SpringBoot系列:Spring Boot异步调用@Async
在实际开发中,有时候为了及时处理请求和进行响应,我们可能会多任务同时执行,或者先处理主任务,也就是异步调用,异步调用的实现有很多,例如多线程、定时任务、消息队列等,
这一章节,我们就来讲讲@Async异步方法调用。
一、@Async使用演示
@Async是Spring内置注解,用来处理异步任务,在SpringBoot中同样适用,且在SpringBoot项目中,除了boot本身的starter外,不需要额外引入依赖。
而要使用@Async,需要在启动类上加上@EnableAsync主动声明来开启异步方法。
@EnableAsync
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootApplication.class, args);
}
}
现假设有3个任务需要去处理,分别对应AsyncTask类的taskOne、taskTwo、taskThree方法,这里做了线程的sleep来模拟实际运行。
@Slf4j
@Component
public class AsyncTask {
private Random random = new Random();
public void taskOne() throws InterruptedException {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(10000));
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("任务一执行完成耗时{}秒", (end - start)/1000f);
}
public void taskTwo() throws InterruptedException {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(10000));
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("任务二执行完成耗时{}秒", (end - start)/1000f);
}
public void taskThree() throws InterruptedException {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(10000));
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("任务三执行完成耗时{}秒", (end - start)/1000f);
}
}
然后编写测试类,由于@Async注解需要再Spring容器启动后才能生效,所以这里讲测试类放到了SpringBoot的test包下,使用了SpringBootTest。
@Slf4j
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = SpringbootApplication.class)
public class AsyncTaskTest {
@Autowired
private AsyncTask asyncTask;
@Test
public void doAsyncTasks(){
try {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
asyncTask.taskOne();
asyncTask.taskTwo();
asyncTask.taskThree();
Thread.sleep(5000);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("主程序执行完成耗时{}秒", (end - start)/1000f);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
运行测试方法,可以在控制台看到任务一二三按顺序执行,最后主程序完成,这和我们的预期一样,因为我们没有任何额外的处理,他们就是普通的方法,按编码顺序依次执行。
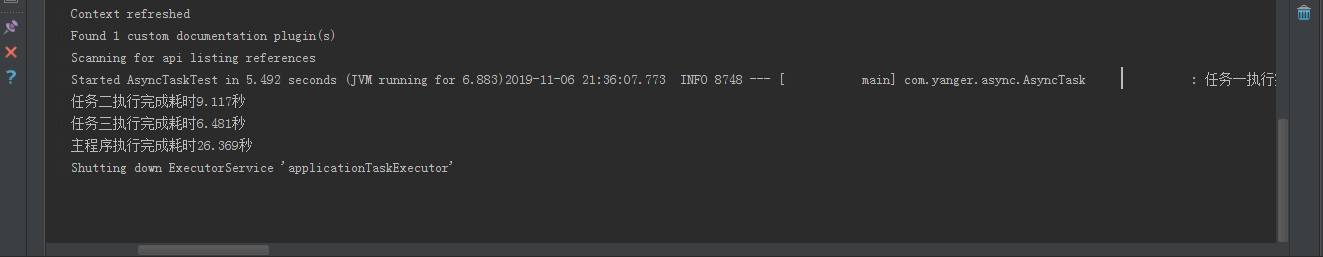
而如果要使任务并发执行,我们只需要在任务方法上使用@Async注解即可,需要注意的是@Async所修饰的方法不要定义为static类型,这样异步调用不会生效。
@Slf4j
@Component
public class AsyncTask {
private Random random = new Random();
//@Async所修饰的函数不要定义为static类型,这样异步调用不会生效
@Async
public void taskOne() throws InterruptedException {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(10000));
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("任务一执行完成耗时{}秒", (end - start)/1000f);
}
@Async
public void taskTwo() throws InterruptedException {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(10000));
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("任务二执行完成耗时{}秒", (end - start)/1000f);
}
@Async
public void taskThree() throws InterruptedException {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(10000));
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("任务三执行完成耗时{}秒", (end - start)/1000f);
}
}
然后我们在运行测试类,这个时候输出可能就五花八门了,任意任务都可能先执行完成,也有可能有的方法因为主程序关闭而没有输出。

二、Future获取异步执行结果
上面演示了@Async,但是有时候除了需要任务并发调度外,我们还需要获取任务的返回值,且在多任务都执行完成后再结束主任务,这个时候又该怎么处理呢?
在多线程里通过Callable和Future可以获取返回值,这里也是类似的,我们使用Future返回方法的执行结果,AsyncResult是Future的一个实现类。
@Slf4j
@Component
public class FutureTask {
private Random random = new Random();
//@Async所修饰的函数不要定义为static类型,这样异步调用不会生效
@Async
public Future<String> taskOne() throws InterruptedException {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(10000));
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("任务一执行完成耗时{}秒", (end - start)/1000f);
return new AsyncResult <>("任务一Ok");
}
@Async
public Future<String> taskTwo() throws InterruptedException {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(10000));
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("任务二执行完成耗时{}秒", (end - start)/1000f);
return new AsyncResult <>("任务二OK");
}
@Async
public Future<String> taskThree() throws InterruptedException {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(10000));
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("任务三执行完成耗时{}秒", (end - start)/1000f);
return new AsyncResult <>("任务三Ok");
}
}
在AsyncResult中:
- isDone()方法可以用于判断异步方法是否执行完成,若任务完成,则返回true
- get()方法可用于获取任务执行后返回的结果
- cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning)可用于取消任务,参数mayInterruptIfRunning表示是否允许取消正在执行却没有执行完毕的任务,如果设置true,则表示可以取消正在执行过程中的任务
- isCancelled()方法表示任务是否被取消成功,如果在任务正常完成前被取消成功,则返回 true
- get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)用来获取执行结果,如果在指定时间内,还没获取到结果,就直接返回null
@Slf4j
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = SpringbootApplication.class)
public class AsyncTaskTest {
@Autowired
private FutureTask futureTask;
@Test
public void doFutureTasks(){
try {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Future <String> future1 = futureTask.taskOne();
Future <String> future2 = futureTask.taskTwo();
Future <String> future3 = futureTask.taskThree();
//3个任务执行完成之后再执行主程序
do {
Thread.sleep(100);
} while (future1.isDone() && future2.isDone() && future3.isDone());
log.info("获取异步方法的返回值:{}", future1.get());
Thread.sleep(5000);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("主程序执行完成耗时{}秒", (end - start)/1000f);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
运行测试类,我们可以看到任务一二三异步执行了,主任务最后执行完成,而且可以获取到任务的返回信息。

源码地址:https://github.com/imyanger/springboot-project/tree/master/p23-springboot-async
SpringBoot系列:Spring Boot异步调用@Async的更多相关文章
- Spring Boot 异步调用
添加一个类ThreadPoolConfig.java package com.cjcx.inter.framework.config; import org.springframework.conte ...
- spring boot中使用@Async实现异步调用任务
本篇文章主要介绍了spring boot中使用@Async实现异步调用任务,小编觉得挺不错的,现在分享给大家,也给大家做个参考.一起跟随小编过来看看吧 什么是“异步调用”? “异步调用”对应的是“同步 ...
- SpringBoot学习笔记(七):SpringBoot使用AOP统一处理请求日志、SpringBoot定时任务@Scheduled、SpringBoot异步调用Async、自定义参数
SpringBoot使用AOP统一处理请求日志 这里就提到了我们Spring当中的AOP,也就是面向切面编程,今天我们使用AOP去对我们的所有请求进行一个统一处理.首先在pom.xml中引入我们需要的 ...
- springboot:异步调用@Async
在后端开发中经常遇到一些耗时或者第三方系统调用的情况,我们知道Java程序一般的执行流程是顺序执行(不考虑多线程并发的情况),但是顺序执行的效率肯定是无法达到我们的预期的,这时就期望可以并行执行,常规 ...
- Spring Boot 异步请求和异步调用,一文搞定
一.Spring Boot中异步请求的使用 1.异步请求与同步请求 特点: 可以先释放容器分配给请求的线程与相关资源,减轻系统负担,释放了容器所分配线程的请求,其响应将被延后,可以在耗时处理完成(例如 ...
- springboot:嵌套使用异步注解@Async还会异步执行吗
一.引言 在前边的文章<[springboot:使用异步注解@Async的那些坑>中介绍了使用@Async注解获取任务执行结果的错误用法,今天来分享下另外一种常见的错误. 二.代码演示 下 ...
- 【SpringBoot】Spring Boot,开发社区讨论交流网站首页。
初识Spring Boot,开发社区讨论交流网站首页. 文章目录 初识Spring Boot,开发社区讨论交流网站首页. 1.项目简介 2. 搭建开发环境 JDK Apache Maven Intel ...
- 56. spring boot中使用@Async实现异步调用【从零开始学Spring Boot】
什么是"异步调用"? "异步调用"对应的是"同步调用",同步调用指程序按照定义顺序依次执行,每一行程序都必须等待上一行程序执行完成之后才能执 ...
- Spring Boot中使用@Async实现异步调用,加速任务的执行!
什么是"异步调用"?"异步调用"对应的是"同步调用",同步调用指程序按照定义顺序依次执行,每一行程序都必须等待上一行程序执行完成之后才能执行 ...
随机推荐
- Mybatis基础知识点
1. Mybatis框架优缺点 优点: 1. 易于上手和掌握. 2. sql写在xml里,便于统一管理和优化. 3. 解除sql与程序代码的耦合. 4. 提供映射标签,支持对象与数据库的orm字段关系 ...
- vue-cli 脚手架安装
1.安装node;选择适合自己系统的文件,下载一路next , a安装成功后,打开运行输入cmd 进入命令行: 在命令行工具中输入 npm -v 检查版本号 如果出现 则安装成功:(npm为node ...
- 14.Django基础之jQuery操作cookie
jquery之cookie操作 定义:让网站服务器把少量数据储存到客户端的硬盘或内存,从客户端的硬盘读取数据的一种技术: 下载与引入:jquery.cookie.js基于jquery:先引入jquer ...
- vue-hash-calendar,移动端日期时间选择插件
按照惯例,先上效果图 vue-hash-calendar 基于 vue 2.X 开发的日历组件 支持手势滑动操作·1 原生 js 开发,没引入第三方库 上下滑动 切换 周/月 模式 [周模式中] 左右 ...
- golang面试题--string操作
题目: 请实现一个算法,确定一个字符串的所有字符[是否全都不同].这里我们要求[不允许使用额外的存储结构].给定一个string,请返回一个bool值,true代表所有字符全都不同,false代表存在 ...
- Java 从入门到进阶之路(八)
在之前的文章我们介绍了一下 Java 中的重载,接下来我们看一下 Java 中的构造方法. 我们之前说过,我们在定义一个变量的时候,java 会为我们提供一个默认的值,字符串为 null,数字为 0. ...
- SpringBoot源码分析之---SpringBoot项目启动类SpringApplication浅析
源码版本说明 本文源码采用版本为SpringBoot 2.1.0BUILD,对应的SpringFramework 5.1.0.RC1 注意:本文只是从整体上梳理流程,不做具体深入分析 SpringBo ...
- 06-01 DeepLearning-图像识别
目录 深度学习-图像识别 一.人脸定位 二.手工提取特征的图像分类 2.1 识图认物 2.2 传统分类系统的特征提取 2.3 计算机眼中的图像 2.4 什么是图像特征? 2.5 卷积运算 2.6 利用 ...
- html隐写术,使用摩尔兹电码/莫尔兹电码存储信息 水波纹样式 Morse code
html水波纹样式,源码直接下载,代码有注释教程,小白可以看懂. 动画啥的都做好了,效果我觉得还不错 网上文章看到xbox 工程师使用隐写术,在界面的右下角放上了含有用户激活码的水波纹样式,一般人还真 ...
- 渗透测试-基于白名单执行payload--Compiler
复现亮神课程 0x01 Compiler前言 说明:Microsoft.Workflow.Comiler.exe是.NET Framework默认自带的一个实用工具,用户能够以XOML工作流文件的形式 ...
