ubutu tornado python3.7.5 nginx supervisor 部署web api
环境:
1、Ubuntu 服务器
2、python3.7.5
安装
1、python3.7.5
安装的话还是比较简单,流程大致是
./configure ->make && make install ->创建python软连接 pip软连接
安装起来倒是简单,安装完成运行才会遇到各种各样的问题,缺少插件啥的。
1.1、下载包 python3.7.5
1.2、问题
a、No module named '_ctypes'
sudo apt-get install libffi-dev 需不需要重新安装看ok不
b、No module named _ssl
安装之前修改下安装包里面的modules里面的setup.dist文件的内容
ex: /usr/web/tornadoTest/package/Python-3.7.5/Modules/Setup.dist 我的安装目录
大约 206行左右,去掉注释即可
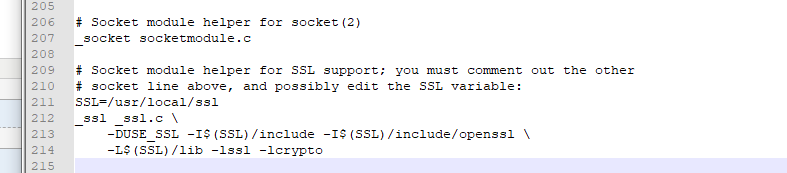
然后再重新安装,等pip这些可以用起来了在开始下一步。
2、安装所需的package
需要的包有mysqldb tornado torndb,看你用的是pymysql还是mysqldb

2.1 普通安装 pip install
2.2 mysqldb 安装
安装mysqldb 之前需要配置mysql_config
sudo apt-get install libmysqlclient-dev
sudo apt-get install python-dev
然后安装。
3、启动错误
3.1 torndb的错误
if MySQLdb is not None:
# Fix the access conversions to properly recognize unicode/binary
FIELD_TYPE = MySQLdb.constants.FIELD_TYPE
FLAG = MySQLdb.constants.FLAG
CONVERSIONS = copy.copy(MySQLdb.converters.conversions)
field_types = [FIELD_TYPE.BLOB, FIELD_TYPE.STRING, FIELD_TYPE.VAR_STRING]
if 'VARCHAR' in vars(FIELD_TYPE):
field_types.append(FIELD_TYPE.VARCHAR)
#for field_type in field_types:
# CONVERSIONS[field_type] = [(FLAG.BINARY, str)] + CONVERSIONS[field_type]
注释掉这个
3.2 然后启动成功查询数据时可能还会原道这种错误。

https://www.cnblogs.com/simplezhuo/p/9811369.html
4、nginx 配置
4.1、tornado服务可以运行
python server.py --port 8888
nohup python server.py 登出也不会停止。
4.2、配置
default.conf
##
# You should look at the following URL's in order to grasp a solid understanding
# of Nginx configuration files in order to fully unleash the power of Nginx.
# http://wiki.nginx.org/Pitfalls
# http://wiki.nginx.org/QuickStart
# http://wiki.nginx.org/Configuration
#
# Generally, you will want to move this file somewhere, and start with a clean
# file but keep this around for reference. Or just disable in sites-enabled.
#
# Please see /usr/share/doc/nginx-doc/examples/ for more detailed examples.
## # Default server configuration
#
upstream tornados{
server 127.0.0.1:8888;
}
proxy_next_upstream error;
server {
listen 80 default_server;
listen [::]:80 default_server; # SSL configuration
#
# listen 443 ssl default_server;
# listen [::]:443 ssl default_server;
#
# Note: You should disable gzip for SSL traffic.
# See: https://bugs.debian.org/773332
#
# Read up on ssl_ciphers to ensure a secure configuration.
# See: https://bugs.debian.org/765782
#
# Self signed certs generated by the ssl-cert package
# Don't use them in a production server!
#
# include snippets/snakeoil.conf;
# Add index.php to the list if you are using PHP
index index.html index.htm index.nginx-debian.html; server_name 111.231.201.164; location /cnc/1/ {
alias /usr/web/cnc/;
index index.html index.htm;
}
location /cnc/2/ {
alias /usr/web/cnc/;
index index.html index.htm;
}
location /cnc/3 {
alias /usr/web/cnc/;
index index.html index.htm;
}
location /cnc/4 {
alias /usr/web/cnc/;
index index.html index.htm;
}
location /cnc/5 {
alias /usr/web/cnc/;
index index.html index.htm;
}
location /cnc/6 {
alias /usr/web/cnc/;
index index.html index.htm;
}
location /cnc/7 {
alias /usr/web/cnc/;
index index.html index.htm;
}
location /api/{
allow 111.231.201.164;
proxy_pass_header Server;
proxy_set_header Host $http_host;
proxy_redirect off;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Scheme $scheme;
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8888/;
} # pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# include snippets/fastcgi-php.conf;
#
# # With php7.0-cgi alone:
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# # With php7.0-fpm:
# fastcgi_pass unix:/run/php/php7.0-fpm.sock;
#} # deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
} # Virtual Host configuration for example.com
#
# You can move that to a different file under sites-available/ and symlink that
# to sites-enabled/ to enable it.
#
#server {
# listen 80;
# listen [::]:80;
#
# server_name example.com;
#
# root /var/www/example.com;
# index index.html;
#
# location / {
# try_files $uri $uri/ =404;
# }
#}
现在就是把tornado的服务127.0.0.1:8888 挂载在了80端口+api/上
原始访问:http://111.231.201.164:8888/houses
现在:http://111.231.201.164/api/houses
5、supervisor 配置
5.1、安装supervisor
sudo apt-get install supervisor
创建配置文件
echo_supervisord_conf > /etc/supervisord.conf
; Sample supervisor config file.
;
; For more information on the config file, please see:
; http://supervisord.org/configuration.html
;
; Notes:
; - Shell expansion ("~" or "$HOME") is not supported. Environment
; variables can be expanded using this syntax: "%(ENV_HOME)s".
; - Quotes around values are not supported, except in the case of
; the environment= options as shown below.
; - Comments must have a leading space: "a=b ;comment" not "a=b;comment".
; - Command will be truncated if it looks like a config file comment, e.g.
; "command=bash -c 'foo ; bar'" will truncate to "command=bash -c 'foo ".
;
; Warning:
; Paths throughout this example file use /tmp because it is available on most
; systems. You will likely need to change these to locations more appropriate
; for your system. Some systems periodically delete older files in /tmp.
; Notably, if the socket file defined in the [unix_http_server] section below
; is deleted, supervisorctl will be unable to connect to supervisord. [unix_http_server]
file=/tmp/supervisor.sock ; the path to the socket file
;chmod=0700 ; socket file mode (default 0700)
;chown=nobody:nogroup ; socket file uid:gid owner
;username=user ; default is no username (open server)
;password=123 ; default is no password (open server) ; Security Warning:
; The inet HTTP server is not enabled by default. The inet HTTP server is
; enabled by uncommenting the [inet_http_server] section below. The inet
; HTTP server is intended for use within a trusted environment only. It
; should only be bound to localhost or only accessible from within an
; isolated, trusted network. The inet HTTP server does not support any
; form of encryption. The inet HTTP server does not use authentication
; by default (see the username= and password= options to add authentication).
; Never expose the inet HTTP server to the public internet. ;[inet_http_server] ; inet (TCP) server disabled by default
;port=127.0.0.1:9001 ; ip_address:port specifier, *:port for all iface
;username=user ; default is no username (open server)
;password=123 ; default is no password (open server) [supervisord]
logfile=/tmp/supervisord.log ; main log file; default $CWD/supervisord.log
logfile_maxbytes=50MB ; max main logfile bytes b4 rotation; default 50MB
logfile_backups=10 ; # of main logfile backups; 0 means none, default 10
loglevel=info ; log level; default info; others: debug,warn,trace
pidfile=/tmp/supervisord.pid ; supervisord pidfile; default supervisord.pid
nodaemon=false ; start in foreground if true; default false
minfds=1024 ; min. avail startup file descriptors; default 1024
minprocs=200 ; min. avail process descriptors;default 200
;umask=022 ; process file creation umask; default 022
;user=supervisord ; setuid to this UNIX account at startup; recommended if root
;identifier=supervisor ; supervisord identifier, default is 'supervisor'
;directory=/tmp ; default is not to cd during start
;nocleanup=true ; don't clean up tempfiles at start; default false
;childlogdir=/tmp ; 'AUTO' child log dir, default $TEMP
;environment=KEY="value" ; key value pairs to add to environment
;strip_ansi=false ; strip ansi escape codes in logs; def. false ; The rpcinterface:supervisor section must remain in the config file for
; RPC (supervisorctl/web interface) to work. Additional interfaces may be
; added by defining them in separate [rpcinterface:x] sections. [rpcinterface:supervisor]
supervisor.rpcinterface_factory = supervisor.rpcinterface:make_main_rpcinterface ; The supervisorctl section configures how supervisorctl will connect to
; supervisord. configure it match the settings in either the unix_http_server
; or inet_http_server section. [supervisorctl]
serverurl=unix:///tmp/supervisor.sock ; use a unix:// URL for a unix socket
;serverurl=http://127.0.0.1:9001 ; use an http:// url to specify an inet socket
;username=chris ; should be same as in [*_http_server] if set
;password=123 ; should be same as in [*_http_server] if set
;prompt=mysupervisor ; cmd line prompt (default "supervisor")
;history_file=~/.sc_history ; use readline history if available ; The sample program section below shows all possible program subsection values.
; Create one or more 'real' program: sections to be able to control them under
; supervisor. ;[program:theprogramname]
;command=/bin/cat ; the program (relative uses PATH, can take args)
;process_name=%(program_name)s ; process_name expr (default %(program_name)s)
;numprocs=1 ; number of processes copies to start (def 1)
;directory=/tmp ; directory to cwd to before exec (def no cwd)
;umask=022 ; umask for process (default None)
;priority=999 ; the relative start priority (default 999)
;autostart=true ; start at supervisord start (default: true)
;startsecs=1 ; # of secs prog must stay up to be running (def. 1)
;startretries=3 ; max # of serial start failures when starting (default 3)
;autorestart=unexpected ; when to restart if exited after running (def: unexpected)
;exitcodes=0 ; 'expected' exit codes used with autorestart (default 0)
;stopsignal=QUIT ; signal used to kill process (default TERM)
;stopwaitsecs=10 ; max num secs to wait b4 SIGKILL (default 10)
;stopasgroup=false ; send stop signal to the UNIX process group (default false)
;killasgroup=false ; SIGKILL the UNIX process group (def false)
;user=chrism ; setuid to this UNIX account to run the program
;redirect_stderr=true ; redirect proc stderr to stdout (default false)
;stdout_logfile=/a/path ; stdout log path, NONE for none; default AUTO
;stdout_logfile_maxbytes=1MB ; max # logfile bytes b4 rotation (default 50MB)
;stdout_logfile_backups=10 ; # of stdout logfile backups (0 means none, default 10)
;stdout_capture_maxbytes=1MB ; number of bytes in 'capturemode' (default 0)
;stdout_events_enabled=false ; emit events on stdout writes (default false)
;stdout_syslog=false ; send stdout to syslog with process name (default false)
;stderr_logfile=/a/path ; stderr log path, NONE for none; default AUTO
;stderr_logfile_maxbytes=1MB ; max # logfile bytes b4 rotation (default 50MB)
;stderr_logfile_backups=10 ; # of stderr logfile backups (0 means none, default 10)
;stderr_capture_maxbytes=1MB ; number of bytes in 'capturemode' (default 0)
;stderr_events_enabled=false ; emit events on stderr writes (default false)
;stderr_syslog=false ; send stderr to syslog with process name (default false)
;environment=A="1",B="2" ; process environment additions (def no adds)
;serverurl=AUTO ; override serverurl computation (childutils) ; The sample eventlistener section below shows all possible eventlistener
; subsection values. Create one or more 'real' eventlistener: sections to be
; able to handle event notifications sent by supervisord. ;[eventlistener:theeventlistenername]
;command=/bin/eventlistener ; the program (relative uses PATH, can take args)
;process_name=%(program_name)s ; process_name expr (default %(program_name)s)
;numprocs=1 ; number of processes copies to start (def 1)
;events=EVENT ; event notif. types to subscribe to (req'd)
;buffer_size=10 ; event buffer queue size (default 10)
;directory=/tmp ; directory to cwd to before exec (def no cwd)
;umask=022 ; umask for process (default None)
;priority=-1 ; the relative start priority (default -1)
;autostart=true ; start at supervisord start (default: true)
;startsecs=1 ; # of secs prog must stay up to be running (def. 1)
;startretries=3 ; max # of serial start failures when starting (default 3)
;autorestart=unexpected ; autorestart if exited after running (def: unexpected)
;exitcodes=0 ; 'expected' exit codes used with autorestart (default 0)
;stopsignal=QUIT ; signal used to kill process (default TERM)
;stopwaitsecs=10 ; max num secs to wait b4 SIGKILL (default 10)
;stopasgroup=false ; send stop signal to the UNIX process group (default false)
;killasgroup=false ; SIGKILL the UNIX process group (def false)
;user=chrism ; setuid to this UNIX account to run the program
;redirect_stderr=false ; redirect_stderr=true is not allowed for eventlisteners
;stdout_logfile=/a/path ; stdout log path, NONE for none; default AUTO
;stdout_logfile_maxbytes=1MB ; max # logfile bytes b4 rotation (default 50MB)
;stdout_logfile_backups=10 ; # of stdout logfile backups (0 means none, default 10)
;stdout_events_enabled=false ; emit events on stdout writes (default false)
;stdout_syslog=false ; send stdout to syslog with process name (default false)
;stderr_logfile=/a/path ; stderr log path, NONE for none; default AUTO
;stderr_logfile_maxbytes=1MB ; max # logfile bytes b4 rotation (default 50MB)
;stderr_logfile_backups=10 ; # of stderr logfile backups (0 means none, default 10)
;stderr_events_enabled=false ; emit events on stderr writes (default false)
;stderr_syslog=false ; send stderr to syslog with process name (default false)
;environment=A="1",B="2" ; process environment additions
;serverurl=AUTO ; override serverurl computation (childutils) ; The sample group section below shows all possible group values. Create one
; or more 'real' group: sections to create "heterogeneous" process groups. ;[group:thegroupname]
;programs=progname1,progname2 ; each refers to 'x' in [program:x] definitions
;priority=999 ; the relative start priority (default 999) ; The [include] section can just contain the "files" setting. This
; setting can list multiple files (separated by whitespace or
; newlines). It can also contain wildcards. The filenames are
; interpreted as relative to this file. Included files *cannot*
; include files themselves. [include]
files = /etc/supervisor/*.conf
再建一个配置文件
tornado.conf
[group:tornadoes]
programs=tornado-8888 [program:tornado-8888]
command=/usr/bin/python /usr/web/tornadoTest/server.py --port=8888 ##python tornado启动py
directory=/usr/web/tornadoTest
user=root
autorestart=true
redirect_stderr=true
stdout_logfile=/usr/web/tornadoTest/logs
loglevel=info
5.2 启动
启动 supervisord -c /etc/supervisord.conf 指定配置文件
supervisorctl shutdown 关闭supervisor

至此。
附上api的代码
server.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import tornado.ioloop
from src.urls import * # 引入urls
import torndb
import conf.db as dbSettings
import os class Application(tornado.web.Application):
def __init__(self):
handlers = [
# (r"/", MainHandler),
# (r"/story/(sishen[0-9]+)", StoryHandler), # 正则url映射,方便get
(r"/houses/([0-9]+)", HouseHandler),
(r"/houses", HouseHandler),
]
settings = dict(
template_path=os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), "templates"),
static_path=os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), "statics"),
debug=True,
)
super(Application, self).__init__(handlers, **settings)
# 获取数据库配置信息
dbInfo = dbSettings.default
# 创建一个全局mysql连接实例供handler使用
self.db = torndb.Connection(host=dbInfo['host'], user=dbInfo['user'],
password=dbInfo['password'], database=dbInfo['dbName'], charset='utf8') if __name__ == "__main__":
application = Application()
application.listen(8888)
tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.instance().start()
urls.py
import tornado.web
import json
from conf.log import decoratore # 引入日志装饰器
from conf.fun import * class BaseHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
# blog.csdn.net/moshowgame 解决跨域问题
def set_default_headers(self):
self.set_header("Access-Control-Allow-Origin", "*") # 这个地方可以写域名
self.set_header("Access-Control-Allow-Headers", "x-requested-with, Authorization")
self.set_header('Access-Control-Allow-Methods', 'POST, GET, OPTIONS')
self.set_header('Access-Control-Allow-Credentials', 'true') # def write(self, chunk):
# self.set_header('Access-Control-Allow-Origin', 'http://localhost:4200')
# self.set_header('Access-Control-Allow-Headers', 'Origin, X-Requested-With, Content-Type, Accept, x-token, X-File-Upload')
# self.set_header('Access-Control-Allow-Methods', 'POST, GET, PUT, OPTIONS, DELETE')
# self.set_header('Access-Control-Allow-Credentials', 'true')
# super(BaseHandler, self).write(chunk) class MainHandler(BaseHandler):
@decoratore
def get(self):
self.write("Hello, World")
# 访问: http://localhost:8888/story/sishen232 # 显示:U get story id is sishen232 class HouseHandler(BaseHandler):
'''house class''' def __init__(self, application, request):
'''必填参数'''
super().__init__(application, request)
# 预处理
self.data = ByteData(self.request.arguments)
self.params = ['title', 'position', 'size', 'address'] @decoratore
def post(self):
'''提交House接口'''
# # 判断提交参数是否有误
# if(('title' not in raw_data) or ('position' not in raw_data)):
# self.write(json.dumps(
# {"false": {"msg": '参数错误'}}, ensure_ascii=False))
# return
code = paramsCheck(self.data, self.params)
if code == 1:
raw_data = self.data
if('year' not in raw_data):
raw_data['year'] = ''
print(raw_data)
data = self.application.db.execute(
"insert into house(title, position, size, address, year) values('{}', '{}', {}, '{}', '{}')".format(raw_data['title'], raw_data['position'], float(raw_data['size']), raw_data['address'], raw_data['year']))
# self.write(json.dumps({"sum": s}))
self.write(json.dumps(
{"success": {"msg": '添加成功'}}, ensure_ascii=False))
else:
self.write(json.dumps(
{"false": {"msg": '参数错误'}}, ensure_ascii=False)) def get(self, House_id=''):
'''
# 获取House接口
# House_id 存在则获取该条数据,不存在获取所有数据
'''
sql = 'select * from house' if House_id == '' else 'select * from house where id = {id}'.format(
id=House_id)
data = self.application.db.query(sql)
# self.write(json.dumps({"sum": s}))
self.write(json.dumps(
{"success": {"msg": '获取成功', "data": data}}, ensure_ascii=False))
日志装饰器和一些通用函数去掉即可。
ubutu tornado python3.7.5 nginx supervisor 部署web api的更多相关文章
- Linux+Nginx+Supervisor部署ASP.NET Core实操手册
一.课程介绍 在上一节课程<ASP.NET Core托管和部署Linux实操演练手册>中我们学过net core的部署方式多样性和灵活性.我们通过远程工具输入dotnet 程序集名称.dl ...
- 基于flask+gunicorn+nginx来部署web App
基于flask+gunicorn&&nginx来部署web App WSGI协议 Web框架致力于如何生成HTML代码,而Web服务器用于处理和响应HTTP请求.Web框架和Web服务 ...
- 用nginx的反向代理机制解决前端跨域问题在nginx上部署web静态页面
用nginx的反向代理机制解决前端跨域问题在nginx上部署web静态页面 1.什么是跨域以及产生原因 跨域是指a页面想获取b页面资源,如果a.b页面的协议.域名.端口.子域名不同,或是a页面为ip地 ...
- Windows Server 部署WEB API时内部错误
Windows Server 部署WEB API时,发生HTTP 错误 500.21 - Internal Server Error,如图所示: 错误原因:IIS注册Framework4.0 解决方法 ...
- CentOS+Nginx+Supervisor部署ASP.NET Core项目
对.Net Core的学习和实践,已经进行了一年多的世间,截止目前,微软已经发布.Net Core2.1,关于.NetCore的应用部署的文章比比皆是.今天借此,回顾下.net core环境的部署过程 ...
- nginx+uwsgi+django+virtualenv+supervisor部署web服务器
wsgi 全称web server gateway interface,wsgi不是服务器,也不是python模块,只是一种协议,描述web server如何和web application通信的规则 ...
- 两篇文章带你走入.NET Core 世界:Kestrel+Nginx+Supervisor 部署上云服务器(二)
背景: 上一篇:两篇文章带你走入.NET Core 世界:CentOS+Kestrel+Ngnix 虚拟机先走一遍(一) 已经交待了背景,这篇就省下背景了,这是第二篇文章了,看完就木有下篇了. 直接进 ...
- python3.x +django + nginx + uwsgi 搭建web服务
最近一直在用django开发自己的网站.在开发和线上环境的对接过程中遇到了许多的坑.所以想以一个老鸟的经历来写一下怎么 搭建web服务 一.python3.x .django .nginx .uwsg ...
- ubuntu Nginx+tomcat 部署web项目
最近学习了一下java web方面的知识,最后终于把项目部署到了阿里云服务器上,还是遇到了一些难点,记录总结一下 首先就是网上资料中,jdk都比较老了,最新的jdk14,没有了jre,这样导致了tom ...
随机推荐
- 【nodejs原理&源码赏析(7)】【译】Node.js中的事件循环,定时器和process.nextTick
目录 Event Loop 是什么? Event Loop 基本解释 事件循环阶段概览 事件循环细节 timers pending callbacks poll阶段 check close callb ...
- 这个立冬,我线下面基了一位TMD高级专家,太牛逼了!
立冬刚过,迎面而来的是一股寒气.天气如此,市场亦是如此.昨天周五,和1个认识的技术专家老刘约饭,也算是线下面基,增进感情.每年我都要向比我高阶的朋友讨教.不由自主聊到了他的职场生涯.鱼哥一直以为自己命 ...
- docker tomcat镜像部署springbootwar包
springboot打war包 1.在pom文件中增加插件 <build> <finalName>xx</finalName> <plugins> &l ...
- IDEA插件开发(一)一个简单的表单demo
- 使用Carthage集成Alamofire
Carthage相较于Cocoapods有着使用灵活,对目标工程改动小的优势,使得它越来越受欢迎.今天就对我使用Carthage集成FBSDK做一个记录. 1.首先https://github.com ...
- 常见的linux快捷方式和英文错误提示
第5章 linux常见的快捷方式 Ctrl +l 清屏的意思 2 Ctrl +c 退出当前的进程 3 Ctrl +w 删除光标到空格之间的信息 4 Ctrl +a 快速移动到光标行首 5 Ctrl + ...
- Ceph 提供iSCSI存储
Tgtd+Ceph部署 一.yum安装tgt [root@c720181 ~]# yum --enablerepo=epel -y install scsi-target-utils libxslt ...
- AddTransient、AddSingleton、AddScoped的区别
权重: AddSingleton→AddTransient→AddScoped AddSingleton的生命周期: 项目启动-项目关闭 相当于静态类 只会有一个 AddScoped的生命周期: ...
- jqurey(尺寸,css操作,效果,遍历)
尺寸: height():设置或返回元素的高度(不包括内边距.边框或外边距). width():设置或返回元素的宽度(不包括内边距.边框或外边距). 例如: $("#box").h ...
- 国内加速git下载速度
主要是配置hosts文件 151.101.72.133 assets-cdn.github.com151.101.73.194 github.global.ssl.fastly.net192.30.2 ...
