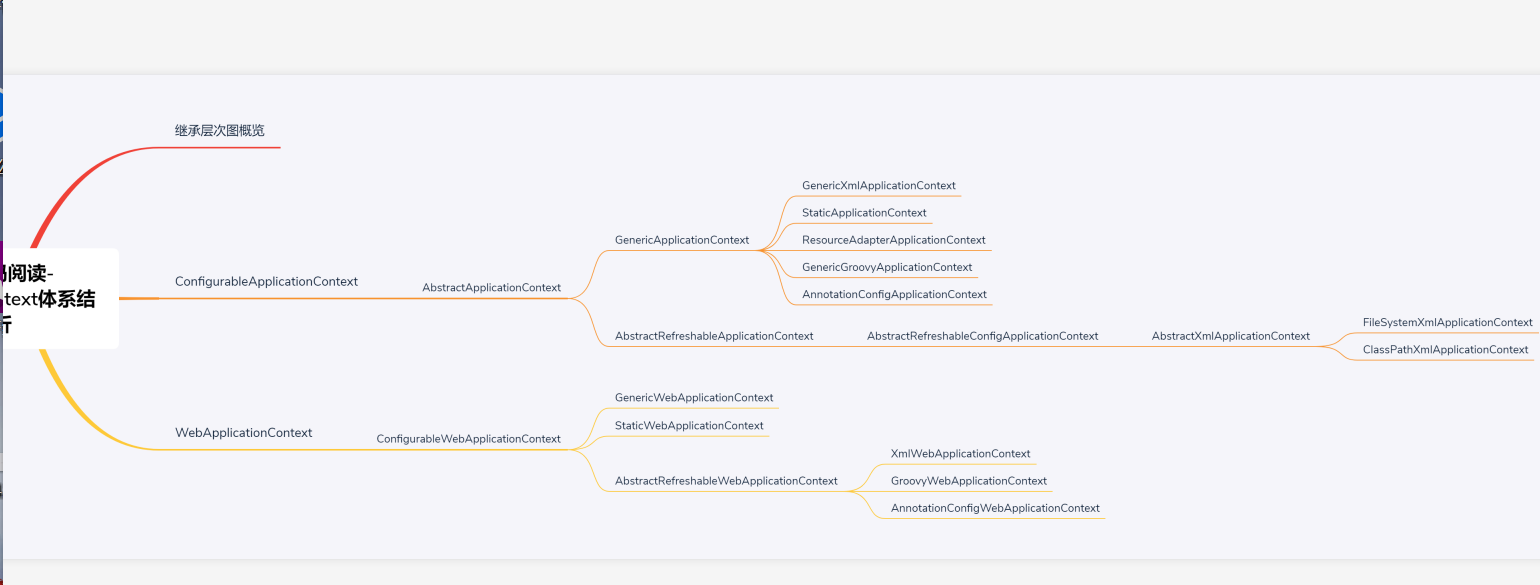
2、Spring-RootApplicationContext-refresh
上一篇文中提到父容器root applicationContext最后是调用XmlWebApplicationContext去实现的,
但是什么时候开始解析标签(默认标签、自定义标签)、注册bean以及注解的bean加载等一些列的操作;
知识点普及:
在 Spring 项目中,加载 applicationContext.xml 的方法
1、FileSystemXmlApplicationContext
这个方法是从文件绝对路径加载配置文件,例如:
ApplicationContext ctx = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext( "G:/Test/applicationcontext.xml ");
如果在参数中写的不是绝对路径,那么方法调用的时候也会默认用绝对路径来找,我测试的时候发现默认的绝对路径是eclipse所在的路径。
采用绝对路径的话,程序的灵活性就很差了,所以这个方法一般不推荐。
(如果要使用classpath路径,需要加入前缀classpath: )
2、ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
这个方法是从classpath下加载配置文件(适合于相对路径方式加载),
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext( "/applicationcontext.xml ");
下面我们就围绕这些问题展开摸索:
参数中classpath: 前缀是不需要的,默认就是指项目的classpath路径下面;
这也就是说用ClassPathXmlApplicationContext时默认的根目录是在WEB-INF/classes下面,而不是项目根目录。这个需要注意!
3、XmlWebApplicationContext
专为web工程定制的方法,推荐Web项目中使用。例如:
ServletContext servletContext = request.getSession().getServletContext(); ApplicationContext ctx = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
***************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************
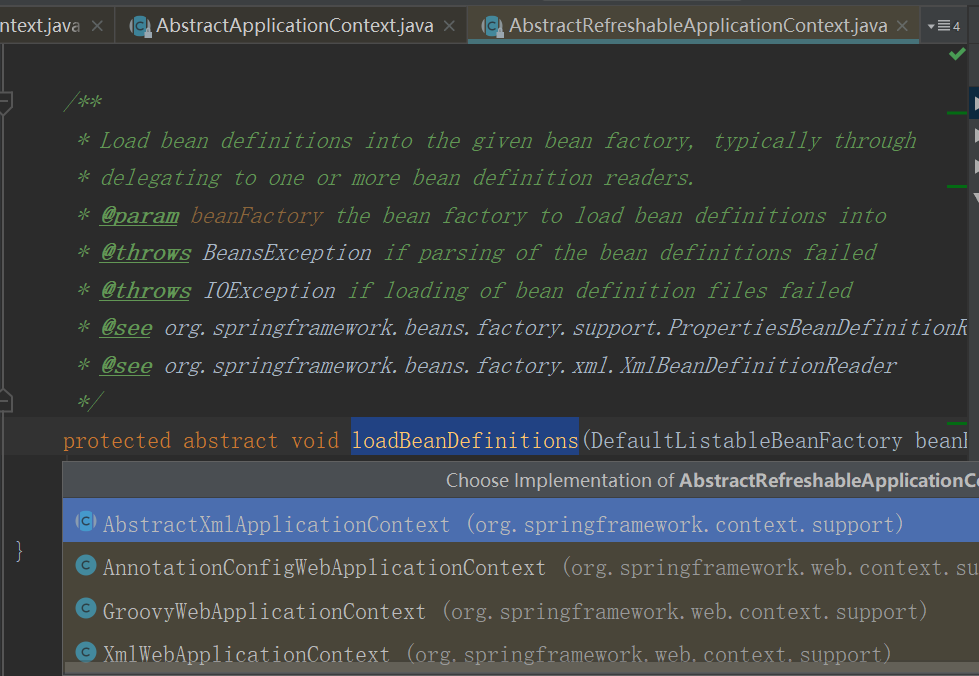
public class XmlWebApplicationContext extends AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext {....}
public abstract class AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext extends
AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext implements ConfigurableWebApplicationContext, ThemeSource {..} 看标红的东东这个就是我们的入口
public abstract class AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext extends AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext
implements BeanNameAware, InitializingBean
/**
* Triggers {@link #refresh()} if not refreshed in the concrete context's
* constructor already.
*/
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
if (!isActive()) {
refresh();
}
}
public abstract class AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext extends AbstractApplicationContext {..}
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh(); // Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); // Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); // Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource(); // Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster(); // Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh(); // Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners(); // Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); // Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
} catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
} // Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans(); // Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex); // Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
} finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
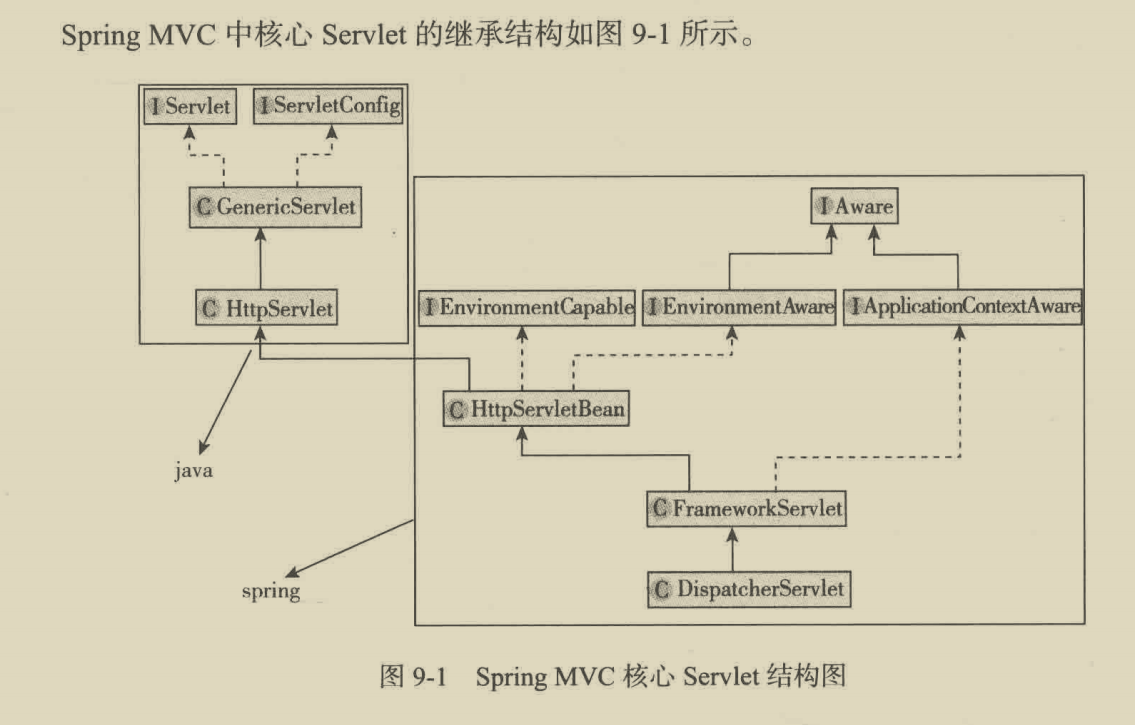
1、boot AppliccationConetxt的Map在哪
2、Servlet ApplicationContext的Map在哪,如何进行参数绑定的?


/**
* Initialize the HandlerMappings used by this class.
* <p>If no HandlerMapping beans are defined in the BeanFactory for this namespace,
* we default to BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping.
*/
private void initHandlerMappings(ApplicationContext context) {
this.handlerMappings = null; if (this.detectAllHandlerMappings) {
// Find all HandlerMappings in the ApplicationContext, including ancestor contexts.
Map<String, HandlerMapping> matchingBeans =
BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerMapping.class, true, false);
if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
this.handlerMappings = new ArrayList<HandlerMapping>(matchingBeans.values());
// We keep HandlerMappings in sorted order.
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.handlerMappings);
}
}
else {
try {
HandlerMapping hm = context.getBean(HANDLER_MAPPING_BEAN_NAME, HandlerMapping.class);
this.handlerMappings = Collections.singletonList(hm);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// Ignore, we'll add a default HandlerMapping later.
}
} // Ensure we have at least one HandlerMapping, by registering
// a default HandlerMapping if no other mappings are found.
if (this.handlerMappings == null) {
this.handlerMappings = getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerMapping.class);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("No HandlerMappings found in servlet '" + getServletName() + "': using default");
}
}
}
DispatcherServlet.java
/**
* Create a List of default strategy objects for the given strategy interface.
* <p>The default implementation uses the "DispatcherServlet.properties" file (in the same
* package as the DispatcherServlet class) to determine the class names. It instantiates
* the strategy objects through the context's BeanFactory.
* @param context the current WebApplicationContext
* @param strategyInterface the strategy interface
* @return the List of corresponding strategy objects
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected <T> List<T> getDefaultStrategies(ApplicationContext context, Class<T> strategyInterface) {
String key = strategyInterface.getName();
String value = defaultStrategies.getProperty(key);
if (value != null) {
String[] classNames = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(value);
List<T> strategies = new ArrayList<T>(classNames.length);
for (String className : classNames) {
try {
// 加载这个class
Class<?> clazz = ClassUtils.forName(className, DispatcherServlet.class.getClassLoader());
// 实例化
Object strategy = createDefaultStrategy(context, clazz);
strategies.add((T) strategy);
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new BeanInitializationException(
"Could not find DispatcherServlet's default strategy class [" + className +
"] for interface [" + key + "]", ex);
}
catch (LinkageError err) {
throw new BeanInitializationException(
"Error loading DispatcherServlet's default strategy class [" + className +
"] for interface [" + key + "]: problem with class file or dependent class", err);
}
}
return strategies;
}
else {
return new LinkedList<T>();
}
}
# Default implementation classes for DispatcherServlet's strategy interfaces.
# Used as fallback when no matching beans are found in the DispatcherServlet context.
# Not meant to be customized by application developers. org.springframework.web.servlet.LocaleResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver org.springframework.web.servlet.ThemeResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.theme.FixedThemeResolver org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerMapping=org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerAdapter=org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.HttpRequestHandlerAdapter,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapter org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerExceptionResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.AnnotationMethodHandlerExceptionResolver,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.ResponseStatusExceptionResolver,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.support.DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver org.springframework.web.servlet.RequestToViewNameTranslator=org.springframework.web.servlet.view.DefaultRequestToViewNameTranslator org.springframework.web.servlet.ViewResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver org.springframework.web.servlet.FlashMapManager=org.springframework.web.servlet.support.SessionFlashMapManager
public abstract class ApplicationObjectSupport implements ApplicationContextAware {...}
@Override
public final void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext context) throws BeansException {
if (context == null && !isContextRequired()) {
// Reset internal context state.
this.applicationContext = null;
this.messageSourceAccessor = null;
}
else if (this.applicationContext == null) {
// Initialize with passed-in context.
if (!requiredContextClass().isInstance(context)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Invalid application context: needs to be of type [" + requiredContextClass().getName() + "]");
}
this.applicationContext = context;
this.messageSourceAccessor = new MessageSourceAccessor(context);
initApplicationContext(context);
}
else {
// Ignore reinitialization if same context passed in.
if (this.applicationContext != context) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Cannot reinitialize with different application context: current one is [" +
this.applicationContext + "], passed-in one is [" + context + "]");
}
}
}
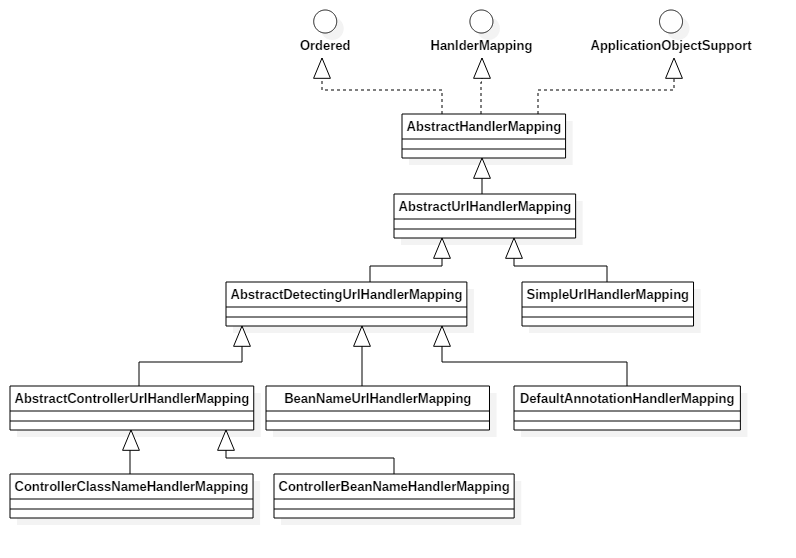
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMapping extends WebApplicationObjectSupport implements HandlerMapping, Ordered {...}
/**
* Initializes the interceptors.
* @see #extendInterceptors(java.util.List)
* @see #initInterceptors()
*/
@Override
protected void initApplicationContext() throws BeansException {
extendInterceptors(this.interceptors);
detectMappedInterceptors(this.adaptedInterceptors);
initInterceptors();
}
public abstract class AbstractDetectingUrlHandlerMapping extends AbstractUrlHandlerMapping {....}
/**
* Calls the {@link #detectHandlers()} method in addition to the
* superclass's initialization.
*/
@Override
public void initApplicationContext() throws ApplicationContextException {
super.initApplicationContext();
detectHandlers();
}
/**
* Register all handlers found in the current ApplicationContext.
* <p>The actual URL determination for a handler is up to the concrete
* {@link #determineUrlsForHandler(String)} implementation. A bean for
* which no such URLs could be determined is simply not considered a handler.
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException if the handler couldn't be registered
* @see #determineUrlsForHandler(String)
*/
protected void detectHandlers() throws BeansException {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Looking for URL mappings in application context: " + getApplicationContext());
}
String[] beanNames = (this.detectHandlersInAncestorContexts ?
BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(getApplicationContext(), Object.class) :
getApplicationContext().getBeanNamesForType(Object.class)); // Take any bean name that we can determine URLs for.
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
String[] urls = determineUrlsForHandler(beanName);
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(urls)) {
// URL paths found: Let's consider it a handler.
registerHandler(urls, beanName);
}
else {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Rejected bean name '" + beanName + "': no URL paths identified");
}
}
}
}
demo
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.SimpleUrlHandlerMapping">
<property name="mappings">
<props>
<prop key="/userlist.htm">userController</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean> <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.support.ControllerClassNameHandlerMapping"/> <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping"/> <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping"/> <bean id="userController" name="/users" class="cn.com.infcn.web.controller.UserController"></bean>
BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping.java
/**
* Checks name and aliases of the given bean for URLs, starting with "/".
*/
@Override
protected String[] determineUrlsForHandler(String beanName) {
List<String> urls = new ArrayList<String>();
if (beanName.startsWith("/")) {
urls.add(beanName);
}
String[] aliases = getApplicationContext().getAliases(beanName);
for (String alias : aliases) {
if (alias.startsWith("/")) {
urls.add(alias);
}
}
return StringUtils.toStringArray(urls);
}
DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping.java
/**
* Checks for presence of the {@link org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping}
* annotation on the handler class and on any of its methods.
*/
@Override
protected String[] determineUrlsForHandler(String beanName) {
ApplicationContext context = getApplicationContext();
Class<?> handlerType = context.getType(beanName);
RequestMapping mapping = context.findAnnotationOnBean(beanName, RequestMapping.class);
if (mapping != null) {
// @RequestMapping found at type level
this.cachedMappings.put(handlerType, mapping);
Set<String> urls = new LinkedHashSet<String>();
String[] typeLevelPatterns = mapping.value();
if (typeLevelPatterns.length > 0) {
// @RequestMapping specifies paths at type level
String[] methodLevelPatterns = determineUrlsForHandlerMethods(handlerType, true);
for (String typeLevelPattern : typeLevelPatterns) {
if (!typeLevelPattern.startsWith("/")) {
typeLevelPattern = "/" + typeLevelPattern;
}
boolean hasEmptyMethodLevelMappings = false;
for (String methodLevelPattern : methodLevelPatterns) {
if (methodLevelPattern == null) {
hasEmptyMethodLevelMappings = true;
}
else {
String combinedPattern = getPathMatcher().combine(typeLevelPattern, methodLevelPattern);
addUrlsForPath(urls, combinedPattern);
}
}
if (hasEmptyMethodLevelMappings ||
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.Controller.class.isAssignableFrom(handlerType)) {
addUrlsForPath(urls, typeLevelPattern);
}
}
return StringUtils.toStringArray(urls);
}
else {
// actual paths specified by @RequestMapping at method level
return determineUrlsForHandlerMethods(handlerType, false);
}
}
else if (AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(handlerType, Controller.class) != null) {
// @RequestMapping to be introspected at method level
return determineUrlsForHandlerMethods(handlerType, false);
}
else {
return null;
}
}
2、Spring-RootApplicationContext-refresh的更多相关文章
- 四、Spring Boot Web开发
四.Web开发 1.简介 使用SpringBoot: 1).创建SpringBoot应用,选中我们需要的模块: 2).SpringBoot已经默认将这些场景配置好了,只需要在配置文件中指定少量配置就可 ...
- JAVAEE——SSH项目实战06:统计信息管理、Spring注解开发和EasyUI
作者: kent鹏 转载请注明出处: http://www.cnblogs.com/xieyupeng/p/7190925.html 一.统计信息管理 二.Spring注解开发 1.service ...
- 四、spring成长之路——springIOC容器(下)
目录 5.spring注解开发(Spring扩展知识) 5.1定义配置类:@Configuration 声明一个类为IOC容器 @Bean定义一个Bean 5.2.按照条件进行注入 5.3.@Impo ...
- 五、spring之DI循环依赖
什么是循环依赖 循环依赖就是循环引用,就是两个或多个Bean相互之间的持有对方,比如CircleA引用CircleB,CircleB引用CircleC,CircleC引用CircleA,则它们最终反映 ...
- MyEclipse中删除对Struts、Hibernate、Spring .
已经导入一下框架,现在发现不想用了,要删除,发现麻烦,添加容易删除不易,下面这个帮你解决删除问题,本文为转载,我试过hibenate,挺好使,你们验证其他的框架 http://blog.csdn.ne ...
- 1、spring与springmvc父子容器
转载于http://www.tianshouzhi.com/api/tutorials/spring 1.0 spring与springmvc父子容器 1.spring和springmvc父子容器概念 ...
- spring自动扫描、DispatcherServlet初始化流程、spring控制器Controller 过程剖析
spring自动扫描1.自动扫描解析器ComponentScanBeanDefinitionParser,从doScan开始扫描解析指定包路径下的类注解信息并注册到工厂容器中. 2.进入后findCa ...
- 1、Spring In Action 4th笔记(1)
Spring In Action 4th笔记(1) 2016-12-28 1.Spring是一个框架,致力于减轻JEE的开发,它有4个特点: 1.1 基于POJO(Plain Ordinary Jav ...
- 转 Netflix OSS、Spring Cloud还是Kubernetes? 都要吧!
Netflix OSS.Spring Cloud还是Kubernetes? 都要吧! http://www.infoq.com/cn/articles/netflix-oss-spring-cloud ...
- EasyUI、Struts2、Hibernate、spring 框架整合
经历了四个月的学习,中间过程曲折离奇,好在坚持下来了,也到了最后框架的整合中间过程也只有自己能体会了. 接下来开始说一下整合中的问题和技巧: 1, jar包导入 c3p0(2个).jdbc(1个). ...
随机推荐
- PHP0010:PHP操作mysql
cmd中清除之前的记录 cmd操作数据库的步骤: php 到 mysql的并发数 15个左右 for循环是要知道起点和终点 foreach是从结果集中取数据 而while可遍历自然结果集
- Cassandra学习&命令行实践
准备 按照Cassandra集群部署搭建两台测试机,环境信息如下: 名称 IP 数据中心名称 node-01 192.168.198.130 datacenter1 node-02 192.168.1 ...
- ADB之安装APK
一.下载安装adb工具 下载安装,cmd测试是否成功 二.连接设备 1.手机打开USB测试 2.测试连接 三.安装应用 adb -s [设备编号] install [apk的完整路径]
- js 字符串中"\"
var a = '\a' console.log(a) // a ???? js 字符串中"\" 有特殊功能,反斜杠是一个转义字符 js 中 遇到字符串中有'\'时候需要注意 '\ ...
- MySQL之分库分表
MySQL之分库分表(MyCAT实现) 分库分表介绍 随着微服务这种架构的兴起,我们应用从一个完整的大的应用,切分为很多可以独立提供服务的小应用.每个应用都有独立的数据库. 数据的切分分为两种: ...
- maven依赖报红的一些解决办法
使用IDEA集成maven管理项目依赖时,经常出现更改pom文件后maven依赖列表并未更改,且依赖报红,此时建议检查maven配置文件maven仓库是否下载好jar包,如果未下载好jar包文件夹内会 ...
- Docker最全教程——从理论到实战(二十)
前言 各种编程语言均有其优势和生态,有兴趣的朋友完全可以涉猎多门语言.在平常的工作之中,也可以尝试选择相对适合的编程语言来完成相关的工作. 在团队技术文档站搭建这块,笔者尝试了许多框架,最终还是选择了 ...
- How to Install Oracle Java 11 on Ubuntu 18.04 LTS (Bionic) Written by Rahul, Updated on April 3, 20
本文系转载备份 请阅读点击下面链接阅读原文以获取更佳地阅读体验.谢谢. How to Install Oracle Java 11 on Ubuntu 18.04 LTS (Bionic) Writt ...
- js前后端交互
1.前后端交互模式 2.promise用法 (1)异步调用 (2)ajax回顾 (3).promise 优点:可以解决回调地狱(多层异步调用嵌套问题)(解决代码可读性低的问题) 提供简洁的api (4 ...
- Meta(其他信息)
简介 元数据就是描述数据的数据 <meta> 元素表示那些不能由其它HTML元相关元素 (<base>, <link>, <script>, <s ...
