一进行了解即可。若文章有错误或不足的地方,请不吝指出!
目录
1. 斐波那契堆的介绍
2. 斐波那契堆的基本操作
3. 斐波那契堆的C实现(完整源码)
4. 斐波那契堆的C测试程序
转载请注明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/p/3659060.html
更多内容:数据结构与算法系列 目录
(01) 斐波那契堆(一)之 图文解析 和 C语言的实现
(02) 斐波那契堆(二)之 C++的实现
(03) 斐波那契堆(三)之 Java的实现
斐波那契堆的介绍
斐波那契堆(Fibonacci heap)是堆中一种,它和二项堆一样,也是一种可合并堆;可用于实现合并优先队列。斐波那契堆比二项堆具有更好的平摊分析性能,它的合并操作的时间复杂度是O(1)。
与二项堆一样,它也是由一组堆最小有序树组成,并且是一种可合并堆。
与二项堆不同的是,斐波那契堆中的树不一定是二项树;而且二项堆中的树是有序排列的,但是斐波那契堆中的树都是有根而无序的。
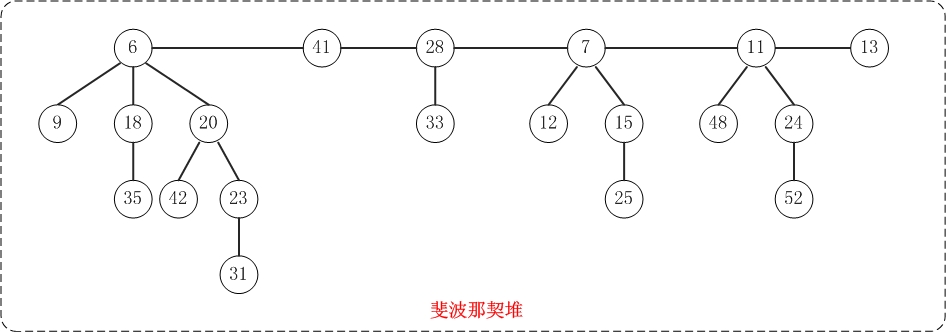
斐波那契堆的基本操作
1. 基本定义
typedef int Type; typedef struct _FibonacciNode
{
Type key; // 关键字(键值)
int degree; // 度数
struct _FibonacciNode *left; // 左兄弟
struct _FibonacciNode *right; // 右兄弟
struct _FibonacciNode *child; // 第一个孩子节点
struct _FibonacciNode *parent; // 父节点
int marked; //是否被删除第1个孩子(1表示删除,0表示未删除)
}FibonacciNode, FibNode;
FibNode是斐波那契堆的节点类,它包含的信息较多。key是用于比较节点大小的,degree是记录节点的度,left和right分别是指向节点的左右兄弟,child是节点的第一个孩子,parent是节点的父节点,marked是记录该节点是否被删除第1个孩子(marked在删除节点时有用)。
typedef struct _FibonacciHeap{
int keyNum; // 堆中节点的总数
int maxDegree; // 最大度
struct _FibonacciNode *min; // 最小节点(某个最小堆的根节点)
struct _FibonacciNode **cons; // 最大度的内存区域
}FibonacciHeap, FibHeap;
FibHeap是斐波那契堆对应的类。min是保存当前堆的最小节点,keyNum用于记录堆中节点的总数,maxDegree用于记录堆中最大度,而cons在删除节点时来暂时保存堆数据的临时空间。
下面看看斐波那契堆的内存结构图。

从图中可以看出,斐波那契堆是由一组最小堆组成,这些最小堆的根节点组成了双向链表(后文称为"根链表");斐波那契堆中的最小节点就是"根链表中的最小节点"!
PS. 上面这幅图的结构和测试代码中的"基本信息"测试函数的结果是一致的;你可以通过测试程序来亲自验证!
2. 插入操作
插入操作非常简单:插入一个节点到堆中,直接将该节点插入到"根链表的min节点"之前即可;若被插入节点比"min节点"小,则更新"min节点"为被插入节点。
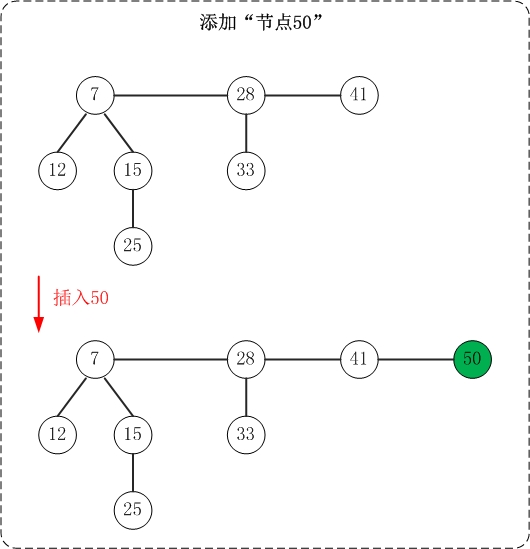
上面是插入操作的示意图。
斐波那契堆的根链表是"双向链表",这里将min节点看作双向联表的表头(后文也是如此)。在插入节点时,每次都是"将节点插入到min节点之前(即插入到双链表末尾)"。此外,对于根链表中最小堆都只有一个节点的情况,插入操作就很演化成双向链表的插入操作。
此外,插入操作示意图与测试程序中的"插入操作"相对应,感兴趣的可以亲自验证。
插入操作代码
/*
* 将"单个节点node"加入"链表root"之前
* a …… root
* a …… node …… root
*
* 注意: 此处node是单个节点,而root是双向链表
*/
static void fib_node_add(FibNode *node, FibNode *root)
{
node->left = root->left;
root->left->right = node;
node->right = root;
root->left = node;
} /*
* 将节点node插入到斐波那契堆heap中
*/
static void fib_heap_insert_node(FibHeap *heap, FibNode *node)
{
if (heap->keyNum == )
heap->min = node;
else
{
fib_node_add(node, heap->min);
if (node->key < heap->min->key)
heap->min = node;
}
heap->keyNum++;
}
3. 合并操作
合并操作和插入操作的原理非常类似:将一个堆的根链表插入到另一个堆的根链表上即可。简单来说,就是将两个双链表拼接成一个双向链表。
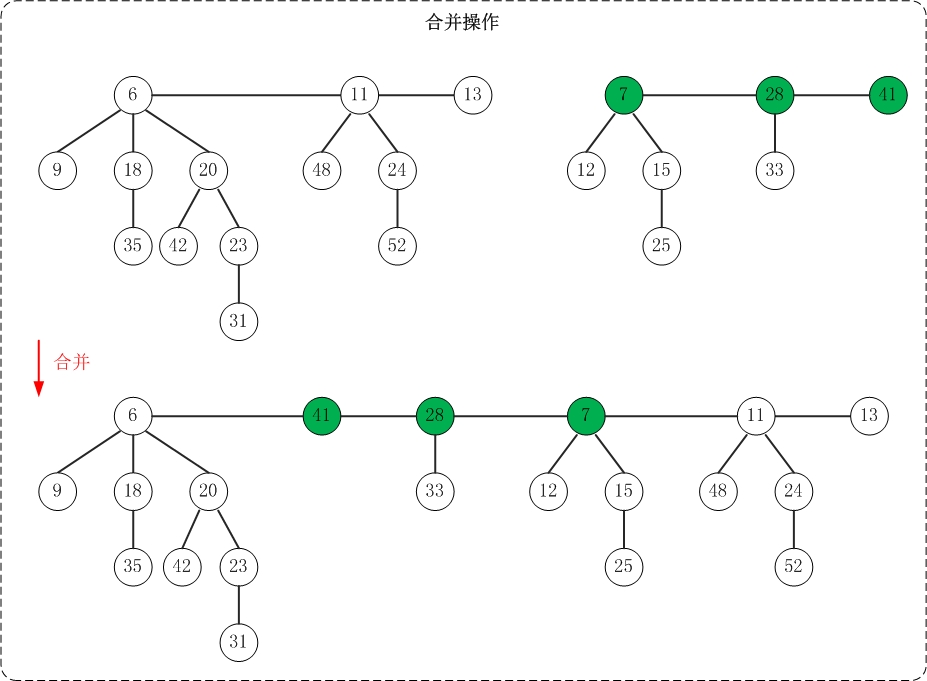
上面是合并操作的示意图。该操作示意图与测试程序中的"合并操作"相对应!
合并操作代码
/*
* 将双向链表b链接到双向链表a的后面
*
* 注意: 此处a和b都是双向链表
*/
static void fib_node_cat(FibNode *a, FibNode *b)
{
FibNode *tmp; tmp = a->right;
a->right = b->right;
b->right->left = a;
b->right = tmp;
tmp->left = b;
} /*
* 将h1, h2合并成一个堆,并返回合并后的堆
*/
FibHeap* fib_heap_union(FibHeap *h1, FibHeap *h2)
{
FibHeap *tmp; if (h1==NULL)
return h2;
if (h2==NULL)
return h1; // 以h1为"母",将h2附加到h1上;下面是保证h1的度数大,尽可能的少操作。
if(h2->maxDegree > h1->maxDegree)
{
tmp = h1;
h1 = h2;
h2 = tmp;
} if((h1->min) == NULL) // h1无"最小节点"
{
h1->min = h2->min;
h1->keyNum = h2->keyNum;
free(h2->cons);
free(h2);
}
else if((h2->min) == NULL) // h1有"最小节点" && h2无"最小节点"
{
free(h2->cons);
free(h2);
} // h1有"最小节点" && h2有"最小节点"
else
{
// 将"h2中根链表"添加到"h1"中
fib_node_cat(h1->min, h2->min);
if (h1->min->key > h2->min->key)
h1->min = h2->min;
h1->keyNum += h2->keyNum;
free(h2->cons);
free(h2);
} return h1;
}
4. 取出最小节点
抽取最小结点的操作是斐波那契堆中较复杂的操作。
(1)将要抽取最小结点的子树都直接串联在根表中;
(2)合并所有degree相等的树,直到没有相等的degree的树。

上面是取出最小节点的示意图。图中应该写的非常明白了,若有疑问,看代码。
此外,该操作示意图与测试程序中的"删除最小节点"相对应!有兴趣的可以亲自验证。
取出最小节点代码
/*
* 移除最小节点,并返回移除节点后的斐波那契堆
*/
FibNode* _fib_heap_extract_min(FibHeap *heap)
{
if (heap==NULL || heap->min==NULL)
return NULL; FibNode *child = NULL;
FibNode *min = heap->min;
// 将min每一个儿子(儿子和儿子的兄弟)都添加到"斐波那契堆的根链表"中
while (min->child != NULL)
{
child = min->child;
fib_node_remove(child);
if (child->right == child)
min->child = NULL;
else
min->child = child->right; fib_node_add(child, heap->min);
child->parent = NULL;
} // 将min从根链表中移除
fib_node_remove(min);
// 若min是堆中唯一节点,则设置堆的最小节点为NULL;
// 否则,设置堆的最小节点为一个非空节点(min->right),然后再进行调节。
if (min->right == min)
heap->min = NULL;
else
{
heap->min = min->right;
fib_heap_consolidate(heap);
}
heap->keyNum--; return min;
}
其中fib_heap_consolidate(heap)的作用是合并斐波那契堆的根链表中相同度数的树,它的相关代码如下:
/*
* 将node链接到root根结点
*/
static void fib_heap_link(FibHeap * heap, FibNode * node, FibNode *root)
{
// 将node从双链表中移除
fib_node_remove(node);
// 将node设为root的孩子
if (root->child == NULL)
root->child = node;
else
fib_node_add(node, root->child); node->parent = root;
root->degree++;
node->marked = ;
} /*
* 创建fib_heap_consolidate所需空间
*/
static void fib_heap_cons_make(FibHeap * heap)
{
int old = heap->maxDegree; // 计算log2(x),"+1"意味着向上取整!
// ex. log2(13) = 3,向上取整为3+1=4。
heap->maxDegree = LOG2(heap->keyNum) + ; // 如果原本空间不够,则再次分配内存
if (old >= heap->maxDegree)
return ; // 因为度为heap->maxDegree可能被合并,所以要maxDegree+1
heap->cons = (FibNode **)realloc(heap->cons,
sizeof(FibHeap *) * (heap->maxDegree + ));
} /*
* 合并斐波那契堆的根链表中左右相同度数的树
*/
static void fib_heap_consolidate(FibHeap *heap)
{
int i, d, D;
FibNode *x, *y, *tmp; fib_heap_cons_make(heap);//开辟哈希所用空间
D = heap->maxDegree + ; for (i = ; i < D; i++)
heap->cons[i] = NULL; // 合并相同度的根节点,使每个度数的树唯一
while (heap->min != NULL)
{
x = fib_heap_remove_min(heap); // 取出堆中的最小树(最小节点所在的树)
d = x->degree; // 获取最小树的度数
// heap->cons[d] != NULL,意味着有两棵树(x和y)的"度数"相同。
while (heap->cons[d] != NULL)
{
y = heap->cons[d]; // y是"与x的度数相同的树"
if (x->key > y->key) // 保证x的键值比y小
{
tmp = x;
x = y;
y = tmp; }
fib_heap_link(heap, y, x); // 将y链接到x中
heap->cons[d] = NULL;
d++;
}
heap->cons[d] = x;
}
heap->min = NULL; // 将heap->cons中的结点重新加到根表中
for (i=; i<D; i++)
{
if (heap->cons[i] != NULL)
{
if (heap->min == NULL)
heap->min = heap->cons[i];
else
{
fib_node_add(heap->cons[i], heap->min);
if ((heap->cons[i])->key < heap->min->key)
heap->min = heap->cons[i];
}
}
}
}
5. 减小节点值
减少斐波那契堆中的节点的键值,这个操作的难点是:如果减少节点后破坏了"最小堆"性质,如何去维护呢?下面对一般性情况进行分析。
(1) 首先,将"被减小节点"从"它所在的最小堆"剥离出来;然后将"该节点"关联到"根链表"中。 倘若被减小的节点不是单独一个节点,而是包含子树的树根。则是将以"被减小节点"为根的子树从"最小堆"中剥离出来,然后将该树关联到根链表中。
(2) 接着,对"被减少节点"的原父节点进行"级联剪切"。所谓"级联剪切",就是在被减小节点破坏了最小堆性质,并被切下来之后;再从"它的父节点"进行递归级联剪切操作。
而级联操作的具体动作则是:若父节点(被减小节点的父节点)的marked标记为false,则将其设为true,然后退出。
否则,将父节点从最小堆中切下来(方式和"切被减小节点的方式"一样);然后递归对祖父节点进行"级联剪切"。
marked标记的作用就是用来标记"该节点的子节点是否有被删除过",它的作用是来实现级联剪切。而级联剪切的真正目的是为了防止"最小堆"由二叉树演化成链表。
(3) 最后,别忘了对根链表的最小节点进行更新。
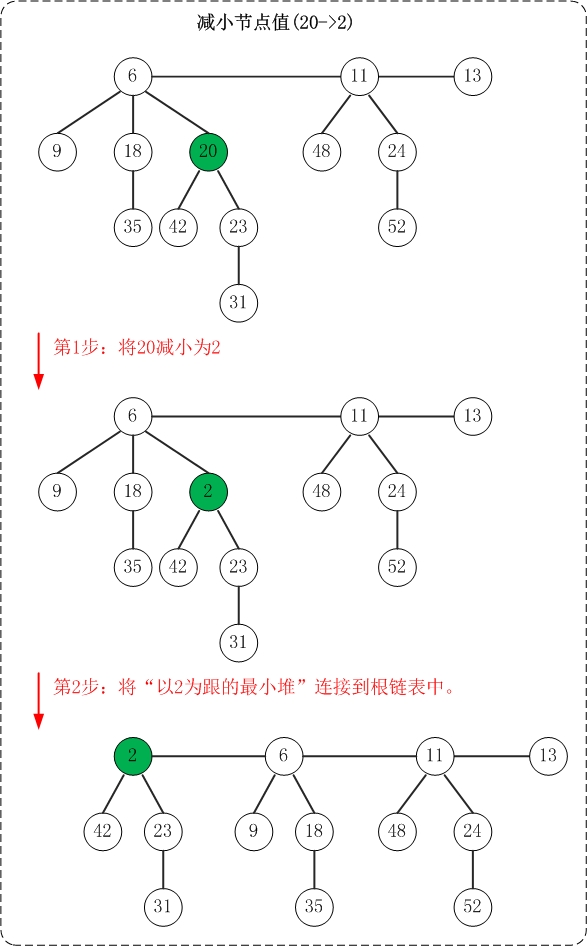
上面是减小节点值的示意图。该操作示意图与测试程序中的"减小节点"相对应!
减小节点值的代码
/*
* 将斐波那契堆heap中节点node的值减少为key
*/
static void fib_heap_decrease(FibHeap *heap, FibNode *node, Type key)
{
FibNode *parent; if (heap==NULL || heap->min==NULL ||node==NULL)
return ; if ( key>=node->key)
{
printf("decrease failed: the new key(%d) is no smaller than current key(%d)\n", key, node->key);
return ;
} node->key = key;
parent = node->parent;
if (parent!=NULL && node->key < parent->key)
{
// 将node从父节点parent中剥离出来,并将node添加到根链表中
fib_heap_cut(heap, node, parent);
fib_heap_cascading_cut(heap, parent);
} // 更新最小节点
if (node->key < heap->min->key)
heap->min = node;
}
其中,fib_heap_cut()和fib_heap_cascading_cut()的相关代码如下:
/*
* 将node从父节点parent的子链接中剥离出来,
* 并使node成为"堆的根链表"中的一员。
*/
static void fib_heap_cut(FibHeap *heap, FibNode *node, FibNode *parent)
{
fib_node_remove(node);
renew_degree(parent, node->degree);
// node没有兄弟
if (node == node->right)
parent->child = NULL;
else
parent->child = node->right; node->parent = NULL;
node->left = node->right = node;
node->marked = ;
// 将"node所在树"添加到"根链表"中
fib_node_add(node, heap->min);
} /*
* 对节点node进行"级联剪切"
*
* 级联剪切:如果减小后的结点破坏了最小堆性质,
* 则把它切下来(即从所在双向链表中删除,并将
* 其插入到由最小树根节点形成的双向链表中),
* 然后再从"被切节点的父节点"到所在树根节点递归执行级联剪枝
*/
static void fib_heap_cascading_cut(FibHeap *heap, FibNode *node)
{
FibNode *parent = node->parent;
if (parent != NULL)
return ; if (node->marked == )
node->marked = ;
else
{
fib_heap_cut(heap, node, parent);
fib_heap_cascading_cut(heap, parent);
}
}
6. 增加节点值
增加节点值和减少节点值类似,这个操作的难点也是如何维护"最小堆"性质。思路如下:
(1) 将"被增加节点"的"左孩子和左孩子的所有兄弟"都链接到根链表中。
(2) 接下来,把"被增加节点"添加到根链表;但是别忘了对其进行级联剪切。

上面是增加节点值的示意图。该操作示意图与测试程序中的"增大节点"相对应!
增加节点值的代码
/*
* 将斐波那契堆heap中节点node的值增加为key
*/
static void fib_heap_increase(FibHeap *heap, FibNode *node, Type key)
{
FibNode *child, *parent, *right; if (heap==NULL || heap->min==NULL ||node==NULL)
return ; if (key <= node->key)
{
printf("increase failed: the new key(%d) is no greater than current key(%d)\n", key, node->key);
return ;
} // 将node每一个儿子(不包括孙子,重孙,...)都添加到"斐波那契堆的根链表"中
while (node->child != NULL)
{
child = node->child;
fib_node_remove(child); // 将child从node的子链表中删除
if (child->right == child)
node->child = NULL;
else
node->child = child->right; fib_node_add(child, heap->min); // 将child添加到根链表中
child->parent = NULL;
}
node->degree = ;
node->key = key; // 如果node不在根链表中,
// 则将node从父节点parent的子链接中剥离出来,
// 并使node成为"堆的根链表"中的一员,
// 然后进行"级联剪切"
// 否则,则判断是否需要更新堆的最小节点
parent = node->parent;
if(parent != NULL)
{
fib_heap_cut(heap, node, parent);
fib_heap_cascading_cut(heap, parent);
}
else if(heap->min == node)
{
right = node->right;
while(right != node)
{
if(node->key > right->key)
heap->min = right;
right = right->right;
}
}
}
7. 删除节点
删除节点,本文采用了操作是:"取出最小节点"和"减小节点值"的组合。
(1) 先将被删除节点的键值减少。减少后的值要比"原最小节点的值"即可。
(2) 接着,取出最小节点即可。
删除节点值的代码
/*
* 删除结点node
*/
static void _fib_heap_delete(FibHeap *heap, FibNode *node)
{
Type min = heap->min->key;
fib_heap_decrease(heap, node, min-);
_fib_heap_extract_min(heap);
free(node);
}
注意:关于斐波那契堆的"更新"、"打印"、"销毁"等接口就不再单独介绍了。后文的源码中有给出它们的实现代码,Please RTFSC(Read The Fucking Source Code)!
斐波那契堆的C实现(完整源码)
斐波那契堆的头文件(fibonacci_heap.h)
#ifndef _FIBONACCI_HEAP_H_
#define _FIBONACCI_HEAP_H_ typedef int Type; typedef struct _FibonacciNode
{
Type key; // 关键字(键值)
int degree; // 度数
struct _FibonacciNode *left; // 左兄弟
struct _FibonacciNode *right; // 右兄弟
struct _FibonacciNode *child; // 第一个孩子节点
struct _FibonacciNode *parent; // 父节点
int marked; //是否被删除第1个孩子(1表示删除,0表示未删除)
}FibonacciNode, FibNode; typedef struct _FibonacciHeap{
int keyNum; // 堆中节点的总数
int maxDegree; // 最大度
struct _FibonacciNode *min; // 最小节点(某个最小堆的根节点)
struct _FibonacciNode **cons; // 最大度的内存区域
}FibonacciHeap, FibHeap; // 创建Fibonacci堆
FibHeap* fib_heap_make();
// 新建键值为key的节点,并将其插入到斐波那契堆中
void fib_heap_insert_key(FibHeap *heap, Type key);
// 删除键值为key的结点
void fib_heap_delete(FibHeap *heap, Type key);
// 移除最小节点
void fib_heap_extract_min(FibHeap *heap);
// 更新heap的中的oldkey为newkey
void fib_heap_update(FibHeap *heap, Type oldkey, Type newkey);
// 将h1, h2合并成一个堆,并返回合并后的堆
FibHeap* fib_heap_union(FibHeap *h1, FibHeap *h2);
// 在斐波那契堆heap中是否存在键值为key的节点;存在返回1,否则返回0。
int fib_heap_contains(FibHeap *heap, Type key);
// 获取最小节点对应的值(保存在pkey中);成功返回1,失败返回0。
int fib_heap_get_min(FibHeap *heap, Type *pkey);
// 销毁斐波那契堆
void fib_heap_destroy(FibHeap *heap);
// 打印"斐波那契堆"
void fib_print(FibHeap *heap); #endif
斐波那契堆的实现文件(fibonacci_heap.c)
/**
* C语言实现的斐波那契堆
*
* @author skywang
* @date 2014/04/05
*/ #include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <float.h>
#include "fibonacci_heap.h" #if 0
#define LOG2(x) ({ \
unsigned int _i = ; \
__asm__("bsr %1, %0" : "=r" (_i) : "r" ((x))); \
_i; })
#else // 注意:通过gcc编译时,要添加 -lm 选项。
#define LOG2(x) ((log((double)(x))) / (log(2.0)))
#endif static FibNode *fib_heap_search(FibHeap *heap, Type key); /*
* 将node从双链表移除
*/
static void fib_node_remove(FibNode *node)
{
node->left->right = node->right;
node->right->left = node->left;
} /*
* 将"单个节点node"加入"链表root"之前
* a …… root
* a …… node …… root
*
* 注意: 此处node是单个节点,而root是双向链表
*/
static void fib_node_add(FibNode *node, FibNode *root)
{
node->left = root->left;
root->left->right = node;
node->right = root;
root->left = node;
} /*
* 将双向链表b链接到双向链表a的后面
*
* 注意: 此处a和b都是双向链表
*/
static void fib_node_cat(FibNode *a, FibNode *b)
{
FibNode *tmp; tmp = a->right;
a->right = b->right;
b->right->left = a;
b->right = tmp;
tmp->left = b;
} /*
* 创建斐波那契堆
*/
FibHeap* fib_heap_make()
{
FibHeap* heap; heap = (FibHeap *) malloc(sizeof(FibHeap));
if (heap == NULL)
{
printf("Error: make FibHeap failed\n");
return NULL;
} heap->keyNum = ;
heap->maxDegree = ;
heap->min = NULL;
heap->cons = NULL; return heap;
} /*
* 创建斐波那契堆的节点
*/
static FibNode* fib_node_make(Type key)
{
FibNode * node; node = (FibNode *) malloc(sizeof(FibNode));
if (node == NULL)
{
printf("Error: make Node failed\n");
return NULL;
}
node->key = key;
node->degree = ;
node->left = node;
node->right = node;
node->parent = NULL;
node->child = NULL; return node;
} /*
* 将节点node插入到斐波那契堆heap中
*/
static void fib_heap_insert_node(FibHeap *heap, FibNode *node)
{
if (heap->keyNum == )
heap->min = node;
else
{
fib_node_add(node, heap->min);
if (node->key < heap->min->key)
heap->min = node;
}
heap->keyNum++;
} /*
* 新建键值为key的节点,并将其插入到斐波那契堆中
*/
void fib_heap_insert_key(FibHeap *heap, Type key)
{
FibNode *node; if (heap==NULL)
return ; node = fib_node_make(key);
if (node == NULL)
return ; fib_heap_insert_node(heap, node);
} /*
* 将h1, h2合并成一个堆,并返回合并后的堆
*/
FibHeap* fib_heap_union(FibHeap *h1, FibHeap *h2)
{
FibHeap *tmp; if (h1==NULL)
return h2;
if (h2==NULL)
return h1; // 以h1为"母",将h2附加到h1上;下面是保证h1的度数大,尽可能的少操作。
if(h2->maxDegree > h1->maxDegree)
{
tmp = h1;
h1 = h2;
h2 = tmp;
} if((h1->min) == NULL) // h1无"最小节点"
{
h1->min = h2->min;
h1->keyNum = h2->keyNum;
free(h2->cons);
free(h2);
}
else if((h2->min) == NULL) // h1有"最小节点" && h2无"最小节点"
{
free(h2->cons);
free(h2);
} // h1有"最小节点" && h2有"最小节点"
else
{
// 将"h2中根链表"添加到"h1"中
fib_node_cat(h1->min, h2->min);
if (h1->min->key > h2->min->key)
h1->min = h2->min;
h1->keyNum += h2->keyNum;
free(h2->cons);
free(h2);
} return h1;
} /*
* 将"堆的最小结点"从根链表中移除,
* 这意味着"将最小节点所属的树"从堆中移除!
*/
static FibNode *fib_heap_remove_min(FibHeap *heap)
{
FibNode *min = heap->min; if (heap->min == min->right)
heap->min = NULL;
else
{
fib_node_remove(min);
heap->min = min->right;
}
min->left = min->right = min; return min;
} /*
* 将node链接到root根结点
*/
static void fib_heap_link(FibHeap * heap, FibNode * node, FibNode *root)
{
// 将node从双链表中移除
fib_node_remove(node);
// 将node设为root的孩子
if (root->child == NULL)
root->child = node;
else
fib_node_add(node, root->child); node->parent = root;
root->degree++;
node->marked = ;
} /*
* 创建fib_heap_consolidate所需空间
*/
static void fib_heap_cons_make(FibHeap * heap)
{
int old = heap->maxDegree; // 计算log2(x),"+1"意味着向上取整!
// ex. log2(13) = 3,向上取整为3+1=4。
heap->maxDegree = LOG2(heap->keyNum) + ; // 如果原本空间不够,则再次分配内存
if (old >= heap->maxDegree)
return ; // 因为度为heap->maxDegree可能被合并,所以要maxDegree+1
heap->cons = (FibNode **)realloc(heap->cons,
sizeof(FibHeap *) * (heap->maxDegree + ));
} /*
* 合并斐波那契堆的根链表中左右相同度数的树
*/
static void fib_heap_consolidate(FibHeap *heap)
{
int i, d, D;
FibNode *x, *y, *tmp; fib_heap_cons_make(heap);//开辟哈希所用空间
D = heap->maxDegree + ; for (i = ; i < D; i++)
heap->cons[i] = NULL; // 合并相同度的根节点,使每个度数的树唯一
while (heap->min != NULL)
{
x = fib_heap_remove_min(heap); // 取出堆中的最小树(最小节点所在的树)
d = x->degree; // 获取最小树的度数
// heap->cons[d] != NULL,意味着有两棵树(x和y)的"度数"相同。
while (heap->cons[d] != NULL)
{
y = heap->cons[d]; // y是"与x的度数相同的树"
if (x->key > y->key) // 保证x的键值比y小
{
tmp = x;
x = y;
y = tmp; }
fib_heap_link(heap, y, x); // 将y链接到x中
heap->cons[d] = NULL;
d++;
}
heap->cons[d] = x;
}
heap->min = NULL; // 将heap->cons中的结点重新加到根表中
for (i=; i<D; i++)
{
if (heap->cons[i] != NULL)
{
if (heap->min == NULL)
heap->min = heap->cons[i];
else
{
fib_node_add(heap->cons[i], heap->min);
if ((heap->cons[i])->key < heap->min->key)
heap->min = heap->cons[i];
}
}
}
} /*
* 移除最小节点,并返回移除节点后的斐波那契堆
*/
FibNode* _fib_heap_extract_min(FibHeap *heap)
{
if (heap==NULL || heap->min==NULL)
return NULL; FibNode *child = NULL;
FibNode *min = heap->min;
// 将min每一个儿子(儿子和儿子的兄弟)都添加到"斐波那契堆的根链表"中
while (min->child != NULL)
{
child = min->child;
fib_node_remove(child);
if (child->right == child)
min->child = NULL;
else
min->child = child->right; fib_node_add(child, heap->min);
child->parent = NULL;
} // 将min从根链表中移除
fib_node_remove(min);
// 若min是堆中唯一节点,则设置堆的最小节点为NULL;
// 否则,设置堆的最小节点为一个非空节点(min->right),然后再进行调节。
if (min->right == min)
heap->min = NULL;
else
{
heap->min = min->right;
fib_heap_consolidate(heap);
}
heap->keyNum--; return min;
} void fib_heap_extract_min(FibHeap *heap)
{
FibNode *node; if (heap==NULL || heap->min==NULL)
return ; node = _fib_heap_extract_min(heap);
if (node!=NULL)
free(node);
} /*
* 在斐波那契堆heap中是否存在键值为key的节点;存在返回1,否则返回0。
*/
int fib_heap_get_min(FibHeap *heap, Type *pkey)
{
if (heap==NULL || heap->min==NULL || pkey==NULL)
return ; *pkey = heap->min->key;
return ;
} /*
* 修改度数
*/
static void renew_degree(FibNode *parent, int degree)
{
parent->degree -= degree;
if (parent-> parent != NULL)
renew_degree(parent->parent, degree);
} /*
* 将node从父节点parent的子链接中剥离出来,
* 并使node成为"堆的根链表"中的一员。
*/
static void fib_heap_cut(FibHeap *heap, FibNode *node, FibNode *parent)
{
fib_node_remove(node);
renew_degree(parent, node->degree);
// node没有兄弟
if (node == node->right)
parent->child = NULL;
else
parent->child = node->right; node->parent = NULL;
node->left = node->right = node;
node->marked = ;
// 将"node所在树"添加到"根链表"中
fib_node_add(node, heap->min);
} /*
* 对节点node进行"级联剪切"
*
* 级联剪切:如果减小后的结点破坏了最小堆性质,
* 则把它切下来(即从所在双向链表中删除,并将
* 其插入到由最小树根节点形成的双向链表中),
* 然后再从"被切节点的父节点"到所在树根节点递归执行级联剪枝
*/
static void fib_heap_cascading_cut(FibHeap *heap, FibNode *node)
{
FibNode *parent = node->parent;
if (parent != NULL)
return ; if (node->marked == )
node->marked = ;
else
{
fib_heap_cut(heap, node, parent);
fib_heap_cascading_cut(heap, parent);
}
} /*
* 将斐波那契堆heap中节点node的值减少为key
*/
static void fib_heap_decrease(FibHeap *heap, FibNode *node, Type key)
{
FibNode *parent; if (heap==NULL || heap->min==NULL ||node==NULL)
return ; if ( key>=node->key)
{
printf("decrease failed: the new key(%d) is no smaller than current key(%d)\n", key, node->key);
return ;
} node->key = key;
parent = node->parent;
if (parent!=NULL && node->key < parent->key)
{
// 将node从父节点parent中剥离出来,并将node添加到根链表中
fib_heap_cut(heap, node, parent);
fib_heap_cascading_cut(heap, parent);
} // 更新最小节点
if (node->key < heap->min->key)
heap->min = node;
} /*
* 将斐波那契堆heap中节点node的值增加为key
*/
static void fib_heap_increase(FibHeap *heap, FibNode *node, Type key)
{
FibNode *child, *parent, *right; if (heap==NULL || heap->min==NULL ||node==NULL)
return ; if (key <= node->key)
{
printf("increase failed: the new key(%d) is no greater than current key(%d)\n", key, node->key);
return ;
} // 将node每一个儿子(不包括孙子,重孙,...)都添加到"斐波那契堆的根链表"中
while (node->child != NULL)
{
child = node->child;
fib_node_remove(child); // 将child从node的子链表中删除
if (child->right == child)
node->child = NULL;
else
node->child = child->right; fib_node_add(child, heap->min); // 将child添加到根链表中
child->parent = NULL;
}
node->degree = ;
node->key = key; // 如果node不在根链表中,
// 则将node从父节点parent的子链接中剥离出来,
// 并使node成为"堆的根链表"中的一员,
// 然后进行"级联剪切"
// 否则,则判断是否需要更新堆的最小节点
parent = node->parent;
if(parent != NULL)
{
fib_heap_cut(heap, node, parent);
fib_heap_cascading_cut(heap, parent);
}
else if(heap->min == node)
{
right = node->right;
while(right != node)
{
if(node->key > right->key)
heap->min = right;
right = right->right;
}
}
} /*
* 更新二项堆heap的节点node的键值为key
*/
void _fib_heap_update(FibHeap *heap, FibNode *node, Type key)
{
if(key < node->key)
fib_heap_decrease(heap, node, key);
else if(key > node->key)
fib_heap_increase(heap, node, key);
else
printf("No need to update!!!\n");
} void fib_heap_update(FibHeap *heap, Type oldkey, Type newkey)
{
FibNode *node; if (heap==NULL)
return ; node = fib_heap_search(heap, oldkey);
if (node!=NULL)
_fib_heap_update(heap, node, newkey);
} /*
* 在最小堆root中查找键值为key的节点
*/
static FibNode* fib_node_search(FibNode *root, Type key)
{
FibNode *t = root; // 临时节点
FibNode *p = NULL; // 要查找的节点 if (root==NULL)
return root; do
{
if (t->key == key)
{
p = t;
break;
}
else
{
if ((p = fib_node_search(t->child, key)) != NULL)
break;
}
t = t->right;
} while (t != root); return p;
} /*
* 在斐波那契堆heap中查找键值为key的节点
*/
static FibNode *fib_heap_search(FibHeap *heap, Type key)
{
if (heap==NULL || heap->min==NULL)
return NULL; return fib_node_search(heap->min, key);
} /*
* 在斐波那契堆heap中是否存在键值为key的节点。
* 存在返回1,否则返回0。
*/
int fib_heap_contains(FibHeap *heap, Type key)
{
return fib_heap_search(heap,key)!=NULL ? : ;
} /*
* 删除结点node
*/
static void _fib_heap_delete(FibHeap *heap, FibNode *node)
{
Type min = heap->min->key;
fib_heap_decrease(heap, node, min-);
_fib_heap_extract_min(heap);
free(node);
} void fib_heap_delete(FibHeap *heap, Type key)
{
FibNode *node; if (heap==NULL || heap->min==NULL)
return ; node = fib_heap_search(heap, key);
if (node==NULL)
return ; _fib_heap_delete(heap, node);
} /*
* 销毁斐波那契堆
*/
static void fib_node_destroy(FibNode *node)
{
FibNode *start = node; if(node == NULL)
return; do {
fib_node_destroy(node->child);
// 销毁node,并将node指向下一个
node = node->right;
free(node->left);
} while(node != start);
} void fib_heap_destroy(FibHeap *heap)
{
fib_node_destroy(heap->min);
free(heap->cons);
free(heap);
} /*
* 打印"斐波那契堆"
*
* 参数说明:
* node -- 当前节点
* prev -- 当前节点的前一个节点(父节点or兄弟节点)
* direction -- 1,表示当前节点是一个左孩子;
* 2,表示当前节点是一个兄弟节点。
*/
static void _fib_print(FibNode *node, FibNode *prev, int direction)
{
FibonacciNode *start=node; if (node==NULL)
return ;
do
{
if (direction == )
printf("%8d(%d) is %2d's child\n", node->key, node->degree, prev->key);
else
printf("%8d(%d) is %2d's next\n", node->key, node->degree, prev->key); if (node->child != NULL)
_fib_print(node->child, node, ); // 兄弟节点
prev = node;
node = node->right;
direction = ;
} while(node != start);
} void fib_print(FibHeap *heap)
{
int i=;
FibonacciNode *p; if (heap==NULL || heap->min==NULL)
return ; printf("== 斐波那契堆的详细信息: ==\n");
p = heap->min;
do {
i++;
printf("%2d. %4d(%d) is root\n", i, p->key, p->degree); _fib_print(p->child, p, );
p = p->right;
} while (p != heap->min);
printf("\n");
}
斐波那契堆的测试程序(main.c)
/**
* C语言实现的斐波那契堆
*
* @author skywang
* @date 2014/04/06
*/ #include <stdio.h>
#include "fibonacci_heap.h" #define DEBUG 0 #if DEBUG
#define log(x, ...) printf(x, __VA_ARGS__)
#else
#define log(x, ...)
#endif #define LENGTH(a) ( (sizeof(a)) / (sizeof(a[0])) ) // 共8个
int a[] = {, , , , ,
, , };
// 共14个
int b[] = {, , , , ,
, , , , ,
, , , }; // 验证"基本信息(斐波那契堆的结构)"
void test_basic()
{
int i;
int blen=LENGTH(b);
FibHeap *hb = fib_heap_make(); // 斐波那契堆hb
printf("== 斐波那契堆(hb)中依次添加: ");
for(i=; i<blen; i++)
{
printf("%d ", b[i]);
fib_heap_insert_key(hb, b[i]);
}
printf("\n");
printf("== 斐波那契堆(hb)删除最小节点\n");
fib_heap_extract_min(hb);
fib_print(hb); fib_heap_destroy(hb);
} // 验证"插入操作"
void test_insert()
{
int i;
int alen=LENGTH(a);
FibHeap *ha = fib_heap_make(); // 斐波那契堆ha
printf("== 斐波那契堆(ha)中依次添加: "); for(i=; i<alen; i++)
{
printf("%d ", a[i]);
fib_heap_insert_key(ha, a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
printf("== 斐波那契堆(ha)删除最小节点\n");
fib_heap_extract_min(ha);
fib_print(ha); // 插入50
printf("== 插入50\n");
fib_heap_insert_key(ha, );
fib_print(ha); fib_heap_destroy(ha);
} // 验证"合并操作"
void test_union()
{
int i;
int alen=LENGTH(a);
int blen=LENGTH(b);
FibHeap *ha = fib_heap_make();
FibHeap *hb = fib_heap_make(); // 斐波那契堆ha
printf("== 斐波那契堆(ha)中依次添加: "); for(i=; i<alen; i++)
{
printf("%d ", a[i]);
fib_heap_insert_key(ha, a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
printf("== 斐波那契堆(ha)删除最小节点\n");
fib_heap_extract_min(ha);
fib_print(ha); // 斐波那契堆hb
printf("== 斐波那契堆(hb)中依次添加: ");
for(i=; i<blen; i++)
{
printf("%d ", b[i]);
fib_heap_insert_key(hb, b[i]);
}
printf("\n");
printf("== 斐波那契堆(hb)删除最小节点\n");
fib_heap_extract_min(hb);
fib_print(hb); // 将"斐波那契堆hb"合并到"斐波那契堆ha"中。
printf("== 合并ha和hb\n");
ha = fib_heap_union(ha, hb);
fib_print(ha); // 销毁堆
fib_heap_destroy(ha);
} // 验证"删除最小节点"
void test_remove_min()
{
int i;
int alen=LENGTH(a);
int blen=LENGTH(b);
FibHeap *ha = fib_heap_make();
FibHeap *hb = fib_heap_make(); // 斐波那契堆ha
printf("== 斐波那契堆(ha)中依次添加: "); for(i=; i<alen; i++)
{
printf("%d ", a[i]);
fib_heap_insert_key(ha, a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
printf("== 斐波那契堆(ha)删除最小节点\n");
fib_heap_extract_min(ha);
//fib_print(ha); // 斐波那契堆hb
printf("== 斐波那契堆(hb)中依次添加: ");
for(i=; i<blen; i++)
{
printf("%d ", b[i]);
fib_heap_insert_key(hb, b[i]);
}
printf("\n");
printf("== 斐波那契堆(hb)删除最小节点\n");
fib_heap_extract_min(hb);
//fib_print(hb); // 将"斐波那契堆hb"合并到"斐波那契堆ha"中。
printf("== 合并ha和hb\n");
ha = fib_heap_union(ha, hb);
fib_print(ha); printf("== 删除最小节点\n");
fib_heap_extract_min(ha);
fib_print(ha); // 销毁堆
fib_heap_destroy(ha);
} // 验证"减小节点"
void test_decrease()
{
int i;
int blen=LENGTH(b);
FibHeap *hb = fib_heap_make(); // 斐波那契堆hb
printf("== 斐波那契堆(hb)中依次添加: ");
for(i=; i<blen; i++)
{
printf("%d ", b[i]);
fib_heap_insert_key(hb, b[i]);
}
printf("\n");
printf("== 斐波那契堆(hb)删除最小节点\n");
fib_heap_extract_min(hb);
fib_print(hb); printf("== 将20减小为2\n");
fib_heap_update(hb, , );
fib_print(hb); fib_heap_destroy(hb);
} // 验证"增大节点"
void test_increase()
{
int i;
int blen=LENGTH(b);
FibHeap *hb = fib_heap_make(); // 斐波那契堆hb
printf("== 斐波那契堆(hb)中依次添加: ");
for(i=; i<blen; i++)
{
printf("%d ", b[i]);
fib_heap_insert_key(hb, b[i]);
}
printf("\n");
printf("== 斐波那契堆(hb)删除最小节点\n");
fib_heap_extract_min(hb);
fib_print(hb); fib_heap_update(hb, , );
printf("== 将20增加为60\n");
fib_print(hb); fib_heap_destroy(hb);
} // 验证"删除节点"
void test_delete()
{
int i;
int blen=LENGTH(b);
FibHeap *hb = fib_heap_make(); // 斐波那契堆hb
printf("== 斐波那契堆(hb)中依次添加: ");
for(i=; i<blen; i++)
{
printf("%d ", b[i]);
fib_heap_insert_key(hb, b[i]);
}
printf("\n");
printf("== 斐波那契堆(hb)删除最小节点\n");
fib_heap_extract_min(hb);
fib_print(hb); fib_heap_delete(hb, );
printf("== 删除节点20\n");
fib_print(hb); fib_heap_destroy(hb);
} void main()
{
// 验证"基本信息(斐波那契堆的结构)"
test_basic();
// 验证"插入操作"
//test_insert();
// 验证"合并操作"
//test_union();
// 验证"删除最小节点"
//test_remove_min();
// 验证"减小节点"
//test_decrease();
// 验证"增大节点"
//test_increase();
// 验证"删除节点"
//test_delete();
}
斐波那契堆的C测试程序
斐波那契堆的测试程序包括了"插入"、"合并"、"增大"、"减小"、"删除"、"基本信息"等几种功能的测试代码。默认是运行的"基本信息(验证斐波那契堆的结构)"测试代码,你可以根据自己的需要来对相应的功能进行验证!
注意:C语言版的斐波那契堆的LOG2宏定义中使用了math.h,记得引入math库。例如,若你是在Linux下通过gcc编译,记得添加-lm参数(gcc *.c -lm)。
下面是基本信息测试代码的运行结果:
== 斐波那契堆(hb)中依次添加:
== 斐波那契堆(hb)删除最小节点
== 斐波那契堆的详细信息: ==
. () is root
() is 's child
() is 's next
() is 's child
() is 's next
() is 's child
() is 's next
() is 's child
. () is root
() is 's child
() is 's next
() is 's child
. () is root
斐波那契堆(一)之 图文解析 和 C语言的实现的更多相关文章
- 斐波那契堆(二)之 C++的实现
概要 上一章介绍了斐波那契堆的基本概念,并通过C语言实现了斐波那契堆.本章是斐波那契堆的C++实现. 目录1. 斐波那契堆的介绍2. 斐波那契堆的基本操作3. 斐波那契堆的C++实现(完整源码)4. ...
- 斐波那契堆(三)之 Java的实现
概要 前面分别通过C和C++实现了斐波那契堆,本章给出斐波那契堆的Java版本.还是那句老话,三种实现的原理一样,择其一了解即可. 目录1. 斐波那契堆的介绍2. 斐波那契堆的基本操作3. 斐波那契堆 ...
- 斐波那契堆(Fibonacci heap)原理详解(附java代码实现)
前言 斐波那契堆(Fibonacci heap)是计算机科学中最小堆有序树的集合.它和二项式堆有类似的性质,但比二项式堆有更好的均摊时间.堆的名字来源于斐波那契数,它常用于分析运行时间. 堆结构介绍 ...
- 基于visual Studio2013解决算法导论之045斐波那契堆
题目 斐波那契堆 解决代码及点评 // 斐波那契堆.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点. // #include<iostream> #include<cstdio> ...
- 笔试算法题(46):简介 - 二叉堆 & 二项树 & 二项堆 & 斐波那契堆
二叉堆(Binary Heap) 二叉堆是完全二叉树(或者近似完全二叉树):其满足堆的特性:父节点的值>=(<=)任何一个子节点的键值,并且每个左子树或者右子树都是一 个二叉堆(最小堆或者 ...
- fibonacci-Heap(斐波那契堆)原理及C++代码实现
斐波那契堆是一种高级的堆结构,建议与二项堆一起食用效果更佳. 斐波那契堆是一个摊还性质的数据结构,很多堆操作在斐波那契堆上的摊还时间都很低,达到了θ(1)的程度,取最小值和删除操作的时间复杂度是O(l ...
- 二叉堆(一)之 图文解析 和 C语言的实现
概要 本章介绍二叉堆,二叉堆就是通常我们所说的数据结构中"堆"中的一种.和以往一样,本文会先对二叉堆的理论知识进行简单介绍,然后给出C语言的实现.后续再分别给出C++和Java版本 ...
- 左倾堆(一)之 图文解析 和 C语言的实现
概要 本章介绍左倾堆,它和二叉堆一样,都是堆结构中的一员.和以往一样,本文会先对左倾堆的理论知识进行简单介绍,然后给出C语言的实现.后续再分别给出C++和Java版本的实现:实现的语言虽不同,但是原理 ...
- 二项堆(一)之 图文解析 和 C语言的实现
概要 本章介绍二项堆,它和之前所讲的堆(二叉堆.左倾堆.斜堆)一样,也是用于实现优先队列的.和以往一样,本文会先对二项堆的理论知识进行简单介绍,然后给出C语言的实现.后续再分别给出C++和Java版本 ...
随机推荐
- springJDBC学习笔记和实例
前言:相对于Mybatis(ibatis),个人感觉springJDBC更灵活,主要实现类JdbcTemplate:它替我们完成了资源的创建以及释放工作,从而简化了我们对JDBC的使用.它还可以帮助我 ...
- 不能返回函数内部new分配的内存的引用
以前在开发电子秤接口动态库时,曾尝试在用于获取重量的函数外面定义一个字符串指针,然后作为参数传入函数内部,然后在函数内部new,用来输出函数执行过程中发生的错误.但是总是出错,没有找到原因,后来无意中 ...
- 12套swift学习资源分享
虽然objective-c编程语言在过去很长一段时间都是iOS应用开发的基础语言,且很多iOS开发者对其也深爱有佳,但是随着swift编程语言的问世,迅速发展为开发者追捧的语言.且今年伴随着swift ...
- PHP中常用的正则表达式由哪些元素构成?
在程序开发中,我们常常要用到正则表达式,对于新手来说,很多时候知道正则表达式是怎么回事,但当真正需要使用的时候,却不知该用什么函数,具体的修饰符也比较混乱.下面小编就为大家整理了一些php正则表达式中 ...
- C++Builder及VC的库相互调用
coff2omf vc.lib bc.lib implib -f xxx.lib xxx.dll dll文件为VC编译的动态库lib文件为你需要转换的c++ builder 使用的静态库. 这也是 ...
- c# 操作excel 替代方案
一直使用excel com 接口进行excel 操作,最近一次因为权限折腾了个够呛,果断放弃,使用 NPOI FileStream file = new FileStream(url, FileMod ...
- 鸡和蛋的OO设计
一个题目:用类图表示出鸡和蛋的关系. 第一版: 第二版: 一个鸡可以下N个蛋,一个蛋可以浮出0或者1个鸡. 问题是公鸡不会下单,第三版:
- 【OpenWRT】 Chaos Calmer 15.05 编译
进入正题,编译环境准备完毕后,下载源码 git clone git://git.coding.net/leop/openwrt.git 复制代码 复制dl包(可以加快初次编译速度,但非必须)链接:pa ...
- 收不到Win10正式版预订通知?一个批处理搞定
目前,已经有不少Win7.Win8.1用户在系统右下角收到Win10正式版的预订提示窗口.点击接受预订后,系统会将Win10正式版所需的安装文件提前下载好,7月29日正式发布的时候,就可以第一时间升级 ...
- WPF Wonders: Transformations (and Robots!)
indows Presentation Framework (WPF) gets a lot of mileage out of being layered on top of DirectX, in ...
