InnoDB Architecture (InnoDB In-Memory Structures 转载)
转载、节选于 https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/innodb-in-memory-structures.html
InnoDB Architecture
The following diagram shows in-memory and on-disk structures that comprise the InnoDB storage engine architecture.
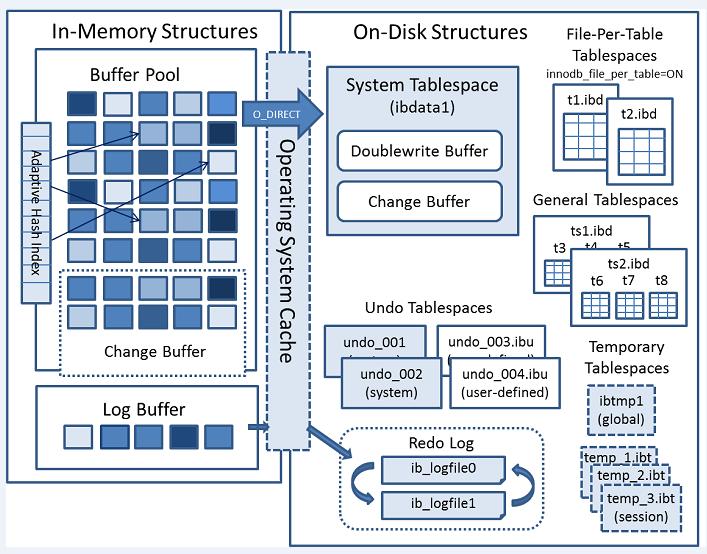
For InnoDB: The name of the data file. File-per-table and general tablespaces have an .ibd file name extension. Undo tablespaces are prefixed by undo. The system tablespace is prefixed by ibdata. The global temporary tablespace is prefixed by ibtmp. The file name includes the file path, which may be relative to the MySQL data directory (the value of the datadir system variable).
2.InnoDB In-Memory Structures
2.1 Buffer Pool
The buffer pool is an area in main memory where caches table and index data as it is accessed. The buffer pool permits frequently used data to be processed directly from memory, which speeds up processing. On dedicated servers, up to 80% of physical memory is often assigned to the buffer pool.
For efficiency of high-volume read operations, the buffer pool is divided into pages that can potentially hold multiple rows. For efficiency of cache management, the buffer pool is implemented as a linked list of pages; data that is rarely used is aged out of the cache using a variation of the LRU algorithm.
Buffer Pool LRU Algorithm
The buffer pool is managed as a list using a variation of the least recently used (LRU) algorithm. When room is needed to add a new page to the buffer pool, the least recently used page is evicted and a new page is added to the middle of the list.
his midpoint insertion strategy treats the list as two sublists:
At the head, a sublist of new (“young”) pages that were accessed recently
At the tail, a sublist of old pages that were accessed less recently

The algorithm keeps pages that are heavily used by queries in the new sublist. The old sublist contains less-used pages; these pages are candidates for eviction.
By default, the algorithm operates as follows:
3/8 of the buffer pool is devoted to the old sublist.
The midpoint of the list is the boundary where the tail of the new sublist meets the head of the old sublist.
When
InnoDBreads a page into the buffer pool, it initially inserts it at the midpoint (the head of the old sublist). A page can be read because it is required for a user-specified operation such as an SQL query, or as part of a read-ahead operation performed automatically byInnoDB.Accessing a page in the old sublist makes it “young”, moving it to the head of the buffer pool (the head of the new sublist). If the page was read because it was required, the first access occurs immediately and the page is made young. If the page was read due to read-ahead, the first access does not occur immediately (and might not occur at all before the page is evicted).
As the database operates, pages in the buffer pool that are not accessed “age” by moving toward the tail of the list. Pages in both the new and old sublists age as other pages are made new. Pages in the old sublist also age as pages are inserted at the midpoint. Eventually, a page that remains unused reaches the tail of the old sublist and is evicted.
By default, pages read by queries immediately move into the new sublist, meaning they stay in the buffer pool longer. A table scan (such as performed for a mysqldump operation, or a SELECT statement with no WHERE clause) can bring a large amount of data into the buffer pool and evict an equivalent amount of older data, even if the new data is never used again. Similarly, pages that are loaded by the read-ahead background thread and then accessed only once move to the head of the new list. These situations can push frequently used pages to the old sublist where they become subject to eviction.
2.2 Change Buffer
The change buffer is a special data structure that caches changes to secondary index pages when those pages are not in the buffer pool. The buffered changes, which may result from INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE operations (DML), are merged later when the pages are loaded into the buffer pool by other read operations.

Unlike clustered indexes, secondary indexes are usually nonunique, and inserts into secondary indexes happen in a relatively random order. Similarly, deletes and updates may affect secondary index pages that are not adjacently located in an index tree. Merging cached changes at a later time, when affected pages are read into the buffer pool by other operations, avoids substantial random access I/O that would be required to read secondary index pages into the buffer pool from disk.Merging cached changes at a later time, when affected pages are read into the buffer pool by other operations, avoids substantial random access I/O that would be required to read secondary index pages into the buffer pool from disk.
Periodically, the purge operation that runs when the system is mostly idle, or during a slow shutdown, writes the updated index pages to disk. The purge operation can write disk blocks for a series of index values more efficiently than if each value were written to disk immediately.
Change buffer merging may take several hours when there are many affected rows and numerous secondary indexes to update. During this time, disk I/O is increased, which can cause a significant slowdown for disk-bound queries. Change buffer merging may also continue to occur after a transaction is committed, and even after a server shutdown and restart
The type of data cached in the change buffer is governed by the innodb_change_buffering variable.
Change buffering is not supported for a secondary index if the index contains a descending index column or if the primary key includes a descending index column.
When INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE operations are performed on a table, the values of indexed columns (particularly the values of secondary keys) are often in an unsorted order, requiring substantial I/O to bring secondary indexes up to date. The change buffer caches changes to secondary index entries when the relevant page is not in the buffer pool, thus avoiding expensive I/O operations by not immediately reading in the page from disk. The buffered changes are merged when the page is loaded into the buffer pool, and the updated page is later flushed to disk. The InnoDB main thread merges buffered changes when the server is nearly idle, and during a slow shutdown.
Because it can result in fewer disk reads and writes, the change buffer feature is most valuable for workloads that are I/O-bound, for example applications with a high volume of DML operations such as bulk inserts.
However, the change buffer occupies a part of the buffer pool, reducing the memory available to cache data pages. If the working set almost fits in the buffer pool, or if your tables have relatively few secondary indexes, it may be useful to disable change buffering. If the working data set fits entirely within the buffer pool, change buffering does not impose extra overhead, because it only applies to pages that are not in the buffer pool.
You can control the extent to which InnoDB performs change buffering using the innodb_change_buffering configuration parameter. You can enable or disable buffering for inserts, delete operations (when index records are initially marked for deletion) and purge operations (when index records are physically deleted). An update operation is a combination of an insert and a delete. The default innodb_change_buffering value is all.
The innodb_change_buffer_max_size variable permits configuring the maximum size of the change buffer as a percentage of the total size of the buffer pool. By default,innodb_change_buffer_max_size is set to 25. The maximum setting is 50.
Test different settings with a representative workload to determine an optimal configuration. The innodb_change_buffer_max_size setting is dynamic, which permits modifying the setting without restarting the server.
2.3 Adaptive Hash Index
The adaptive hash index feature enables InnoDB to perform more like an in-memory database on systems with appropriate combinations of workload and sufficient memory for the buffer pool without sacrificing transactional features or reliability. The adaptive hash index feature is enabled by the innodb_adaptive_hash_indexvariable, or turned off at server startup by --skip-innodb-adaptive-hash-index.
Based on the observed pattern of searches, a hash index is built using a prefix of the index key. The prefix can be any length, and it may be that only some values in the B-tree appear in the hash index. Hash indexes are built on demand for the pages of the index that are accessed often.
If a table fits almost entirely in main memory, a hash index can speed up queries by enabling direct lookup of any element, turning the index value into a sort of pointer. InnoDB has a mechanism that monitors index searches. If InnoDB notices that queries could benefit from building a hash index, it does so automatically.
With some workloads, the speedup from hash index lookups greatly outweighs the extra work to monitor index lookups and maintain the hash index structure. Access to the adaptive hash index can sometimes become a source of contention under heavy workloads, such as multiple concurrent joins. Queries with LIKE operators and %wildcards also tend not to benefit. For workloads that do not benefit from the adaptive hash index feature, turning it off reduces unnecessary performance overhead. Because it is difficult to predict in advance whether the adaptive hash index feature is appropriate for a particular system and workload, consider running benchmarks with it enabled and disabled. Architectural changes in MySQL 5.6 make it more suitable to disable the adaptive hash index feature than in earlier releases.
The adaptive hash index feature is partitioned. Each index is bound to a specific partition, and each partition is protected by a separate latch. Partitioning is controlled by the innodb_adaptive_hash_index_parts variable. The innodb_adaptive_hash_index_parts variable is set to 8 by default. The maximum setting is 512.
You can monitor adaptive hash index use and contention in the SEMAPHORES section of SHOW ENGINE INNODB STATUS output. If there are numerous threads waiting on RW-latches created in btr0sea.c, consider increasing the number of adaptive hash index partitions or disabling the adaptive hash index feature.
2.4 Log Buffer
The log buffer is the memory area that holds data to be written to the log files on disk. Log buffer size is defined by the innodb_log_buffer_size variable. The default size is 16MB. The contents of the log buffer are periodically flushed to disk. A large log buffer enables large transactions to run without the need to write redo log data to disk before the transactions commit. Thus, if you have transactions that update, insert, or delete many rows, increasing the size of the log buffer saves disk I/O.
The innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit variable controls how the contents of the log buffer are written and flushed to disk. The innodb_flush_log_at_timeout variable controls log flushing frequency.
转载、节选于 https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/innodb-in-memory-structures.html
InnoDB Architecture (InnoDB In-Memory Structures 转载)的更多相关文章
- [转帖]mysql常用存储引擎(InnoDB、MyISAM、MEMORY、MERGE、ARCHIVE)介绍与如何选择
mysql常用存储引擎(InnoDB.MyISAM.MEMORY.MERGE.ARCHIVE)介绍与如何选择原创web洋仔 发布于2018-06-28 15:58:34 阅读数 1063 收藏展开 h ...
- MySQL存储引擎【InnoDB、MyISAM、Memory】
数据库,MySQL这样存在多存储引擎的数据库软件,清楚常见的存储引擎的区别,使用合适的存储引擎,使得项目跑的更顺畅,有时候对于一个项目,甚至比项目本身都重要.这篇文章,旨在浅谈常见的三种存储引擎的区别 ...
- 主流存储引擎详解:Innodb,Tokudb、Memory、MYISAM、Federated
主流存储引擎: Innodb:推荐使用,主力引擎,使用99%以上的场景 Tokudb:高速写入使用,日用量大量写入eg:500G可压缩为50G.适用于访问日志的写入,相对MYISAM有事务性,相对于I ...
- 14.6.4 Configuring the Memory Allocator for InnoDB 配置InnoDB 内存分配器
14.6.4 Configuring the Memory Allocator for InnoDB 配置InnoDB 内存分配器 当InnoDB 被开发时,内存分配提供了操作系统和 run-time ...
- MySQL常见的三种存储引擎(InnoDB、MyISAM、MEMORY)
简单来说,存储引擎就是指表的类型以及表在计算机上的存储方式. 存储引擎的概念是MySQL的特点,Oracle中没有专门的存储引擎的概念,Oracle有OLTP和OLAP模式的区分.不同的存储引擎决定了 ...
- MySQL三种InnoDB、MyISAM和MEMORY存储引擎对比
什么是存储引擎? MySQL中的数据用各种不同的技术存储在文件(或者内存)中.这些技术中的每一种技术都使用不同的存储机制.索引技巧.锁定水平并且最终提供广泛的不同的功能和能力.通过选择不同的技术,你能 ...
- 14.8.11 Physical Structure of an InnoDB Index InnoDB Index 的物理结构
14.8.11 Physical Structure of an InnoDB Index InnoDB Index 的物理结构 所有的InnoDB indexes 是 B-trees Index r ...
- 14.8.3 Physical Row Structure of InnoDB Tables InnoDB 表的物理行结构
14.8.3 Physical Row Structure of InnoDB Tables InnoDB 表的物理行结构 一个InnoDB 表的物理行结构取决于在创建表指定的行格式 默认, Inno ...
- 14.8.2 Role of the .frm File for InnoDB Tables InnoDB 表得到 .frm文件的作用
14.8.2 Role of the .frm File for InnoDB Tables InnoDB 表得到 .frm文件的作用 Vsftp:/data01/mysql/zjzc# ls -lt ...
随机推荐
- Prometheus笔记(二)监控go项目实时给grafana展示
欢迎加入go语言学习交流群 636728449 Prometheus笔记(二)监控go项目实时给grafana展示 Prometheus笔记(一)metric type 文章目录 一.promethe ...
- python3如何随机生成大数据存储到指定excel文档里
本次主要采用的是python3的第三方库xlwt,来创建一个excel文件.具体步骤如下: 1.确认存储位置,文件命名跟随时间格式 2.封装写入格式 3.实现随机数列生成 4.定位行和列把随机数写入 ...
- C语言之推箱子游戏代码
前言本文的文字及图片来源于网络,仅供学习.交流使用,不具有任何商业用途,版权归原作者所有,如有问题请及时联系我们以作处理.作者:Yan_Less 正文 新手注意:如果你学习遇到问题找不到人解答,可以点 ...
- tensorflow add_to_collection用法
训练代码: # coding: utf-8 from __future__ import print_function from __future__ import division import t ...
- 可扩展的Java线程池执行器
分享一下最近优锐课学习笔记. Java线程池执行程序偏向于排队而不是产生新线程.从好的方面来说,我们有两种解决方法. 理想情况下,对任何线程池执行程序而言,期望如下: 预先创建了一组初始线程(核心线程 ...
- 【Web技术】286- 自定义错误及扩展错误
英文:Ilya Kantor 译文:LeviDing https://zh.javascript.info/custom-errors 当我们在进行开发的时候,通常需要属于我们自己的错误类来反映任务 ...
- 一篇文章带你解读Redis分布式锁的发展史和正确实现方式
前言 近两年来微服务变得越来越热门,越来越多的应用部署在分布式环境中,在分布式环境中,数据一致性是一直以来需要关注并且去解决的问题,分布式锁也就成为了一种广泛使用的技术,常用的分布式实现方式为Redi ...
- [权限管理系统篇] (五)-Spring security(授权过程分析)
欢迎关注公众号[Ccww笔记],原创技术文章第一时间推出 前言 权限管理系统的组件分析以及认证过程的往期文章: Spring security (一)架构框架-Component.Service.Fi ...
- 视频剪辑什么鬼?Python 带你高效创作短视频
阅读文本大概需要 10 分钟. 近两年,抖音.快手将短视频推到风口浪尖上,要生产出高质量的视频,离不开视频剪辑这一环节:在全民剪片浪潮中,大众使用最多的剪辑软件如:Pr.FCPX.剪印.Vue 等. ...
- Python基础-day01-5
注释 目标 注释的作用 单行注释(行注释) 多行注释(块注释) 01. 注释的作用 使用用自己熟悉的语言,在程序中对某些代码进行标注说明,增强程序的可读性 02. 单行注释(行注释) 以 # 开头,# ...
